40 how to read a stuve diagram
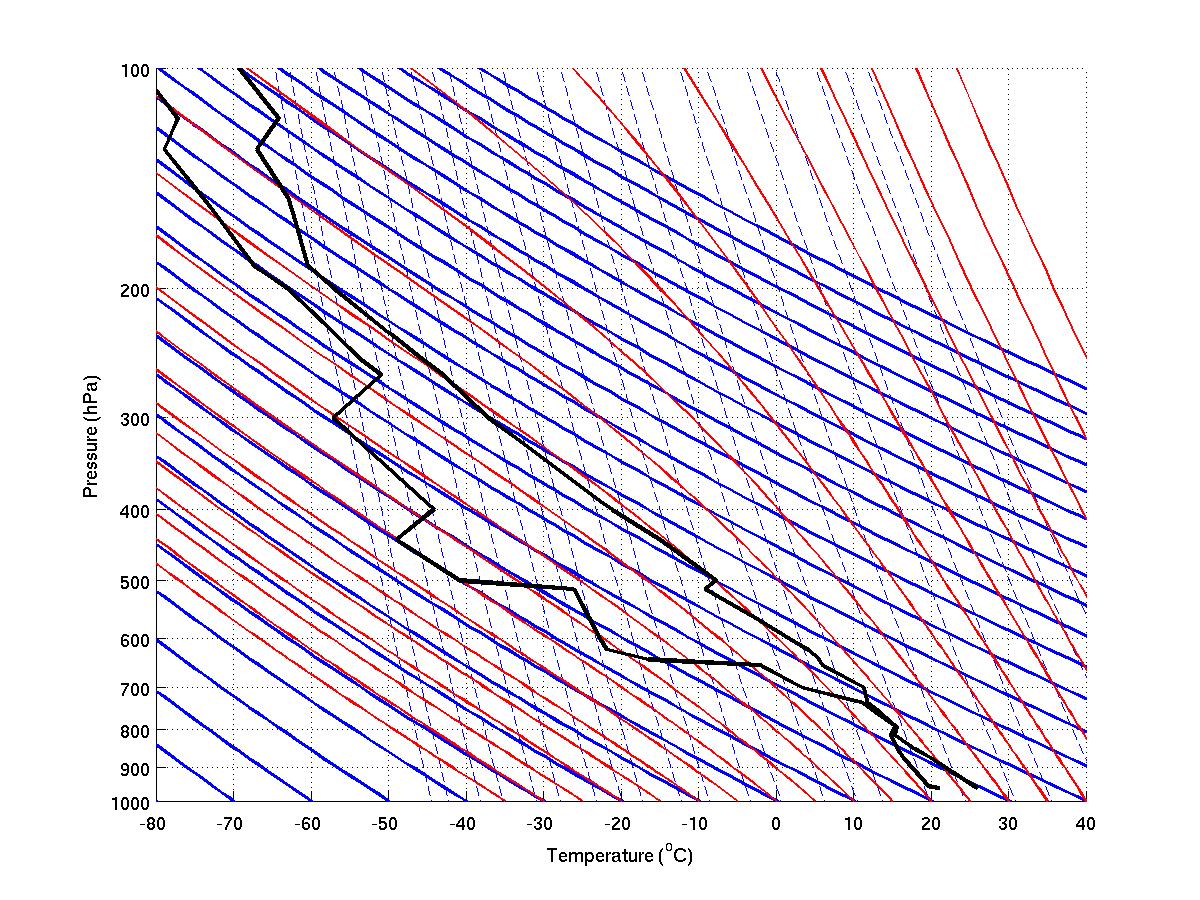
The red numbers on the left side of the diagram are altitude values in kilometers (SFC means the surface, where the balloon was launched). The black numbers on the bottom of the diagram are temperature values in degrees Celsius. Note the temperature lines are tilted up to the upper right (the light pink dashed lines). A Stüve diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting. It was developed circa 1927 by the German meteorologist Georg Stüve (1888–1935) and quickly gained widespread acceptance in the United States to plot temperature and dew point data from radiosondes.. This diagram has a simplicity in that it uses straight lines for the three primary ...
