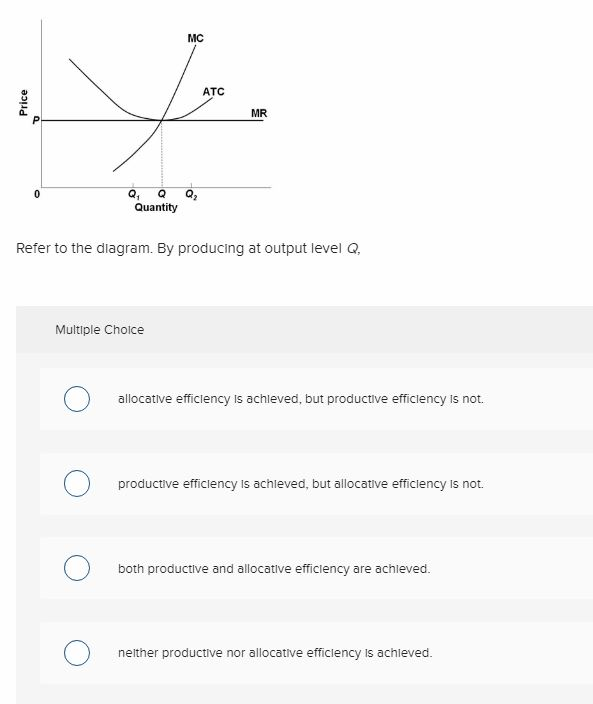
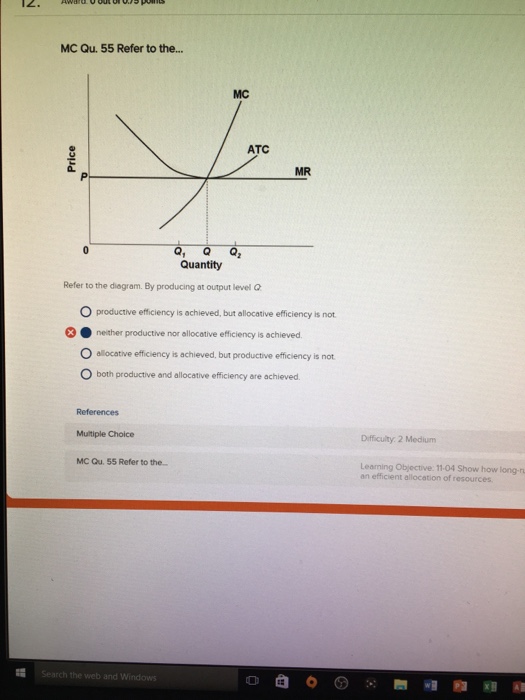
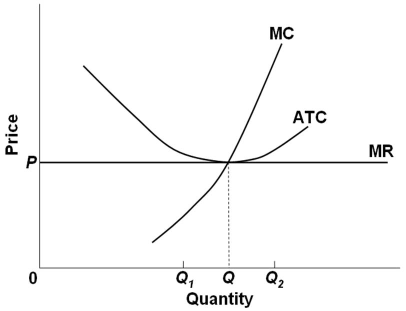
37 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
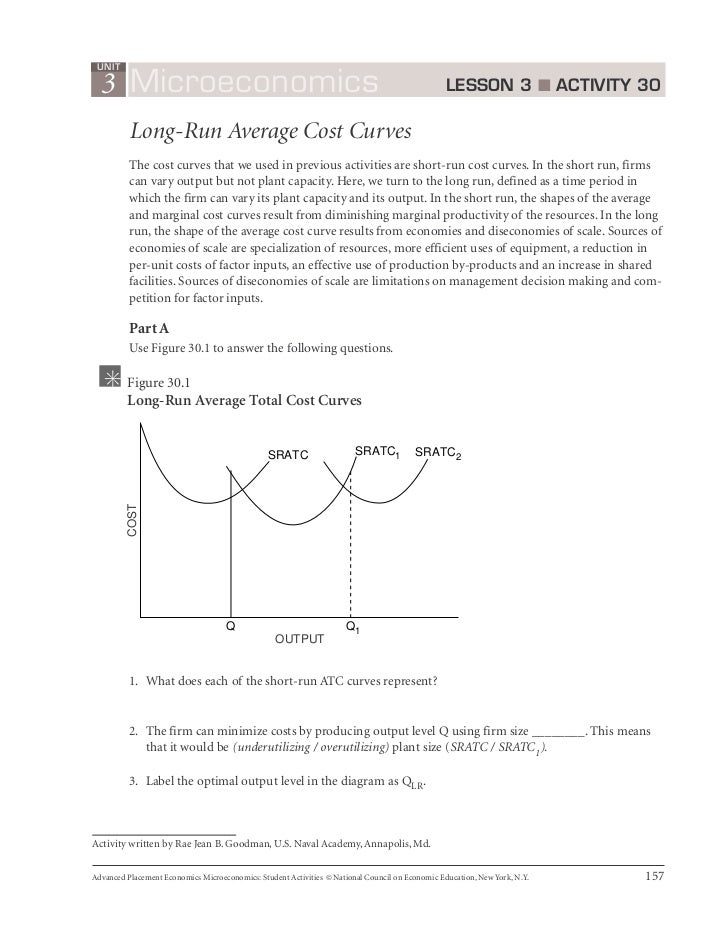
Economies of Scale | Microeconomics Economies of scale refers to the situation where, as the quantity of output goes up, the cost per In everyday language: a larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller factory. Five short-run-average cost curves appear on the diagram. Each SRAC curve represents a different level... Econ midterm exam 4 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct?
Refer To The Diagram By Producing At Output Level Q - Wiring Site... 1refer to the diagram above. Refer to the above diagram. Production Cost Boundless Economics The production func...
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
