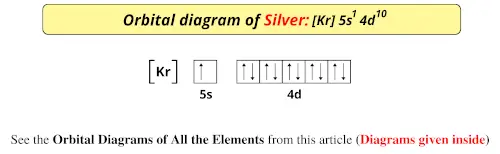
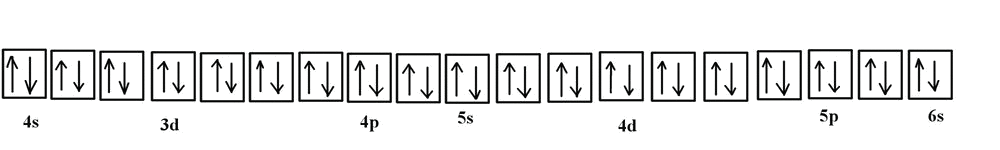
40 orbital diagram for silver
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
So, lithium has two electrons in the 1s orbital and a third electron in the 2s orbital, giving it the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 1. Orbital Diagram Beryllium has an atomic number of 4, so it has 4 electrons available to place in the orbital diagram. The chemical symbol for Gold is Au. 19 × 10 −17 seconds.

Orbital diagram for silver
Answer: Silver (Ag) has an electron configuration of [Kr] 4d 10 5s 1. The element is much more stable and has a lower energy when the 4d orbital is filled, so one electron is placed there, rather than in the 5s orbital. When it is ionized, the electron is removed from the outermost shell, which is the 5s orbital. Orbital notation: 1s2 2s62p6 3s2 3p 4s1 3d5 Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation:1[Ar] 4s 3d5 c) Molybdenum Orbital notation: 1s262s2 52p103s 3p6 4s2 3d 4p6 5s1 4d Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation: [Ar] 5s1 4d5 d) Silver Orbital notation: 1s222s262p6 13s 103p 4s 3d10 4p6 5s 4d Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation ... Silver (Ag). Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of silver-108 (atomic number: 47), an isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 47 protons (red) and 61 neutrons (orange). 47 electrons (white) successively occupy available electron shells (rings).
Orbital diagram for silver. Write the electron configuration b. Write the abbreviated orbital diagram a c. Give a set of four quantum numbers for the two highest energy electrons in ge. 1. Consider Silver atom (Ag, At. No.=47) a. Write its electron configuration b. Write its orbital diagram c. Write its abbreviated electron configuration d. Write its abbreviated orbital ... Silver-Line SL-1218R Orbital Floor Refinisher Owners Manual Thank you for purchasing a SL-1218R floor refinisher. When used properly this unit will perform well as a rental machine. Please review and follow the suggested procedures for operation of this machine. Aug 12, 2018 · Well, we can write the electronic configuration of the silver atom... A quick glance at the Periodic Table tells us that Z_"Ag"=47..and so for the NEUTRAL atom.... We use the Aufbau process to write the electronic distribution of the SILVER atom... underbrace(1s^(2)2s^(2)2p^(6)3s^(2)3p^(6)3d^(10)4s^(2)4p^(6))_"electronic configuration of krypton"5s^(1)4d^(10) That the configuration shows 5s^(1 ... To create the orbital configuration, we can refer to the orbital diagram below. As silver has an atomic number of 47, a neutral atom has 47 protons...
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Silver [Z=47] Uranium [Z=92] Which elements are represented by these noble gas configurations? [Ar] 4s2 63d . [Xe] 6s2. [Ne] 3s2 13p . [Kr] 5s2 104d 5p2. Another way to represent the electrons is called . This is similar to the electron configuration, but it includes a diagram of the Silver has electronic configuration as [Kr] 4d10 5s1 . The s orbital ( 5s ) has only one electron. And the s orbital here has n = 5 (as it is in the fifth period) and l = 0 . The s orbital is symmetric in space (sphere) which has only one orientation and hence has no "different" orientations each of which is represented by a particular value of ml. Orbital notation is a drawing of the electron configuration. It is very useful in determining electron pairing and thus predicting oxidation numbers. The orbital notation for sulfur would be represented as ... [Silver is an exception and only makes an oxidation state of +1.] The +1 oxidation state for copper
You might notice that the orbital correlation diagram that we drew above is actually similar to that for the disrotatory ring-opening of cyclobutene. The principles are exactly the same, and the state correlation diagram can be constructed exactly analogously (and in fact, the state correlation diagram for this process is found in Fig. 2 of the ... The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ... Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau... The orbital diagram for hydrogen can be represented in the following way. This notation uses a box to represent the orbital, the label for the orbital and an arrow to represent the electron. The electronic configuration for hydrogen can be written as 1s 1. This is a short-hand notation which identifies the level, the sublevel and the number of ...
