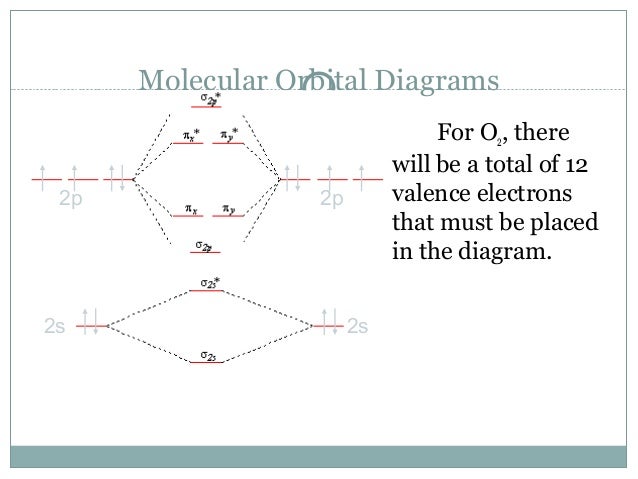
38 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
Transcribed image text: sopling earning Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed. Electronic configuration of Oxygen is So in O2 there is 12 valence e… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, 0, 1,00 JT Žp 2p Answer Bank 02pm 21 Os
In order to draw oxygen's molecular orbital diagram, you need to start by taking a look at what atomic orbitals you have for an oxygen atom, #"O"#.. As you know, oxygen is located in period 2, group 16 of the periodic table and has an atomic number equal to #8#.This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for #8# electrons.
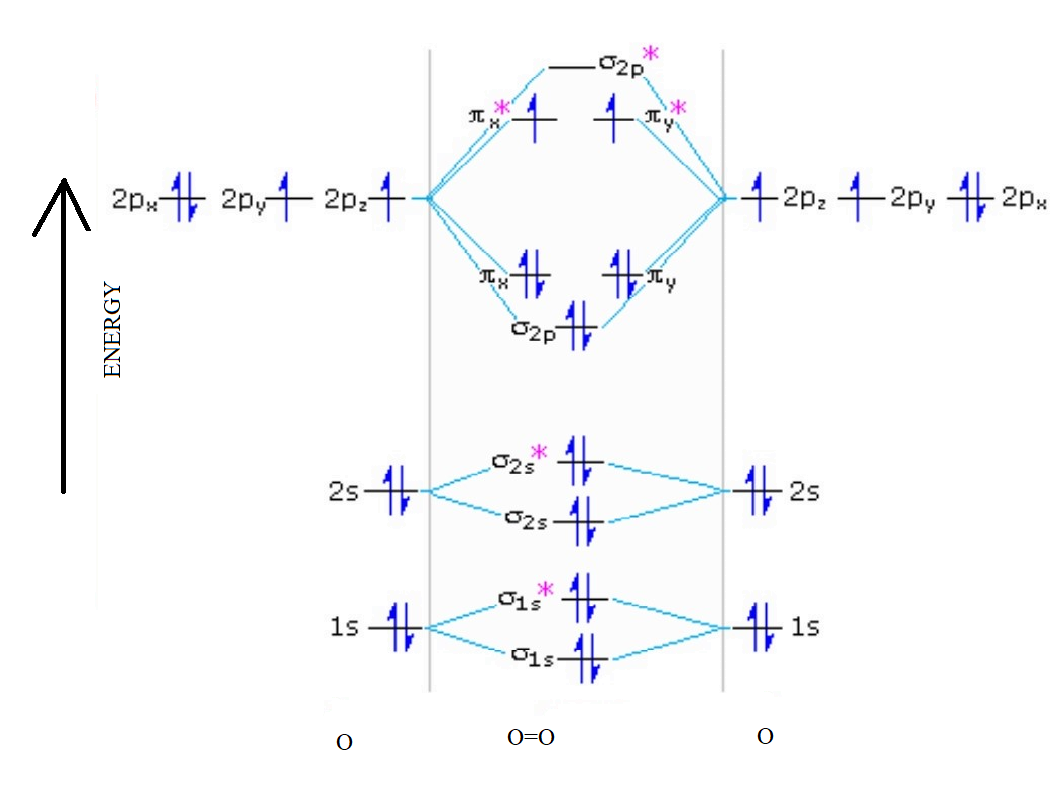
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
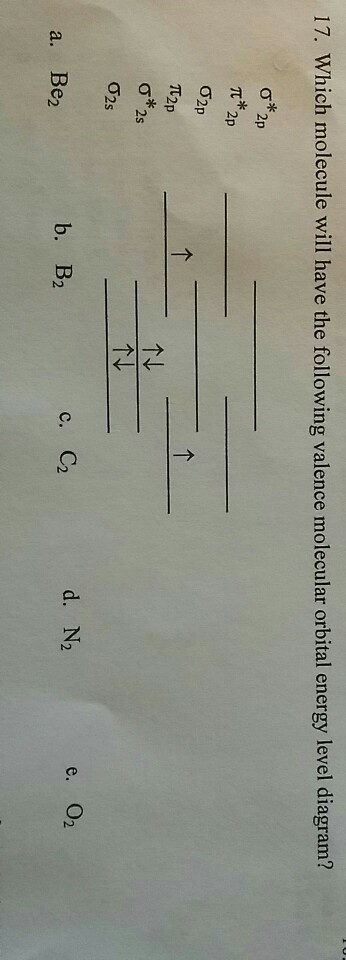
