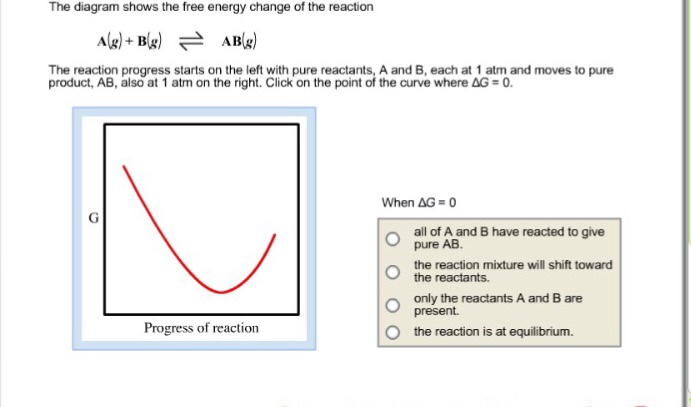
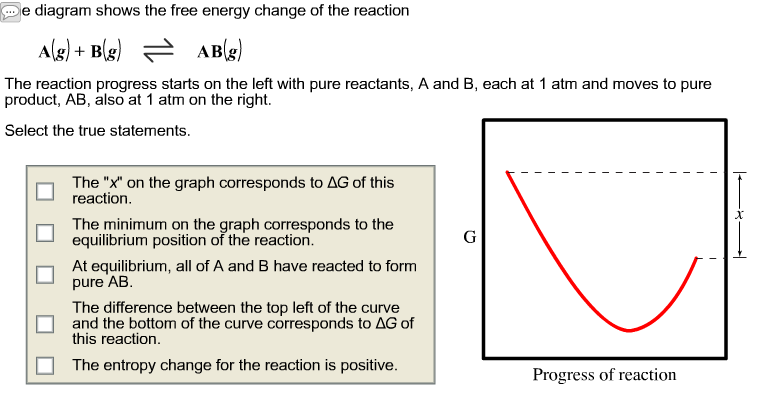
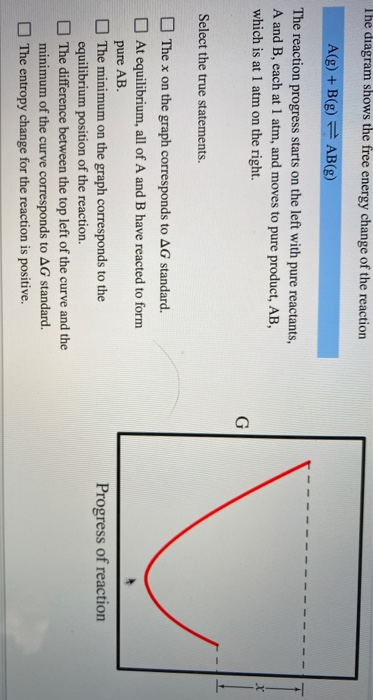
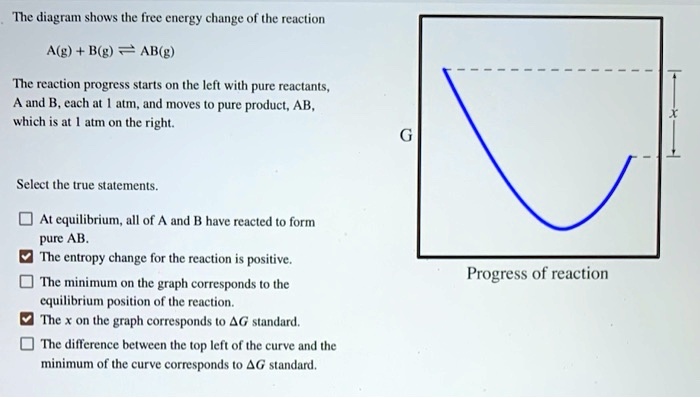
38 the diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction
11 Dec 2019 — Get the detailed answer: The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction: The reaction progress starts on the left with pure ... The Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) and how it's related to reaction spontaneity and equilibrium.
The relationship between the free energy of reaction at any moment in time (G) and the standard-state free energy of reaction (G o) is described by the following equation. G = G o + RT ln Q In this equation, R is the ideal gas constant in units of J/mol-K, T is the temperature in kelvin, ln represents a logarithm to the base e , and Q is the reaction quotient at that moment in time.

