40 molecular orbital diagram b2
7:14The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively. B2 has two unpaired electrons with the same ...20 Jun 2019 · Uploaded by Physical Chemistry Tutorial 14:24This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the ...26 Mar 2014 · Uploaded by Diego Troya
6:25This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2(+) molecule. The bond ...4 Jun 2021 · Uploaded by Principia
Molecular orbital diagram b2
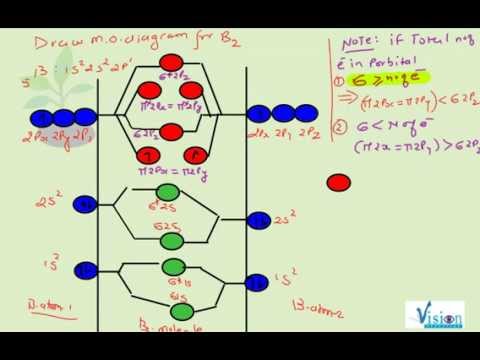
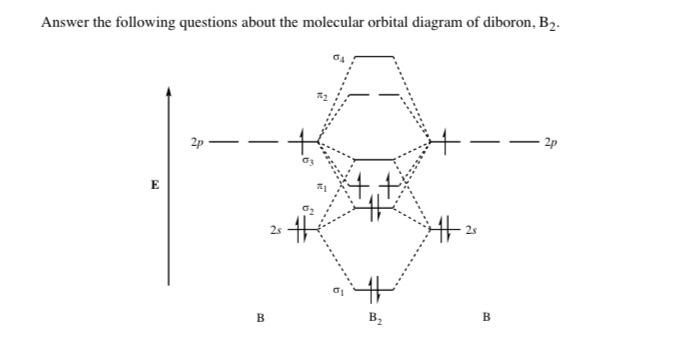
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ... What is the molecular orbital diagram for B2? As discussed in class the MO diagram for B2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
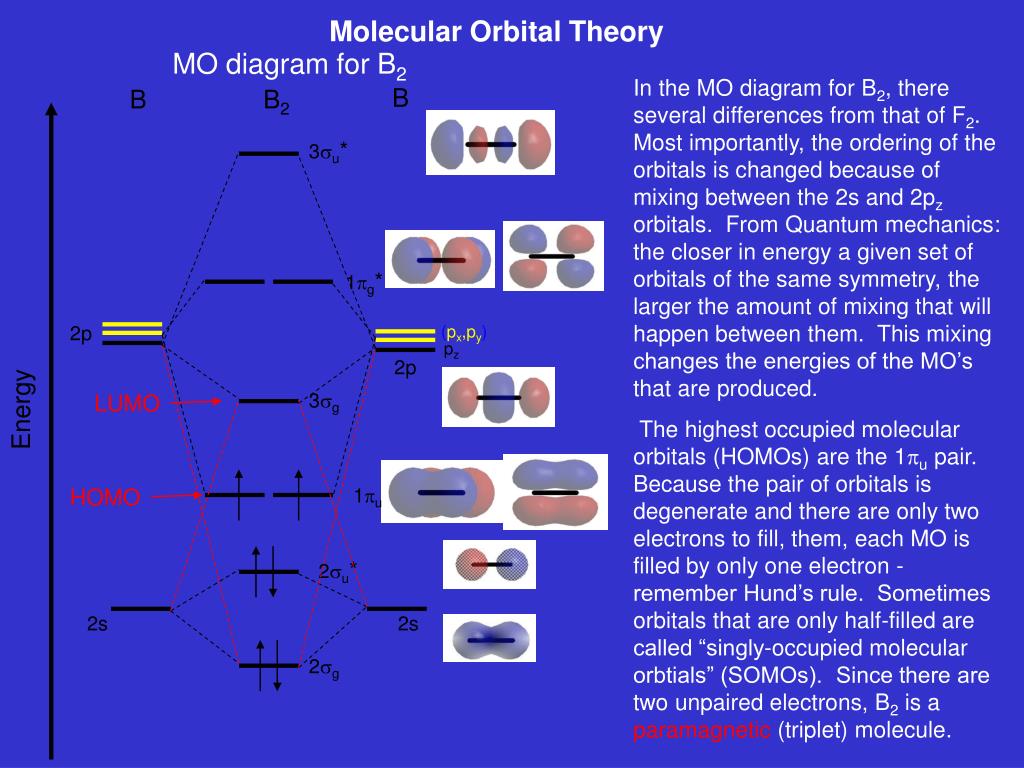
Molecular orbital diagram b2. ⇒ A homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which the same atoms combine together. example- N2, O2, B2, etc. ⇒ A hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which different atoms combine together. example- CN, HF, NO, etc. Clearly, Cyanide (CN) lies in a hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital as it contains two different atoms. Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can ... 23.10.2021 · Summary of licorice components properties: molecular weight (MW), number of H-bond donor/acceptor (HA/HD), water solubility (WS), and quantum chemical parameters, including the energy levels of the highest occupied molecular orbital (E HOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (E LUMO), energy gap (ΔE), dipole moment (μ), electronegativity (χ), global hardness (η) and the … Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. This example was covered in class to show the rare exception that this single bond is a bond.
