40 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
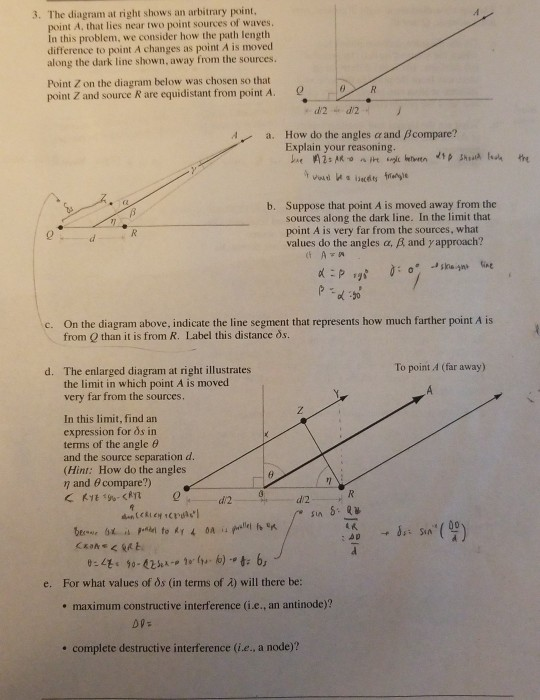
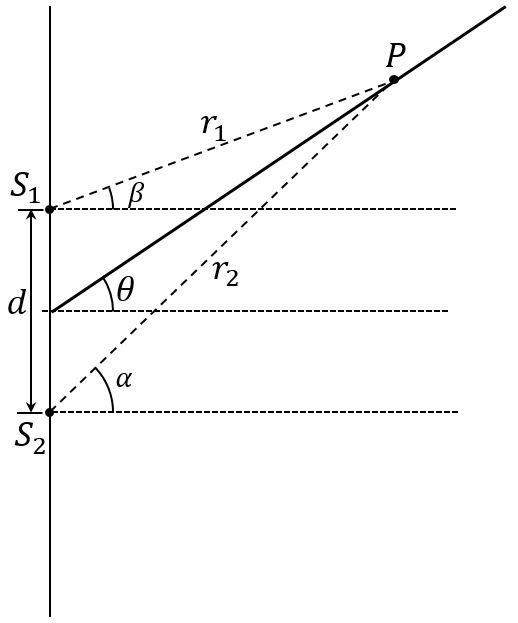
The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point | Chegg.com The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point .A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A. Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. - Chegg Transcribed image text: 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider ...
geometry - Distance an arbitrary point is found along a ... Say I have a vector in 2D space defined by two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$: $$\vec{v}=(x_2 - x_1, y_2 - y_1)$$ I would like to find how far along that vector an arbitrary point $(x_3, y_3)$ is. This very woolly language $^*$, so I've attempted to create a diagram showing the sitation.
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
PDF G10 Bio - lyceumpasspapers (13) The diagram shows a cross-section of a root. Which tissue transports water to the leaves? (B) (C) (D) (B) (D) The roots cannot take up mineral salts. The surface area of the root is reduced. (14) The diagram shows part of a tissue. The arrows show movement of fluids. At which point is the pressure highest ? lymph vessel (A) capillary ... Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S_2 are equidistant from point A. PDF LAB 8: Static Equilibrium - De Anza College arbitrary point on the meter stick is zero, to support the idea that the net torque on the meter stick about any point is zero. Theory: An object is in static equilibrium if it meets the following conditions: 1.The net force on the object is zero, P i ~F i = 0. Equivalently, this means that the sum of the x, y, and z components of the forces ...
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point - Chegg The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S, are equidistant from point A. 1-d2+d2 a. PDF Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Straight Rod—C.E ... arbitrary point in space. The result includes the case of the field on the axis of the rod beyond one of its ends, and the case of an infinitely long rod. The general answer is most conveniently expressed in terms of the linear charge density λ; for a finite rod of length L and total charge Q, that charge density is equal to Q/L. To begin with ... PDF ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis body diagram of the foot pedal. EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM (Section 5.3) A body is subjected to a system of forces that lie in the x-y plane. When in equilibrium, the net force and net moment Fx = 0 Fy = 0 MO = 0 where point O is any arbitrary point equilibrium, the net force and net moment acting on the body are zero (as discussed Schreinemakers Method - Teaching Phase Equilibria Schreinemakers' method is a geometric approach used to determine the relationships of reaction curves that intersect at an invariant point in multicomponent systems. This method produces topologically correct bundles or sequences of reactions around an invariant point, and can be applied to a wide variety of phase diagrams such as P-T, T-X ...
