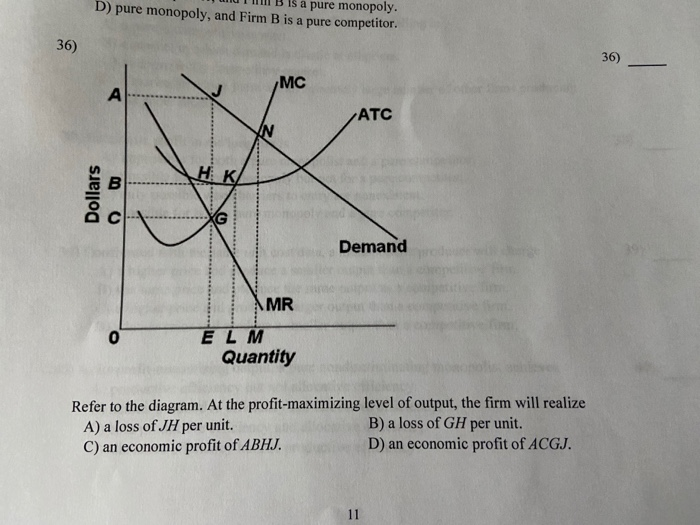
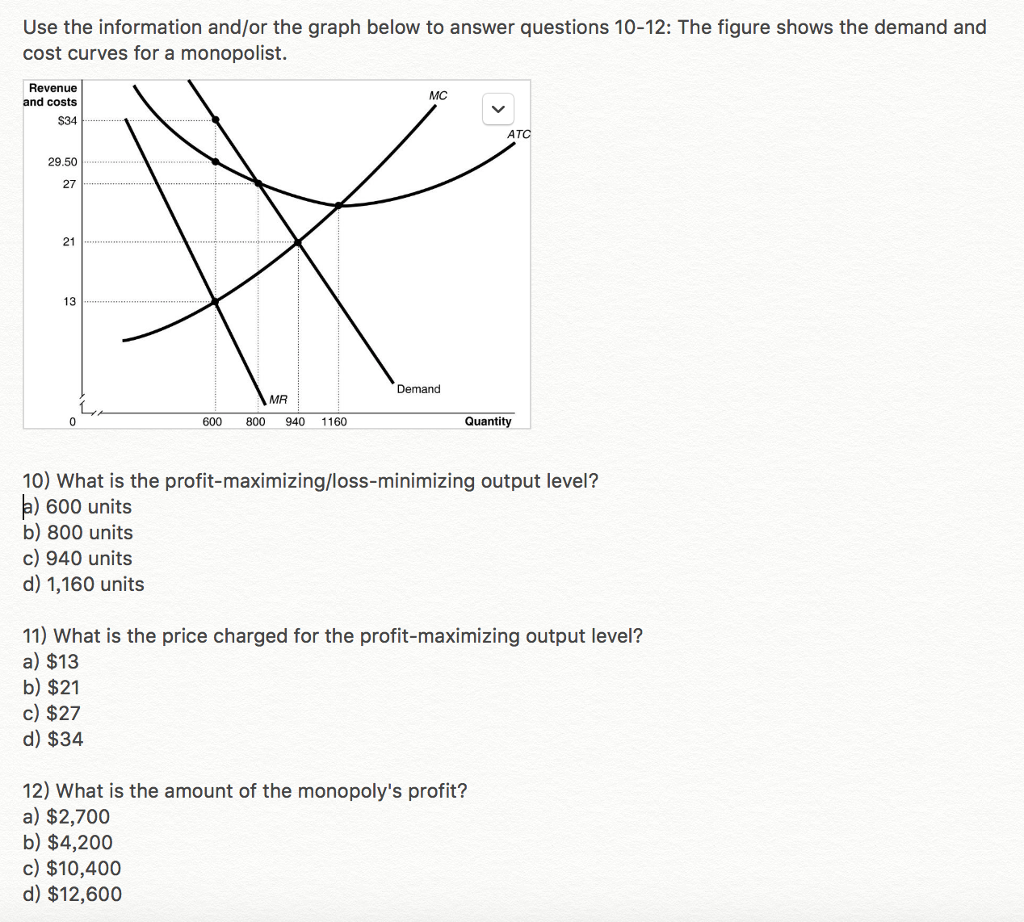
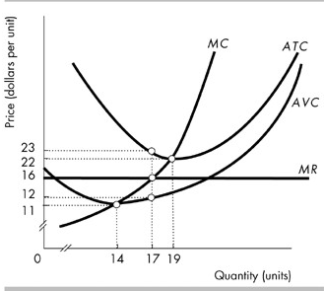
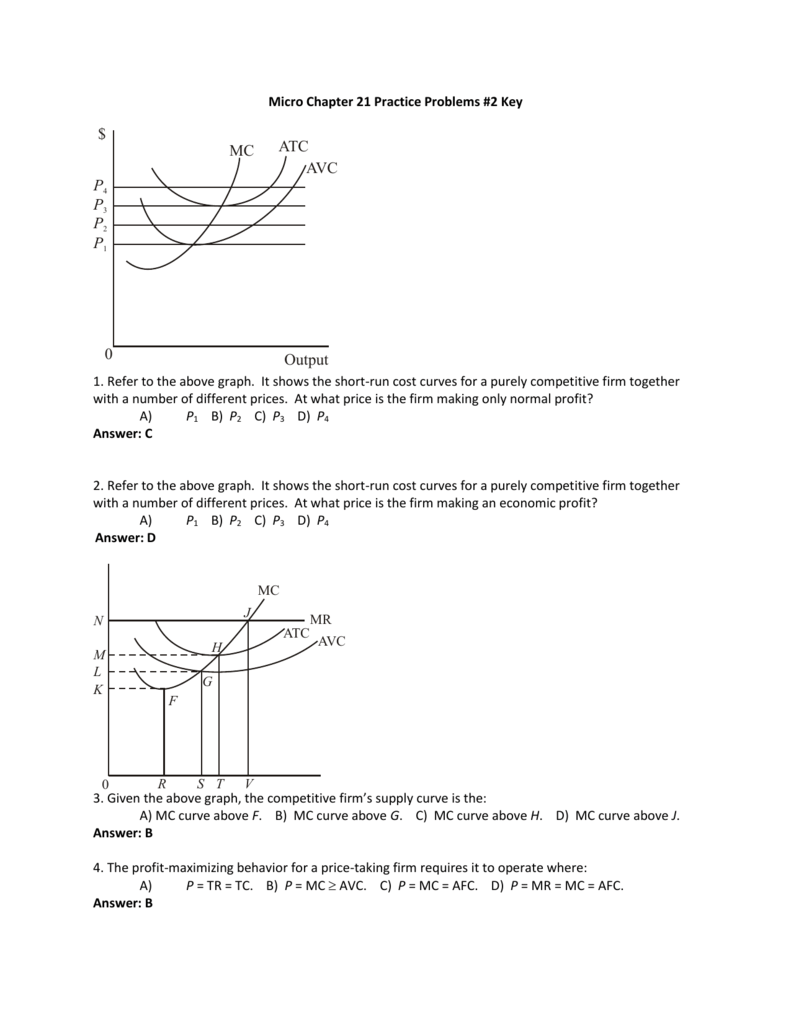
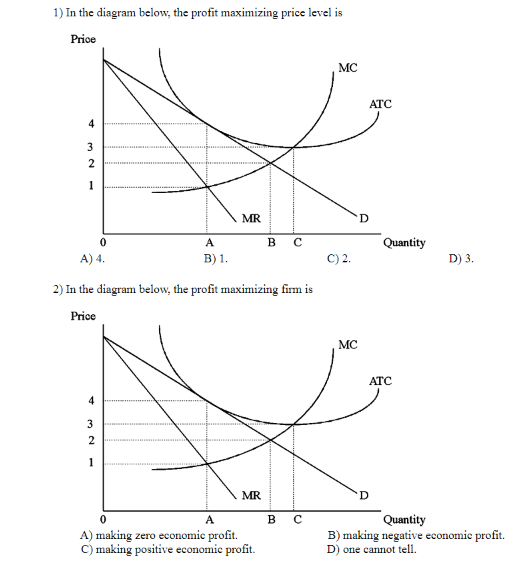
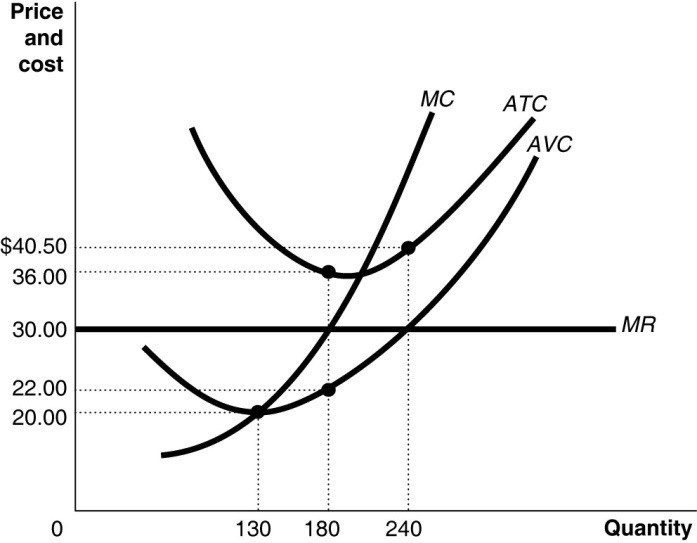
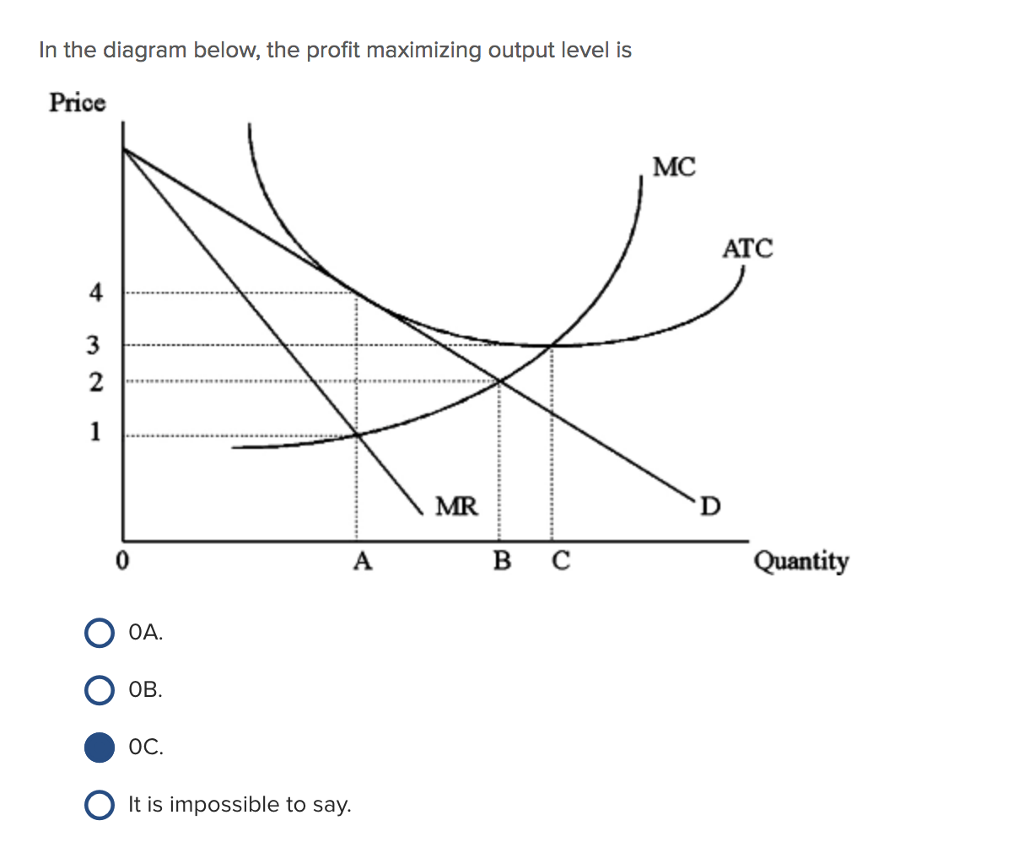
35 refer to the diagram. the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm
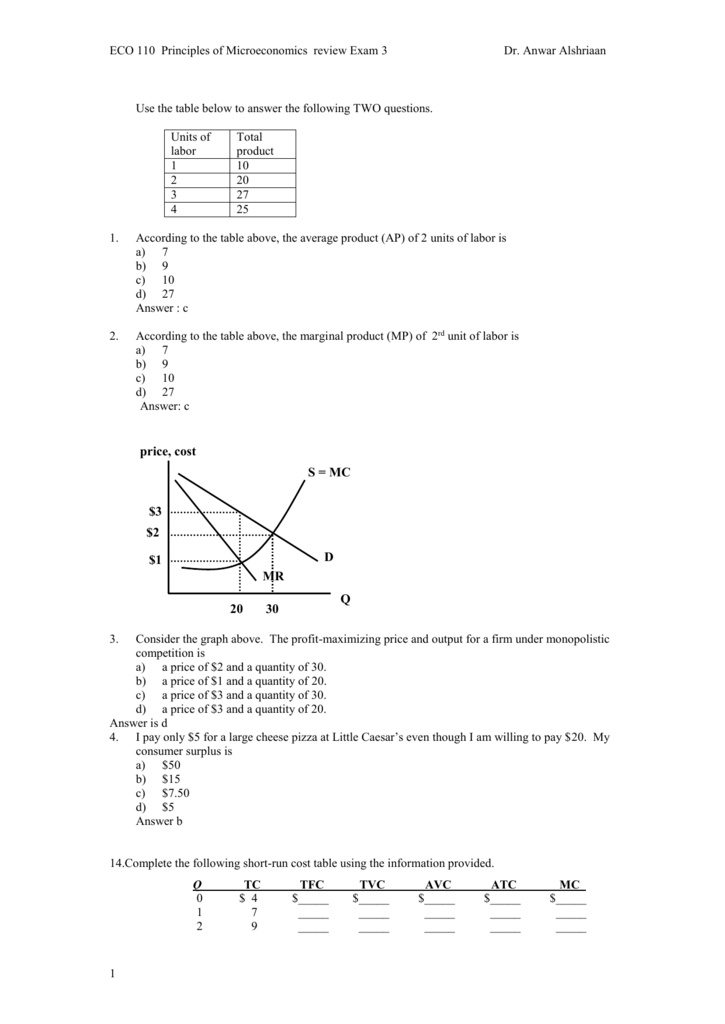
Short‐run profit maximization. A firm maximizes its profits by choosing to supply the level of output where its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost. When ... The firm always makes production decisions based on the Marginal Cost curve. It always produces where MC (Q)=P. Thus, the short run supply curve is the formula for the MC function. …. Set MC=AVC and solve. MC=10+Q=10+.5Q—>minimized at Q=0. At Q=0, AVC=10. Thus the cutoff price at which to temporarily shut down is P=10.
The following diagram shows the cost structure of a monopoly firm as well as market demand. Identify on the graph and calculate the following: a. Profit-maximizing output level b. Profit-maximizing price c. Total revenue d. Total . Economics/Math. In a perfectly competitive industry, the market price is $25.
Refer to the diagram. the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm
Refer to Exhibit 8.3, which shows short-run profit maximization by a perfectly competitive firm. _____, the marginal revenue of the firm is equal to its marginal cost. At the output level represented by point c The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits, it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. In