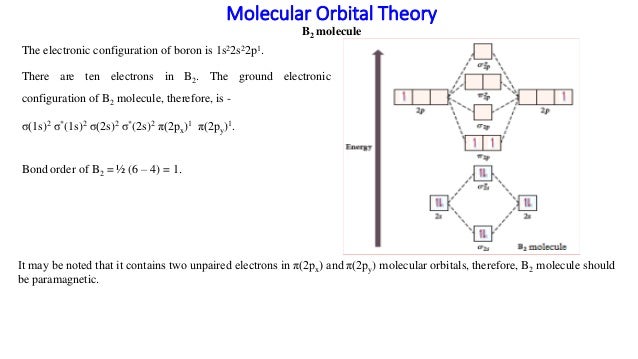
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron. Inorganic Chemistry (Atkins, Shriver).PDF Strong interactions between the Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) of the Ga atom and the surface state of the Al(2)O(3) surface are observed. This interaction promotes charge transfer from ... B2 molecular orbital diagram. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist. This was on a quiz and i somehow got the bond order and the lumo indicated wrong. I also calculated the bond order of this molecule to be 32. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms.
Department of Molecular & Cell Biology, Science Faculty: Thomas Scriba: TB vaccines and immunology: SATVI & Immunology, Department of Pathology: Edward Sturrock: Protein biochemistry, angiotensin-converting enzyme: Chemical & Systems Biology, Department of Integrative Biomedical Sciences: Digby Warner : Mycobacterial physiology & pathogenesis: Medical Microbiology, Department of Pathology ... 6:08This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2(-) molecule. The bond order ...2 Jun 2021 · Uploaded by Principia 30.10.2021 · The energy level diagram and molecular structures of the used materials in devices. Fig. 5 and Table 2 presented the electroluminescence performances of tDPAC-BN and tDMAC-BN at the optimal doping concentration. tDPAC-BN and tDMAC-BN-based devices exhibited deep-blue and pure-blue emission, respectively. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both ...
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H 2), and the formation of H II regions.This is in contrast to other areas of the interstellar medium that contain predominantly ionized gas.
10:50From the periodic table as we have already discussed the Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules of ...24 Jun 2020 · Uploaded by Edmerls
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2 (boron) molecule. The bond order of the boron molecule is also calculated and ...

Ppt Chemistry 445 Lecture 4 Molecular Orbital Theory Of Diatomic Molecules Powerpoint Presentation Id 794473
Effusion of a 1:1 mixture of two gases, represented by unshaded and shaded spheres in the diagram below, through a small pinhole produces the result shown below. The shaded spheres have a molecular mass of 32 amu. Which gas molecules have the higher average speed and what is the molecular mass of the unshaded molecules?