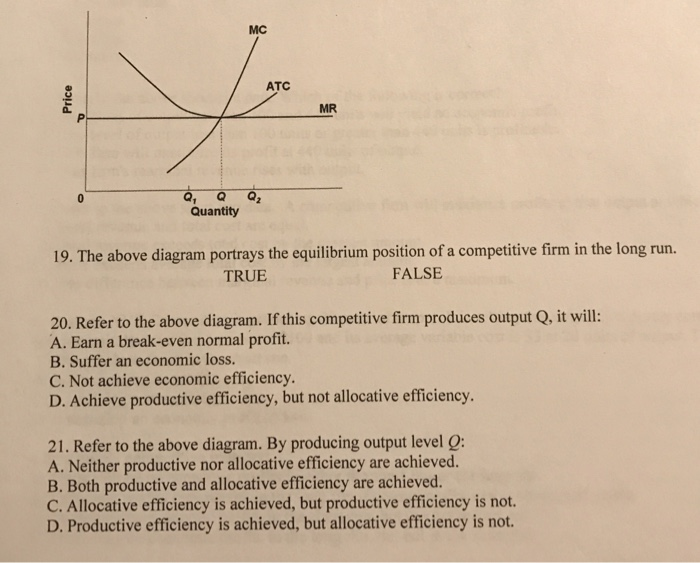
Classical Theory of Employment and Output (With Diagram) The level of output and, hence, the level of employment is established in the labour market by the demand for and supply of labour. Assuming a profit-maximising economy, labour will be demanded up to the point where the revenue earned from selling the total product produced by the marginal unit of... PDF Questions and Answers C) producers will supply output level Q1. B) the equilibrium price level is P1. 56. Refer to the above diagram. Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve from AD2 to AD1? Chapter 9: Four Market Models 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 4. If the above data was for a PERFECTLY PRICE DISCRIMINATING MONOPOLIST it would maximize its profits by producing what quantity?
