39 which part of the constitution is the basis for this diagram
Which part of the Constitution is the basis for this diagram. 2. See answers. Advertisement. Advertisement. PriatouriPriatouri. Option D, the Necessary and Proper Clause, is the right answer. By contrast, the Necessary and Proper Clause clearly grants incidental authorities upon Congress.
Nov 13, 2017 · What part of the Constitution is the basis for this diagram? See Answer. Best Answer. Copy. The necessary and proper clause. (I think don't quote me-) Lovely Roses ∙. Lvl 7. ∙ 2019-10-22 15:16:01.
Articles 36-51 under Part-IV of Indian Constitution deal with Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP). Borrowed from Irish Constitution, DPSPs are of three types - Gandhian, Socialistic, Liberal-Intellectual. Download Directive Principles of State Policy notes PDF for IAS Exam. For UPSC 2021 Preparation, follow BYJU'S.
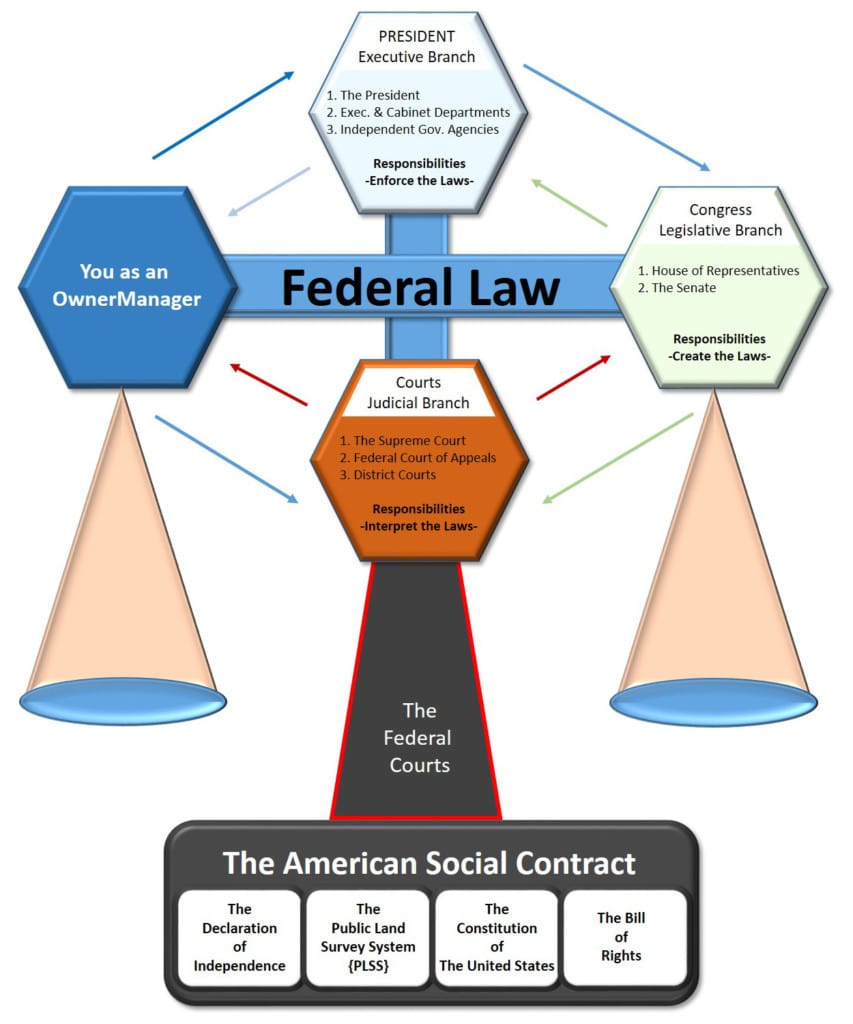
Which part of the constitution is the basis for this diagram
The Diagram of the Federal Government and American Union is an organizational chart of the Federal Government and the American Union designed by N. Mendal Shafer, and published circa July 15, 1862.. By the end of the American Civil War in 1865, the political landscape was radically altered and the diagram was probably outdated. The diagram eventually ended up in the archives of the US Library ...
Which part of the Constitution is the basis for this diagram? The federal government has the power to organize armed forces. The federal government can order a draft to force people to serve in the military 2 See answers Advertisement Answer 1.4 /5 1 propheticterrence Go down to the next answer and read it mostly the answer is there Answer:
Most importantly, the Declaration, the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights are based on the idea that all people have certain fundamental rights that governments are created to protect. Those rights include common law rights, which come from British sources like the Magna Carta, or natural rights, which, the Founders believed, came from God.
Which part of the constitution is the basis for this diagram.
A well-known concept derived from the text and structure of the Constitution is the doctrine of what is commonly called separation of powers. The Framers' experience with the British monarchy informed their belief that the concentration of distinct governmental powers in a single entity would subject the nation's people to arbitrary and oppressive government action. 1 Footnote
Article II Section 2 begins with the Commander in Chief Clause, stating the President is the commander of the nation's armed forces. While the Constitution vests Congress with the ability to declare war, it is the Executive that actually manages and commands the armed forces once war has been declared. This has inevitably created a continuing ...
Current constitutional issues related to vaccine mandates. The Covid-19 delta variant’s spread may force federal and state authorities to re-examine public safety policies related to vaccine requirements. Here is a brief review of the constitutional precedents and laws related to mandates at the federal and state levels.
