36 free body diagram constant velocity
Free Body Diagrams 1 Constant Velocity - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Free Body Diagrams ...Basics A little bit about me, Tony Wayne · by Tony Wayne ...(If you are a teacher, please feel free to use these resources in your teaching.)
Free Body Diagrams UC Irvine Physics and Astronomy Videos · School blocks YouTube? Download file below
Free body diagram constant velocity
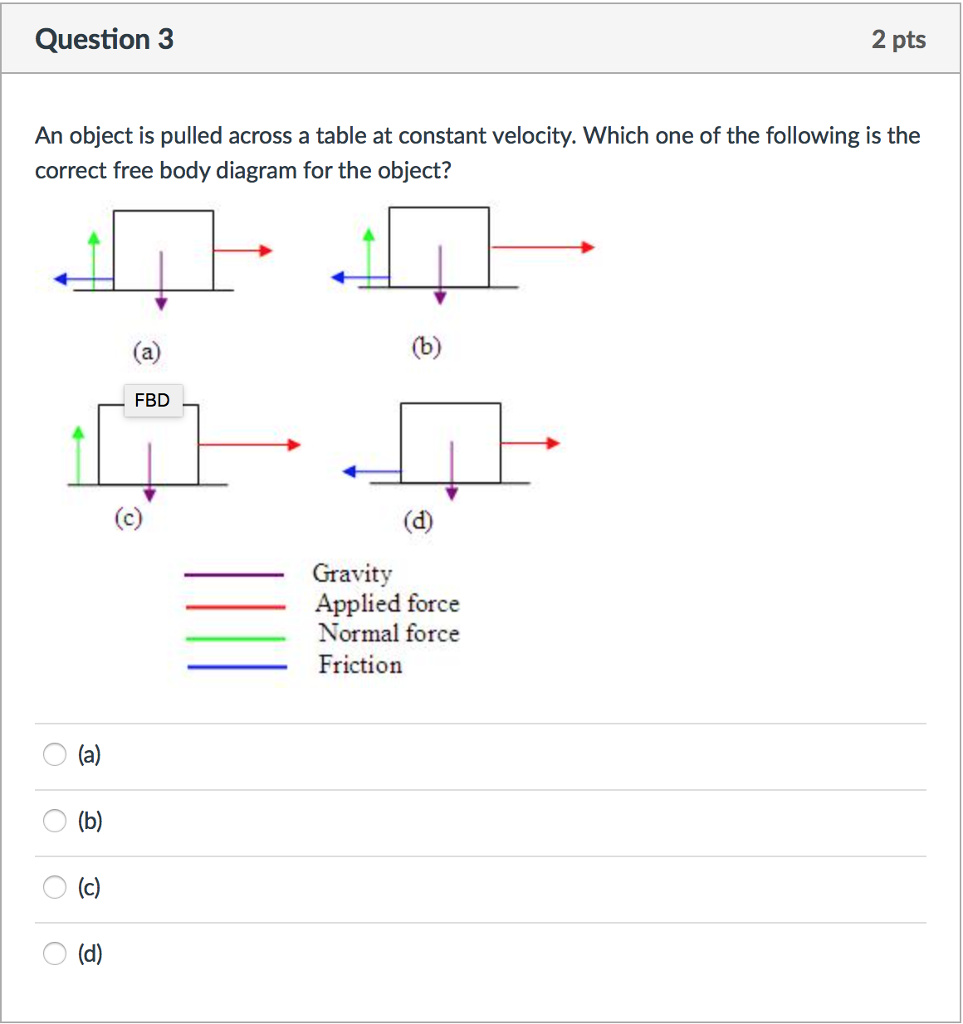
Free Body Diagrams | Science Quiz - Quizizz Which of the following is true about this free-body diagram? answer choices . the forces are are balanced. the object is free-falling. the object is moving upward. the forces are unbalanced ... (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Tags: Question 16 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. Match description ... Free-body diagram: simple cases - Boston University Physics Constant Velocity: A box is moving at constant velocity to the right. Which free-body diagram is correct? mg down and N up mg down, N up, some other force F to the right mg down, N up, equal-and-opposite forces left and right could be 1 or 3 In both cases above, mg and N are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Black-body radiation - Wikipedia Black-body radiation has a characteristic, continuous frequency spectrum that depends only on the body's temperature, called