PDF Representing a Reaction with a Potential Energy Diagram The diagram correctly shows the potential energy of the product lower than the potential energy of the reactant. Unit 3 Part B MHR 129 16. For a reaction, on an arbitrary scale, the potential energies are as follows: activated Q Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run ... Q: Refer to the diagram to the right. Diminishing marginal productivity sets in after A: the 2nd worker is hired. 49) Q: The graph in this figure illustrates an initial competitive equilibrium in the market for apples at the intersection of D 2 and S 1 (point C ). Need help understanding 16QAM constellation diagram The mapping is arbitrary as long as the receiver correctly determines which constellation point a symbol is. If the receiver makes a mistake, though, it is most likely going to pick a "neighbor" constellation point (i.e. a constellation point that is only one spot away). PDF HW 10 SOLUTIONS - University of Utah - diagram of the beam's left through an arbitrary shown in fig. b will be to write the and mcnnent quations. The inœnsity the triangldar útributed load at of sectioning is — = 3333r Referring Fig. b , o V = {-300- 1b — +3001-0 The shear and diagrams shown in Figs. c d are plotted using Eqs. (l ) (2), reqxcüvely.
(Get Answer) - The diagram shows the variation with ... The diagram shows the variation with distance from the centre of the planet of the gravitational potential due to the planet and its moon. The planet's centre is at = 0 and the centre of the moon is at = 1.The units of separation are arbitrary. At the point where = 0.75 the gravitational field is zero.. a Determine the ratio of the mass of the planet to that of the moon. Answered: 3. The diagram on the right shows an… | bartleby The diagram on the right shows an open box with a square base of side x cm and a height of h cm. The box is made from a piece of cardboard with an area of 75 cm². (a) Show that the volume of the box, V cm², is given by V= (75x - x). h cm x cm x cm (b) Find the value of x such that the volume, V is maximum and also the maximum volume of the box. Point-Group Diagrams - University College London In addition, the figure shows how an arbitrary point (shown top right as an open circle with a "+" symbol), which is not lying on any of the symmetry elements, is symmetry related to three other points, two of which have an opposite handedness to the original. Solved 3 The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point - Chegg Advanced Physics. Advanced Physics questions and answers. 3 The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source R are equidistant from point A. 0 How do the.
Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point - Chegg The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point point A, that lies near two point sources of waves In this problem, we consider how the path lengtlh difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources.
PDF ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape.
PDF UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL ... - GCE Guide 3 The diagram shows some cells in the root of a plant that is absorbing water from the soil. 2 1 3 ... / arbitrary units 30 °C 20 °C 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 ... Which position on the graph corresponds to the point at which the ribs are beginning to be lowered? expiration inspiration
Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A.
International Economics Flashcards - Quizlet Using the diagram on the right, show what effect a devaluation will have on the current account. Note: 'E' = E$/€. 1) Using the line drawing tool , shift any lines, making sure to label them appropriately. 2) Using the point drawing tool, label new equilibrium "B".
PDF Motion Diagrams reading - Columbia Public Schools point with reference to a coordinate axis. The origin of the coordinate axis may be arbitrary. Position to right of origin, position(x) is positive Position to left of origin, position(x) is negative ... • A motion diagram shows only the POSITION of the object on the position axis.
Answered: Planetary motion. A planet or asteroid… | bartleby The diagram shows two points of interest: point P, the perihelion, where the planet is nearest to the Sun, and the far point, or aphelion, at point A. At these two points (and only these two points), the velocity v of the planet is perpendicular to the corresponding "radius" vector i, from the Sun to the planet. An arbitrary point Q is also shown.
General formalism for calculating the thermal efficiency ... We develop a general method for calculating the thermal efficiency of arbitrary thermodynamic cycles defined in the pressure-volume (p-V) diagram.To demonstrate how effective our approach is, we calculate the thermal efficiency of ideal gas engines for a few non-trivial cycles in the p-V diagram, including a circular shape, a heart shape, a cycloid of Ceva, and a star-shaped curve.
International Econ- Exam 1 Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram to the right shows the Home economy's pretrade equilibrium at point X. (Click anywhere on the graph and move the slider to vary the relative price.) In this closed economy, it is the case that
Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S, are equidistant from point A. -d2+d2- a.
Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point Question: The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path ...
Figure shows a wire of arbitrary shape carrying a current ... Figure shows a wire of arbitrary shape carrying a current I between points a and b. The length of the wire is L and the distance between points a and b is d. The wire lies in a plane at right angle to a uniform magnetic field B. Then the force on the wire is :
Physics Undergraduate Practicals The diagram at the right shows an arbitrary point, point P, that lies near two point sources of sinusoidal waves. The two sources are in phase with each other. In this activity, we consider how the phase difference of the waves arriving at point P changes as point P is moved outward along the dark line, away from the sources.
