40 xef4 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules follow the online tutorial for CNвЂ" o Draw the MO diagram for the o the molecular dipole on CO is very. In this series of problems, we are going to apply the concept of atomic orbital hybridization to construct the molecular orbital diagrams of... Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or Heteronuclear Diatomic Species The following is a molecular orbital energy level diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, XY, in...
Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 8.37. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram...
Xef4 molecular orbital diagram
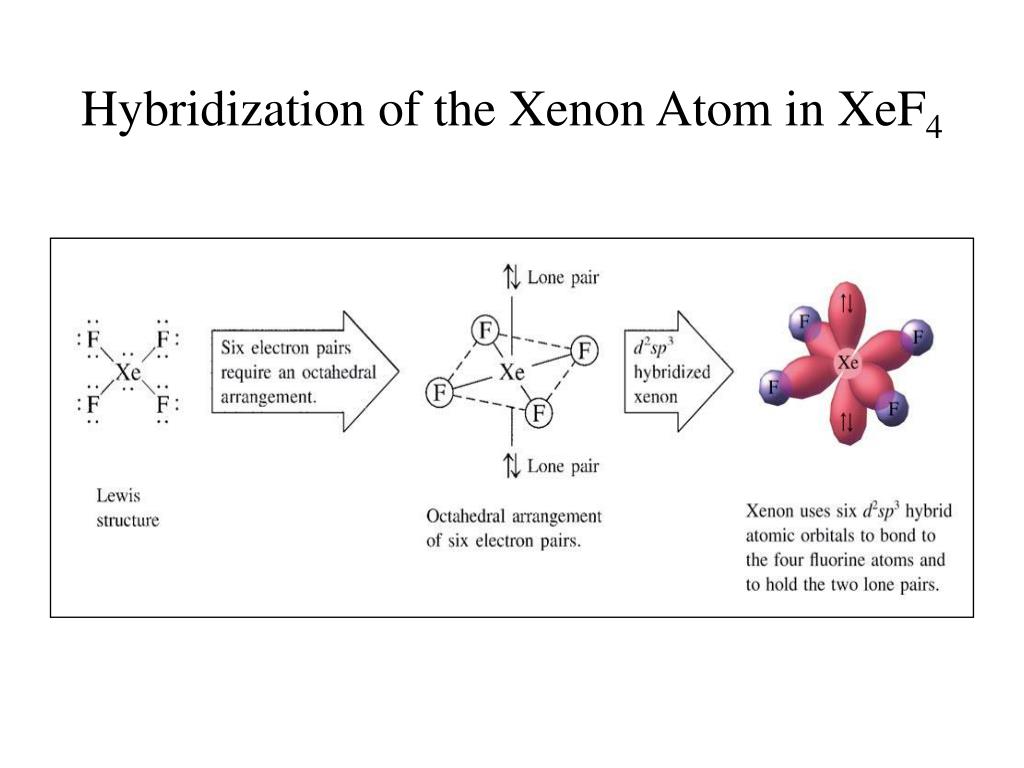
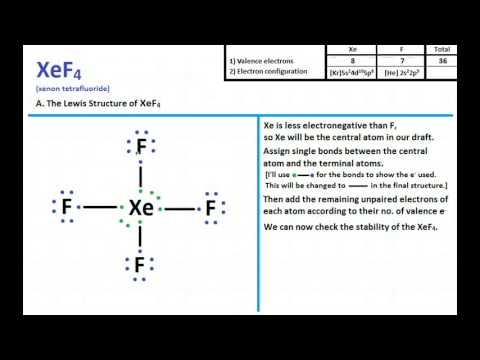
XeF4 is the chemical formula of the compound Xenon Tetrafluoride. This chemical compound is formed when xenon reacts with fluorine. An MO diagram is a descriptive instrument that is particularly used to explain the formation of chemical bonds in molecules with the help of molecular orbital theory. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon. Bonding & Molecular Structure: Orbital Hybridization & Molecular Orbitals. 1. All of the following 10. In which of the following molecules or ions does the central atom have sp3 hybridization: SO42-, XeF4, ICl4-, and Answer: d. The following molecular orbital diagram may be used for problems 32-46.