the Planck spectrum or Planck's law.The spectrum is peaked at a characteristic frequency that shifts to higher frequencies with increasing temperature, and at room temperature most of the emission is in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
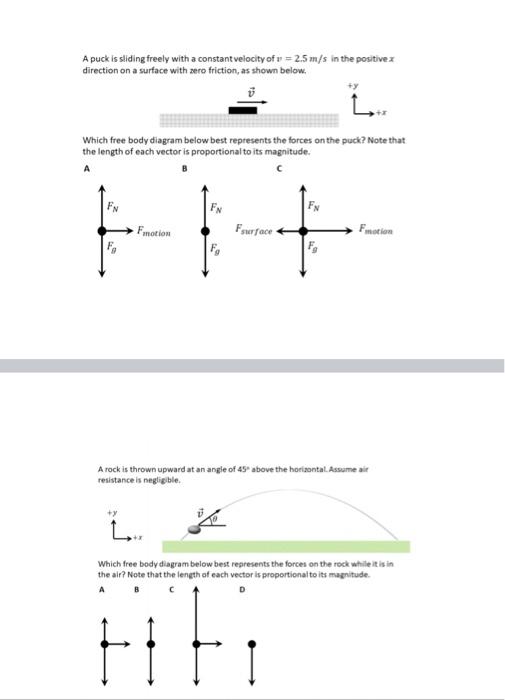
Free body diagram constant velocity. Types of forces and free body diagrams (video) | Khan Academy Sal defines and compares tension, weight, friction and normal forces using free body diagrams. A free body diagram challenge: the constant velocity buggy | Quantum ... June 30, 2013 - Here's a deceptively hard free body diagram problem: draw a free body diagram for a motorized cart moving at constant velocity. Even though these constant velocity buggies are staples of the first weeks of many physics classes, I've come to realize the free body diagrams for these buggies are ... Freebody_Solved.pdf - Free-body Diagrams To help us ... Question 2 about free-body diagrams An object moves at constant velocity to the right across a table. Which free-body diagram(s) of the object match(es) this motion? 1. Force of gravity directed down, normal force from the table directed up. 2. Force of gravity down, normal force up, and some other force directed to the right. 3. Speed and Velocity: Difference and Examples - Study.com Sep 24, 2021 · Like I just stated, constant velocity requires both a constant speed and an unchanging direction. If you change your speed at all, even if you are moving in a straight line, your velocity must change.