Eight possible homonuclear diatomic ... C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. However, we can predict that the Be2 molecule and the Ne2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron configurations (Table 2). We predict valence molecular orbital electron ... Question: complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen O2 click the blue boxes to add electrons. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... Penguin Ski Club of New Hampshire. Located in Lincoln NH near Loon Mountain. Menu and widgets
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2. August 11, 2020 - The bond length in the oxygen species can be explained by the positions of the electrons in molecular orbital theory. To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for \(\ce{O2}\), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure ... FREE Answer to Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as... September 15, 2016 - The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps! Eight possible homonuclear diatomic ... C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. However, we can predict that the Be2 molecule and the Ne2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron configurations (Table 3). We predict valence molecular orbital electron ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem This video shows the construction of a molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the diatomic molecule, O2, using the valence electrons of each oxygen. The diagram... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Bond order: a) 0. b) 0.5. c) 1. d) 1.5. e) 2. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos.
09/06/2017 · Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*... So, next one electron will go into 1s shell of anti-bonding orbital. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here. There is one other feature of the valence bond model that deserves discussion. It is nicely illustrated by our familiar oxygen molecule, O2. Figure 35 shows the overlap of two px-orbitals to give us a single bond. If we are to obey the octet rule, we must also form another bond. February 3, 2018 - Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
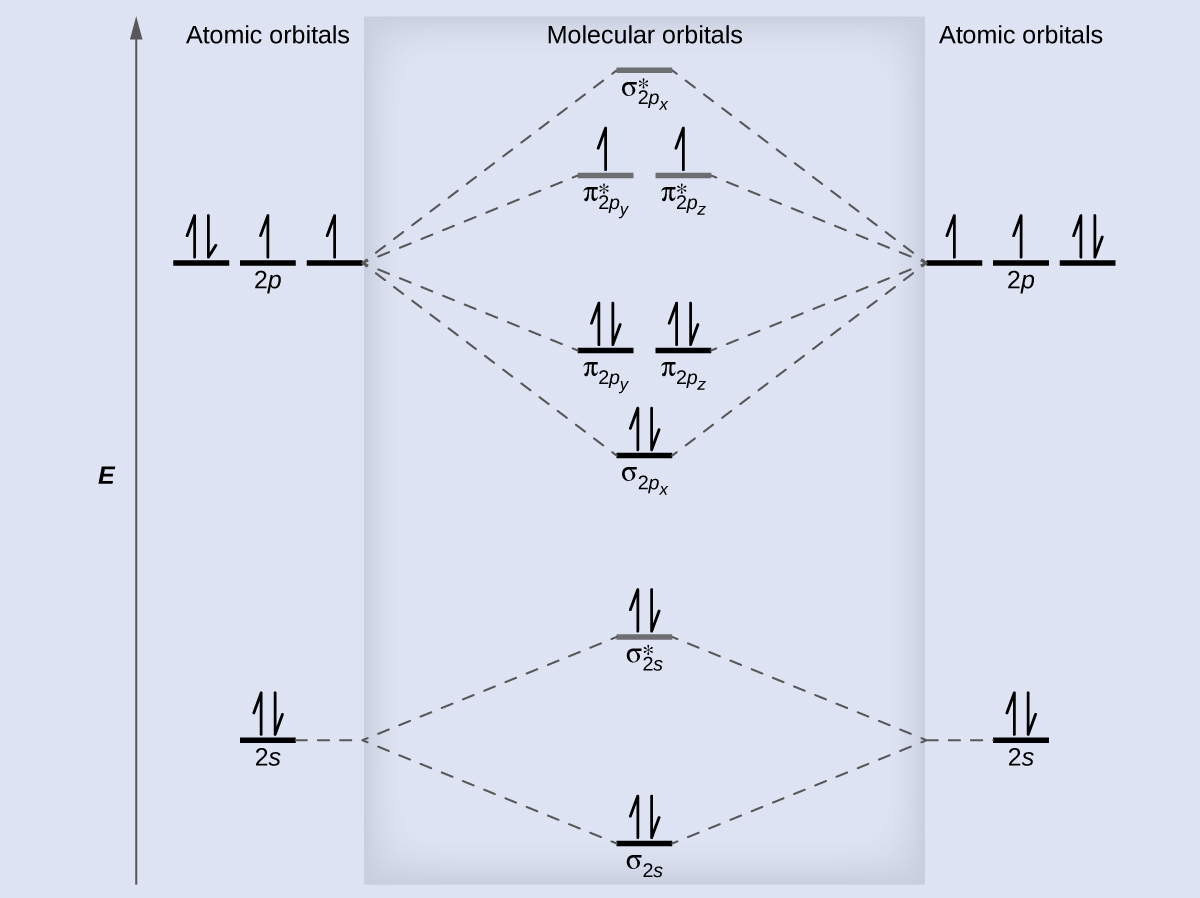
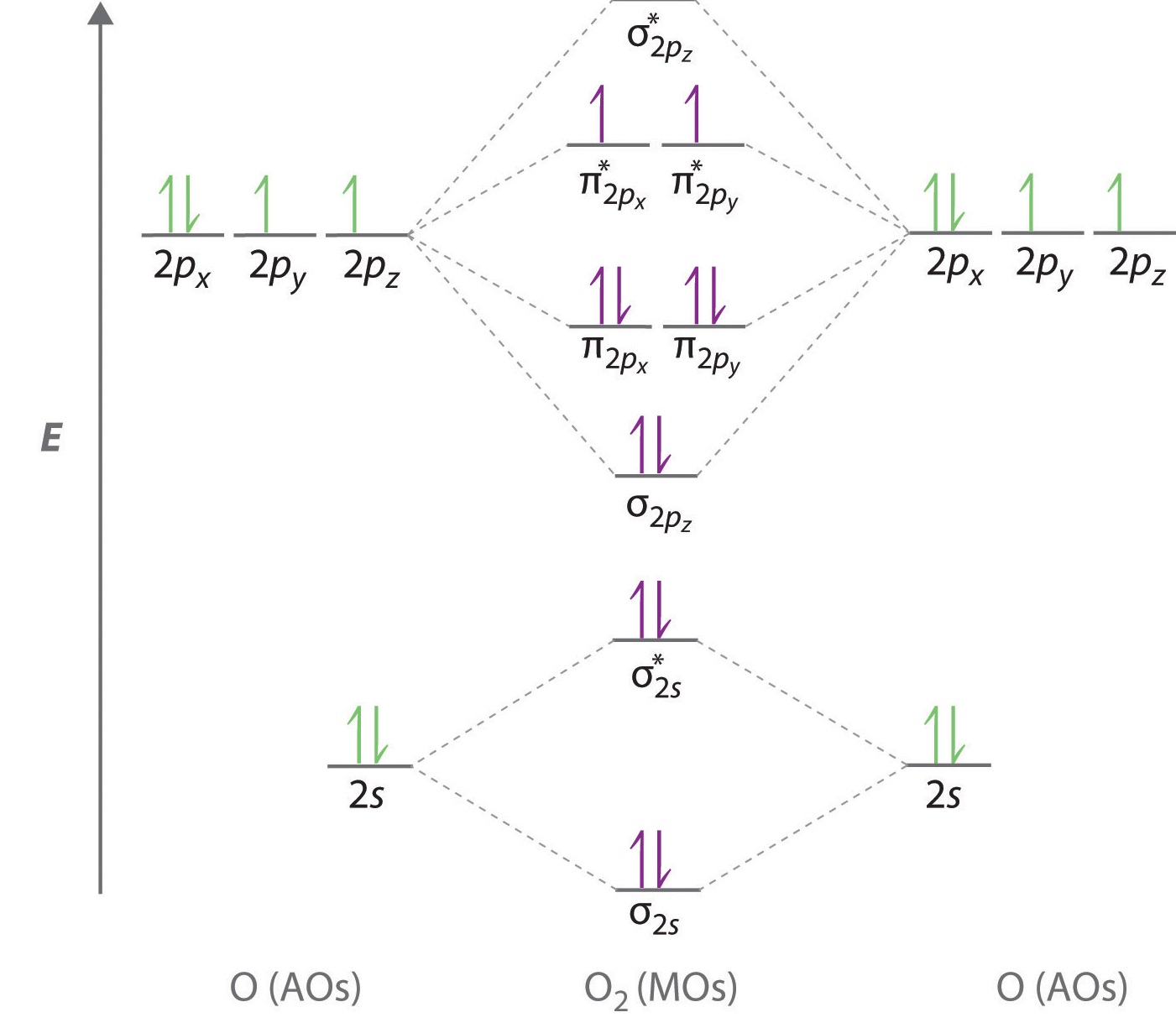
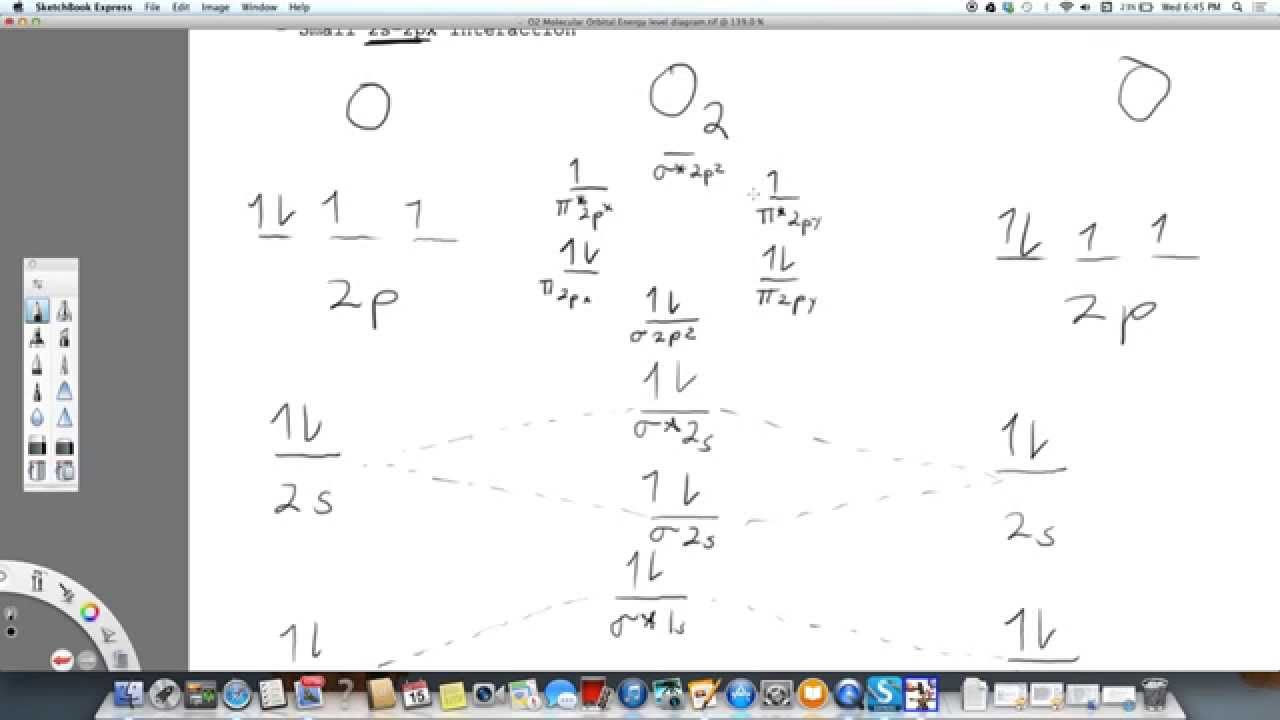
You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a σ2s bonding and σ* 2s antibonding MO.