Stuve diagrams show the relationship between Air Temperature and Dew Point Temperature from the surface to about 55,000ft.

How to read a stuve diagram
Here is an example of how we can. Question: I am supposed to use this Stuve diagram to answer the questions below 1. Use the accompanying Stuve diagram to find the saturation mixing ratio for:10oC and 1000 mb_______g/kg, 20oC and 1000 mb________g/kg, 30oC and 1000 mb_______g/kg 20oC and 900 mb________g/kg, 20oC and 800 mb_________g/kg, 20oC and ... One version of the thermodynamic diagram is the Stuve diagram, shown in our textbook. Another is the skew-T/log-P, or "skew-T" for short, so named because one of the primary axes of the graph (temperature) is skewed clockwise by 45°. It is harder to learn to read but a little more useful meteorologically. Stuve and Skew-T/Log-P Diagrams THERMODYNAMIC DIAGRAMS. The thermodynamic diagram is a tool frequently used by meteorologists to solve atmospheric temperature and humidity problems using simple graphical techniques. Lengthy calculations are avoided since the mathematical relationships have been accounted for in the arrangement of this diagram.
How to read a stuve diagram. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Aug 26, Stuve Diagrams are one type of thermodynamic diagram used to then the saturation mixing ratio can be read directly from the chart. Also, the tropopause (the boundary between the troposphere & the stratosphere) is shown to be at about mb. This is the height in the very high levels of the. From the Stuve diagram, it seems the atmosphere is unstable in the low levels from the surface up ... How To Read Skew-T Charts If you haven't seen a Skew-T chart before, to say they can look a little intimidating is a huge understatement. But with a little practice, you can become a Skew-T master and open up new doors to learn about a variety of meteorological subjects. Stuve Diagrams. Stuve Diagrams are one type of thermodynamic diagram used to represent or plot atmospheric data as recorded by weather balloons in their ascent through the atmosphere. The data the balloons record are called soundings. To see how to make your own Stuve diagram try following the sounding exercises.
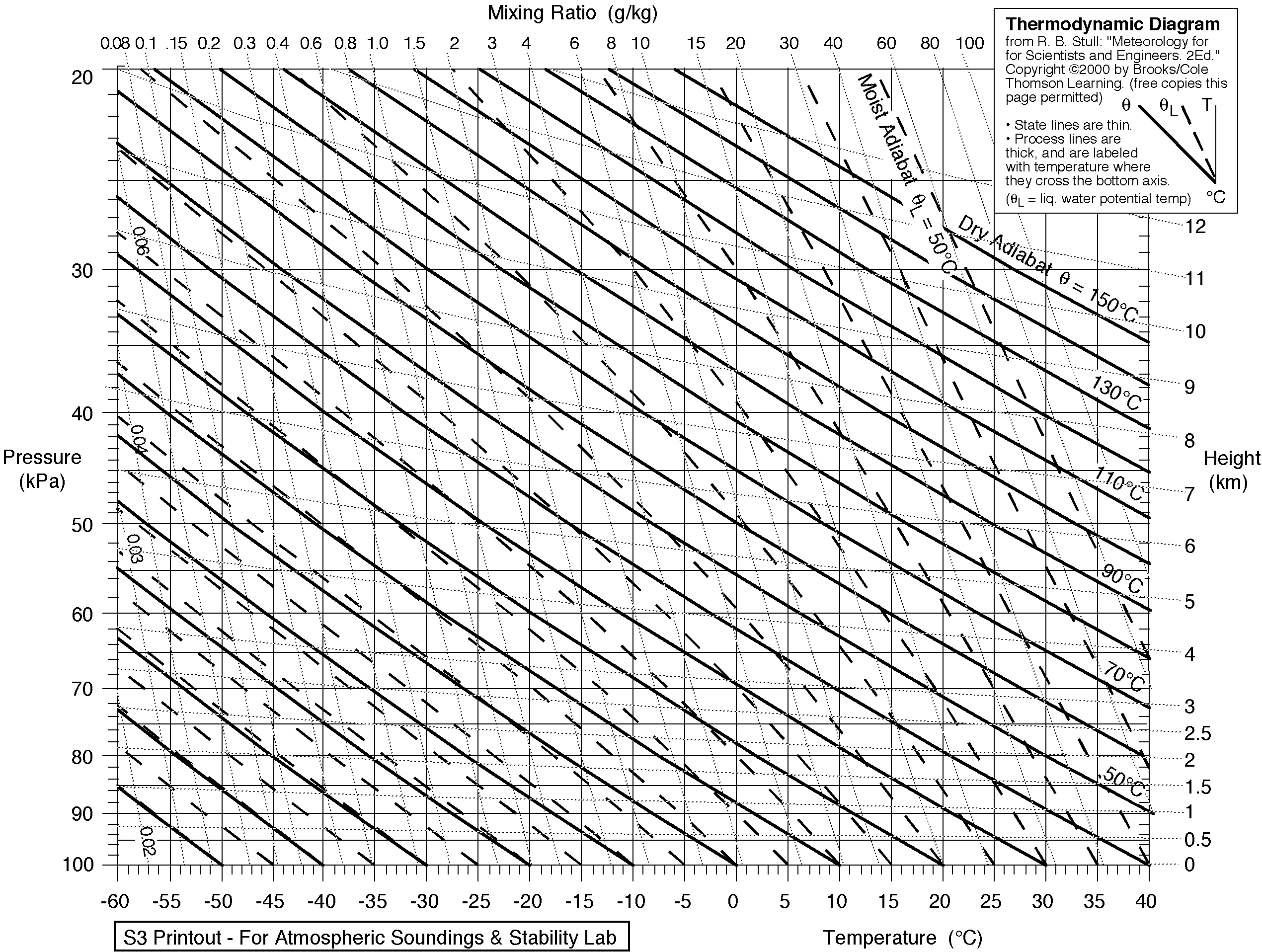
