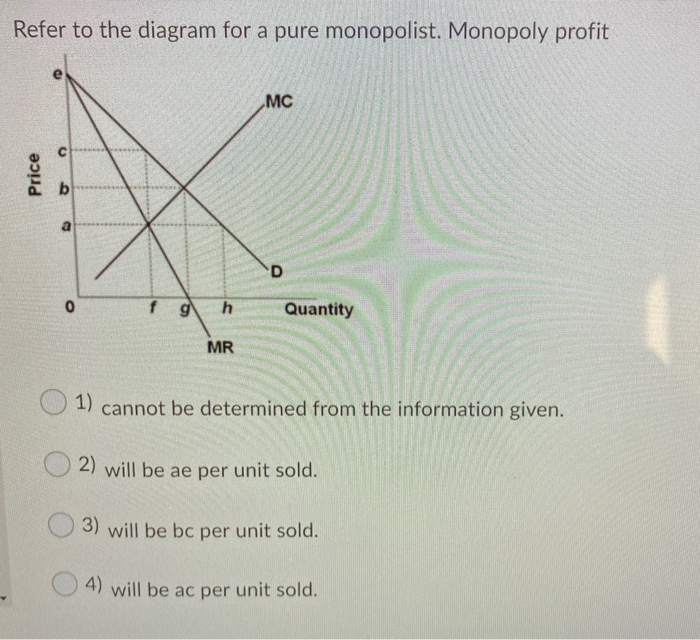
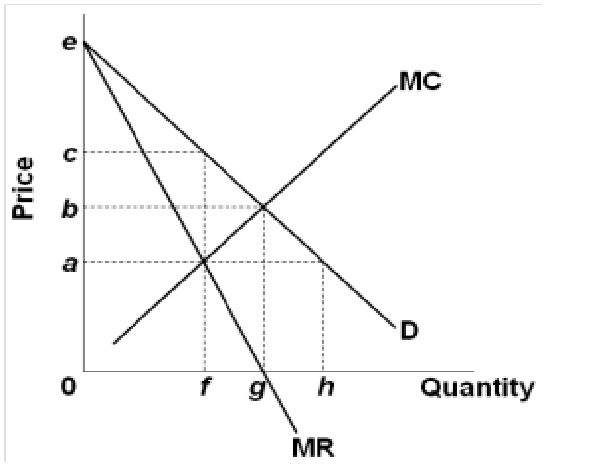
40 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output
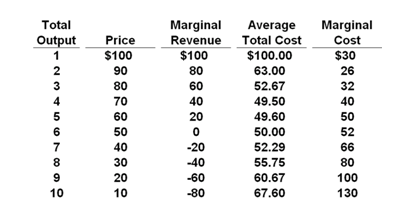
Chap 024 | Monopoly | Price Elasticity Of Demand Type: G Topic: 3 E: 442 MI: 198 53. zero at output: A) Answer: C Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be. q4. B) q3. C) q2. D) q1. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 444 MI: 200 54. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Profit Maximization in a Perfectly Competitive Market ... Unlike marginal revenue, ordinarily, marginal cost changes as the firm produces a greater quantity of output. At first, marginal cost decreases with additional output, but then it increases with additional output. Again, note this is the same as we found in the module on production and costs. Table 3 presents the marginal revenue and marginal ...
11. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. 11. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1. B. q2. Correct.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output
PDF Answers to End-of-chapter Questions sell four, the monopolist had to lower the price of the first three from $5.50 to $5.00, sacrificing $.50 on each for a total of $1.50. This "loss" of $1.50 explains the difference between the $5.00 price obtained on the fourth unit of output and its marginal revenue of $3.50. Demand is elastic from P= $6.50 to P= $3.50, a range where TR is rising. A nondiscriminating profit maximizing monopolist A will ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q 2 B. always produce more than q 2 C. never produce an output larger than q 2 D. never produce an output larger than q 1 . . . . 45. Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com 51. For a pure monopolist marginal revenue is less than price because: A) the monopolist's demand curve is perfectly elastic. B) the monopolist's demand curve is perfectly inelastic. C) when a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output. Profit Maximization - CliffsNotes The fourth column reports the monopolist's marginal revenue that is just the change in total revenue per 1 unit change of output. The fifth column reports the monopolist's total cost of providing 0 to 5 units of output. The sixth and seventh columns report the monopolist's average total costs and marginal costs per unit of output. Chapter 12 - Pure Monopoly - Subjecto.com If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be: A. equal to its price. B. the price at which that unit is sold less the price reductions which apply to all other units of output. Economics 370 Microeconomic Theory Problem Set 6 Answer Key The monopoly's marginal cost is m = 30. Solve for the equilibrium price in each country. The price-discriminating monopoly maximizes its profit by operating where its marginal revenue for each country equals the firm's marginal cost. Hence, the marginal revenues for the two countries are equal; MR1 = MC = MR2. P1 = 100 - Q1 Solved > 11. Fiat money is: A)money backed by gold.:235353 ... B)zero. C)the interest rate when someone uses a credit card. D)the discount rate. 14. Fiscal policy that decreases aggregate demandis: A)balanced. B)expansionary. C)contractionary. D)supplemental. 15. A decrease in the money supply is likely tocause: A)a decrease in borrowing and interest rates and an increase inaggregate demand.
Micro Chapter 12 Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm will be operating in the. Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips For a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm: A. the marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve. B. the demand and marginal revenue curves coincide. C. the demand curve intersects the horizontal axis where total revenue is at a maximum. D. marginal revenue will become zero at that output where total revenue is at a maximum. 20. Solved Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: q1. q2. q3. q4. Question: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: q1. q2. q3. q4. Solved > 11. Problems and Applications Q9 Hotel rooms in ... 11. Problems and Applications Q9 Hotel rooms in Smalitown go for $100, and 1,000 rooms are rented on a typical day. To raise revenue, the mayor decides to charge hotels a tax of $10 per rented room. After the tax is imposed, the going rate for hotel rooms rises to $108, and the number of rooms rented falls to 900.
Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. This ... A nondiscriminating monopolist earning positive short-run economic profit determines that its current marginal cost is $15 and its current marginal revenue is $20 . To maximize profit, a firm should The revenue-maximizing output for a nondiscriminating monopolist represented in the table given below is Microeconomics Ch. 10-13 Flashcards | Quizlet To maximize profit, a pure monopolist must: ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output:. Chapter 12- Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet (Supposed to be a graph) Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output Microeconomics Exam 2 Chapter 12 - Subjecto.com 2. For a pure monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because: C. when a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. 3. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic: C. for all levels of output less than q 2. 4. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: - ScieMce A nondiscriminating profit-maximizing monopolist: asked Aug 6, 2018 in Economics by Guitar_Hero. A. will never produce in the output range where marginal revenue is positive. B. will never produce in the output range where demand is inelastic. C. will never produce in the output range where demand is elastic.
Chapter 12 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its ...
ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: Q2. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: never produce an output larger than q2.
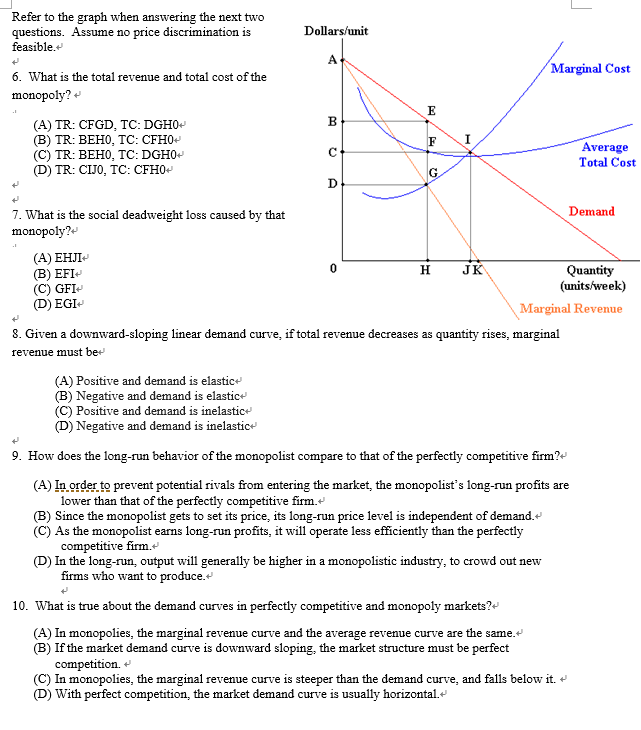
PDF AP Unit 6 At the profit-maximizing output the firm's economic profit will beBAFG. True False 59. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output R economic profits will be zero. True False 60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61.