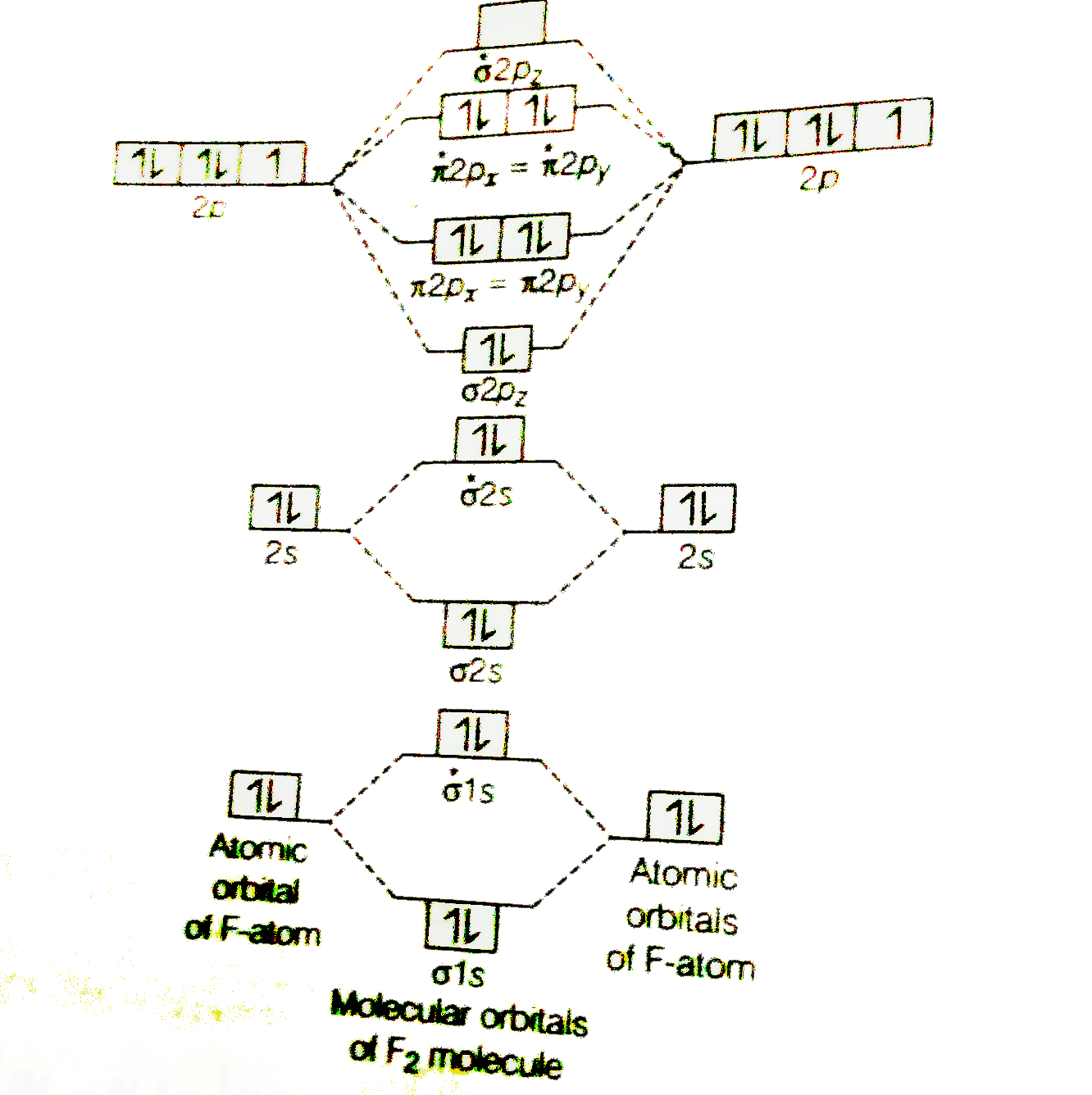
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
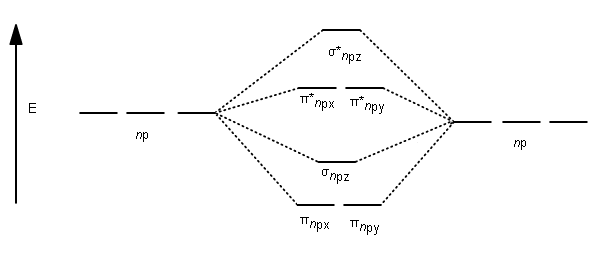
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
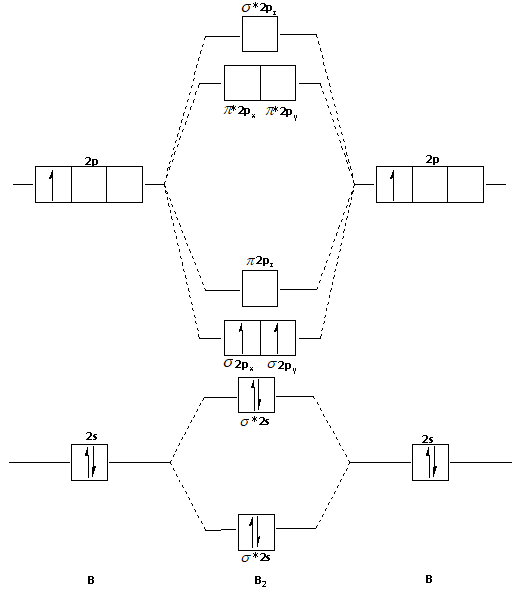
The molecular orbital diagram for B 2 molecule is as follows: We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds. Now, we have to calculate the bond order of B 2 molecule using the formula as follows: Bond order = 