other words, it must produce at a level where MC = MR. Profit Maximization Formula. The profit maximization rule formula is. MC = MR ... E units and charge price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: Refer to the above diagram to maximize profits or. 80. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: A. Eunits and charge price CB.Eunits and charge price AC.
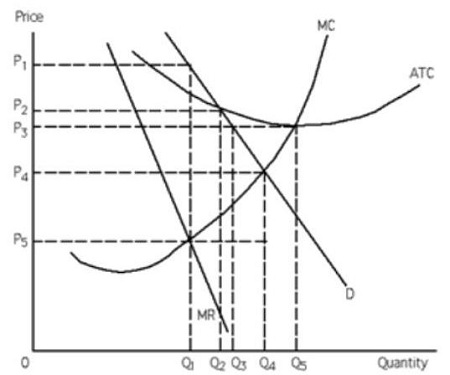
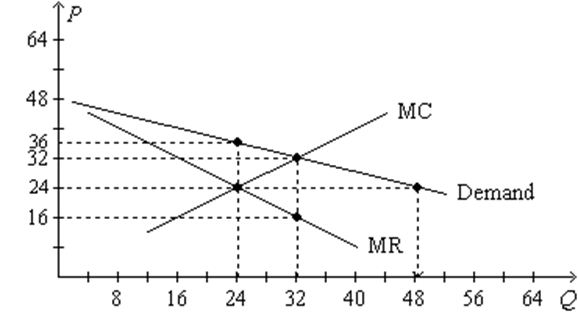
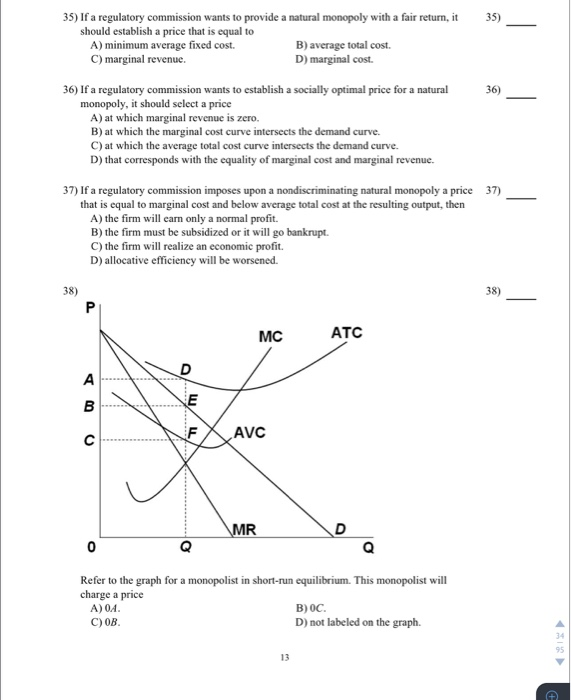
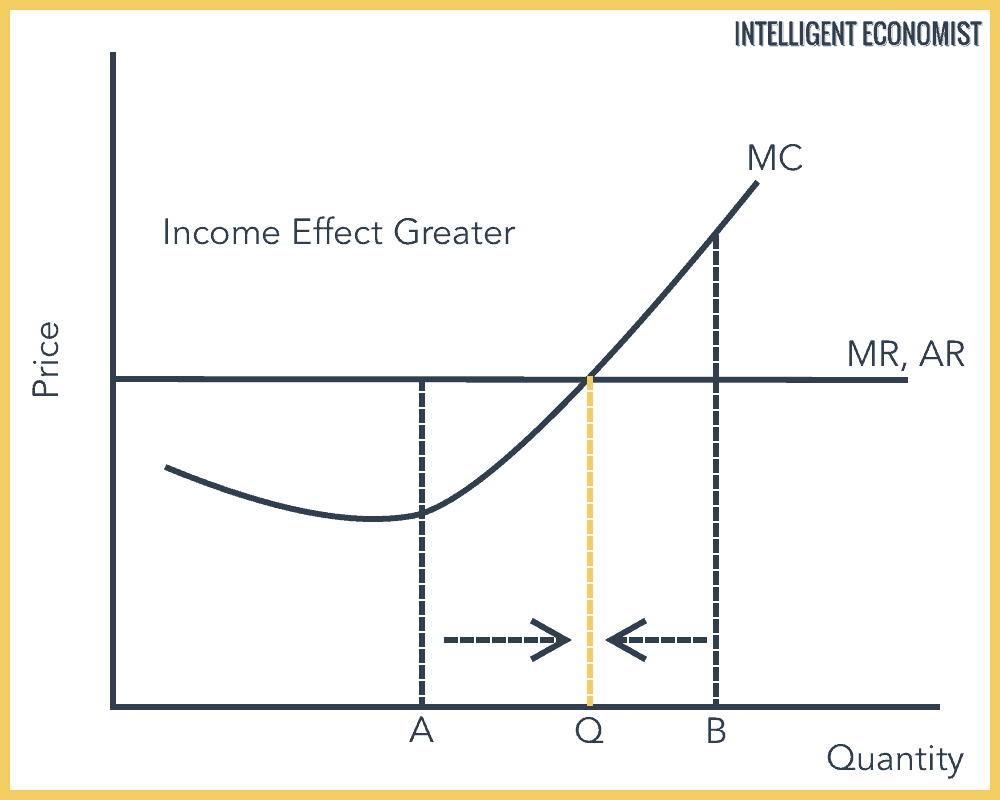
Refer to the diagram. the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm. Microeconomics. A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market is currently producing 100 units of output. It has average revenue of $10, average total cost of $8, and ficed costs of $200. What are the firm's profit, marginal cost, and average. The profit maximizing output level for a perfectly competitive firm is always where ... In the above diagram profit is maximized at point Indicate in the diagram the profit-maximizing level of output and shade in the area corresponding to the firm's economic profit/loss, if any. c. Which one of the conditions is true for a representative firm in the corn industry: P>ATC, P Refer to the above diagram. To maximize ... At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: ... In the above diagram by producing output level Q: Then label the profit of the firm in the short run. In a second diagram show the long-run equilibrium of the firm and its profit-maximizing level of output. In one to two sentences explain the cause(s) of the difference between the short-run and long-run equilibrium for the perfectly competitive firm. Diagram a perfectly competitive firm that ... Profit Maximization Definition. Profit maximization can be defined as a process in the long run or. short run to identify the most efficient manner to increase profits. It is mainly concerned with the determination of price and output. level that returns the maximum profit. It is an important assumption. Suppose that a firm's total profit is a function of output To maximize total profits, the firm must. Suppose that a firm's total profit is a function of output To maximize total profits, the firm must produce at an output level at which Do you agree? Explain. Maximizing per-unit profit is equivalent to maximizing total profit. -Refer to Figure 16-8. Assume a monopolistically competitive firm is currently producing the profit-maximizing level of output. Which of the following represents the excess capacity of this firm? A)BJ B)GH C)LM D)There is no excess capacity. Profit Maximization. There are two steps a firm must make when finding its profit maximizing level of output. The first step is the output decision. Market Competition MCQ Questions Class 12 Economics. Question. One of the requirements for a monopoly is that. A) the product cannot be produced by small firms. B) there are several close substitutes for the product. C) there is a unique product with no close substitutes. D) products are high priced. Question. Please refer to Chapter 5 Market Competition MCQ Class 12 Economics with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Economics. ... the profit-maximizing level of output D) whether or not to enter or exit an industry. Answer. D. ... a firm maximizes profit in the short run by ... Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for candles is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market.In the short run, at a market price of $20 per candle, this firm will choose to produce candles per day. Not sure if this is the place to post this (if not I'd really appreciate if someone could point me to the appropriate subreddit) but I'm a high school student studying IBDP economics HL. As part of the IB course we're supposed to write a 4000 word extended Essay in one of our subjects and I've chosen Economics.This essay is ideally supposed to be an exploration of either an application or extension of the concepts of the chosen subject *beyond* the syllabus. So what I'm essentially looking for... 1. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: ... Refer to the above two diagrams for individual firms. To maximize profits, each output level must be produced at minimum costs. ... The diagram shows the firm's per unit cost curves: MC, or marginal cost; AC, ... The marginal cost may first decline, as in the diagram, if the additional cost per unit is high if the firm operates at too low a level of output, ... Marginal Cost-Marginal Revenue Perspective. Profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm determines the price and output level that ... The payoff matrix