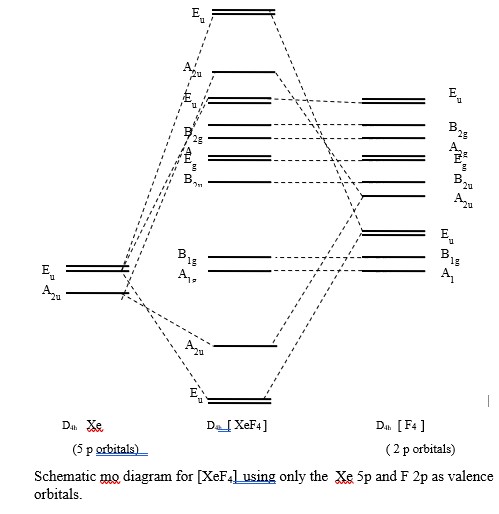
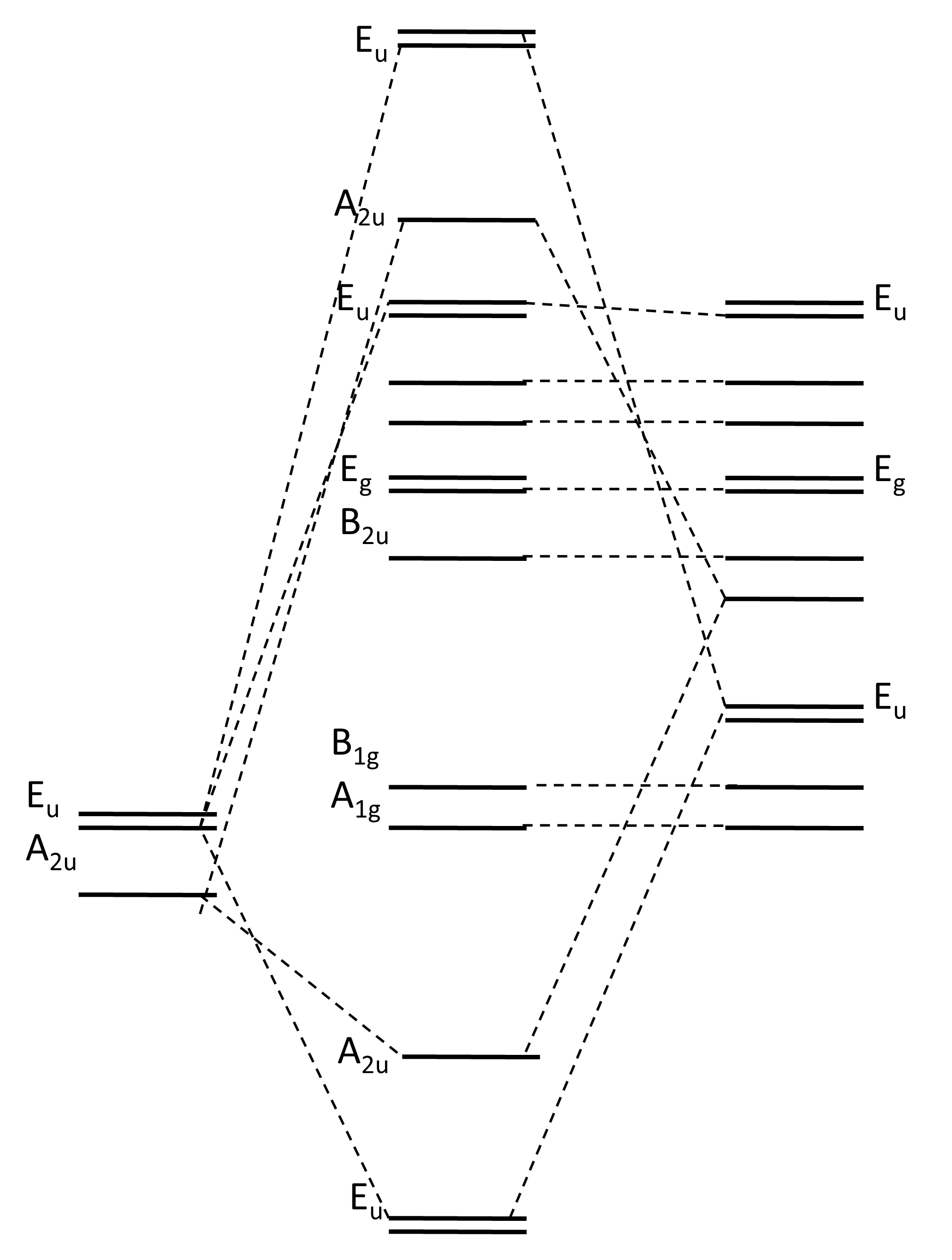
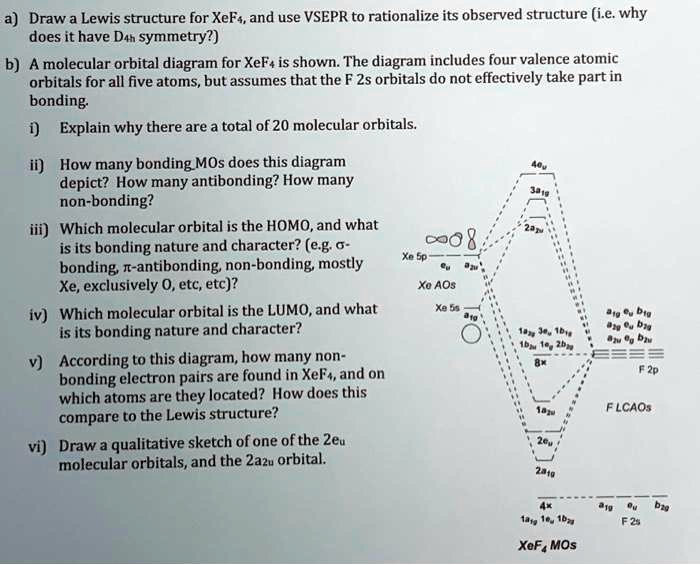
Xef4 molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory. Energy Level Diagram. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion. Linear Combination Of Atomic Orbitals. Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of XeF2. eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg= linear. Chemistry questions and answers. Create a molecular orbital diagram for XeF4 assuming the F atoms only participate in sigma bonding with the center. Indicate corresponding symmetry. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. But experimental evidence for some diatomic molecules have shown that the above sequence of energy levels of MOs is not correct for all the molecules.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. On the other hand, Molecular Orbital Theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule. Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12. Molecular symmetry, point groups and character tables. NOTE: lab write-up Look at the example of XeF4, it has both principal and secondary axes which are perpendicular to An energy diagram of this is drawn as shown: Notice the differences in the MO diagrams for the... 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. Assume the valence 5s-orbitals of Xe are sufficiently lower in energy than the valence 5p-orbitals that the valence 5s-orbital of Xe and the 2s-orbitals of the F-atoms form an inner core set.