Economics (McGraw-Hill Economics) 18th Edition Quiz 140 ... A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at a short-run output level where average total cost is $10.00, marginal cost is $5.00, marginal revenue is $6.00, and price is $12.00. In the short run, the firm should: A. Decrease the level of output B. Increase the level of output C. Make no change in the level of output D. Increase product price
Microeconomics Exam 2 Chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: B. q 2. 5. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. ... If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be:
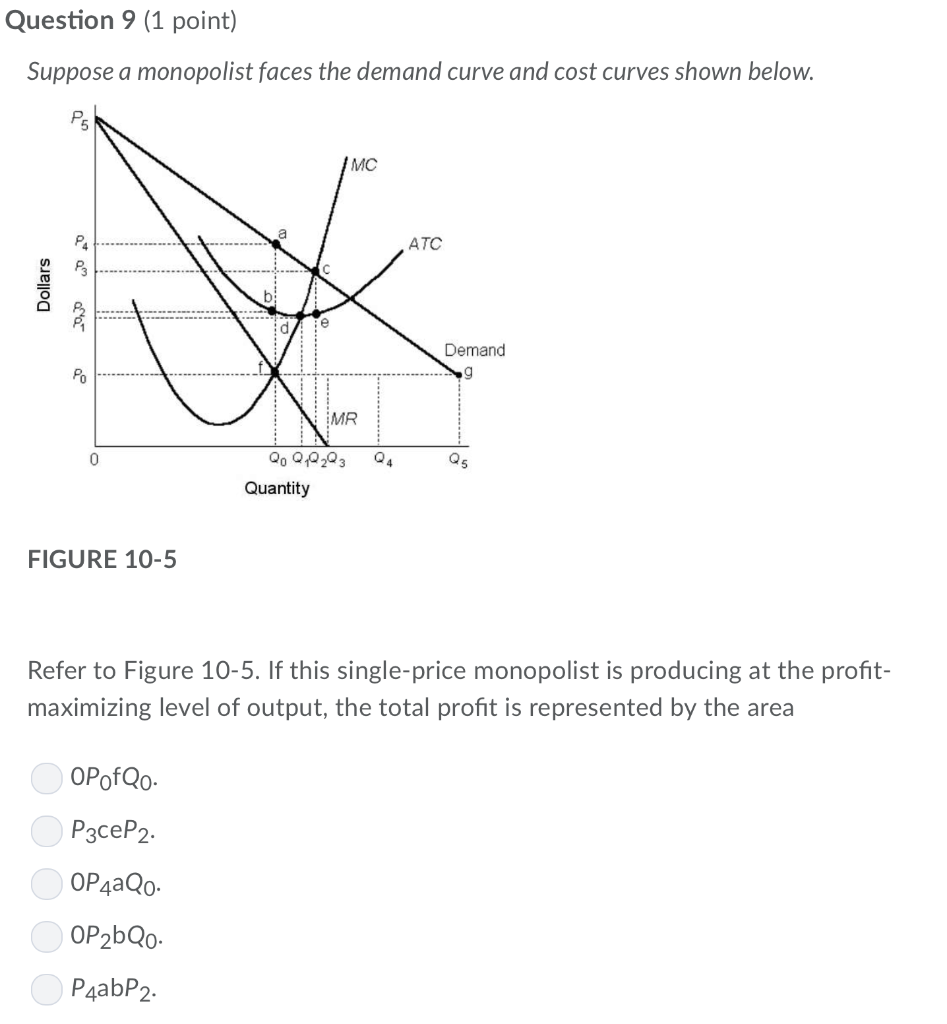
Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics As a result, the marginal cost of the second unit will be: MC = $775−$500 1 = $275 MC = $ 775 − $ 500 1 = $ 275 Step 3. Remember that, similarly, marginal revenue is the change in total revenue from selling a small amount of additional output.
44 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output Chapter 12 - Pure Monopoly - Subjecto.com If a nondiscriminating pure monopolist decides to sell one more unit of output, the marginal revenue associated with that unit will be: A. equal to its price.