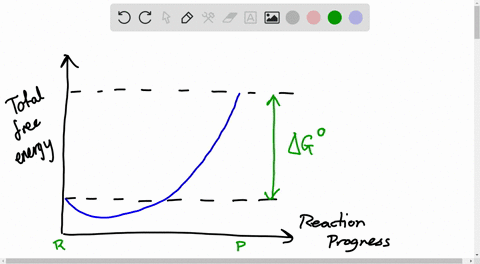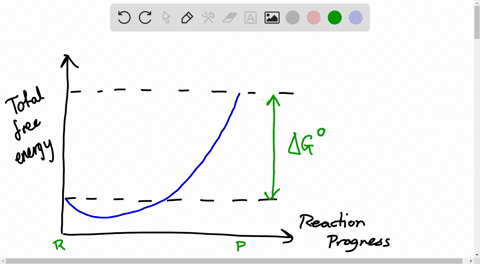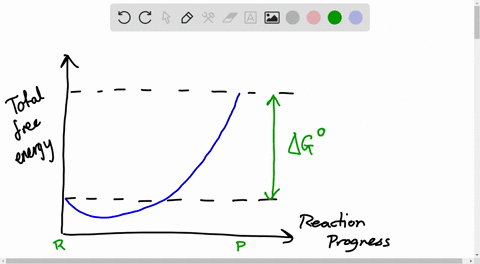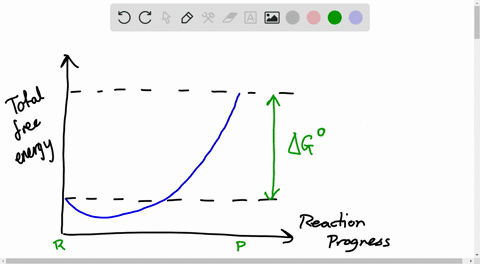
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction
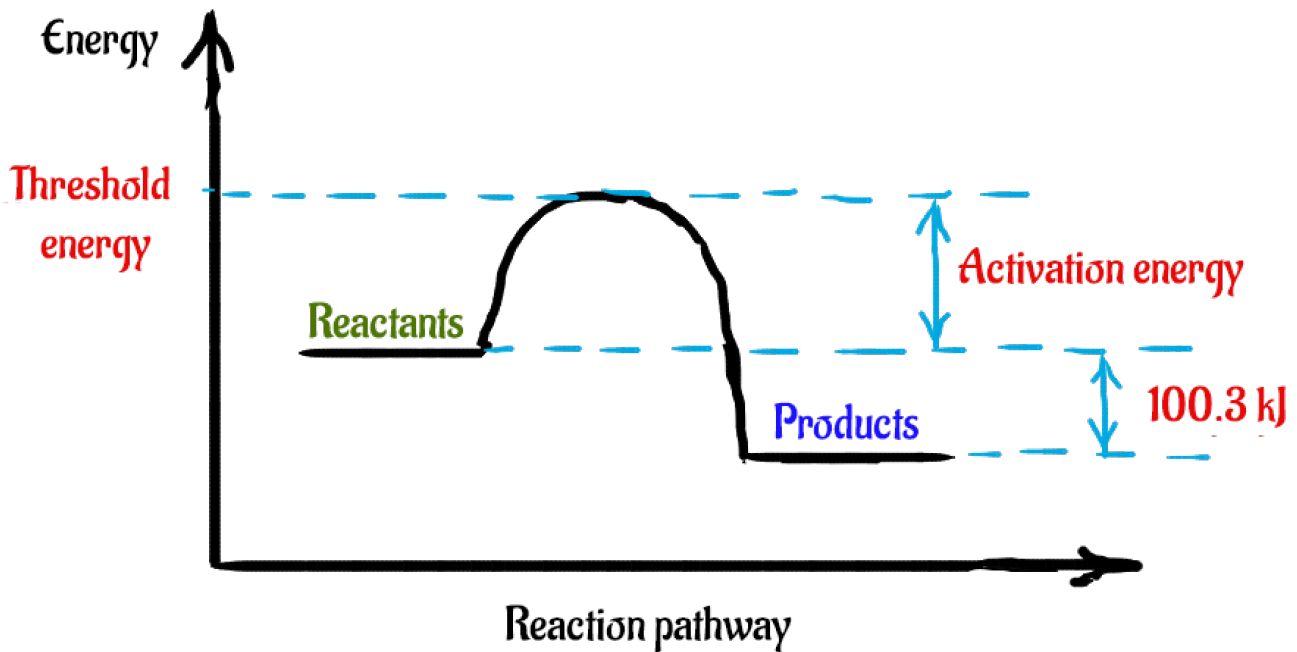
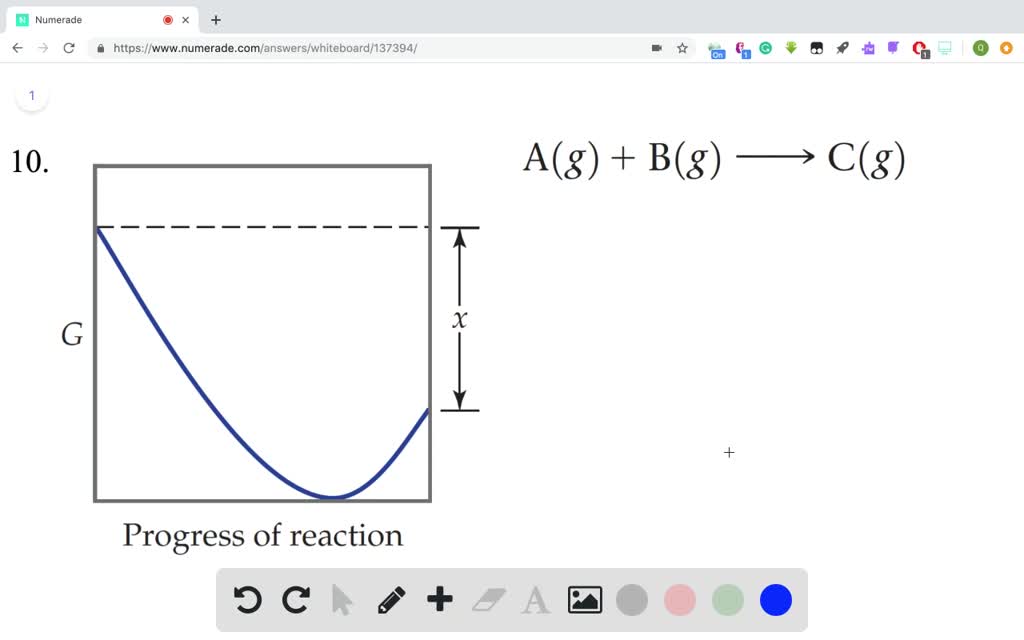
Question: The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) rightarrow C(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, ... A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. Each force arrow in the diagram is labeled to indicate the exact type of ... Observe in the diagram above that a downward vector will provide a partial or full cancellation of an upward vector. And a leftward vector will provide a partial or full cancellation of a rightward vector. The addition of force vectors can be done in the same manner in order to determine the net force (i.e., the vector sum of all the individual forces). Consider the three situations below in ...