Advertising entities affected by paragraph (2), Section 11 of Article XVI of this Constitution shall have five years from its ratification to comply on a graduated and proportionate basis with the minimum Filipino ownership requirement therein.
Which part of the Constitution is the basis for this diagram? The federal government has the power to regulate commerce between the states. The federal government can build highways to allow commercial goods to be moved. O A. The expressed powers O B. The Bill of Rights O C. The necessary and proper clause O D. The denied powers
There is strong constitutional basis of RTI in India i.e. there is inherent RTI in Indian Constitution. Let me provide you judicial interpretation of various provisions of constitution. Preamble. As the preamble describes, one of the significant objectives of Indian Constitution is to secure liberty of thought and expressions to the citizens of ...
Oct 02, 2018 · Article I of the U.S. Constitution establishes all the power that the Congress has, such as the power to regulate commerce within the states, provide and maintain a navy, establish post offices, etc. And although it does not specifically state how the Congress shall fulfill those legal powers, the Constitution does have a clause that guarantees ...
A constitution is an aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.. When these principles are written down into a single document or set of legal documents, those documents may be said to embody a written constitution; if they are ...
a. The amendments arose from the controversy over ratification of the Constitution. b. The amendments were ratified at the same time as the Constitution. c. The amendments guarantee such basic rights as freedom of expression and fair and equal treatment before the law. d. The amendments are the first ten of the Constitution.
United States, 1671 the Court holding that "the requirements of the Constitution are not violated where . . . a court-martial is convened to try a serviceman who was a member of the armed services at the time of the offense charged." 1672 Chief Justice Rehnquist's opinion for the Court insisted that O'Callahan had been based on ...
That being a part of the Constitution ... Indeed, the explicit limitation in article five is the basis of an argument denying the existence of various limitations on the subject matter of amendments supposed to be implicit in the constitutional scheme. The unamendable amendment, however, stands on a different footing.
The three main parts of the U.S. Constitution are the Preamble, the Articles (numbering seven) and the Amendments (numbering 27). The Constitution was drafted by the Founding Fathers in 1787 at the Constitutional Convention.
It also stands for our basic ideals, such as personal liberty and democracy. The Constitution has three main parts. First is an introduction called the Preamble (PREE• am•buhl). It states the goals and purposes of the government. Next are seven articles,or main parts. They describe the way the government is set up. Third are 27 amendments.
Feb 01, 2019 · Which part of the Constitution is the basis for this diagram the federal government has the power to regulate commerce? This Necessary and Proper Article is sometimes called the elastic clause. This clause comes under the section VIII of the Article I, in the constitution of the United States. What is the basis of the Constitution?
Sep 25, 2018 · A triple bar graph titled Increase in Black Populations of Northern Cities from 1910 to 1930. The x-axis is labeled city with New York, Chicago, Phila …. delphia, Detroit, Cleveland, Pittsburgh, Gary, Buffalo, Toledo, and Akron. The y-axis is labeled Population from 1 to 1,000,000. The left bar is 1930.
They argued that any amendment to the Constitution had the status of a law as understood by Article 13 (2). In 1952 (Sankari Prasad Singh Deo v. Union of India5) and 1955 (Sajjan Singh v. Rajasthan6), the Supreme Court rejected both arguments and upheld the power of Parliament to amend any part of the Constitution including that which affects the
Birthright Citizenship and the Constitution. The following is an entry concerning the first section of Amendment 14 of the Constitution as found in The Heritage Guide to the Constitution. Before ...
US Constitution 1. 65 terms. ashleypearson12. 8th grade Constitution Test. 61 terms. Pam_Atkinson TEACHER. Constitution Chapter 8 Social Studies. 52 terms. McCaulS.
Documents may be used more than once or not at all. Questions. 1. Maintained that major power in the new government would reside with individual states. 2. Guaranteed that colonists would have the same rights as Englishmen. 3. Affirmed "certain unalienable rights"--life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. 4.
The Preamble is also a very short part of the Constitution, as it is actually a single sentence, and therefore, does not make up any significant part of the Constitution in terms of length. The importance of the Preamble lies not in these two senses, but instead lies in the precedent the Preamble establishes for the rest of the Constitution.
The Constitution, on the other hand, was only written down once, although 14 copies of the Bill of Rights were produced, one for each of the original 13 states and one for the federal government ...
Part Contains Articles; Part I: Union and its Territory: 1 to 4: Part II: Citizenship: 5 to 11: Part III: Fundamental Rights: 12 to 35: Part IV: Directive Principles of State Policy: 36 to 51: Part IVA: Fundamental Duties: 51A: Part V: The Union: 52 to 151: Part VI: The States: 152 to 237: Part VII: States in the B part of the First schedule ...
The third part of the Constitution consist of 27 amendments - formal changes to the basic document.The first 10 Amendments are known as the Bill of Rights." We the people of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union,establish Justice,insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence promote the general welfare and ...
























/dotdash_Final_What_is_the_Gold_Standard_Aug_2020-01-69c4a997a13c47b5ad16e16d9a91d59a.jpg)




0 Response to "39 which part of the constitution is the basis for this diagram"
Post a Comment