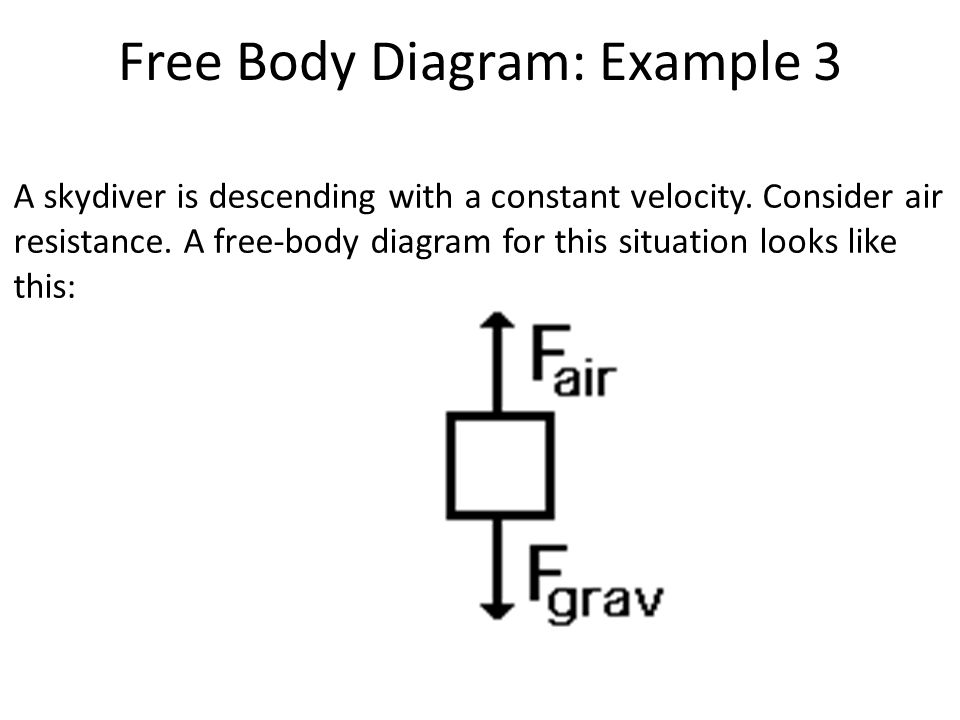
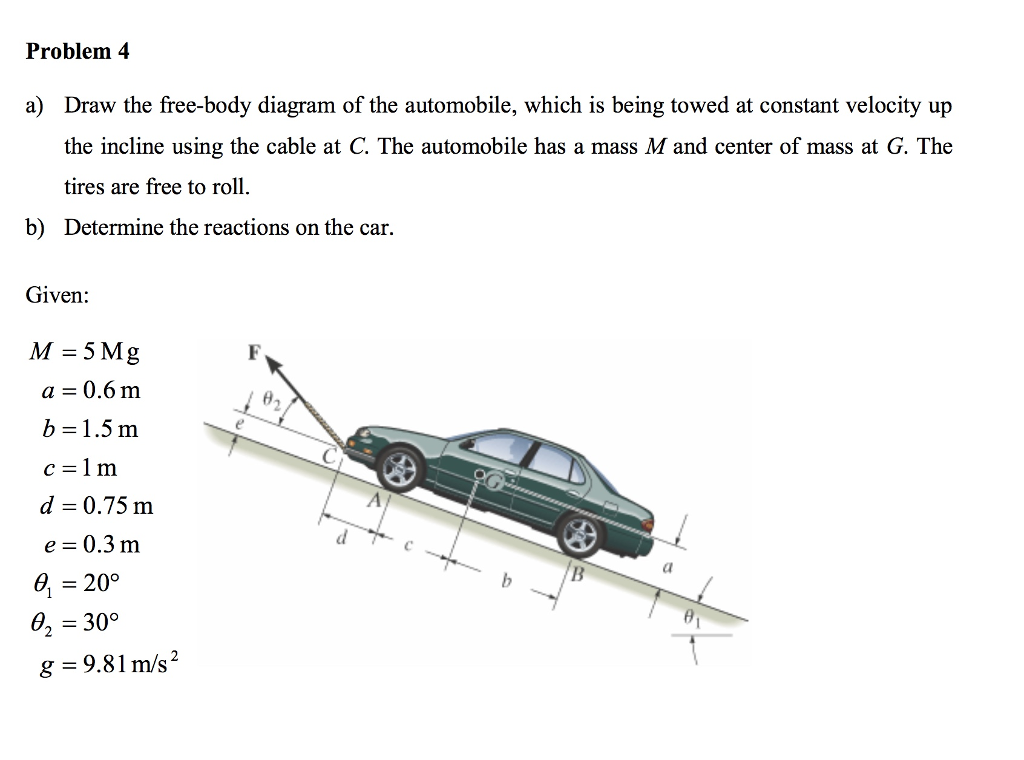
Chapter 2 Actuators and Drive Systems - MIT OpenCourseWare From the free body diagram of the motor rotor, m m m r load I ω τ τ 1 = − (2.2.4) where load r τ 1 − is the torque acting on the motor shaft from the joint axis through the gears, and ω m is the time rate of change of angular velocity, i.e. the angular acceleration. Let be the Solved Draw a Free-Body Diagram for the friction block ... Draw a Free-Body Diagram for the friction block being pulled by the string if the block moves with a constant velocity. Include coordinate axes. Write out the Newton's 2nd Law equation for each axis including all details of the forces. (You should have two equations, one for each axis.) Free Body Diagram - Definition, Examples, Solved Problems ... A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Normally, a free body diagram consists of the following components: The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Commonly, air resistance and friction are neglected. PDF Free Body Diagram PRACTICE PROBLEMS - Yola 8. A skydiver is descending with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 9. A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 10.