above shows the economic profit; Figure 16-12 -Refer to Figure 16-12. Which letter identifies the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm? True or False: Other things being equal, the confidence interval for the mean will be wider for 95% confidence than for 90% confidence. Figure 16-11 -Refer to Figure 16-11. D. one firm has a dominant strategy to price high, the other to price low. D. ... The firm's marginal costs can sometimes shift without changing the profit-maximizing price and output. B. ... 57. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total fixed cost is: 2 answers. a) A competitive firm maximizes profit by producing the level of output at which price equal ... The following THREE questions refer to the diagram below, ... *This post has been split into a two-part series to work around Reddit’s per-post character limit. Please find Part 1 in the preceding post: Overviewing AMD’s GPU Architectures over here:* [https://www.reddit.com/r/hardware/comments/dr59gg/part\_1\_an\_overview\_of\_amds\_gpu\_architectures/](https://www.reddit.com/r/hardware/comments/dr59gg/part_1_an_overview_of_amds_gpu_architectures/) *Having overviewed AMD’s GPUs and gone over background and pre-requisite material, it’s time to delve into ... The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost: that is, MR = MC. If the monopoly produces a lower quantity, then MR > MC at those levels of output, and the firm can make higher profits by expanding output. Use the letters to identify the deadweight loss from this firm producing at its profit-maximizing level of output. Figure 16-12 -Refer to Figure 16-12. Use the letters to identify the deadweight loss from this firm producing at its profit-maximizing level of output. Categories Questions. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. To maximize its profit, the firm must its of the product for $20 per unit. The total profit of this firm is then $25, or: T R − T C = 100 − 75 TR - TC = 100 - 75 T R − T C = 1 0 0 − 7 5 ... by the monopolist, the monopoHst's marginal revenue and marginal cost curves, the profit-maximizing level of output, and the profits earned by the firm. factor markets, and in the second stage assumes firms maximize profits by ... firms to take price as given when they make their output decisions. One way. E units and charge price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: Refer to the above diagram to maximize profits or. 80. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: A. Eunits and charge price CB.Eunits and charge price AC. The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits, it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. In other words, it must produce at a level where MC = MR. Profit Maximization Formula. The profit maximization rule formula is. MC = MR ... Refer to Exhibit 8.3, which shows short-run profit maximization by a perfectly competitive firm. _____, the marginal revenue of the firm is equal to its marginal cost. At the output level represented by point c


















0 Response to "35 refer to the diagram. the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm"
Post a Comment