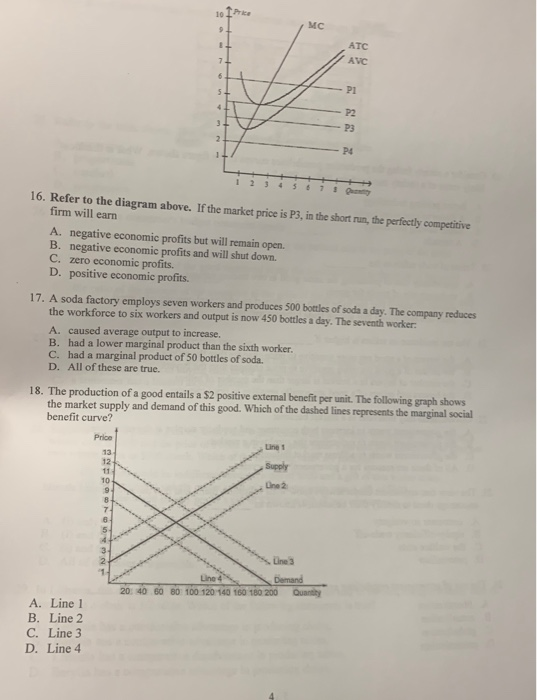
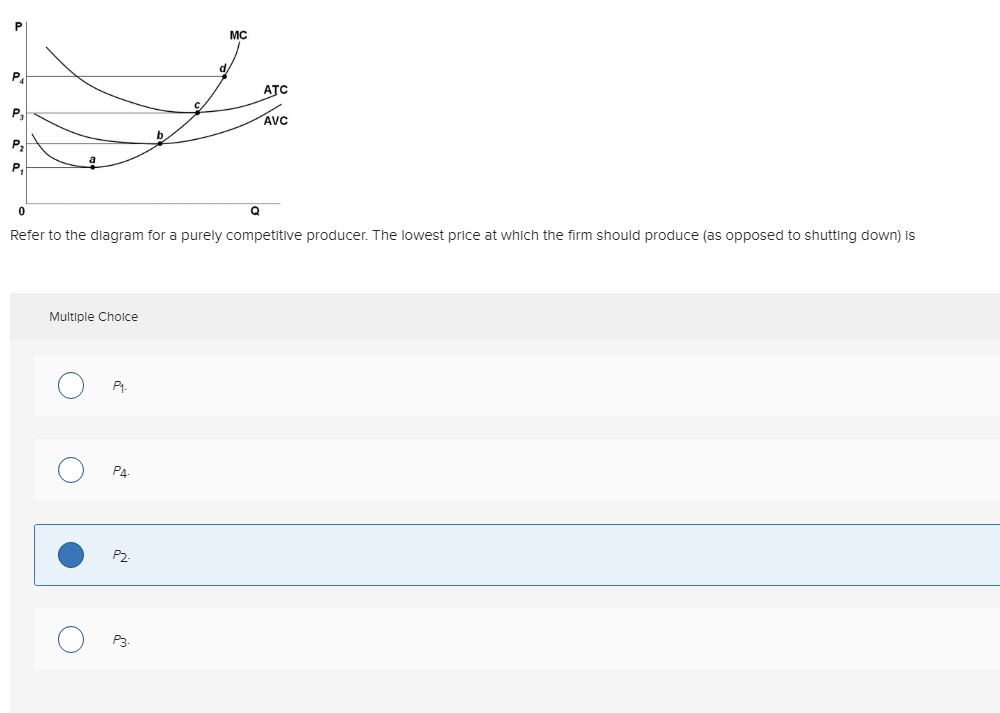
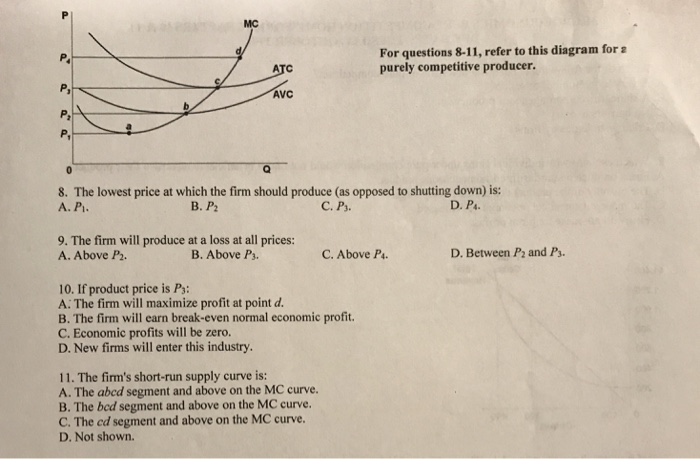
38 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3:
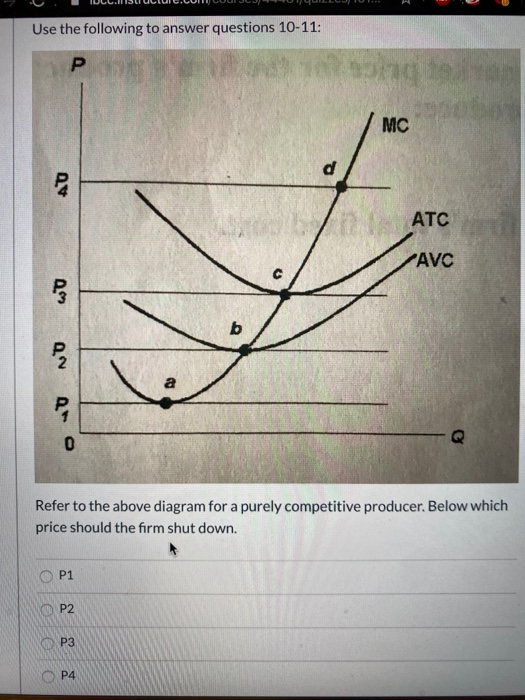
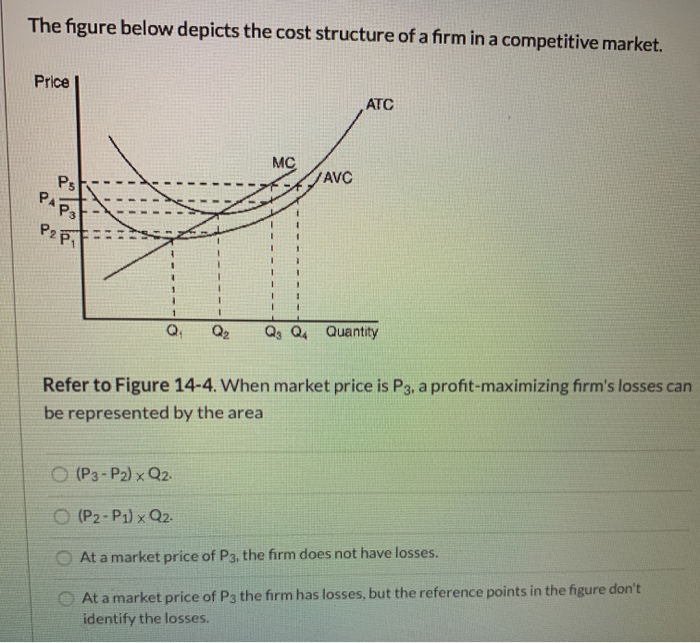
If product price is p 3 economic profits will be zero. The lowest price at which the firm should produce as opposed to shutting down is. Refer to the diagram. The firm will produce at a loss at all pricesbetween p 2 and p 3. The short run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based... a. At a product price of $56, will this firm produce in the short run? Explain why price can be substituted for marginal revenue in the MR = MC rule when an industry is purely competitive. WRITE: The figure to the right shows Bob's demand for pizzas and the market price. a. What is the...