Newton's Laws & Free body diagrams • Cartoon - MSU P-A ... This stands in for a top-level web page. The site is meant to provide files in various sub-directories, not here at the top level Free Body Diagrams ...Basics - mrwaynesclass.com Using Free Body Diagrams to Develop a Math Model: ... If the body is moving at a constant velocity then the summation will equal zero. (Recall that a body at rest is moving at a constant velocity of zero.) If the body is accelerating, then the summation will equal F net or as it is sometimes written, ma net. Free body diagram - Wikipedia A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it. In physics and engineering , a free body diagram ( FBD ; also called a force diagram ) [1] is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces , moments , and ... Answers: Free Body Diagrams Biology, Chemisty, Physics, Engineering, Earth Science, Environmental Science · The Science Department promotes active learning as a model for lifelong self-education. The pursuit of scientific knowledge, development of learning skills, and enhancement of positive social interactions are all ...
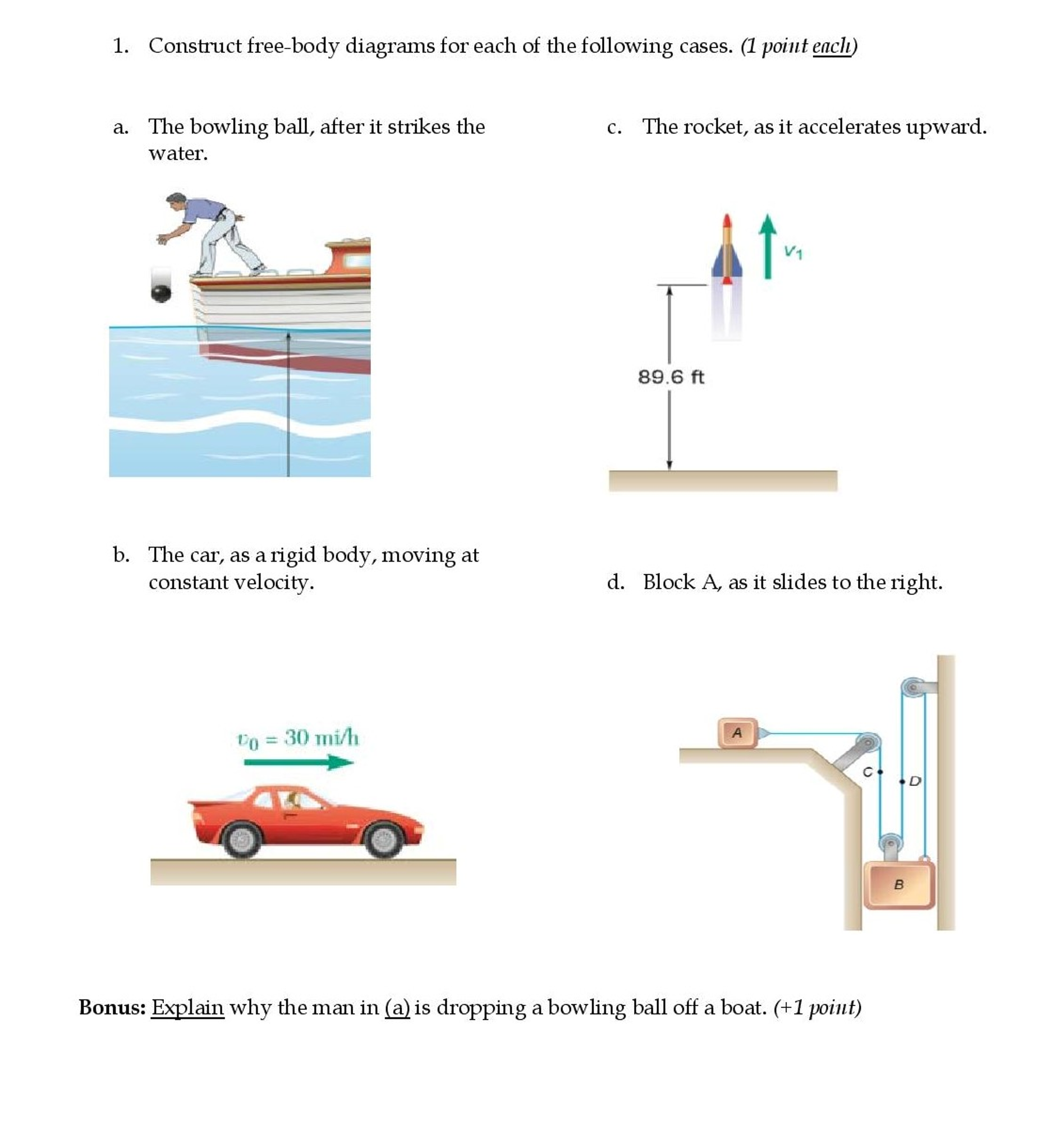
Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. Use the following forces. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3.