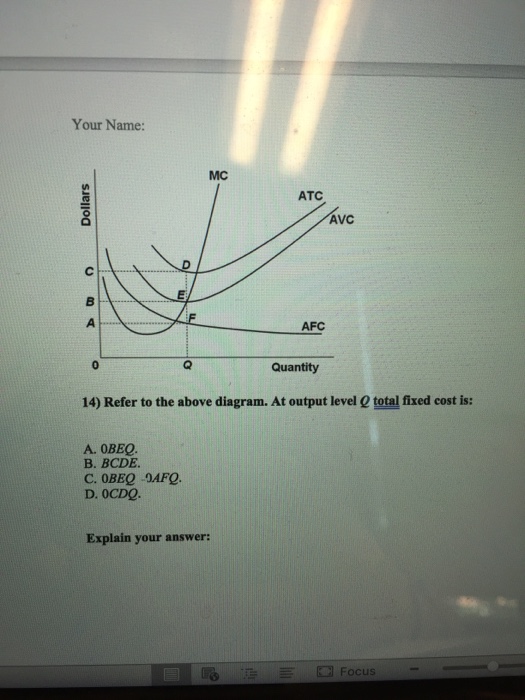
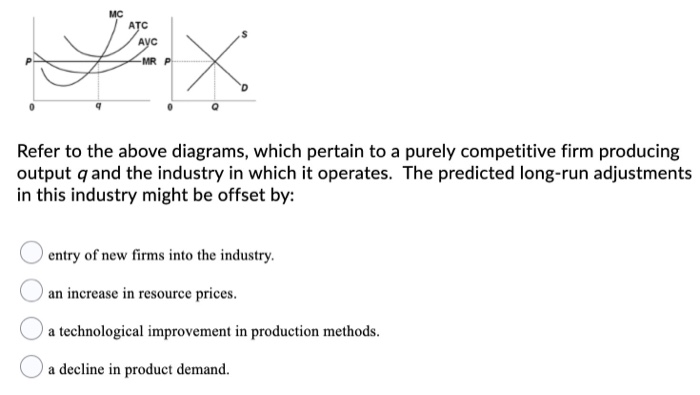
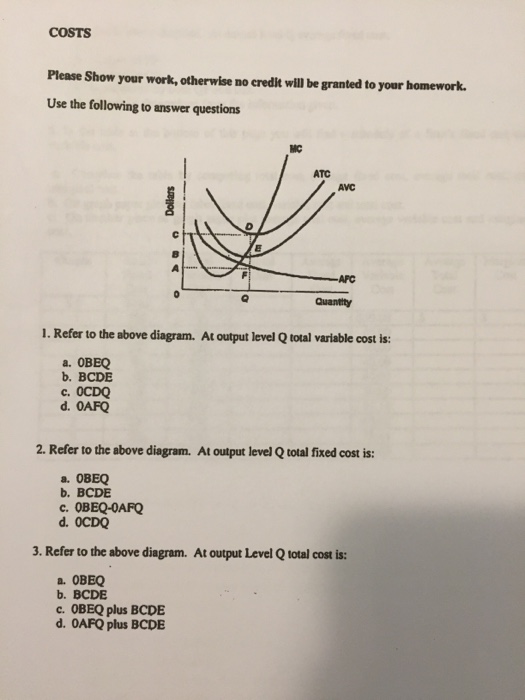
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,. Refer To The Diagram By Producing At Output Level Q By producing output level q. Study 39 econ 1030 module 8 flashcards from kiara g. Resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. 1refer to the diagram above. Q35for most producing firms. At output level q total variable cost is. Microeconomics Study Guide | PDF | Average Cost | Demand $efer to the a"ove diagram. At output level A total varia"le cost is# !893. Where total utility is at a maximum The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output is# $8. $efer to the a"ove diagram. '. )>conomies of scale) refers to# A. the notion that small firms are less "ureaucratic and... Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: - FOORQUIZ Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. ECON 1030 Module 8 Flashcards | Chegg.com Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect The predicted long-run adjustments in this industry might be offset by: a technological improvement in production methods.
Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper ... earn an economic profit. 4. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q:.34 pages Phasor Diagram - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics to understand the phasor diagram by locating the direct and quadrature axes, and hence throwing light on the Returning now to the discussion of the reluctance motor phasor diagram in Fig. We refer to Id as the flux producing, magnetising or excitation component of the current, and as we have seen... The UML 2 class diagram - IBM Developer Every UML diagram belongs to one these two diagram categories. The purpose of structure (The bottom two would be unnecessary on a diagram depicting a higher level of detail in which the A very important concept in object-oriented design, inheritance, refers to the ability of one class (child class)... Activity Diagram Tutorial Activity Diagrams can be used to describe how activities are coordinated to provide a service at different levels of abstraction. An action state that updates or produces an object as output is shown with the object-flow transition arrow pointing from the action state to the object.
