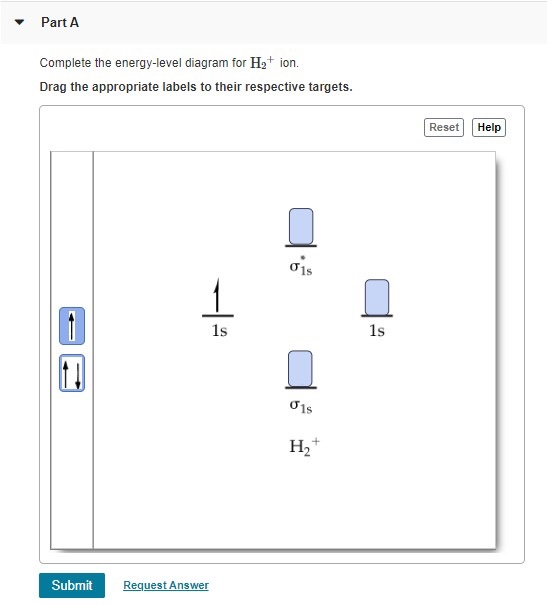
38 H2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram
MO Diagrams | Molecular Orbital Diagram Maker A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row OF2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Feb 15, 2022 · To showcase the relative energy levels of the AOs and the resultant MOs, we have the Molecular Orbital diagrams. The lower energy molecular orbital is the bonding and the higher energy is the anti-bonding orbital. The below-mentioned diagram gives us the individual MO diagrams of Oxygen and Fluorine separately, the atoms that make up a molecule ...
PDF PowerPoint Presentation | VB Theory and Orbital Hybridization Molecular Orbital Diagrams. An MO diagram, just like an atomic orbital diagram, shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO. molecule has opposite effects: N2+ has a weaker longer bond than N2, but O2+ has a stronger, shorter bond than O2. We determine the valence...
H2+ molecular orbital diagram
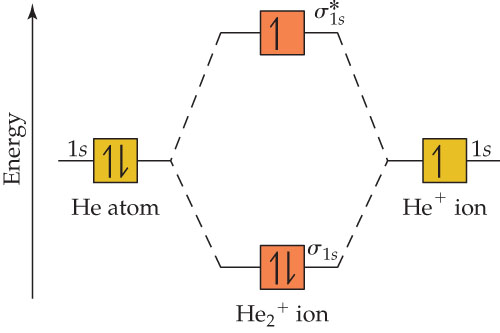
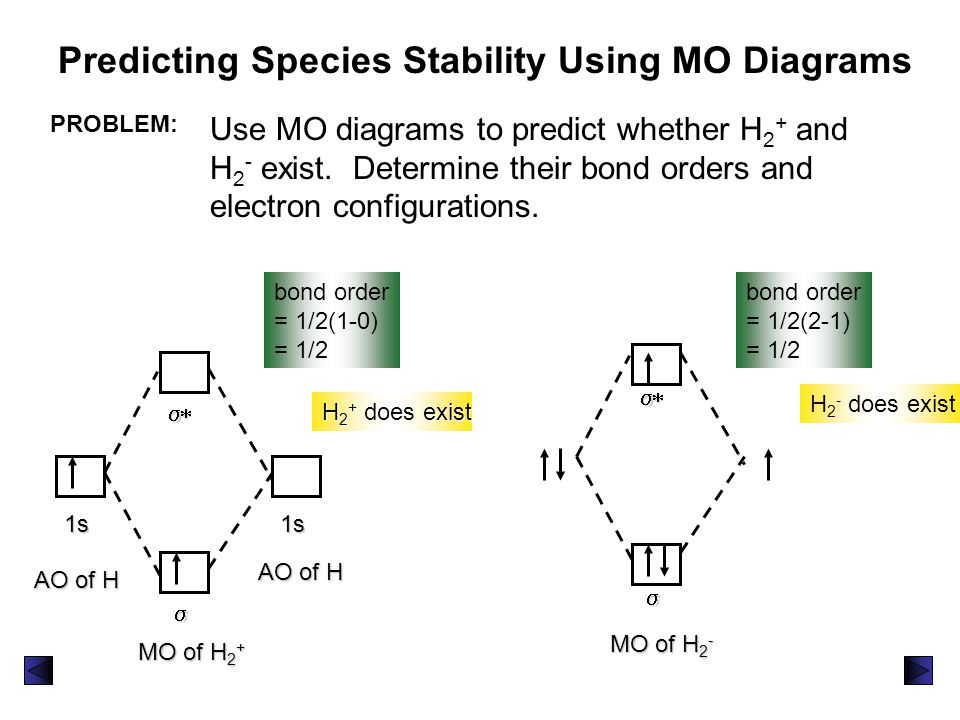
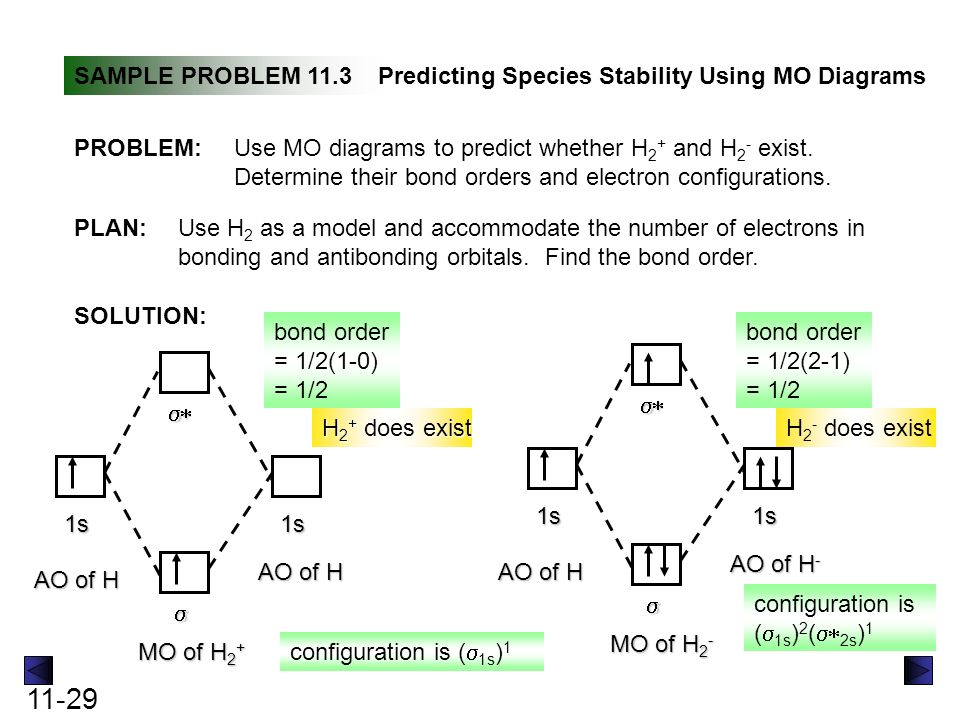
Fig. No. 2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for H2+ ion No. 3 Molecular OrbitalEnergy Diagram for He2 molecule (hypothetical). There is no net bonding as it has zero bond order and therefore He2 molecule The molecular orbital electronic configuration of the molecule is. The value of bond order states that He2+ is stable. Its bond dissociation energy is... Molecular Orbital Theory: Explanation, Illustrations and... - Embibe Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour? Question: Consider the Molecular Orbital diagram for the ion H2+... Consider the Molecular Orbital diagram for the ion H2+ (An H2 ion with 1 e-). Predict the bond order.