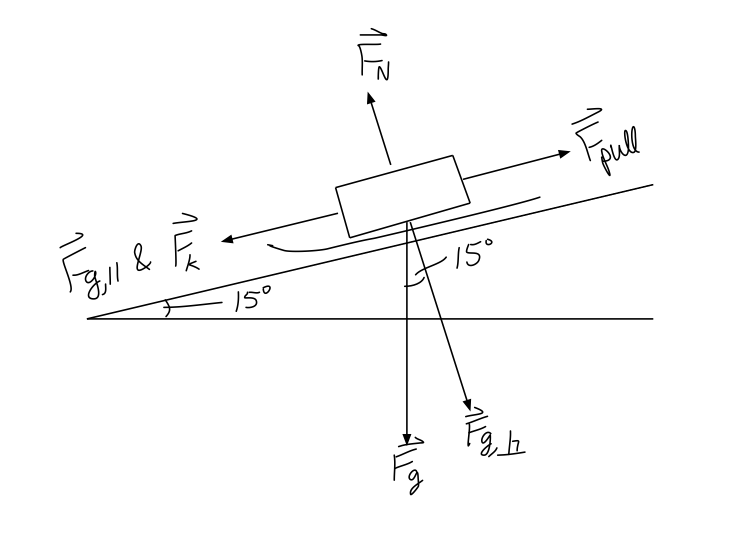
Solved A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 ... A skier of mass 63 kg skis straight down a 140 slope at constant velocity. Draw a free-body diagram of the skier with the various external forces acting on her. Include the force of air resistance, which is directed opposite the velocity. (Do this on paper. Your instructor may ask you to turn in this work.) (a) Find the value of the normal force.
Physics – Kinematics, Projectile Motion, Free-Body Diagrams ... Take classes in-person or online at San Jacinto College's five campuses in Houston and Pasadena, including the newest location, Generation Park Campus in northeast Houston. Complete your basics and transfer to a university or get skills for a well-paying career with over 200 degrees and ...