BEEB1013 A172 Exercise 7 - BEEB1013 PRINCIPLE OF ... - StuDocu A natural monopoly occurs when: A. long-run average costs decline continuously through the range of demand. B. a firm owns or controls some resource essential to production. C. long-run average costs rise continuously as output is increased. D. economies of scale are obtained at relatively low levels of output. f18.
Economic profit for a monopoly (video) - Khan Academy So that might be the demand curve. Now what's interesting about any imperfectly competitive firm, and the extreme case is a monopoly, is what the marginal revenue curve looks like given this demand curve. In a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal revenue curve is equal to the demand curve, and in that situation, it's actually a horizontal line.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating - Course Hero Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist Marginal revenue will be from ECON 1116 ... Marginal revenue will be zero at output A. q 1 B. q 2 .
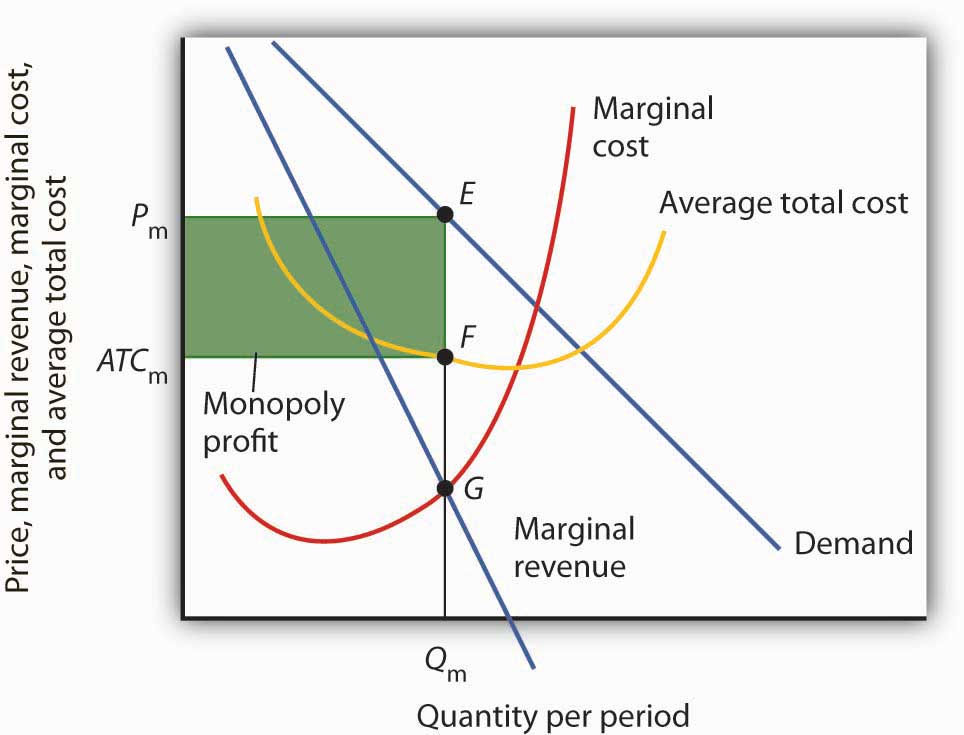
Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help Monopoly Graph A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q
Ch11quiz The nondiscriminating monopolist's demand curve: A. is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. B. is perfectly elastic. C. coincides with its marginal revenue curve. D. is perfectly inelastic. 11. What do economies of scale, the ownership of essential raw materials, and patents have in common? A.