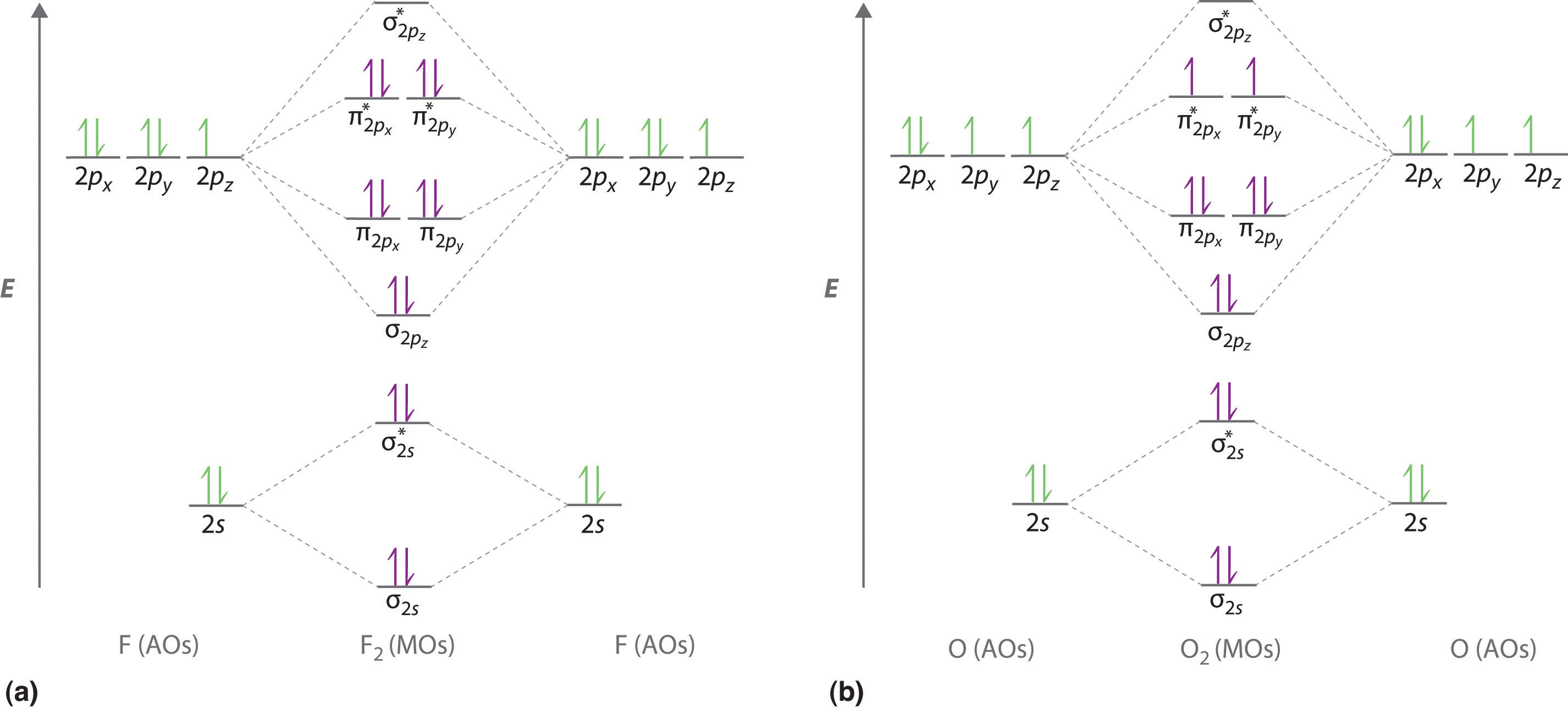
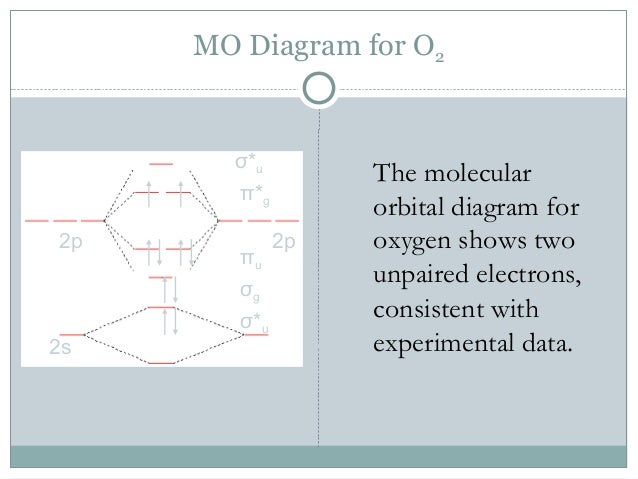
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule. It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules, such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding (beyond the scope of this text) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures.
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
Jan 31, 2018 — To find the bond order of O2+ we can use the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory. In this method we have to count the number of molecules in the Bonding ...7 answers · 57 votes: O2 2- bond order = 1 O2 - bond order = 1.5 O2 bond order = 2 O2+ bond order = 2.5 O2 ...What is the molecular orbital diagram for O2- and ...5 answersMar 27, 2017How do I find the bond order of Cl2?
Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for O2. Now we add the 12 electrons, 6 from each oxygen atom. There is one electron each in the 2 pi antibonding orbitals. This means that there is only 1 net pi bond. Also, the molecules has 2 unpaired electrons and therefore has magnetic properties.