H2+ molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. H2+. Lewis Structure: Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram. Total # of bonding electrons. Molecular orbital diagram - WikiMili, The Best Wikipedia Reader A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms. Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomics (Worksheet) Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. Calculate the number of bonding and antibonding electrons in simple molecules. Should this molecule exist? MO electron configuration: H2+. Lewis Structure: Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram. Total # of bonding electrons. Mo Theory - Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry The Rules of Molecular Orbital Theory: First principle: The number of molecular orbitals produced is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals brought by the atoms that have combined. Second principle: Bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy that the parent orbitals, and the antibonding orbitals are higher in energy.
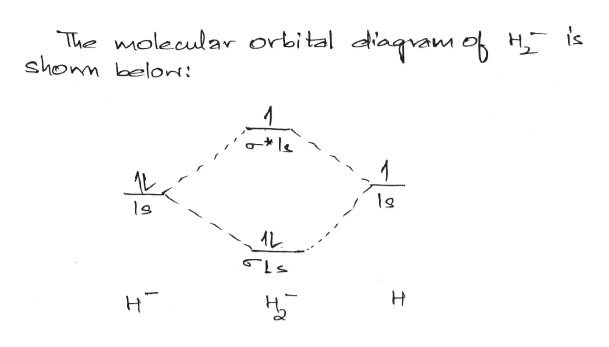
Figure 9.20 Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic... We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H2+. Fill the molecular orbitals in the energy-level diagram beginning with the orbital with the lowest energy. Be sure to obey the Pauli principle and... Is H2 a viable molecule for the molecular orbital theory? - Quora The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. The question is not that clear, but due to the fact that [math] H^{2+}[/math] doesn't exist... How do I calculate the bond order for H2- and H2+? | Socratic Apr 01, 2017 · Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals. Molecular Orbital Theory - GeeksforGeeks The Molecular Orbital Theory is a chemical bonding theory developed at the turn of the twentieth century by F. R. Hund and R. S. Mulliken to explain the structure and properties of various molecules. The valence-bond theory failed to adequately explain how certain molecules, such as...
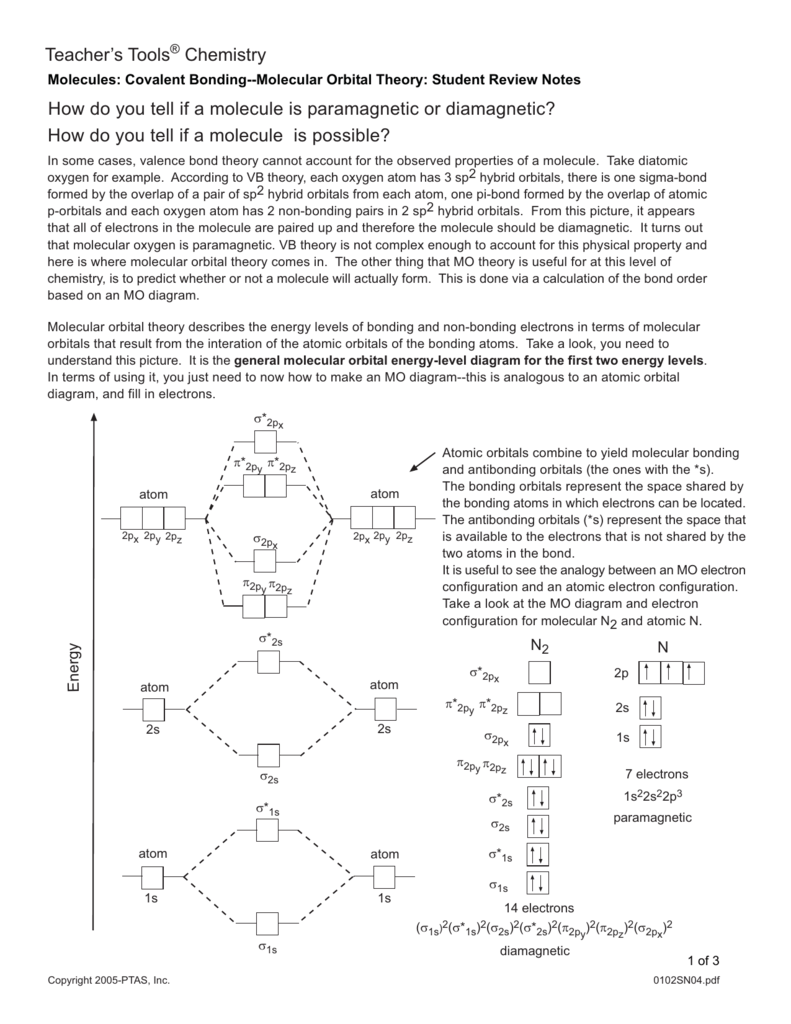
Lecture 25. Optimizing H2+ Molecular Orbital, H2, and Configuration... Lecture 25. Quantum Principles: Optimizing H2+ Molecular Orbital, H2, and Configuration Interaction. things that with this qualitative pictures neurons 617 which is a molecular orbital diagram which some of you may already have used without understanding exactly what that meant in... Molecular cloud - Wikipedia A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H 2), and the formation of H II regions.This is in contrast to other areas of the interstellar medium that contain predominantly ionized gas. 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. Molecular Orbital diagram of NO(nitric oxide) molecule Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
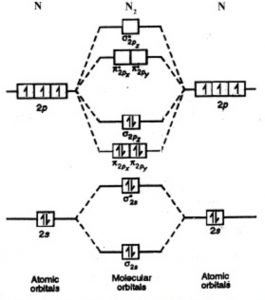
Molecular Orbital Theory - ppt video online download 43 Diatomic Molecular Orbital Diagram Strong pz-s interaction energy 2s 1s 2p Homonuclear Examples: Li2, B2, C2, N2 Heteronuclear Examples: NO, BO, BO+, CO, CO+, CN, CN- 4/17/2017. 44 Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Determine is the sequence of molecular orbitals based on the...
Molecular orbital - Wikipedia In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one …
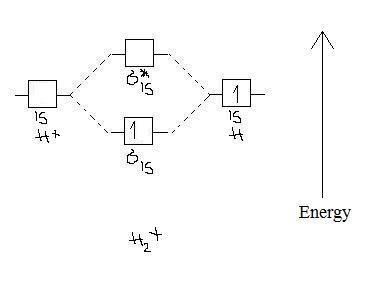
Molecular Orbital Theory Diagram Below mentioned is the molecular orbital diagram of the hydrogen ion H2+. Orbitals have space for a maximum of two electrons, and therefore the bonding orbital in H2+ is half-filled. This single electron doesn't have the required energy; the lower the potential energy of one mole of hydrogen nuclei pairs...
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure.