6. Draw the orbital energy (i.e., box) diagram for the electrons beyond the [Kr) core of the element silver (Ag). If all the electrons are paired in the orbital energy diagram, the element is said to be diamagnetic, meaning that atoms of the element will interact weakly with an external magnetic field.
Orbital diagram of Silver (Ag) 48: Orbital diagram of Cadmium (Cd) 49: Orbital diagram of Indium (In) 50: Orbital diagram of Tin (Sn) 51: Orbital diagram of Antimony (Sb) 52: Orbital diagram of Tellurium (Te) 53: Orbital diagram of Iodine (I) 54: Orbital diagram of Xenon (Xe) 55: Orbital diagram of Caesium (Cs) 56:
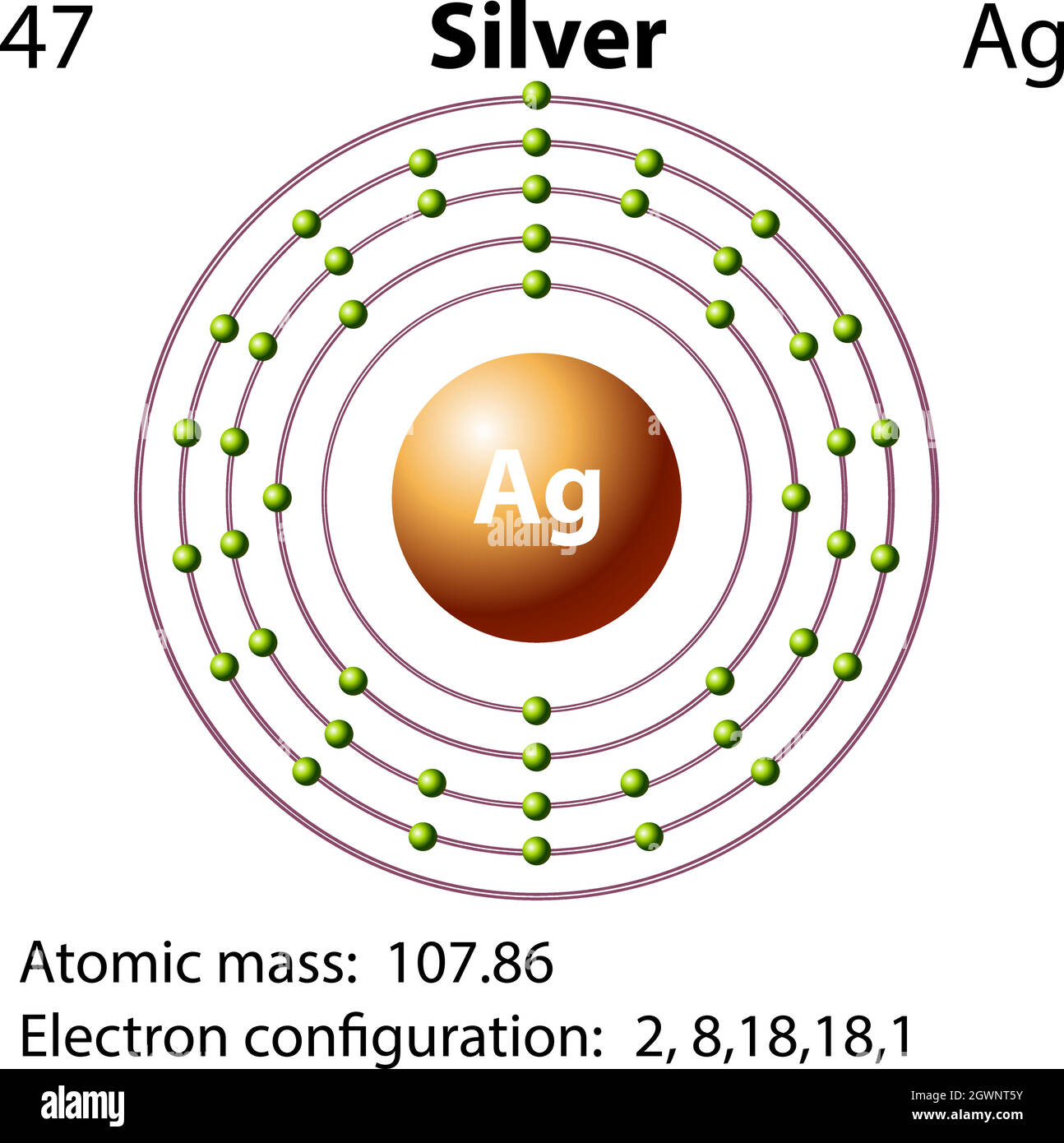
The silver atom has 5 electron orbits (energy levels) with a total of 47 electrons. Beginning with the orbit closest to the nucleus and working outward, the number of electrons per orbit should be: 2, 8, 18, 18, 1. What is the electron configuration for Ag +? Silver/Electron configuration What is the SPDF notation of silver?
The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms.
Sources of Silver: Found in ores called argentite (AgS), light ruby silver (Ag 3 AsS 3), dark ruby silver (Ag 3 SbS 3) and brittle silver. Silver is often obtained as a by-product of refining other metals like copper and gold. World wide production is around 9950 tons per year. Primary mining areas are Mexico, Bolivia, Honduras, Canada, USA ...
Answer: Silver (Ag) has an electron configuration of [Kr] 4d 10 5s 1. The element is much more stable and has a lower energy when the 4d orbital is filled, so one electron is placed there, rather than in the 5s orbital. When it is ionized, the electron is removed from the outermost shell, which is the 5s orbital.
2. Electron Configuration (quicker to draw than orbital filling diagrams) Ex. O2 1s2 2s2 2p4. 3. Electron Dot shows only the valence (outer energy level) electrons. . Ex. Oxygen atom . O :. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams . for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram
Silver (Ag) has an atomic mass of 47. Find out about its chemical and physical ... Orbital Diagram. Ag - Silver - Orbital Diagram - Electron Configuration ...Atomic Number: 47Atomic Weight: 107.8682 Isotopes
Silver electron configuration. Ag (Silver) is an element with position number 47 in the periodic table. Located in the V period. Melting point: 961.9 ℃. Density: 10.49 g/cm 3 . The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Ag atom is an exception to the rule. Expected electronic configuration. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d9.
An orbital diagram is used to show how the orbitals of a subshell areoccupied by electrons. The two spin projections are given by arrowspointing up (ms =+1/2) and down (ms = -1/2).
Silver (Ag). Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of silver-108 (atomic number: 47), an isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 47 protons (red) and 61 neutrons (orange). 47 electrons (white) successively occupy available electron shells (rings).
Orbital notation: 1s2 2s62p6 3s2 3p 4s1 3d5 Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation:1[Ar] 4s 3d5 c) Molybdenum Orbital notation: 1s262s2 52p103s 3p6 4s2 3d 4p6 5s1 4d Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation: [Ar] 5s1 4d5 d) Silver Orbital notation: 1s222s262p6 13s 103p 4s 3d10 4p6 5s 4d Orbital notation + Arrows: Noble gas notation ...
Answer: Silver (Ag) has an electron configuration of [Kr] 4d 10 5s 1. The element is much more stable and has a lower energy when the 4d orbital is filled, so one electron is placed there, rather than in the 5s orbital. When it is ionized, the electron is removed from the outermost shell, which is the 5s orbital.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Silver-58b601c15f9b5860464c0e8f.jpg)




![Electron Configuration | Chemistry [Master]](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1941/2017/05/30162457/cg10c3-010.png)


/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)














0 Response to "40 orbital diagram for silver"
Post a Comment