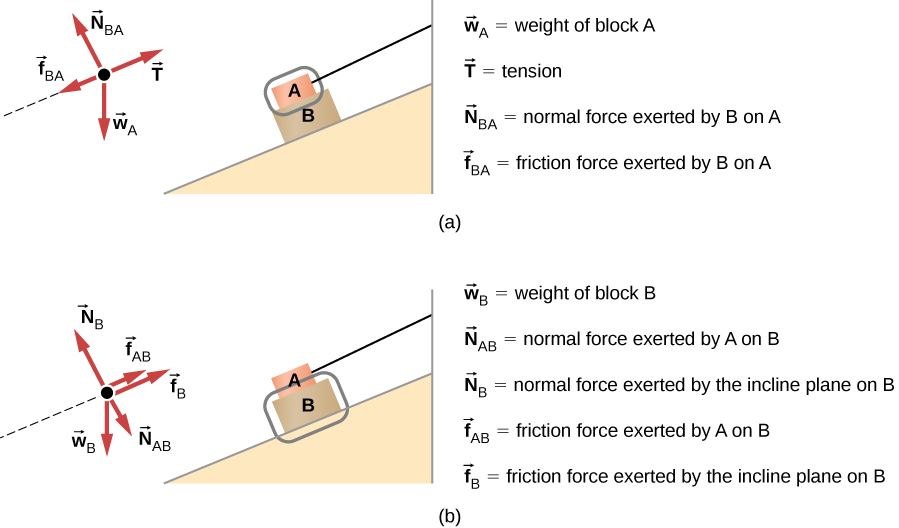
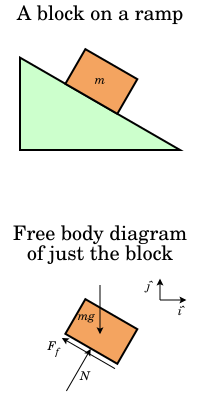
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams | University Physics Volume 1 Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
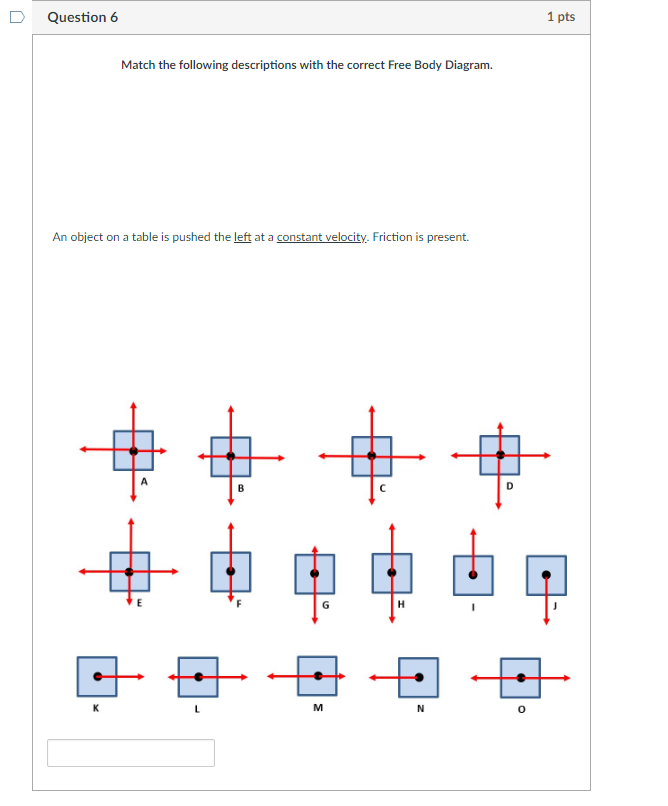
PDF Free-Body Diagrams - Ms. Poulton's Science & Math Class ... Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached
PDF 3-3 Constant Velocity, Acceleration, and Force Figure 3.7: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for an object drifting to the right through space. Figure 3.8: Motion diagram and free-body diagram for a box being dragged to the right, by means of a string, across a flat surface.
Identifying Free-Body Diagrams for Accelerating Objects ... The free-body diagram in figure 1 shows 4 forces being exerted on an object. {eq}F_2 {/eq} and {eq}F_4 {/eq} seem to have the same length and are pointing to opposite directions.
PDF Notes: Free Body Diagrams - Weebly Level 3: Drawing Free Body Diagrams When we are working with forces, we often need to find the net force acting on an object. To do this, we first start by sketching a picture of the forces acting on it. We call this picture a free body diagram. There are a few rules we should follow when drawing a free body diagram. 1.
Free Body Diagrams - Tension, Friction, Inclined Planes ... This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acc...
DOC Free Body Diagrams Worksheet - Reynolds School District An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this:
Friction - University of Tennessee constant velocity <--> no acceleration <--> no net force The x- and y-components of all forces have to add up to zero. To keep track of all the forces, it helps to draw a free-body diagram. Details of the calculation: (a) See the drawing on the right. (b) The suitcase moves with constant velocity, the net force on the suitcase is zero.
Free Body Diagram | Laws of Motion Quiz - Quizizz Question 2. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. Match description with free-body diagram. answer choices. A book is at rest on a tabletop. A gymnast holding onto a bar, is suspended motionless in mid-air. The bar is supported by two ropes that attach to the ceiling. Diagram the forces acting on the combination of gymnast and bar.