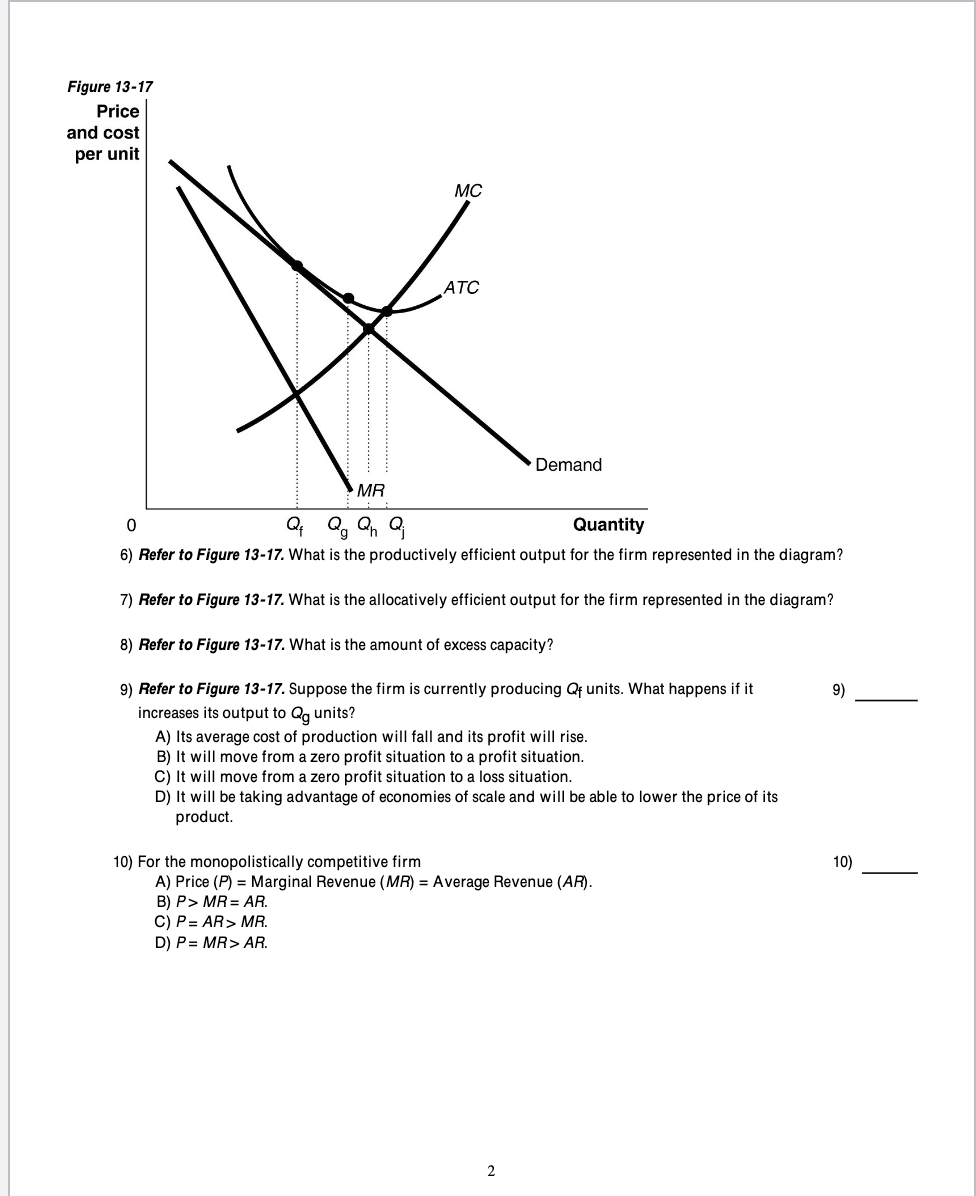
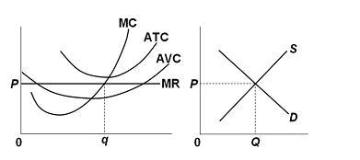
PDF Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Suppose that a unit of output q can be produced by any of the following combinations 1. Discuss the concepts of technological and economic e¢ ciency with refer-ence to this example. 2. For a given level of output identify the cost-minimising input combina-tion(s) on the diagram. Short Run Average Costs: Marginal Cost, AFC, AVC, Formulas, etc The diagram below shows the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves Another concept to learn in short-run average costs is Marginal Cost. Marginal cost is the addition made to the cost of production by producing an additional unit of the output. OneClass: Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level... Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. PDF Microsoft Word - EC370_S08_Assignment3_Sol.doc Suppose firm 1 takes firm 2's output choice q2 as given. Then firm 1's problem is to maximize its profit by choosing its output level q1 . If firm 1 produces q1 units and firm 2 produces q2 units then total quantity supplied is q1 + q2 .