1 2 ( Number of electrons in BMO) − ( Number of electrons in ABMO) From the diagram, we can ...
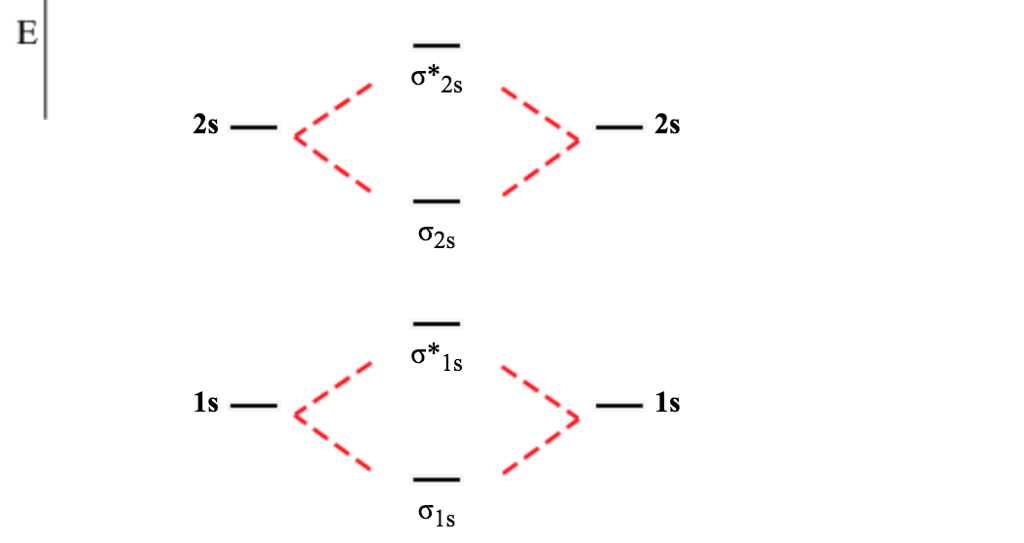
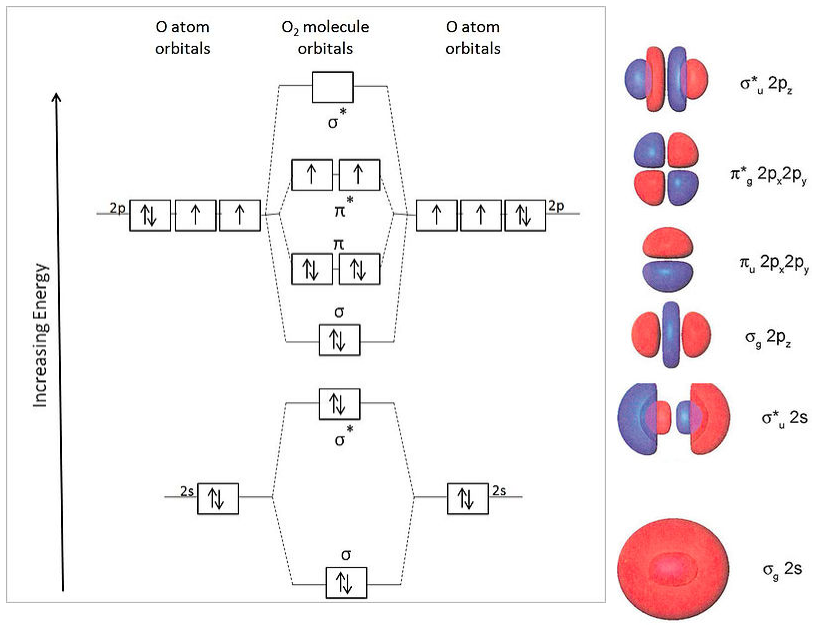
Molecular Orbital Theory allows us to predict the distribution of electrons within a molecule. This allows us to predict properties such as bond order, magnetism, and shape . There are two types of MO diagrams: Recall that the bonding MOs are those without an asterisk (e.g., σ1s), while the antibonding MOs are those with an asterisk (e.g., σ1s*).
Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
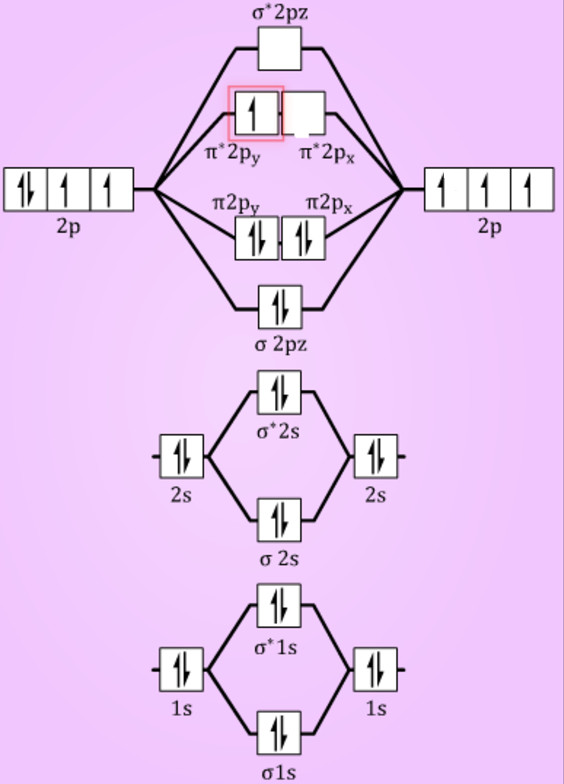
Solved Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stab Alomic Orbitals Molaular Orbiuak Alomic Orbital B C N B2 Nz2
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B2? As discussed in class the MO diagram for B2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond.