2.04 ** Constant Velocity Worksheet.pdf - 2.04 Constant ... 2.04 Constant Velocity and Free Body Diagrams [Emma Neubauer] Background Information Velocity = Displacement / Time v = d / t On all of these problems, show your work (the numbers that you are using and how you are using them) and the answer with the proper significant digits and the proper units. If you write out your answers (neatly) with pen or pencil and paper - you may take a picture or ...
Forces, Free Body Diagrams, and Newton's First Law of ... Try drawing some system diagrams and free-body diagrams of your own. Check your answers when finished. A sign, hanging by a string. Answer ... A car, travelling at constant speed down a straight stretch of highway. Answer
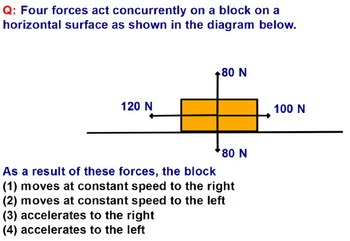
PDF Forces and Free-Body Diagrams - pnhs.psd202.org Free-body diagrams Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. This diagram shows four forces acting upon an object. There aren't ... constant velocity, meaning a net force of 0N, the F app will equal the F f.
Free body diagrams - Higher - Forces and their interactions - Eduqas ... Learn about and revise contact and non-contact forces, gravity, weight, free body diagrams and resolving forces with GCSE Bitesize Physics.
Free Body Diagram - 941 Words | Cram the ramp and draw a free body diagram of the cabinet in the box here: ... Force Applied is the force required (by you for instance) to make the cabinet move at a constant velocity in either direction or keep it from accelerating (if applicable). Recall…constant velocity = _____ net force. ...
An Easy Guide to Understand Free Body Diagrams in Physics ... The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. These vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force.
What is a Free-Body Diagram and How to Draw it (with ... A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
free-body diagram Flashcards | Quizlet Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces involved. Gravity is the only force acting on the egg as it falls. A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk. Consider frictional forces. ... A skydiver is descending with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram. Gravity pulls down on the ...
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams – University Physics ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
On a free body diagram, how can I tell the difference between an ... Answer (1 of 5): That’s the cool thing, it usually doesn’t matter. Begin at rest or at constant velocity does not change the answer, so long as you have accounted for all relevant external forces in your diagram. This is pivotal to our understanding of relativity, that all inertial frames ...
Free-body Diagram - Physics Forums Free-body Diagram. Not sure about the correct wording for this question! A brick of mass M sits on a rubber pillow of mass m . Together they are sliding to the right at constant velocity on an ice-covered parking lot. (a) Draw a free-body diagram of the brick and identify each force acting on it. (b) Draw a free-body diagram of the pillow and ...
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
DOC Free Body Diagrams - erhsnyc.org Drawing a free body diagram involves at least the first two of the following steps: Draw a dot to represent the center of gravity of the object. Draw and label arrows extending outward from the dot to represent the forces acting on the object. Drawing the arrows at least approximately to scale and correct angles helps.
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
15A: Newton's Laws #2: Kinds of Forces, Creating Free Body ... November 5, 2020 - Do not add a bogus “force of motion” to your free body diagram. It is especially tempting to add a bogus force when there are no actual forces in the direction in which an object is going. Keep in mind, however, that an object does not need a force on it to keep going in the direction in which it is going; moving along at a constant velocity ...
Black-body radiation - Wikipedia Black-body radiation has a characteristic, continuous frequency spectrum that depends only on the body's temperature, called the Planck spectrum or Planck's law.The spectrum is peaked at a characteristic frequency that shifts to higher frequencies with increasing temperature, and at room temperature most of the emission is in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Free-body diagram: simple cases - Boston University Physics Constant Velocity: A box is moving at constant velocity to the right. Which free-body diagram is correct? mg down and N up mg down, N up, some other force F to the right mg down, N up, equal-and-opposite forces left and right could be 1 or 3 In both cases above, mg and N are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Free Body Diagrams | Science Quiz - Quizizz Which of the following is true about this free-body diagram? answer choices . the forces are are balanced. the object is free-falling. the object is moving upward. the forces are unbalanced ... (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Tags: Question 16 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. Match description ...