The stueve diagramm allows you to know a lot about the air conditions within only one diagram. The temperature is shown on the abscissa axis, with vertical lines (isotherms). The air pressure is shown on the ordinate axis with horizontal lines (isobars) and an exponential scale. name skew) across the diagram and are SOLID. Increment are given for every 10 degrees They are labeled at the bottom of the diagram. (Saturation mixing ratio lines)- Lines of equal mixing ratio (mass of water vapor divided by mass They are labeled on the bottom of the diagram. (Wind barbs)- Wind speed and direction given for each plotted barb. Use this Word document for this lab. In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day. TornadoStuveLab_v1-1.docx Settings You will be filling out information for several Stuve diagrams which are provided below as well. The values of CAPE, LI, PW ... Weather and Climate PHYS 189 NAME: 1 Stuve diagrams We are going to use Stuve diagrams to understand some of the concepts we learned in previous classes.
Skew-T Log-P Diagrams. The "Skew-T Log P" thermodynamic diagram used for plotting upper air observations. Once the radiosonde observation is plotted, the Skew-T will show the temperature, dew point, and wind speed/direction. From these basic values a wealth of information can be obtained concerning the meteorological condition of the upper air. Stuve Diagrams are one type of thermodynamic diagram used to then the saturation mixing ratio can be read directly from the chart.For completeness, the dewpoint temperature of the parcel (Td) can be plotted upon the diagram at the same pressure level. 3) Dry adiabats. The straight, solid, green lines sloping upward to the left on the diagram ... [help] Stuve Diagram. Close. 5. Posted by 3 years ago [help] Stuve Diagram. I’ll preface this by saying I am taking an intro meteorology class however it’s online and I’m struggling. I cannot for the life of me find a good video or explanation on how to understand what I’m looking at. Here’s what I do know: Y axis is the atmospheric pressure in mb. X axis is temperature. Right hand ... Sarah's Stuve diagram Matlab assignment. 1. From the Stuve diagram, it seems the atmosphere is unstable in the low levels from the surface up to 700 hPa. It continues to be unstable up into the mid-levels until 500 hPa. At about 500 hPa, the environmental lapse rate begins to follow the process lapse rate so the atmosphere has become neutral.