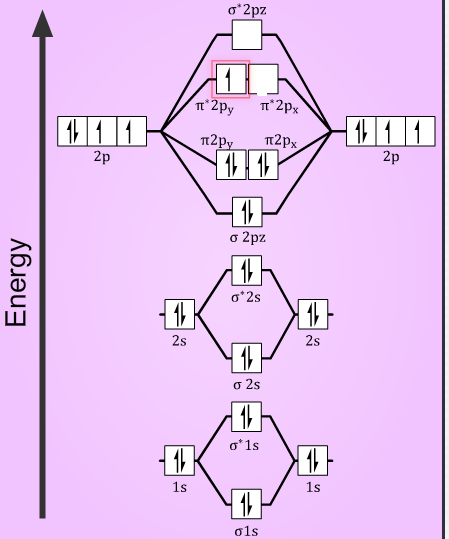
molecular orbitals are those formed when valence-shell orbitals are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2molecule would therefore ignore the 1selectrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2sand 2pvalence orbitals. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level
The only orbitals that are important in our discussion of molecular orbitals are those formed when valence-shell orbitals are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the ...
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
As we studied above that one oxygen atom has a deficiency of two valence electrons, it readily accepts two electrons. So, a single oxygen molecule has six electrons in its octet. If we look for O2, then the number will be O2: 6+6 = 12. In total, an O2 molecule needs four valence electrons to complete its octet and achieve a stable condition.
Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank. Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
Of oxygen is 8. Atoms can either donate or receive electrons only in valence shell. 8 electrons in outermost shell is considered the most stable state of an atom as the shell will be fully occupied. The valency of oxygen is 2 as its electronic configuration is 2,6 and it need 2 electron to complete their octet.
January 22, 2021 - Here this site has been provided the Various Ways To Find a Oxygen Electron Configuration (O) with the orbital diagram of Oxygen.
May 19, 2014 - O2+ is more stable than O2-. Reason: According to molecular orbital theory O2+ has 15 electrons &it has one electron in antibonding orbital. molecular orbital diagram of O2+ Electronic configuration of O2+ In the case of O2- 17 electrons are present &3 electrons are present in antibonding orbitals.
O2 molecule two oxygen atoms are involved .Oxygen atom has six electrons in its outermost orbit. So valency of oxygen atom is 2. Of these six electrons,two electrons from each oxygen atom are shared between two oxygen atoms. By sharing of two electrons from each oxygen atom,the octet of both oxygen atoms is completed.
We can use the molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecules to explain the paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen atoms. We also have to know that for the paramagnetic nature of a molecule, it should contain a minimum of one unpaired electron. Complete answer: The valence bond theory could not explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen molecules.
Jan 21, 2022 · Sketch the Molecular Orbital diagram for O2 being sure to: A. Designate bonding and anti-bonding orbitals, B. Show the location of all electrons in the molecular orbitals, C. Calculate the bond order, and D. Indicate whether this molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. For your diagram, assume that one oxygen atom contributes its six (6 ...
Oxygen (O) electron configuration with full orbital diagram. Oxygen (O) is the 8th element in the periodic table and the first element in group-16. The standard atomic mass of oxygen is 15.99903 and its symbol is ‘O’. The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen ...
Be Be, Be Answer Bank 11 1 25 Identify the bond order. 0 0.5 1.5 O2 25 3. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as – $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$ One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as –
The energy of σ 2 p z molecular orbital is greater than and molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule. Write the complete sequence of energy levels in the increasing order of energy in the molecule. Compare the relative stability and the magnetic behavior of the following species: N 2 , N 2 + , N 2 − , N 2 2 +
12/11/2021 · Well, s-p mixing doesn’t occur with diatomic oxygen, creating a molecular orbital diagram like the first in this article. This is because, as more electrons are added to a system, the higher the energy becomes, due to their electrostatic repulsion. If the energy of the 2s and 2p orbitals are too far apart, mixing won’t occur. Therefore, you get a molecular orbital diagram …
March 18, 2018 - Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has ...
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram for O2 in order to explain its paramagnetism. http://ukcata...
August 15, 2020 - Molecular orbitals (MO) are constructed from atomic orbitals. In O2 and F2, there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials: the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals'. Information from the MO diagram justify O2's stability and show that it's bonding ...
number of valence electrons) with O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold
Penguin Ski Club of New Hampshire. Located in Lincoln NH near Loon Mountain. Menu and widgets
Question: complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen O2 click the blue boxes to add electrons. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Eight possible homonuclear diatomic ... C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. However, we can predict that the Be2 molecule and the Ne2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron configurations (Table 2). We predict valence molecular orbital electron ...