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
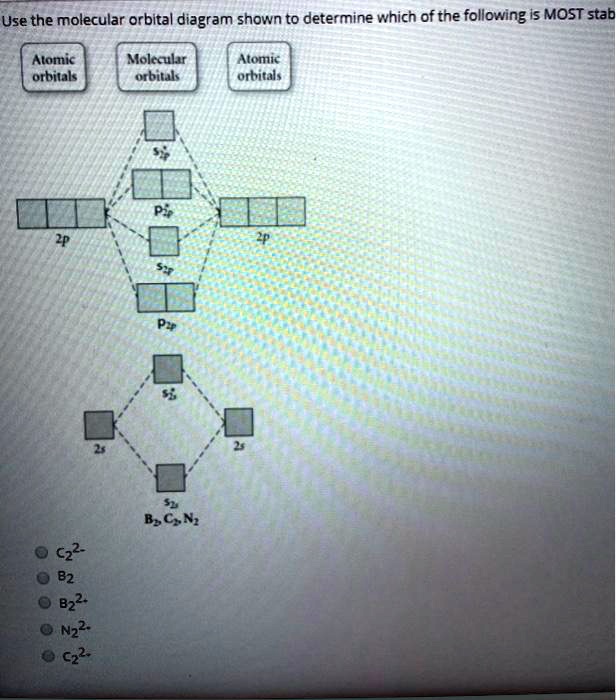
Solved Using The Molecular Orbital Diagram Depicted Below Which Species Have Bond Order Of 3 2p 2p 02p 72p Energy 2s Oa B2 B 02 2 C C22 D N2 Oeco Of Cn G
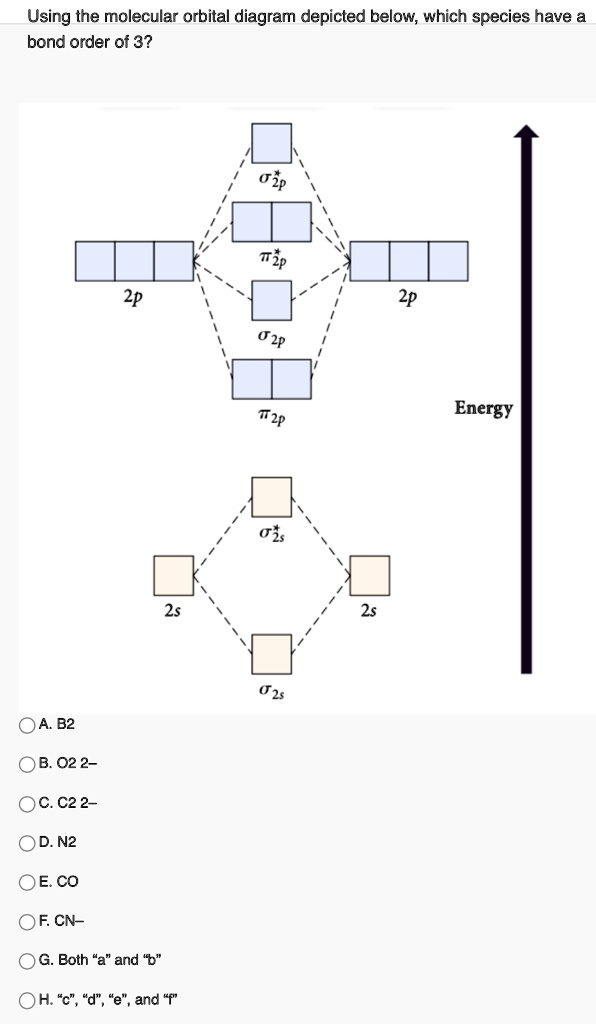
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond

A Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Paramagnetic B 2 2 B2 C 2 2 B 2 2 And N 2 2 B Draw The Lewis Structures And Molecular Orbital Diagrams For

Please Tell Me Why In B2 C2 And N2 In P Orbital Order Is Taken As Pi Sigma Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure 1452912 Meritnation Com

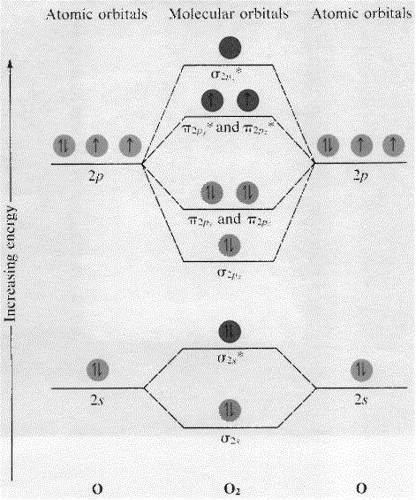
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of O2 And Calculate The Bond Order Is O2 Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic Explain Your Answer Study Com

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Paramagnetic N22 B22 Homeworklib

3 Which Of The Following Species Have Both O And It Bond According To Molecular Orbital Theory 1 Nz 2 B2 3 Cz Canly Tband 4 All Of These












0 Response to "40 molecular orbital diagram b2"
Post a Comment