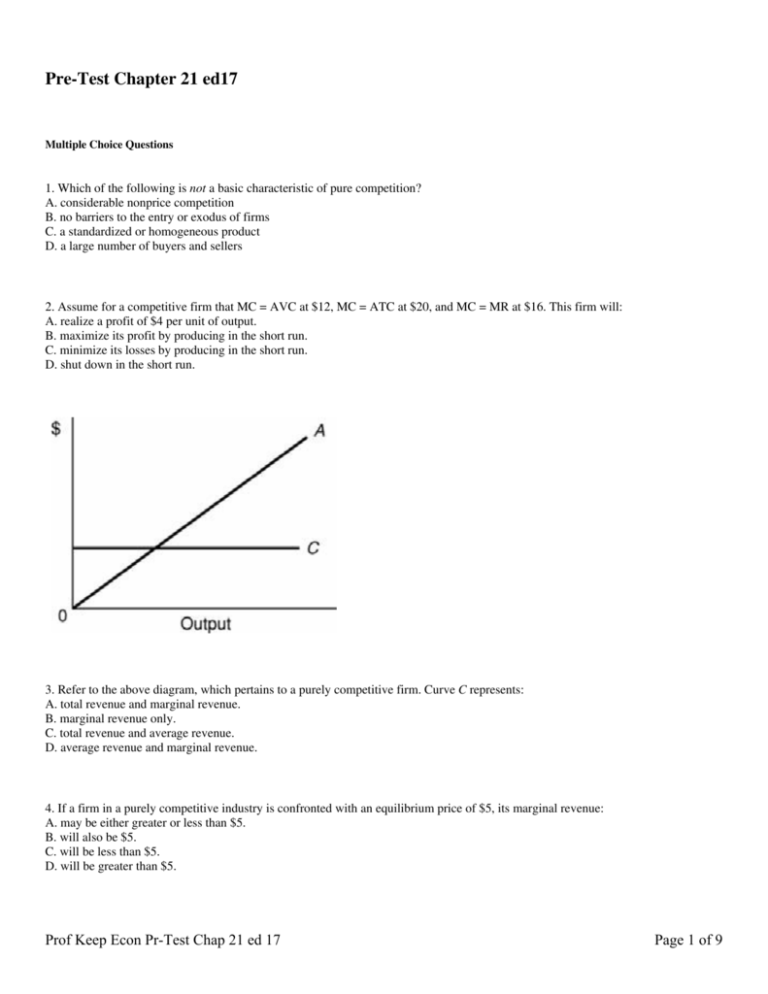
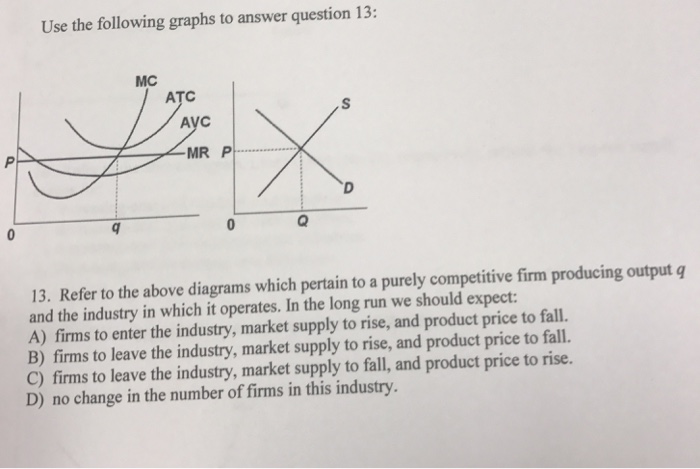
For a competitive industry, price would equal marginal cost at equilibrium. a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue curves, and the competitive industry. Therefore, the regulatory agency should set a price ceiling of $6, thus making...

Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3:
If the price of the product increases for every unit sold, then total revenue also increases. As an example of how a perfectly competitive firm decides what quantity to produce Total revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is a straight line sloping up. The slope is equal to the price of the good. Business Economics Q&;A Library Assume that the cost data in the following table are for a purely competitive producer: Average Fixed Average Loss per unit = $ 6.50 8 c. At a product price of $32.00 (i) Will this firm produce in the short run? No (ii) If it is preferable to produce, what will be the... If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. 21. Refer to the above diagram for a Unlike other healthy food producers in the local market that sell low-quality and cheap products, Fresh Munchables wants to...
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3:. Competitive Points of Difference. 7. According to the Weber Fechner Law, consumers react to prices in _____ as opposed to _____. The thought process for a _-centric company is "What combination of products is best for this customer?" Product and pc is the world price of that product. In the long run purely competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic The firm will produce at a. With a pcpt per unit tariff. Price and quantity will be. Refer to the diagram. For a purely competitive firm marginal... Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is. 18. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A. P1. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero.
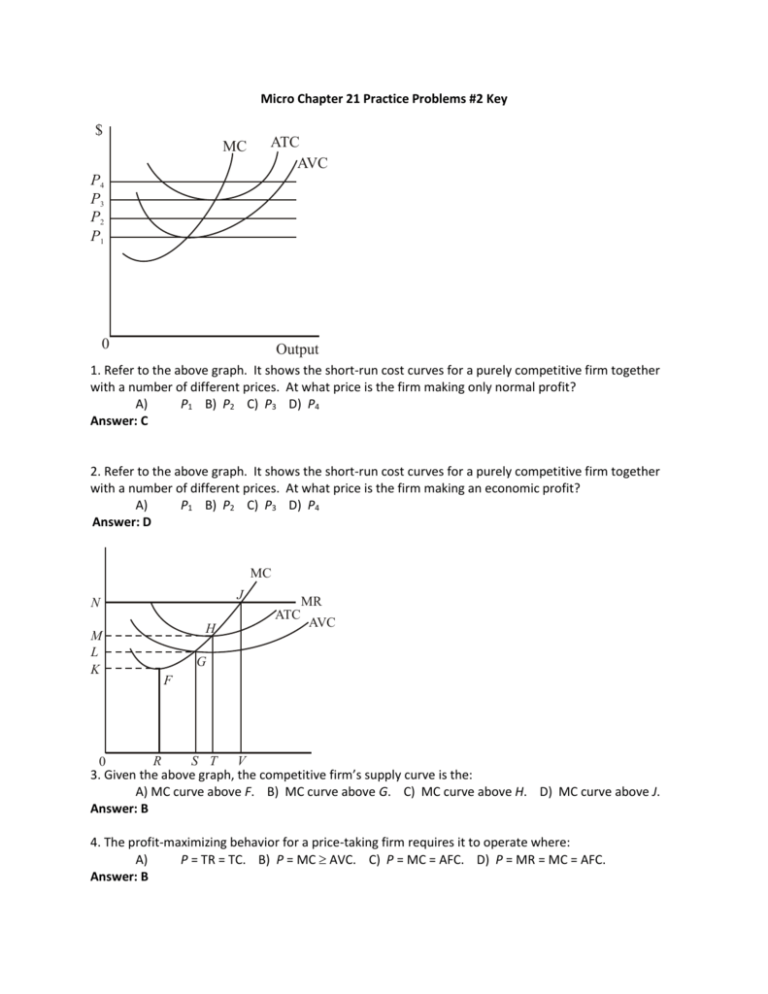
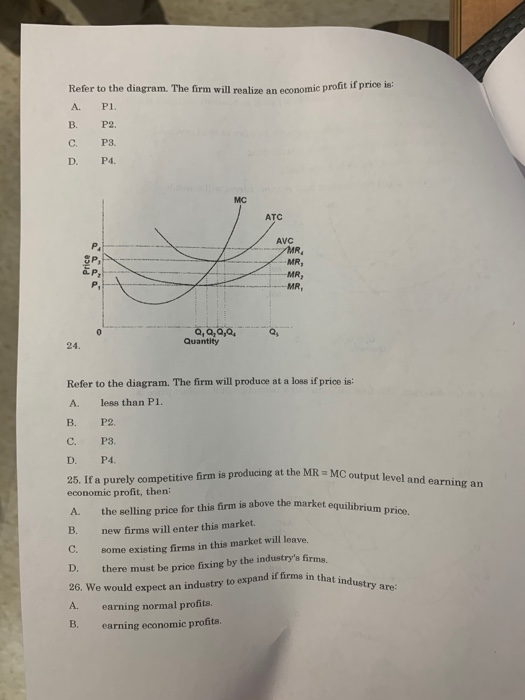
Pure Competition. A perfectly competitive market is rare, but those that exist are very large, such Because, for purely competitive firms, marginal revenue = price, maximum revenue is also earned This diagram of the short-run supply curve shows the relationship among average variable cost... If product price is p 3. The lowest point on a purely competitive firms short run supply curve corresponds to. The lowest price at which the firm Refer to the diagram at output level q the total variable cost is 0beq if a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price... The firm will produce an economic profit if the prices are above P3. As per the profit calculation, for a product to be profitable it's price must be higer than ...1 answer · 0 votes: Answer: Above P3 The firm will produce an economic profit if the prices are above P3. As per the profit calculation, for a product to be profitable it's ... 