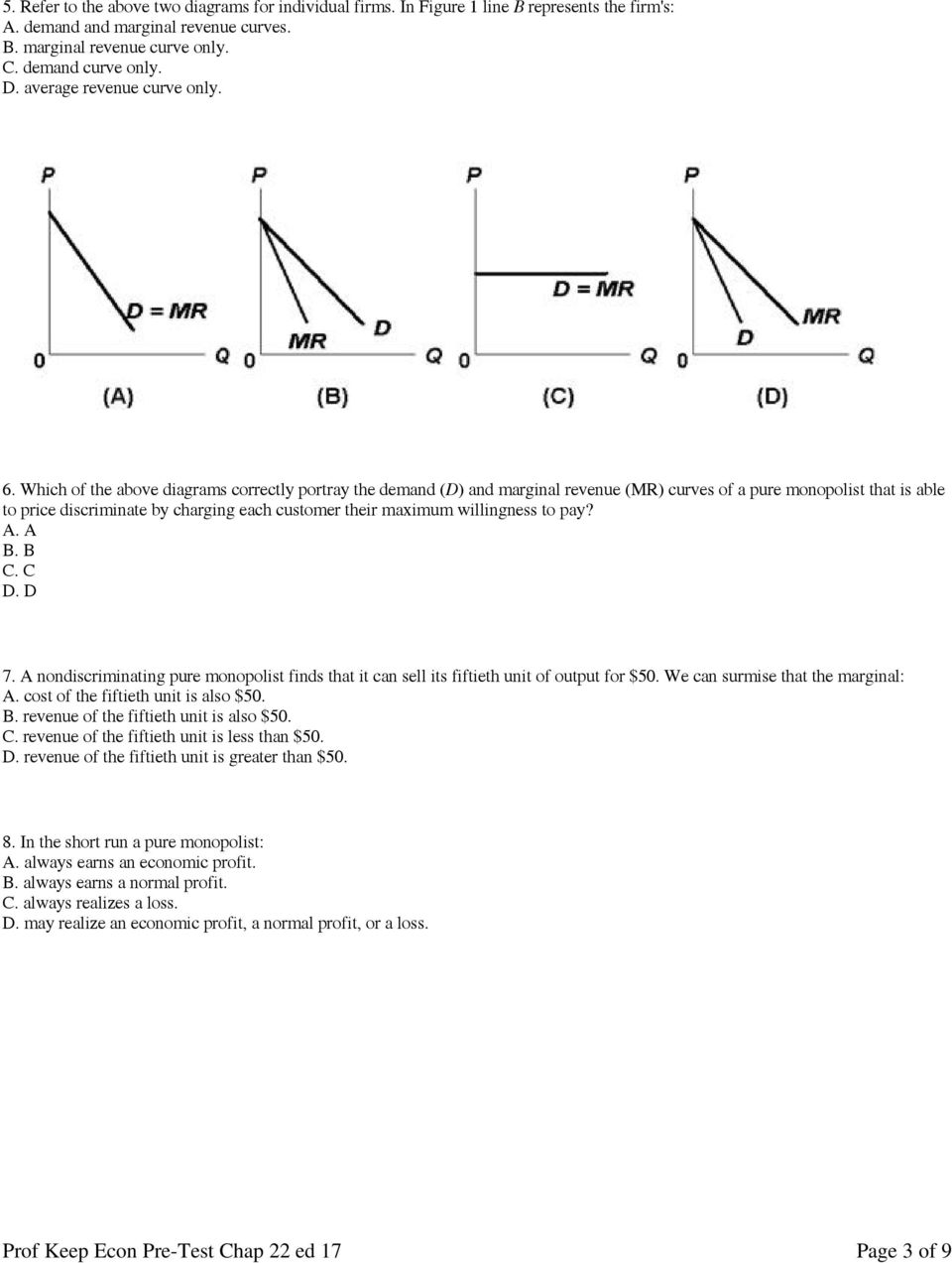
ch12.docx - Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms ... Marginal revenue will be zero at output q 2 . Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will never produce an output larger than q 2 . Suppose a pure monopolist is charging a price of $12 and the associated marginal revenue is $9. We thus know that total revenue is increasing.
Pre-Test Chapter 22 ed17 - AZSLIDE.COM Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its ...
Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com 51. For a pure monopolist marginal revenue is less than price because: A) the monopolist's demand curve is perfectly elastic. B) the monopolist's demand curve is perfectly inelastic. C) when a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold.
A nondiscriminating profit maximizing monopolist A will ... Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A. always produce at output q 2 B. always produce more than q 2 C. never produce an output larger than q 2 D. never produce an output larger than q 1 . . . . 45.
PDF Answers to End-of-chapter Questions sell four, the monopolist had to lower the price of the first three from $5.50 to $5.00, sacrificing $.50 on each for a total of $1.50. This "loss" of $1.50 explains the difference between the $5.00 price obtained on the fourth unit of output and its marginal revenue of $3.50. Demand is elastic from P= $6.50 to P= $3.50, a range where TR is rising.















0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output"
Post a Comment