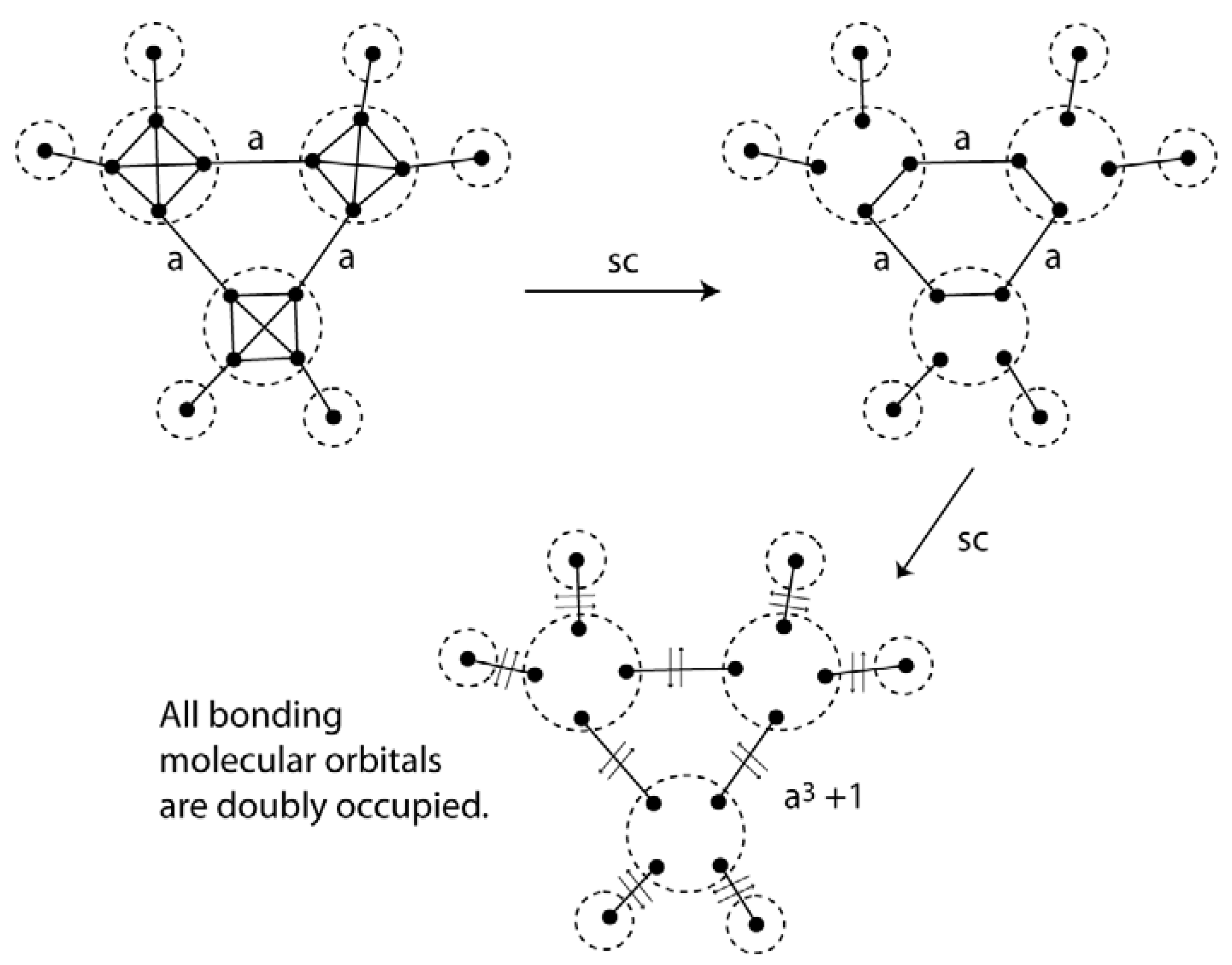
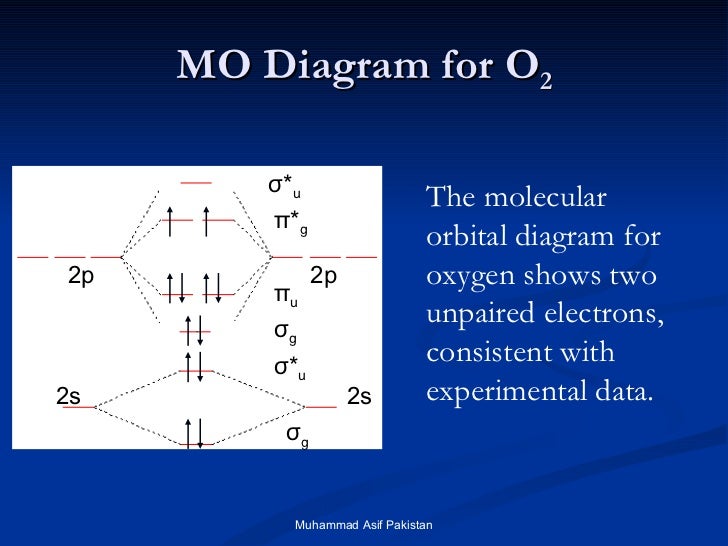

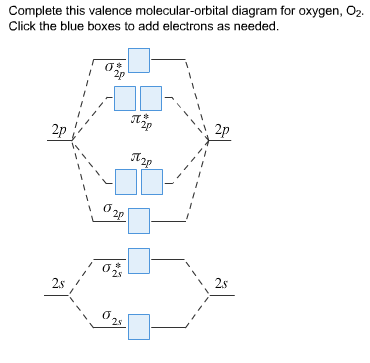


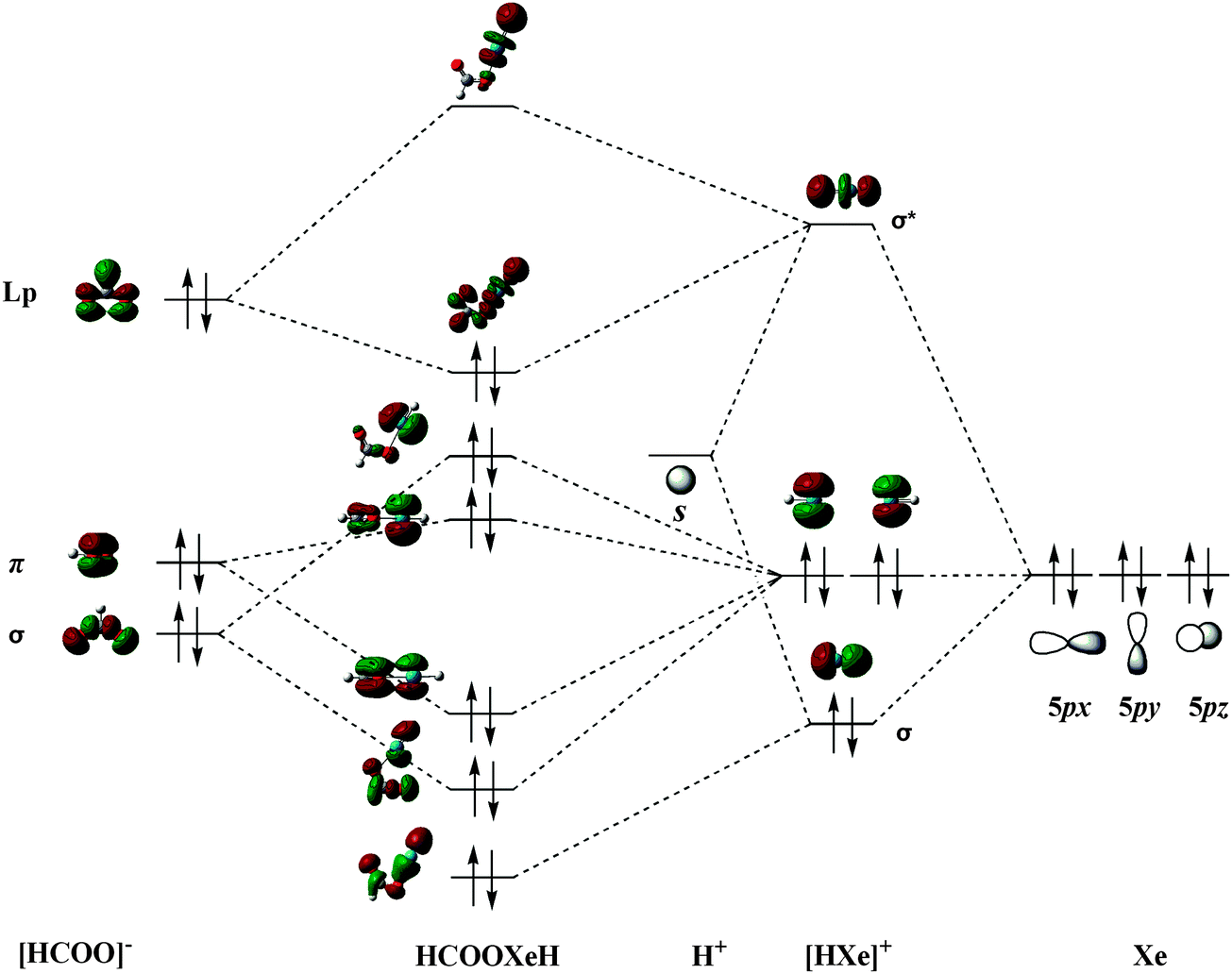









0 Response to "38 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2"
Post a Comment