Use this Word document for this lab. In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day. TornadoStuveLab_v1-1.docx Settings You will be filling out information for several Stuve diagrams which are provided below as well. The values of CAPE, LI, PW ...
Sounding andSounding and Stuve Diagram • The vertical structure of the atmosphere above a location on the Earth measured by athe Earth measured by a rawinsonde is called a sounding. • The sounding is usually plotted on a Stuve Diagram which uses pressure (bi(mb ; in log f)form) as its vertical axis and temperature (°C) as the horizontal axis. ESS124 Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu. A ...
In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day. TornadoStuveLab_v1-1.docx. Settings. You will be filling out information for several Stuve diagrams which are provided below as well.
Il-6: tornado forecasting with stuve diagrams. Homework Paper Help. Use this Word document for this lab. In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day. TornadoStuveLab_v1-1.docx.
Il-6: tornado forecasting with stuve diagrams Use this Word document for this lab. In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day.
These include the tephigram, Skew-T Log P (known as Skew-T for short), Stuve, and pseudoadiabatic diagrams. The Stuve and pseudoadiabatic diagrams look very similar to the emagram that was explained here. So these should be relatively easy for you to use too. a) The tephigram and skew-T look similar to each other, but not to the emagram.
Il-6: tornado forecasting with stuve diagrams. Homework Help. Use this Word document for this lab. In this lab you will use Stuve diagrams (from radiosonde soundings) and a surface weather map to forecast the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the United States for a specific day. TornadoStuveLab_v1-1.docx.
How to read a stuve diagram. A Stüve diagram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis. This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please . Thermodynamic (also called adiabatic or aerological) diagrams of various types are in use, and the. The Stüve diagram was ...
26 Aug 2004 — Stuve Diagrams are one type of thermodynamic diagram used to represent or plot atmospheric data as recorded by weather balloons in their ascent ...
One version of the thermodynamic diagram is the Stuve diagram, shown in our textbook. (Another is the skew-T/log-P, or "skew-T" for short, so named because one of the primary axes of the graph [temperature] is skewed clockwise by 45°. It is harder to learn to read but a little more useful meteorologically.) Construction of a Stuve Diagram
stuve
A Stüve diagram with sounding data contains: Temperature sounding data- black jagged line to right. The temperature scale is given in degrees Celsius along the bottom from -80 C to +40 C. Dewpoint sounding data- black jagged line to left. the dewpoint data are a measure of the water vapor
Exercise 1: Plot the temperature sounding. Using the blank Stuve diagram plot the temperature vs pressure. These are in columns D and B of the Excel file. Put a dot or X at each data point and then connect these with straight lines. Use the vertical gray lines for temperature and the horizontal gray lines for pressure.
THERMODYNAMIC DIAGRAMS. The thermodynamic diagram is a tool frequently used by meteorologists to solve atmospheric temperature and humidity problems using simple graphical techniques. Lengthy calculations are avoided since the mathematical relationships have been accounted for in the arrangement of this diagram.
One version of the thermodynamic diagram is the Stuve diagram, shown in our textbook. Another is the skew-T/log-P, or "skew-T" for short, so named because one of the primary axes of the graph (temperature) is skewed clockwise by 45°. It is harder to learn to read but a little more useful meteorologically. Stuve and Skew-T/Log-P Diagrams
Here is an example of how we can. Question: I am supposed to use this Stuve diagram to answer the questions below 1. Use the accompanying Stuve diagram to find the saturation mixing ratio for:10oC and 1000 mb_______g/kg, 20oC and 1000 mb________g/kg, 30oC and 1000 mb_______g/kg 20oC and 900 mb________g/kg, 20oC and 800 mb_________g/kg, 20oC and ...

























0 Response to "40 how to read a stuve diagram"
Post a Comment