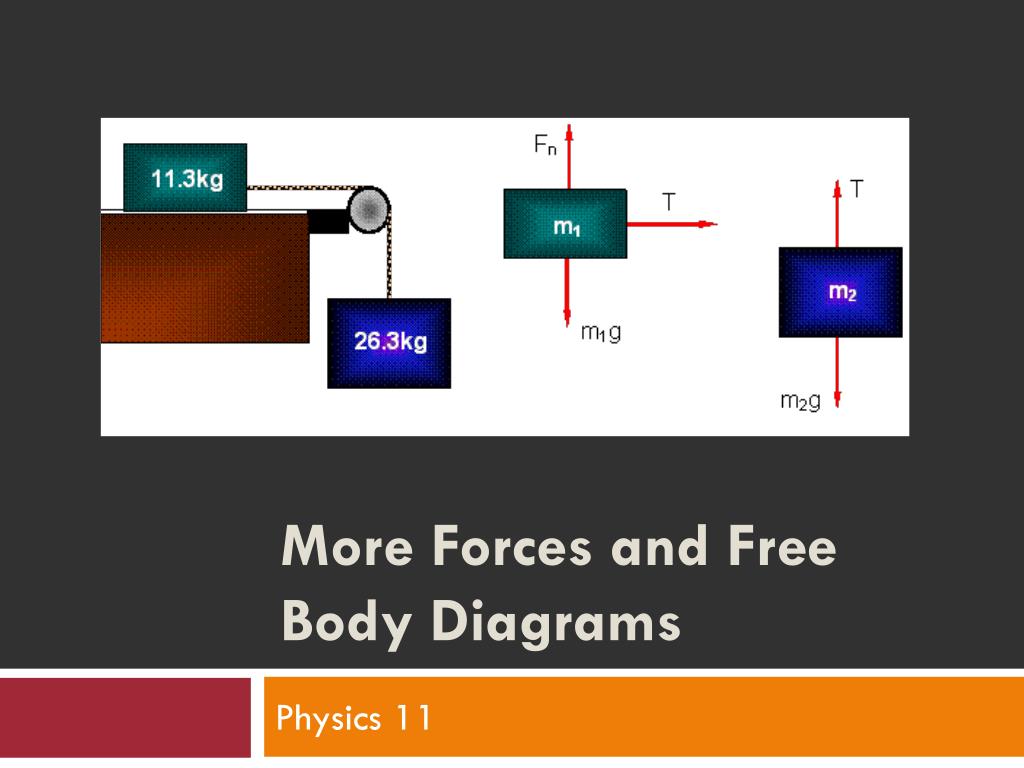
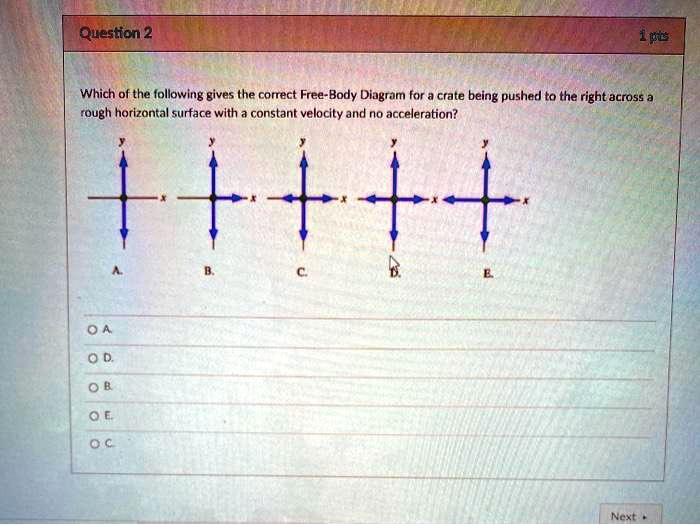
0 Response to "36 free body diagram constant velocity"
Post a Comment