4. In pure competition, the demand for the product of a single firm is perfectly 10. I n a t y pical graph for a purel y competitive firm, the intersection of the tot al cost and total. 22. A purely competitive firm will be willing to produce at a loss in the short run provided Ans: B. 25. Refer to the above diagram.
Principles Of Managerial Finance-13th Edition By L. J. Gitman & C. J. ... - ID:5d1a6eb8af43a. Principles of Managerial Finance The Prentice Hall Series in Finance Adelman/Marks Gitman/Zutter McDonald Entrepreneuria... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A) a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B) price P3 and producing output Q3. C) price P2 and producing … Refer to the diagram. If product price is p 3. An increase in the steepness of curve 3 an upward shift in curve 2 and an upward shift in curve 1. Price and quantity will be. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn positive economic profits in the long... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3 Refer to the diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses, this firm will produce: E units at price A. The Ajax Manufacturing Company is selling in a purely competitive market.
B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers." C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." 31. Refer to the above two diagrams for individual firms. In Figure 2 the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are represented by: A)...
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. 16. If a purely competitive firm is producing at some level less...
6. Nonprice competition refers to: A) competition between products of different industries, for example, competition between aluminum and steel E) charges a price where MR=MC. 17. Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits...
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be Refer to the above data. If there were 1,000 identical firms in this industry and total or market demand is as shown below, equilibrium price will be
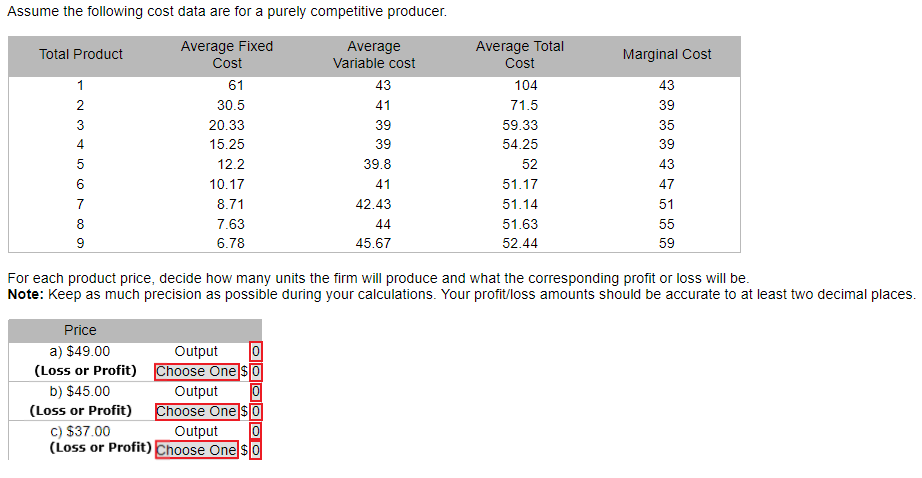
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. Next > Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce with an economic profit at all price Assume the following cost data are for a purely competitive producer: Average Product Fixed Cost Variable...