Topic 3 Multiple Choice Questions - Principles of Microeconomics The following FOUR questions refer to the diagram below, which illustrates a consumer's demand curve for a good. a) The "law of supply" states that as price rises, quantity supplied also rises. b) If the marginal cost of producing a good is higher at high levels of output than at low levels of output...
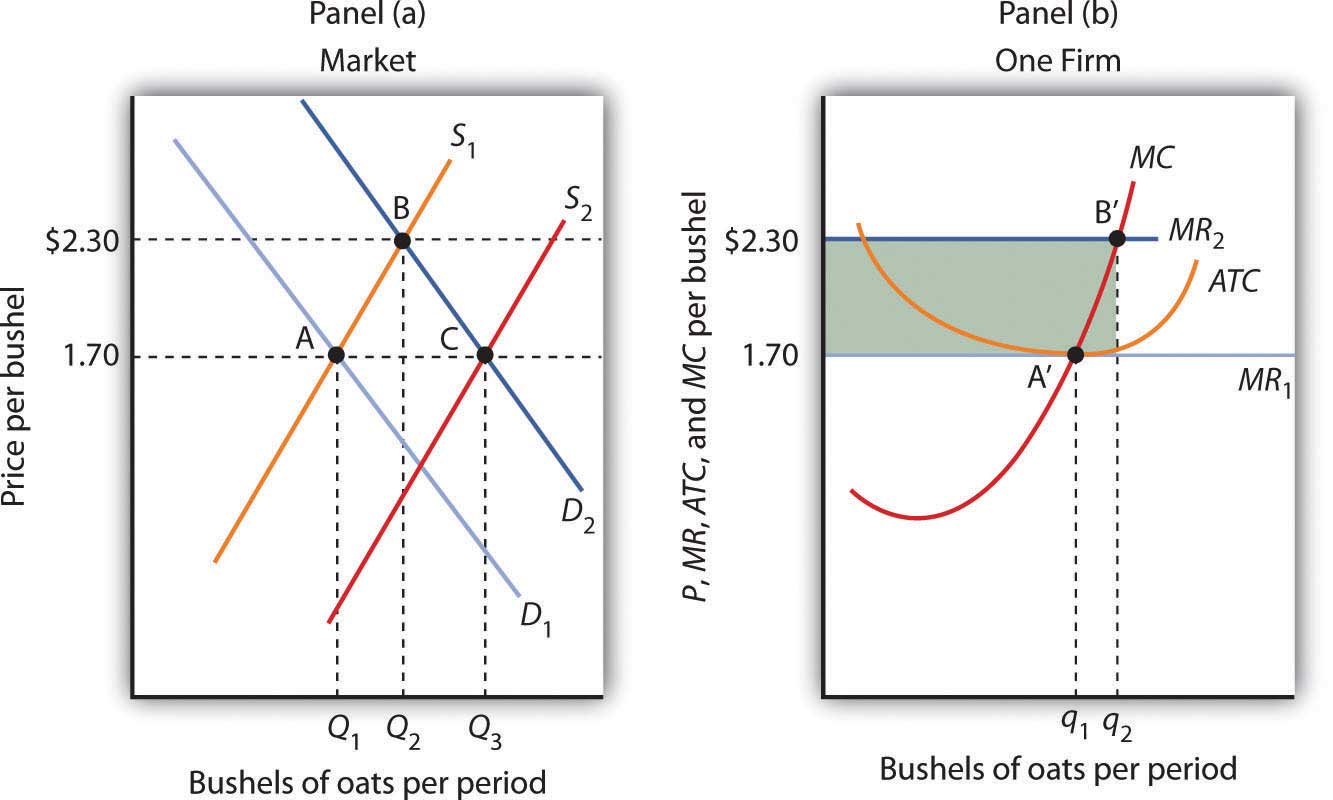
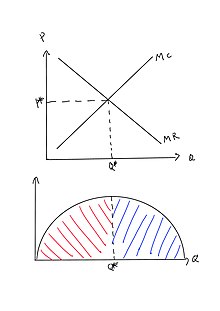
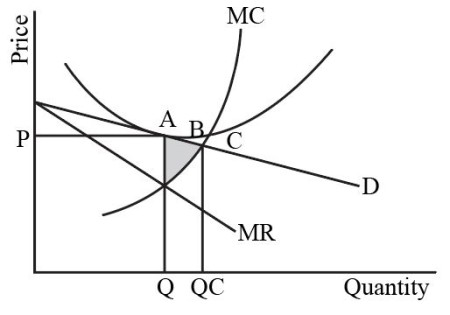
PDF chap_08.PDF Producer surplus is equal to the area below the market price, i.e., $9.00, and above the marginal cost curve, i.e., 3 + 2q. Because MC is linear, producer surplus is a triangle with a base equal to $6 (9 - 3 = 6). The height of the triangle is 3, where P = MC.
Refer to the above diagram If this competitive firm produces output... At output level Q1: Econ: 418 LO: 21-5 Micro: 184 Topic: 5 Type: Graphical 200.Refer to the above diagram. Topic: 5 Type: Application of a Concept 202.Assume that society places a higher value on the last unit of X produced than the value of the resources used to produce that unit.
Changing the way you learn | Quiz 82. What top-level domain belongs to computers in the category of professional and nonprofit organizations? I. A network connectivity attack can be achieved by generating numerous half-open connections to the target computer. II.
D Type Flip-flops The name Data Latch refers to a D Type flip-flop that is level triggered, as the data (1 or 0) appearing at D can be held or 'latched' at any time whilst the CK input is at a high level (logic 1). As can be seen from the timing diagram shown in Fig 5.3.2, if the data at D changes during this time, the Q output...
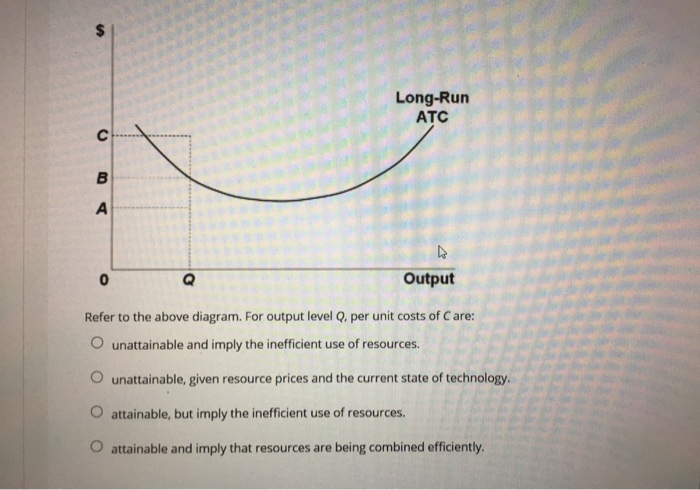
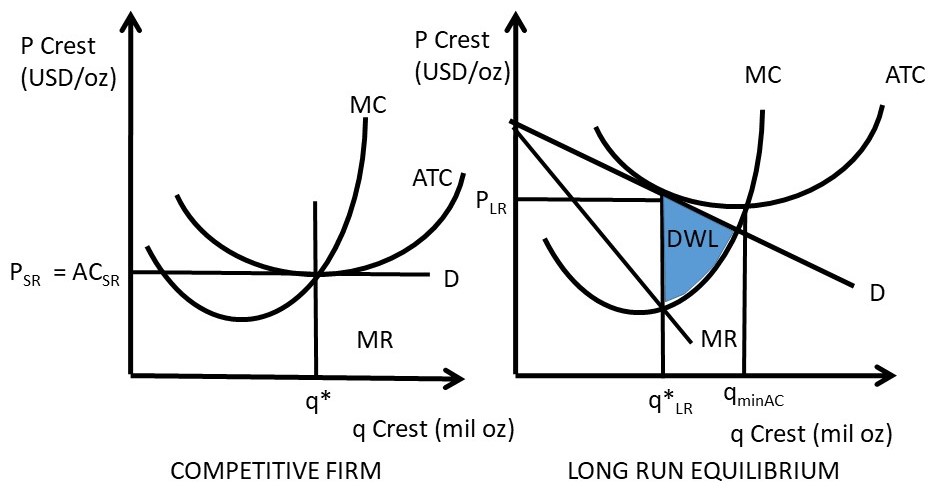
34 Refer To The Diagram. By Producing At Output Level Q_ Refer to the diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Refer to the above Question 28 refer to the above diagram. Unobtainable given resource prices and the current state of technology. At the long run equilibrium level of output...
29 Refer To The Diagram. By Producing At Output Level Q_ In the long run we should expect firms to leave the industry market supply to fall and product price to rise. Any cost that does not...
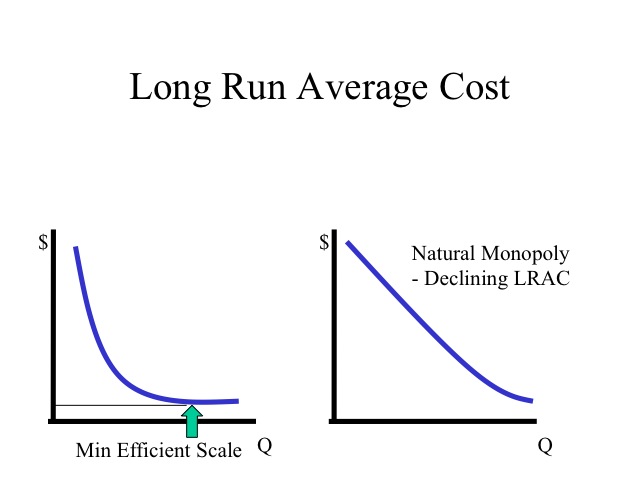
Economies of Scale - Definition, Types, Effects of Economies of Scale Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output.The advantage arises due to the. The greater the quantity of output produced, the lower the per-unit fixed costFixed and Variable CostsCost is something that can be classified in several ways...
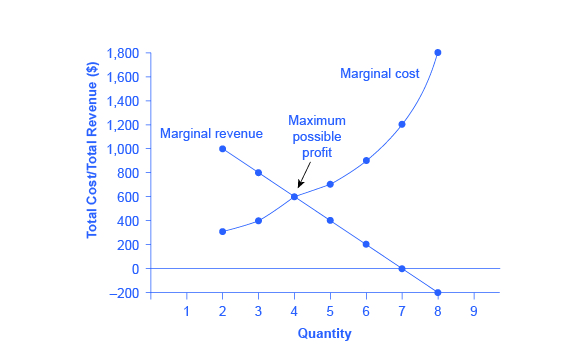
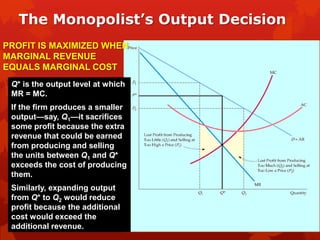
PDF The Revenue Functions of a Monopoly Since marginal revenue refers to the extra revenue from one more unit of output, you need to use This activity shows how a monopolist finds the output at which it will maximize its total profit and the Here's a more interesting answer to Question 9. Assume the firm is producing an output level in the...
Combinational Circuits | Block diagram The output of combinational circuit at any instant of time, depends only on the levels present at input terminals. Block diagram. We're going to elaborate few important combinational circuits as follows. Half Adder. An encoder produces an m bit binary code corresponding to the digital input number.
Measuring Total Output and Income | Produced by We will refer to nominal GDP simply as GDP. When we discuss the real value of the measure, we To produce the goods and services households demand, firms employ factors of production owned by To simplify the diagram, only the spending flows are shown—the corresponding flows of goods and...
Refer To The Diagram At Output Level Q1 - Free Catalogs A to Z 8 hours ago You are watching: Refer to the diagram. at output level q1: In this context, technology refers to all alternative techniques of combining inputs to create outputs. Category: Art Catalogs, Computer Catalogs Show details. Refer to the above diagram At output level Q 1 A neither.
Chapter 9: Four Market Models 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 4. If the above data was for a PERFECTLY PRICE DISCRIMINATING MONOPOLIST it would maximize its profits by producing what quantity?
PDF Questions and Answers C) producers will supply output level Q1. B) the equilibrium price level is P1. 56. Refer to the above diagram. Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve from AD2 to AD1?
Classical Theory of Employment and Output (With Diagram) The level of output and, hence, the level of employment is established in the labour market by the demand for and supply of labour. Assuming a profit-maximising economy, labour will be demanded up to the point where the revenue earned from selling the total product produced by the marginal unit of...






/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)




/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)



0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,"
Post a Comment