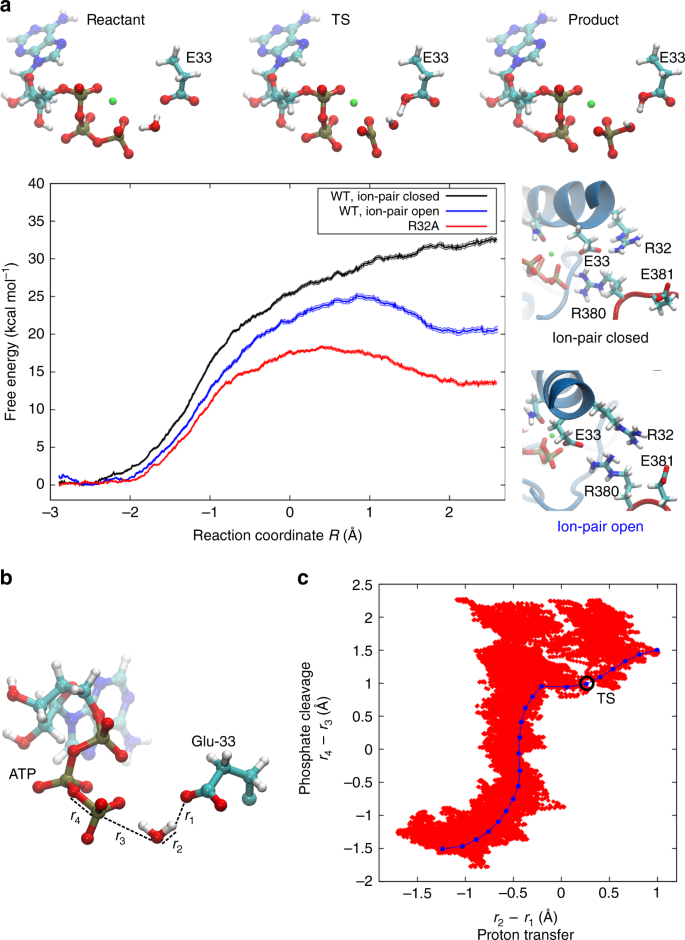
The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction. Chemistry Help! GDie diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g)+ B(g) AB(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, ... Willard Gibbs’ 1873 available energy (free energy) graph, which shows a plane perpendicular to the axis of v and passing through point A, which represents the initial state of the body. MN is the section of the surface of dissipated energy. Qε and Qη are sections of the planes η = 0 and ε = 0, and therefore parallel to the axes of ε (internal energy) and η , respectively. AD and AE are ... The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) AB(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants.4 answers · Top answer: So here's the problem term for Chapter 19 part, eh? This is asking if the minimum off the ... 01/11/2021 · a, Free energy diagram of Ti-OH − adsorption and Ti-OH * creation in the context of the full reaction scheme. Photo-excitation (yellow arrow) separates the diagram into the dark, equilibrated ...
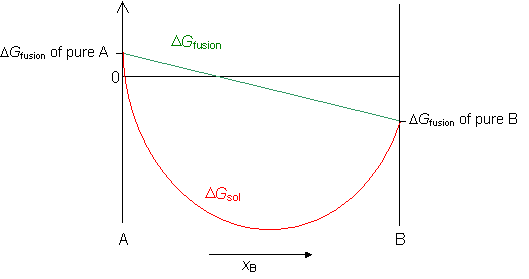
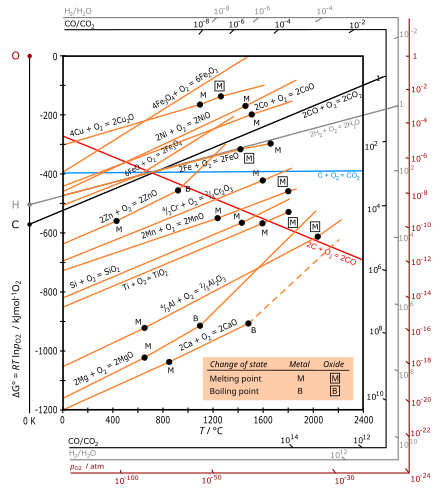
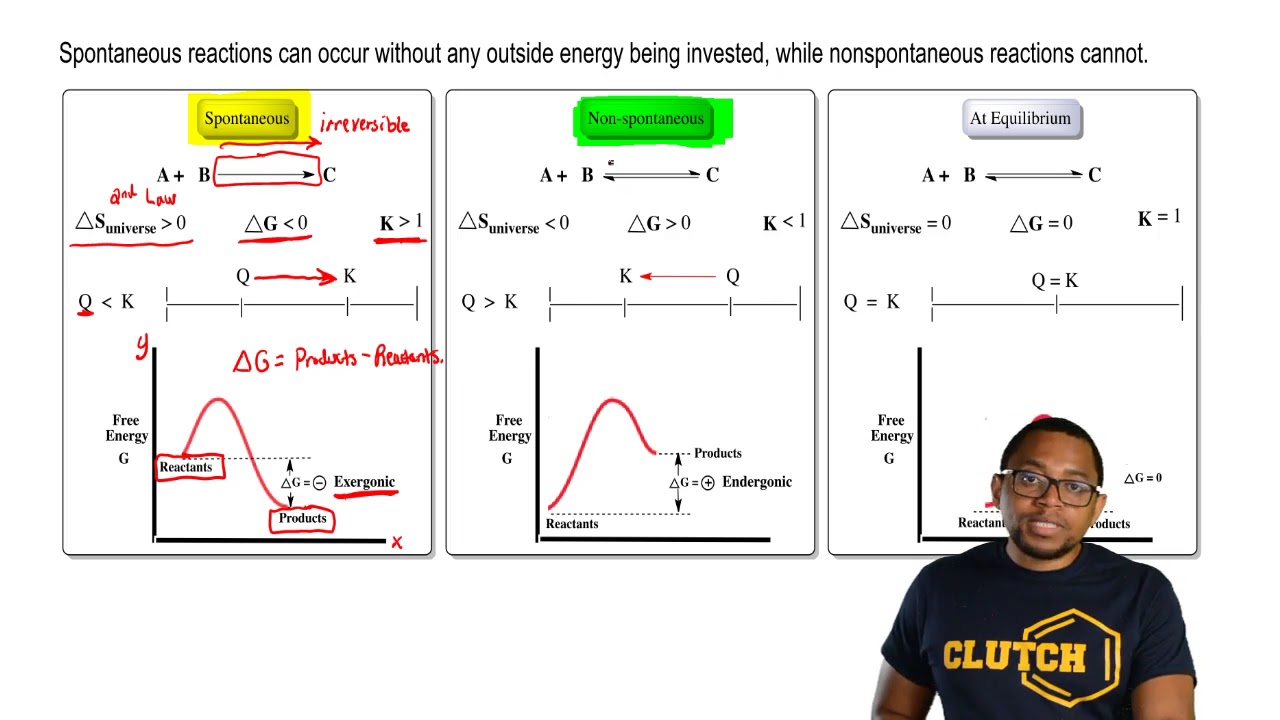