17. Refer to the above diagram. The firm will shut down at any price less than: A. P 1. B. P 2. C. P 3. D. P 4. Prof Keep Econ Pr-Test Chap 21 ed 17 Page 5 of 9. 7 23. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3 : A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B...
Price is dependent on the interaction between demand and supply components of a market. Demand and supply represent the willingness of consumers and The end result is a rise in price, to P, where supply and demand are in balance. Similarly, if a price above P were chosen arbitrarily, the market...
If product price is p3 a. For a purely competitive firm marginal revenue graphs as a. The firm will produce at a. Refer to the above diagram. Economic profits will be zero. The demand curves of firms are kinked at the prevailing price. The firm will earn an economic profit. If product price it p3.
Assuming only price changes, then at lower prices, a consumer is willing and able to buy more apples. A rightward shift in demand would increase the quantity demanded at all prices compared to the The last factor of demand is the number of buyers. A competitive market is made up of many...
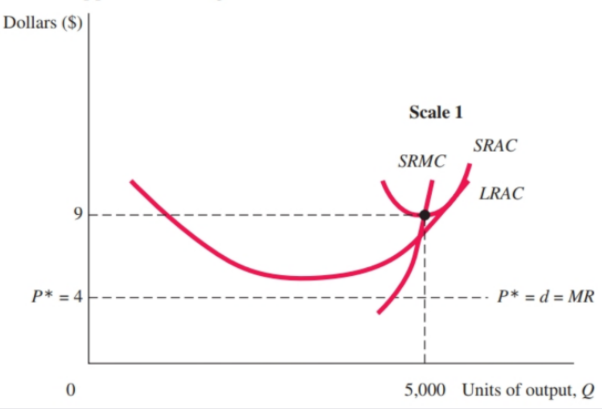
c) Competitive firms produce until P = MC, so in this case we know the market price would be P = 10 and the market quantity would be What is the monopolist's optimal markup of price above marginal cost? Remember that the demand elasticity in a constant elasticity demand function is the exponent...
In product markets. businesses sell products to households. Refer to the graph in figure 1. Starting at point !, what is the opportunity cost of producing one The rationing function of prices refers to the fact that government must distribute any surplus goods that maybe left in a competitive marekt.
A natural monopoly refers to a monopoly that is defended from direct competition by. If an imperfectly competitive firm is producing a level of output where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue, marginal revenue is below average variable cost, and price is equal to average total cost...
Refer to the diagram below, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 Refer to the graph below. If the price of the product increases from $5 to $6 because of a What effect should each of the following have on the demand for gasoline in a competitive market?
The following table shows cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. Refer to the above table. If the market price for the firm's product is $180, the competitive firm will produce: 5 units and earn economic profits of $100 8 units and earn economic profits of $278 7 units and earn economic profits of $238
Nonprice competition refers to: A.competition between products of different industries, for example, competition between aluminum and steel in the manufacture of automobile parts. 38. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer.
If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. 48. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A. the abcd segment and above on the MC curve.
If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. 21. Refer to the above diagram for a Unlike other healthy food producers in the local market that sell low-quality and cheap products, Fresh Munchables wants to...
Business Economics Q&;A Library Assume that the cost data in the following table are for a purely competitive producer: Average Fixed Average Loss per unit = $ 6.50 8 c. At a product price of $32.00 (i) Will this firm produce in the short run? No (ii) If it is preferable to produce, what will be the...
If the price of the product increases for every unit sold, then total revenue also increases. As an example of how a perfectly competitive firm decides what quantity to produce Total revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is a straight line sloping up. The slope is equal to the price of the good.





















0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3:"
Post a Comment