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Figure 8. This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
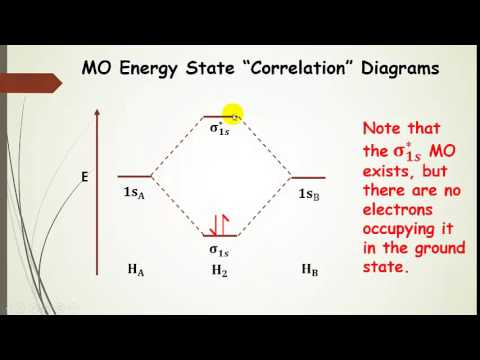
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) About molecular orbitals. The simplest molecule: H2+. Bonding and antibonding orbitals. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules This order of energies of various molecular orbitals is valid for molecules or ions like, H2, H2+, He2+, He2 (hypothetical), Li2, Be2(hypothetical)...
PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Diagrams such as these are used to describe the bonding in a molecule in MO terms. Electrons occupy MOs according to the same rules developed...
(PDF) Physical Chemistry a molecular ... - Academia.edu Physical Chemistry a molecular approach; McQuarrie Donald A., Simon John A.; University Science Books; 1997; California
Advanced Inorganic Chemistry/NH3 Molecular Orbitals Molecular orbital diagram is useful in displaying and explaining the chemical bonds of molecules in conjunction with the molecular orbital theory. The molecular orbital diagram of NH3 is presented in Figure 5 and will be elaborated in regards to its interactions. The s orbitals for the 3 hydrogens are...
PDF Molecular Orbital Theory … Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar... The molecular orbital theory is highly dependent on the geometry of the complex and can successfully be used for describing octahedral complexes, tetrahedral and square-planar According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration octahedral complexes of Cu 2+ will be t2g6 , e*g3 .
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical Bonding and... 3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding Greater value of bond order for H2 molecule than H2+ ion shows that two H2 molecule is more stable than H2+.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... - Molecular orbital are formed by addition and subtraction of AO's. Æ Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO). - like hybrid AO's but the • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital.
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
C2H6 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Feb 15, 2022 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule.
How to Make the Molecular Orbital Diagram for H2+ (Bond Order...) This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2+ ion. The bond order of H2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this number...
9.8: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Mar 04, 2021 · Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ...
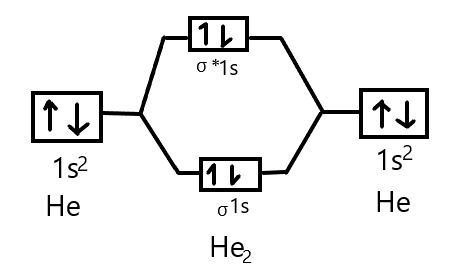
Molecular Orbital Theory This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why He2 molecules don't exist. Combining a pair of helium atoms with 1s2 electron configurations The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions...
Figure 14: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for diatomic... The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of internuclear nodal planes, the orbital with no such nodal plane lying at lowest energy and the orbital with nodal planes between all the atoms lying at highest energy.
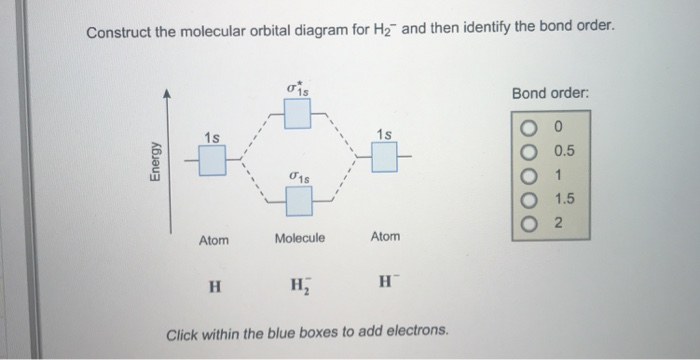
480 To 120/240 Transformer Wiring - Wiring Diagram Pictures Jun 04, 2019 · Tmo-3310001 Wiring Diagram; Cummins Signature /isx Wiring Diagram; Honeywell Rth7600d Wiring Heat Pump; Integumentary System Diagram Labeled; Pioneer Avh 4200nex Wiring Diagram; Sears Bench Grinder 397 19671 Wiring Diagram; Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. Troy Bilt Bronco Parts …
Question: Consider the Molecular Orbital diagram for the ion H2+... Consider the Molecular Orbital diagram for the ion H2+ (An H2 ion with 1 e-). Predict the bond order.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Explanation, Illustrations and... - Embibe Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour?
Fig. No. 2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for H2+ ion No. 3 Molecular OrbitalEnergy Diagram for He2 molecule (hypothetical). There is no net bonding as it has zero bond order and therefore He2 molecule The molecular orbital electronic configuration of the molecule is. The value of bond order states that He2+ is stable. Its bond dissociation energy is...













0 Response to "38 H2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram"
Post a Comment