The Ellingham diagram plots the Gibbs free energy change ΔG ... The diagram shown refers to 1 mole O 2, so that e.g. the line for the oxidation of chromium shows ΔG for the reaction 4 ⁄ 3 Cr(s) + O 2 (g) → 2 ⁄ 3 Cr 2 O 3 (s), which is 2 ⁄ 3 of the molar Gibbs energy of formation ΔG f °(Cr 2 O 3, s). In the temperature ranges commonly used, the metal and the oxide are in a condensed ... 16 May 2018 — The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B each at 1 atm and moves to pure product, C, also at 1 atm on the right.1 answer · Top answer: At Equilibrium: Q (reaction quotient) = K (equilibrium constant)[readmore]• At Equilibrium: Q = K• Left side of Equilibrium: Products < Reactant• ... Fig. 4.2 A free energy (G) diagram for a simple reversible exothermic reaction A↔P(solid and broken lines). G A and G P represent the average free energies per mole for the reactant A and the product P, the initial and final states respectively. The standard state free energy change for the reaction is ΔG . In order for reactant A to undergo transformation to product P, it must pass ... The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction. A(g) + B(g) ⇌ AB(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, A and B, at 1 atm and moves to pure product, AB, also at 1 atm on the right. Select the true statements.A. The "x" on the graph corresponds to ΔG of this reaction.B. The minimum on the graph corresponds to the equilibrium position of the reaction.C. At ...