Use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram, such as those in Figure 9.20 "Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only Fill the molecular orbitals in the energy-level diagram beginning with the orbital with the lowest energy. Be sure to obey the Pauli principle... Now according to Molecular Orbital Theory…. Let's start with NO first. Follow Hund's rule and fill the bonding electrons then ( the stared ones The energy level diagram is just for understanding how the electrons occupy the orbitals …as said before the bonding electrons occupy first then the antibonding. Molecular Orbital Diagram Help. I have a homework problem asking me to construct the molecular orbital diagram for methylene chloride, and I am not too sure what to do next. CD contains interactive energy diagrams. • Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and hybridisation (these are not MO). - Molecular orbitals are formed which involve all of the atoms of the molecule.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here.
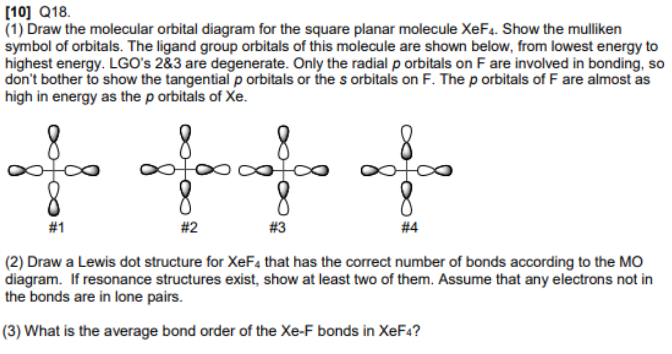
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Ǘ¡ $M molecular geometry around the N trigonal pyramid 367 '. c. XeF4 9F ' ' '.
Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. m. XeF 2 ' 9F. 'hybridization for the Xe sp 3 d hybridization for each F sp 3. There are two sigma bonds due to sp 3 d-sp 3 overlap.
Molecular orbital (MO) theory describes the behavior of electrons in a molecule in terms of combinations of the atomic wavefunctions. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O2.
The four simplest molecules we have examined so far involve molecular orbitals that derived from two 1s atomic orbitals. If we wish to extend our model to larger Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or...
The D4h point group are one of the most common molecular symmetry found in nature. For example, the XeF4 molecule belongs to the D4h point group. the XeF4 contains one C4 rotation axis, one C2 rotation axis, and four C2 perpendicular rotation axis, 2σv planes, 2σd planes and 1σh plane...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations. Metal reaction mechanisms. The Resolver thinks Mol. Molecule-1.
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular in the schematic sketches on the left of the energy level diagram and in the calculated molecular orbital images on the right.*
MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. XeF4 is the formula for Xenon tetrafluoride. The negative sign for the s h element indicates that this representation will reduce to double primed (") reducible representations.
#MOT Molecular Orbital Diagram Of #XeF2 #Xenon Di FluoRide In English #NobleGases #InertGases #Chemistry #XenonDiFluoride #Bonding #MolecularOrbitalDiagram...
Bonding & Molecular Structure: Orbital Hybridization & Molecular Orbitals. 1. All of the following 10. In which of the following molecules or ions does the central atom have sp3 hybridization: SO42-, XeF4, ICl4-, and Answer: d. The following molecular orbital diagram may be used for problems 32-46.
Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon.
XeF4 is the chemical formula of the compound Xenon Tetrafluoride. This chemical compound is formed when xenon reacts with fluorine. An MO diagram is a descriptive instrument that is particularly used to explain the formation of chemical bonds in molecules with the help of molecular orbital theory.
Solved How Do I Construct An Mo Diagram For Xef4 Using Mullikan Symbols A Drawing Would Be Great Thank You Course Hero
Solved Balance The Following Equations A Fe2o3 H2 Fe H2o B Xef4 H2o Xe O2 Hf What Is The Lewis Structure Electron Pair Geometry Mole Course Hero
Solved Balance The Following Equations A Fe2o3 H2 Fe H2o B Xef4 H2o Xe O2 Hf What Is The Lewis Structure Electron Pair Geometry Mole Course Hero



















0 Response to "40 xef4 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment