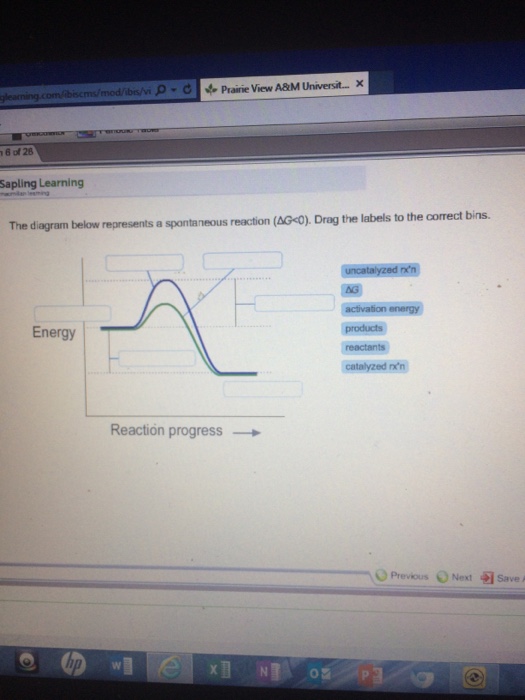
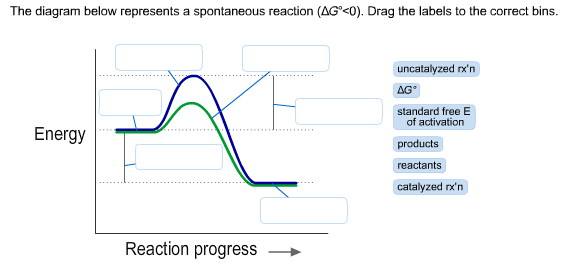
37 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°
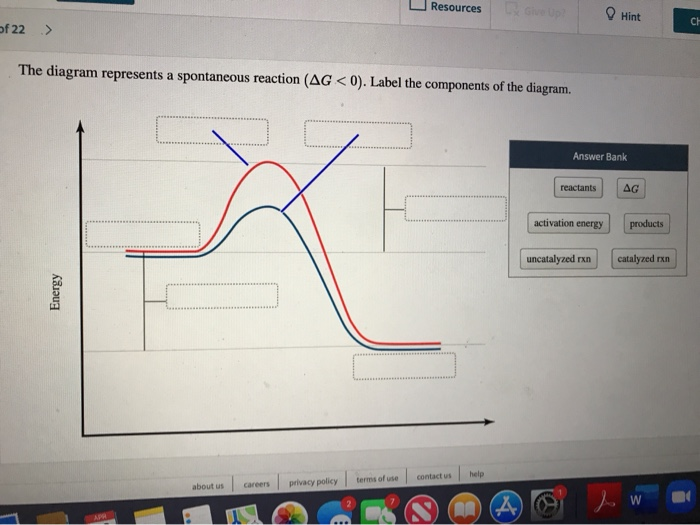
Chem 180 Exam 3 Flashcards - Quizlet The image represents a spontaneous, gaseous reaction at a constant temperature T K. Predict whether ΔH, ΔS, and ΔG for this reaction are positive, negative, or zero. Acetylene, C2H2, can be converted to ethane, C2H6, by a process known as hydrogenation. Solved The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction ... The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. uncatalyzed rx'n Delta G degree standard free E of activation products reactants catalyzed rx?n. Question: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG degree < 0).
Thermodynamics Flashcards - Quizlet For the reaction below ΔG° = + 33.0 kJ, ΔH° = + 92.2 kJ, and ΔS° = + 198.7 J/K. Estimate ... The figure below represents the spontaneous reaction of H2 (shaded spheres) with O2 (unshaded spheres) to produce gaseous H2O. ... According to the diagram above, ΔG° is positive and the equilibrium composition is rich in reactants.

The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°
Solved The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use ... The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Question: The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? KEYPRE-NATCHEM.docx - _1 Refer to the table below Which ... The potential energy diagram of the reaction is shown below. Which arrow represents the heat of reaction (ΔH) for the reverse reaction? ... When a reaction is exothermic and the products have more entropy than the reactants, the reaction is A. spontaneous, with a positive ΔG. Prepared by: Maria Michelle V. Junio and Esperanza R. Sabangan 1. Answered: Consider the weak acid H2A and its… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Consider the weak acid H,A and its conjugate base HA-. Which diagram below represents a buffer solution? Explain your answer. = H2A = HA- A В. Expert Solution.
The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°. Gibbs free energy and spontaneity (article) | Khan Academy Gibbs free energy and spontaneity. When a process occurs at constant temperature and pressure , we can rearrange the second law of thermodynamics and define a new quantity known as Gibbs free energy: where is enthalpy, is temperature (in kelvin, ), and is the entropy. Gibbs free energy is represented using the symbol and typically has units of . Solved The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction ... 100% (22 ratings) Left side must include REACTANTS right side (on the bottom) must be products, since they must be accordingly to the r …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (deltaG < 0). Drag the labels to the correct bins. Part A The image represents a spontaneous gaseous reaction ... Part A The image represents a spontaneous, gaseous reaction at a constant temperature T K. Predict whether Δ H, Δ S, and Δ G for this reaction are positive, negative, or zero. ΔG ˂ 0 for spontaneous reactions Moles of gases decreases, meaning entropy (ΔS) decreases If the sign of Δ G is negative and the sign of Δ S is negative then ΔH must be negative Part B For the gaseous reaction ... PDF CHM 152 Exam 4 Review Ch. 18 19 KEY j. Based on your answers from c, g and h, determine if the following reaction is spontaneous. Explain. 2Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) No, the reaction a written above is not spontaneous. Based on the spontaneous reaction written in part c, Cu(s) is more likely to give up electrons and Ag+(aq) is more likely to accept electrons.
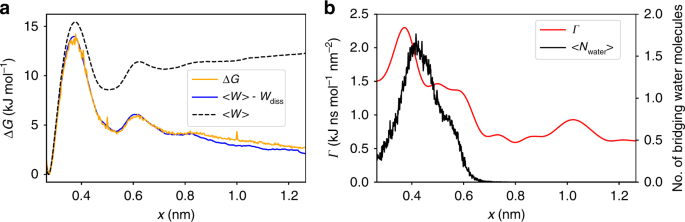
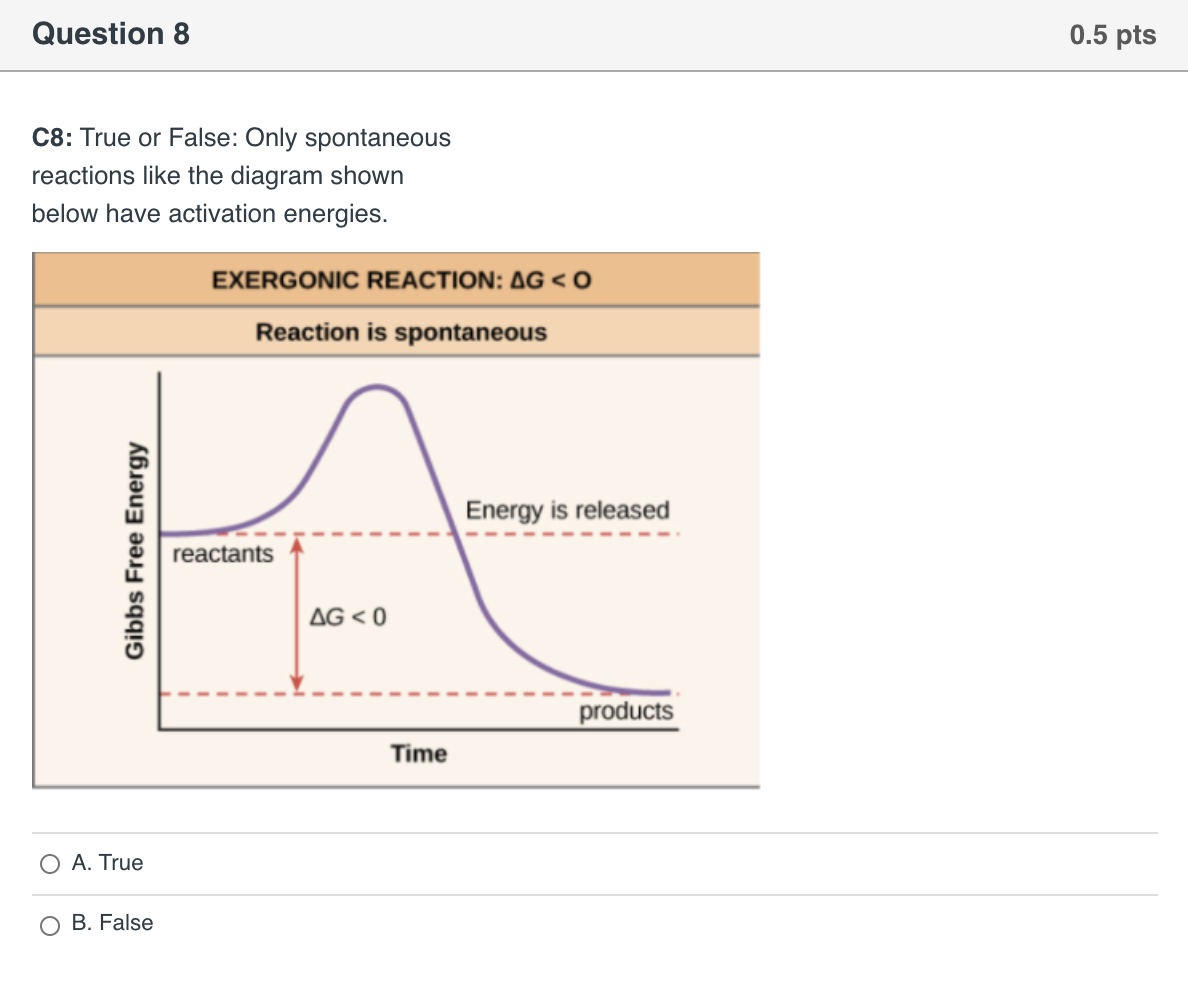
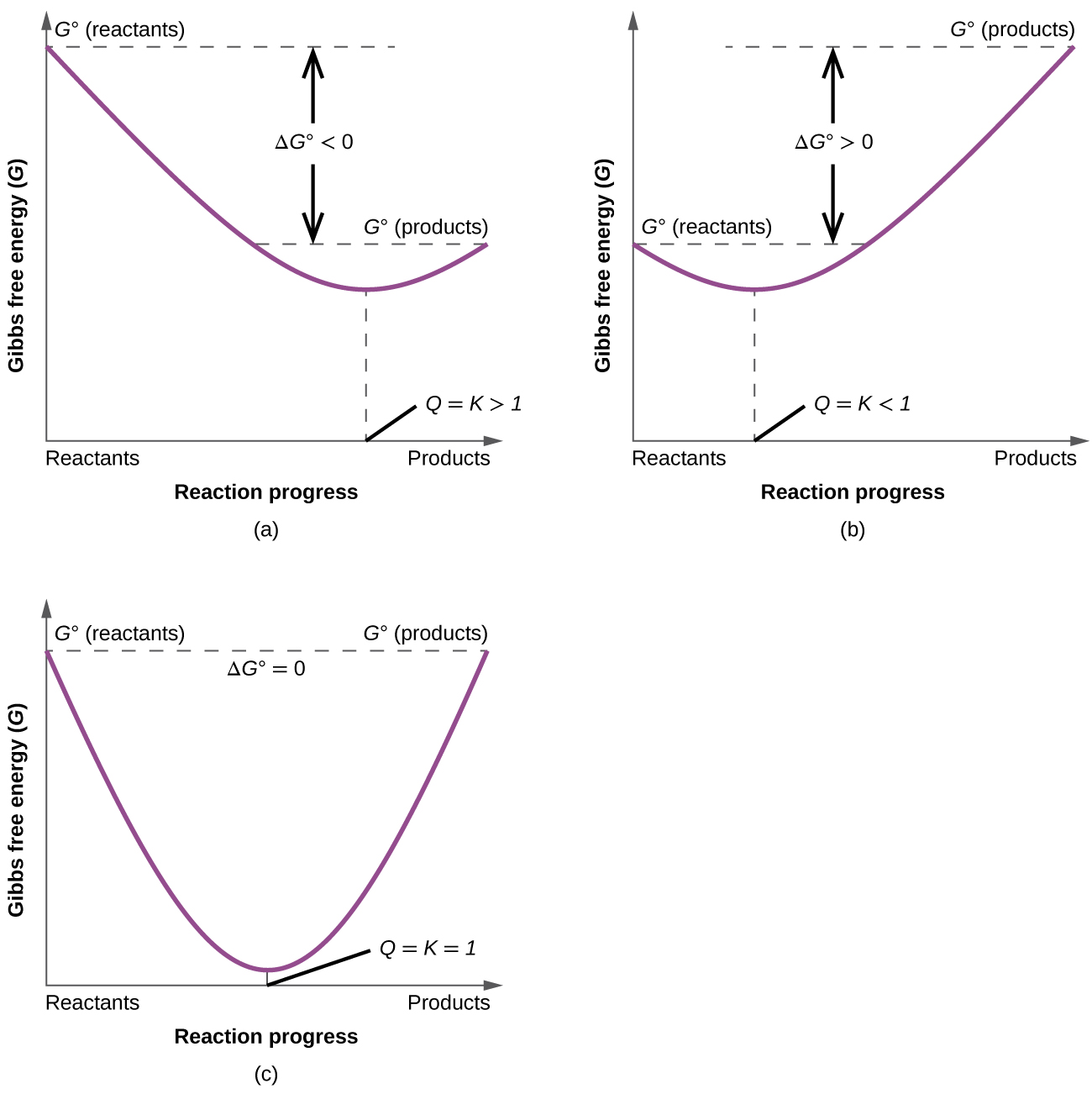
19.6: Gibbs Energy Change and Equilibrium - Chemistry LibreTexts Feb 03, 2022 · Use Equation \(\ref{Eq5}\), the calculated value of ΔS°, and other data given to calculate ΔG° for the reaction. Use the value of ΔG° to determine whether the reaction is spontaneous as written. Solution. A To calculate ΔG° for the reaction, we need to know ΔH°, ΔS°, and T. We are given ΔH°, and we know that T = 298.15 K. The diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction ... In energy profile diagram, if the reactants are at lower energy and products are at higher energy, then the reaction is non-spontaneous reaction.1 answer · 0 votes: Concepts and reason In energy profile diagram, if the reactants are at lower energy and products are at higher energy, then the reaction is non-spontaneous ... Which of the following statement is true about ΔG? When it ... When delta G is equal to zero, neither the forward nor the reverse reaction is spontaneous. The correct option is A. A system at equilibrium has its delta G equals to zero, at this point, the free energy change is neither positive nor negative; the reaction is at equilibrium and both the forward and the reverse reactions are not spontaneous. Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity of Reactions Chemistry ... ΔG represents the change in Gibbs free energy for a chemical system at constant temperature and pressure ΔG = ΔH -TΔS ... We can write an equation to represent this entropy change in the surroundings at constant temperature as shown below: ... For a spontaneous reaction, ΔG for the reaction is negative (ΔG < 0).
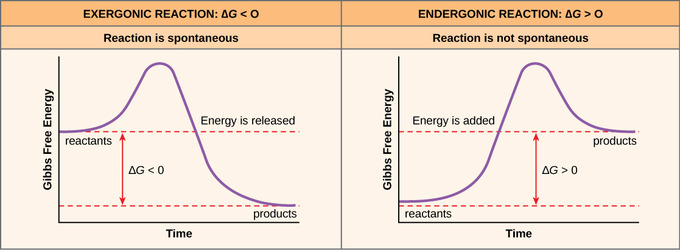
(PDF) ESSENTIAL CELL BIOLOGY ESSENTIAL CELL ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Gibbs free energy - Wikipedia The reaction will only be allowed if the total entropy change of the universe is zero or positive. This is reflected in a negative ΔG, and the reaction is called an exergonic process. If two chemical reactions are coupled, then an otherwise endergonic reaction (one with positive ΔG) can be made to happen. Gibbs free energy - chemguide ΔG = ΔH - TΔS. Remember that for a reaction to be feasible, ΔG has to be negative. ΔH could be negative (an exothermic reaction) or positive (an endothermic reaction). Similarly ΔS could be either positive or negative. There are four possible combinations of the signs of ΔH and ΔS. I want to look at those in turn. Solved Label the components of an energy diagram for a ... Question: Label the components of an energy diagram for a spontaneous reaction. Answer Bank reactants activation energy products uncatalyzed reaction catalyzed reaction Reaction progress- This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
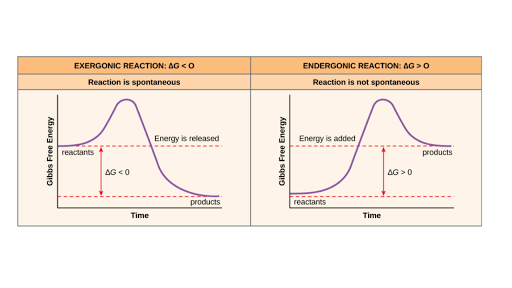
Free energy | Endergonic vs exergonic reactions (article ... The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and how it's related to reaction spontaneity and equilibrium. The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and how it's related to reaction spontaneity and equilibrium. ... Gibbs free energy and spontaneous reactions. Endergonic, exergonic, exothermic, and endothermic. Free energy. This is the currently selected item.
Which of the following must be true about a reaction if it ... Endothermic reactions (ΔH>0) that increase the entropy of the system (ΔS>0) are spontaneous at high temperatures. ΔH is the change in enthalpy. ΔS is change in entropy. T is temperature of the system. When ΔG is negative, a reaction (occurs without the addition of external energy) will be spontaneous (exergonic).
16.4: The Nernst Equation - Chemistry ... - Chemistry LibreTexts Feb 20, 2022 · which represents the transport of cupric ion from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. The driving force for this process is the free energy change ΔG associated with the concentration gradient (C 2 – C 1), sometimes known as the free energy of dilution: \[ΔG_{dilution} = RT \ln(C_2 – C_1)\]
How to calculate the temperature at which a reaction becomes ... What you really want to do here is use $ΔG = ΔH - TΔS$, use the given data for enthalpy and entropy. Set $ΔG$ to $0$, and solve for temperature, as that is the criteria for equilibrium and the point for $ΔG$ below which the reaction will be spontaneous
Solved The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use ... The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? What is the activation energy of the reaction? Question: The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
Gibbs Free Energy - Definition, Equations, 2nd Law of ... ΔG > 0; the reaction is non-spontaneous and endergonic. ΔG < 0; the reaction is spontaneous and exergonic. ΔG = 0; reaction is at equilibrium. Note: According to the second law of thermodynamics entropy of the universe always increases for a spontaneous process. ΔG determines the direction and extent of chemical change.
CHEM 152 UNIT III Flashcards | Quizlet The spontaneous redox reaction in a voltaic cell has _____ A) a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of ΔG. B) a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of ΔG. C) a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of ΔG. D) a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of ΔG. E) a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for ΔG.
CHEM 4311 HW4 *in progress collab Flashcards - Quizlet The reaction SO2(g)+2H2S(g)⇌3S(s)+2H2O(g)SO2(g)+2H2S(g)⇌3S(s)+2H2O(g) is the basis of a suggested method for removal of SO2SO2 from power-plant stack gases. The values below may be helpful when answering questions about the process. Calculate the equilibrium constant KpKpK_p for the reaction at a temperature of 298 KK.
Cumalative Chem Final Flashcards | Quizlet a. The reaction is only spontaneous at low temperatures. b. The reaction is at equilibrium at 25°C under standard conditions. c. ΔG° becomes less favorable as temperature increases. d. The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures. e. The reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures.
Exam 1 Flashcards - Quizlet Exam 1. Find ΔE° for the reaction below if the process is carried out at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm and ΔV (the volume change) = -24.5 L. (1 L • atm = 101 J)2 CO (g) + O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) ΔH° = -566. kJ. The following drawing is a representation of a reaction of the type A → B, where different shaded spheres represent different ...
Answered: Consider the weak acid H2A and its… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Consider the weak acid H,A and its conjugate base HA-. Which diagram below represents a buffer solution? Explain your answer. = H2A = HA- A В. Expert Solution.
KEYPRE-NATCHEM.docx - _1 Refer to the table below Which ... The potential energy diagram of the reaction is shown below. Which arrow represents the heat of reaction (ΔH) for the reverse reaction? ... When a reaction is exothermic and the products have more entropy than the reactants, the reaction is A. spontaneous, with a positive ΔG. Prepared by: Maria Michelle V. Junio and Esperanza R. Sabangan 1.
Solved The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use ... The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Question: The diagram represents a spontaneous reaction. Use the diagram to answer the questions below. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?



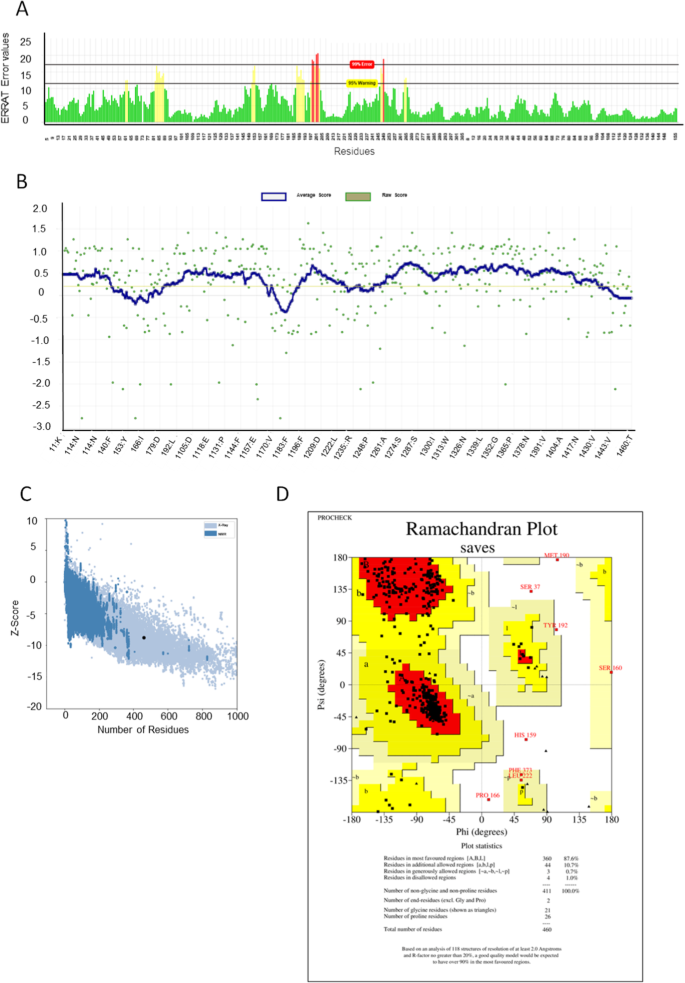

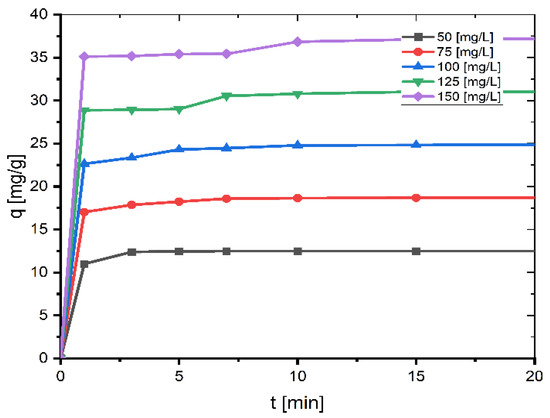


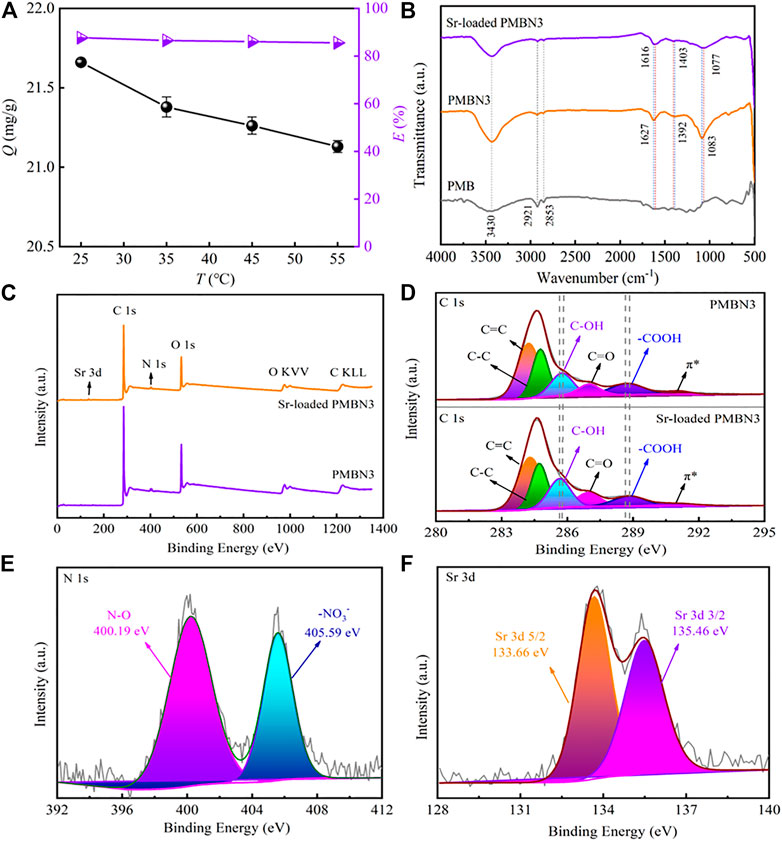
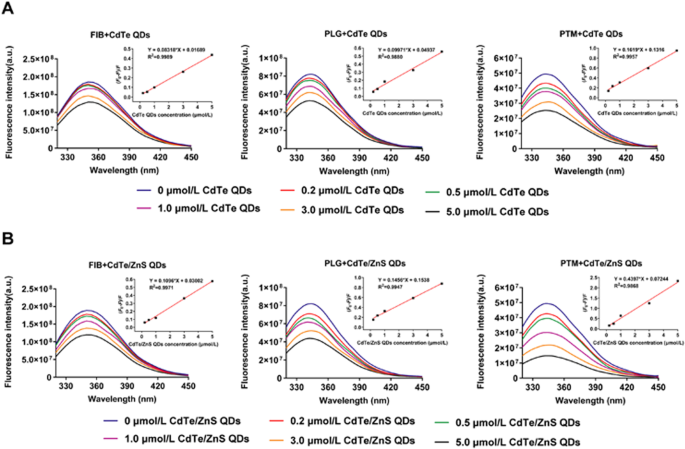



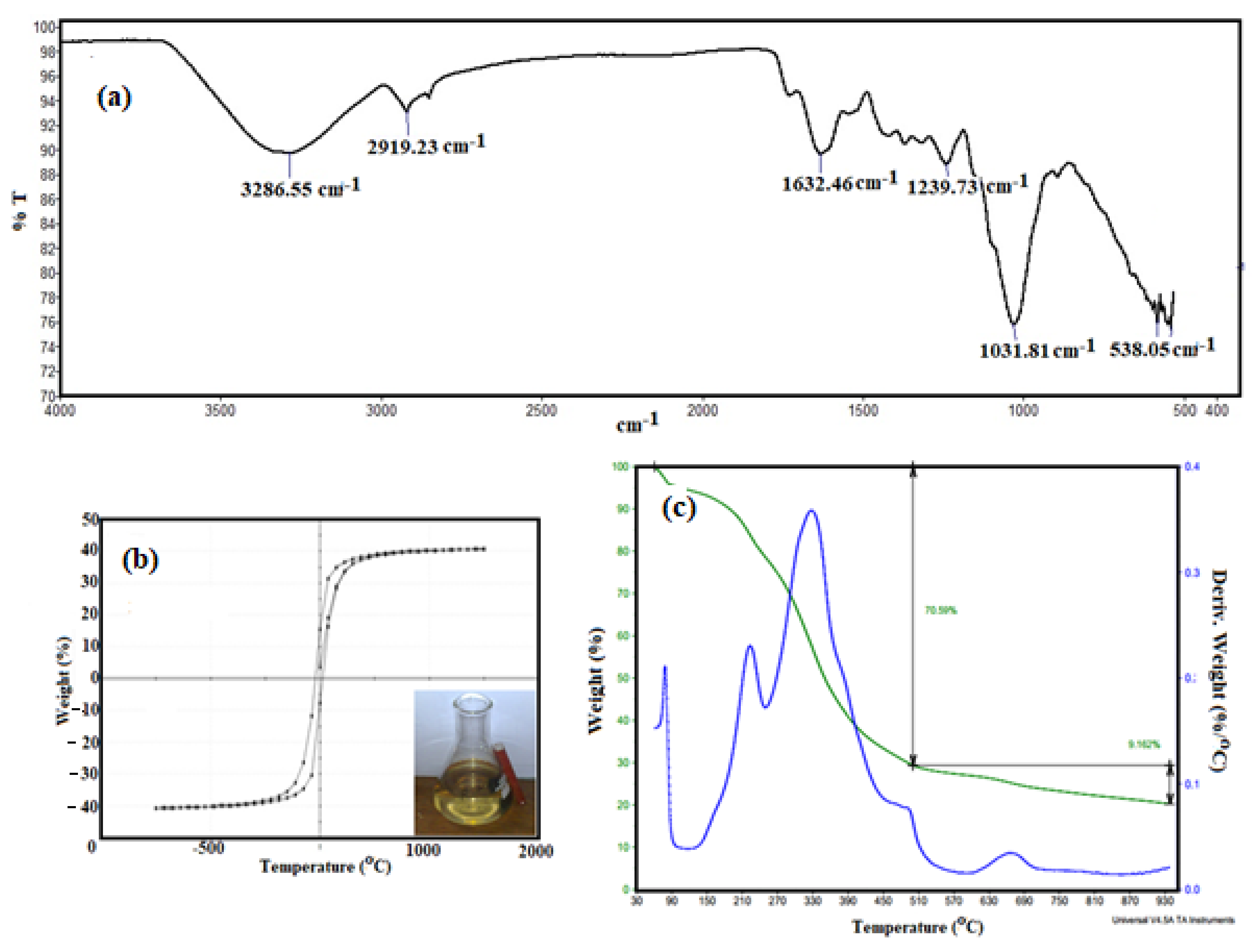

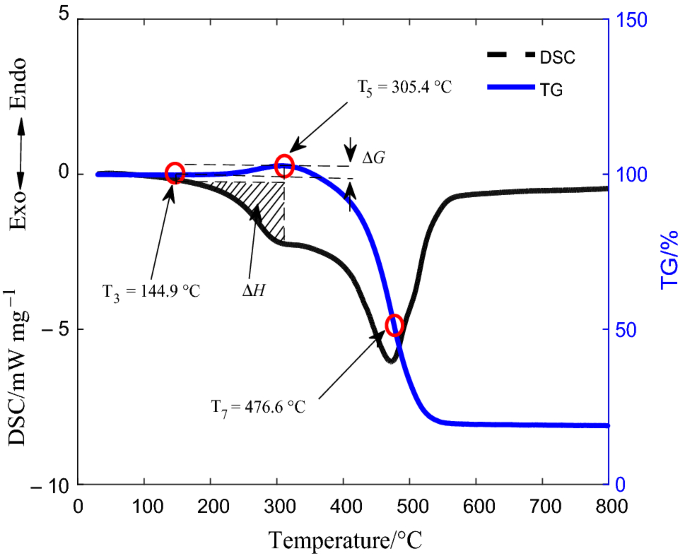

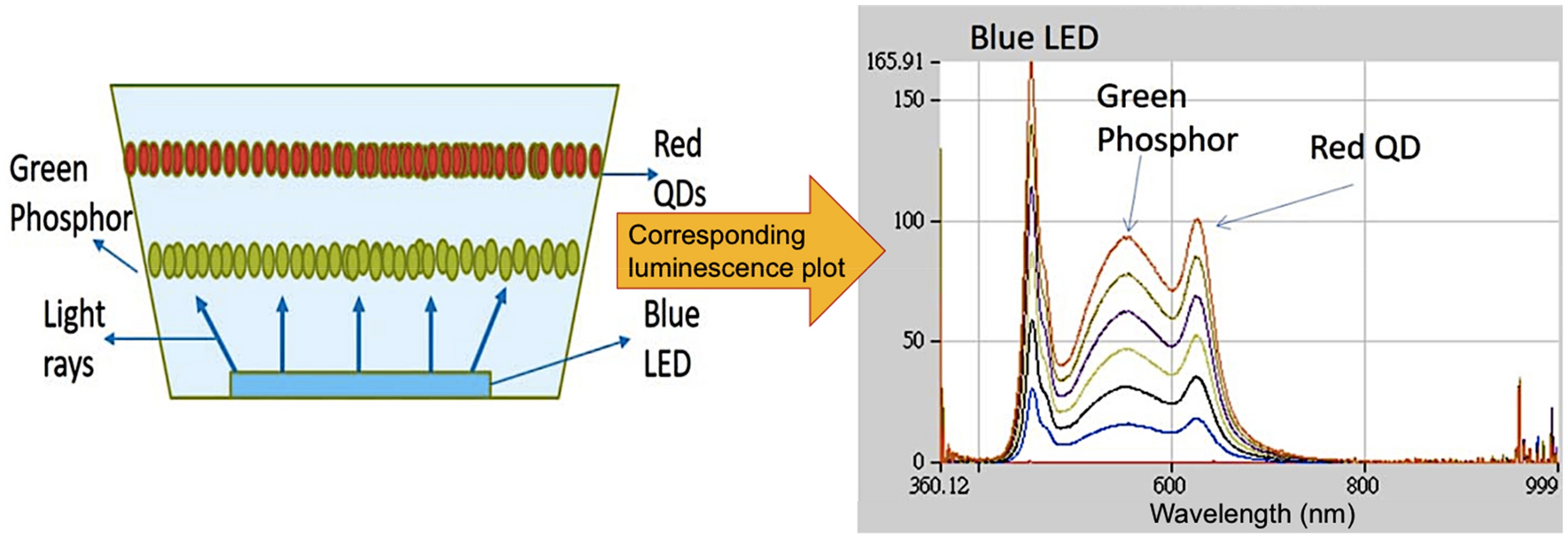
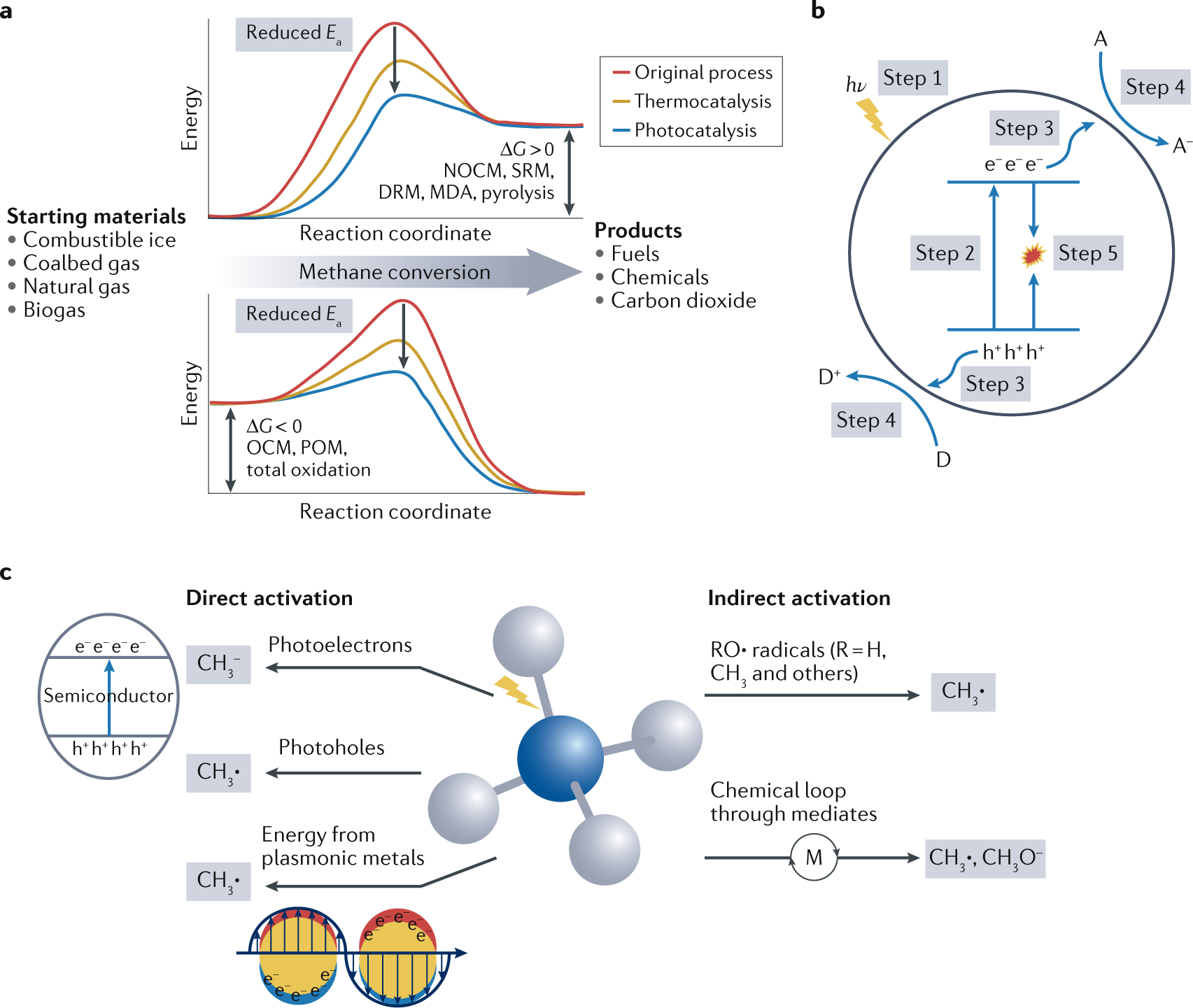

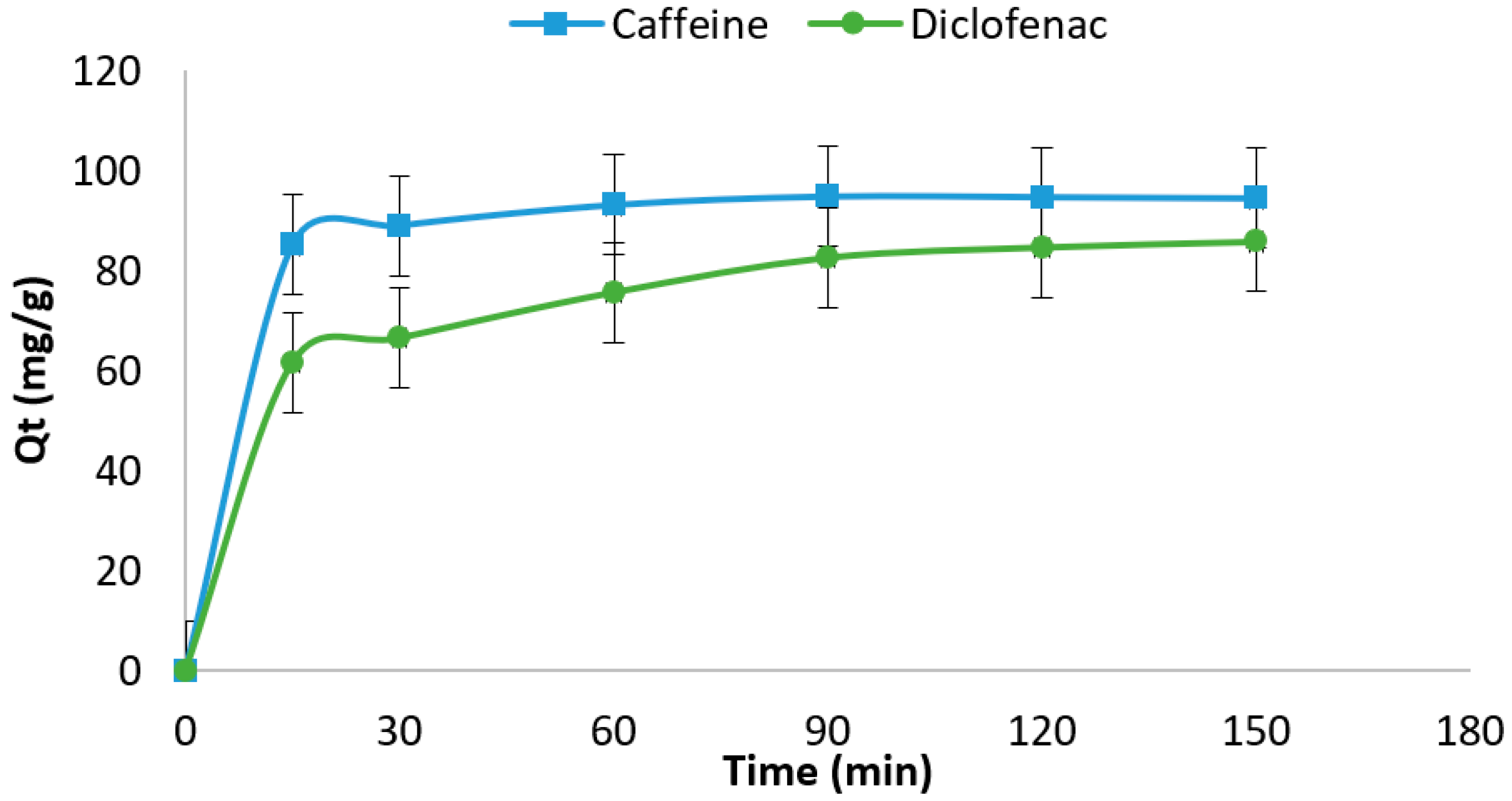



0 Response to "37 the diagram below represents a spontaneous reaction (δg°"
Post a Comment