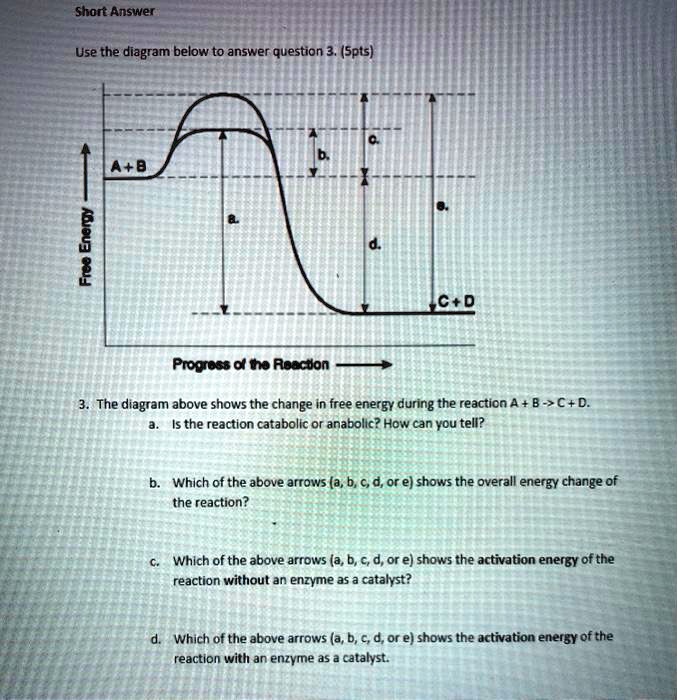
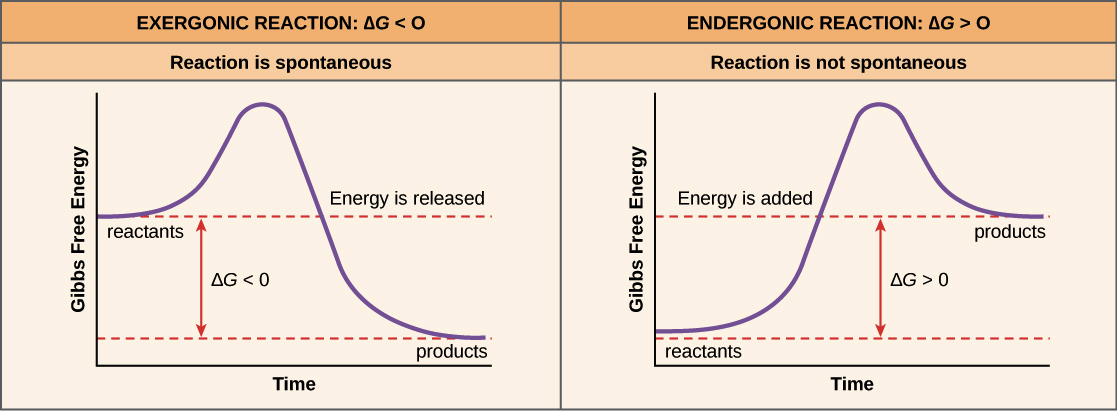
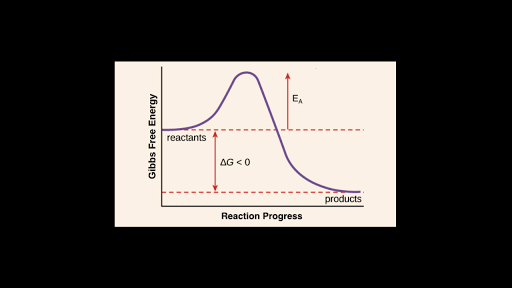
Chemical Reaction Formula Examples: 1. Methane (CH 4) and oxygen (O 2) react to produce carbon dioxide (CO 2) and water (H 2 O). CH 4 + 2O 2 → CO 2 + 2H 2 O. CH4 and O2 are the reactants, while CO 2 and H 2 O are the products. 2. Sodium metal (Na) reacts with water (H 2 O) to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen gas (H 2). The total entropy change of a system and its surroundings can be used to predict ... Graphs of ΔG against temperature show how reaction feasibility changes. positive change in the entropy for the reaction. Construction of an Ellingham Diagram An Ellingham diagram is a plot of ∆G versus temperature. Since ∆H and ∆S are essentially constant with temperature unless a phase change occurs, the free energy versus temperature plot can be drawn as a series of straight lines, where ∆S is the slope ... 25 Aug 2020 — 2: These plots show the free energy versus reaction progress for systems whose standard free changes are (a) negative, (b) positive, and (c) ...
Observe in the diagram above that a downward vector will provide a partial or full cancellation of an upward vector. And a leftward vector will provide a partial or full cancellation of a rightward vector. The addition of force vectors can be done in the same manner in order to determine the net force (i.e., the vector sum of all the individual forces). Consider the three situations below in ...
A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting. Each force arrow in the diagram is labeled to indicate the exact type of ...
Question: The diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction A(g) + B(g) rightarrow C(g) The reaction progress starts on the left with pure reactants, ...



















0 Response to "38 the diagram shows the free energy change of the reaction"
Post a Comment