PDF LAB 8: Static Equilibrium - De Anza College arbitrary point on the meter stick is zero, to support the idea that the net torque on the meter stick about any point is zero. Theory: An object is in static equilibrium if it meets the following conditions: 1.The net force on the object is zero, P i ~F i = 0. Equivalently, this means that the sum of the x, y, and z components of the forces ...
Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S_2 are equidistant from point A.
PDF G10 Bio - lyceumpasspapers (13) The diagram shows a cross-section of a root. Which tissue transports water to the leaves? (B) (C) (D) (B) (D) The roots cannot take up mineral salts. The surface area of the root is reduced. (14) The diagram shows part of a tissue. The arrows show movement of fluids. At which point is the pressure highest ? lymph vessel (A) capillary ...








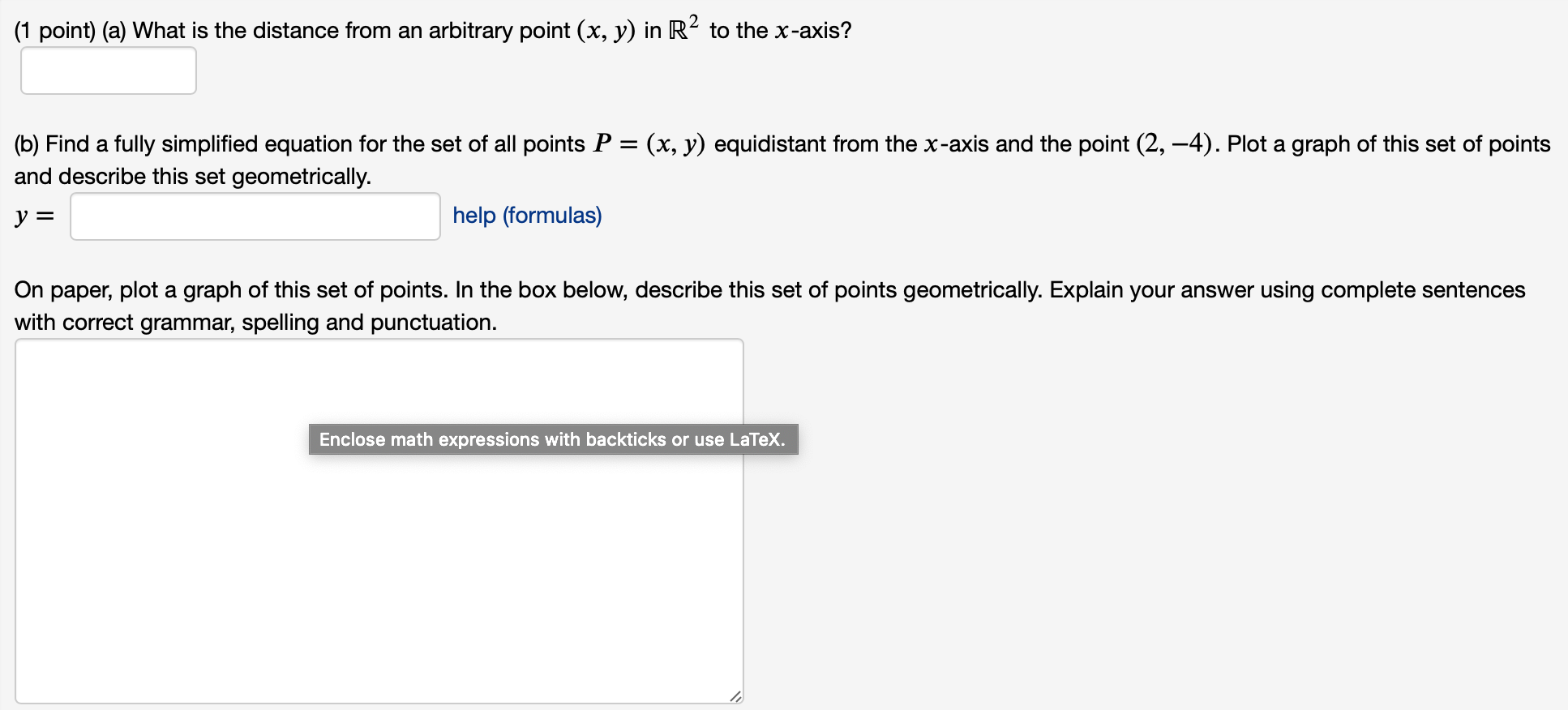








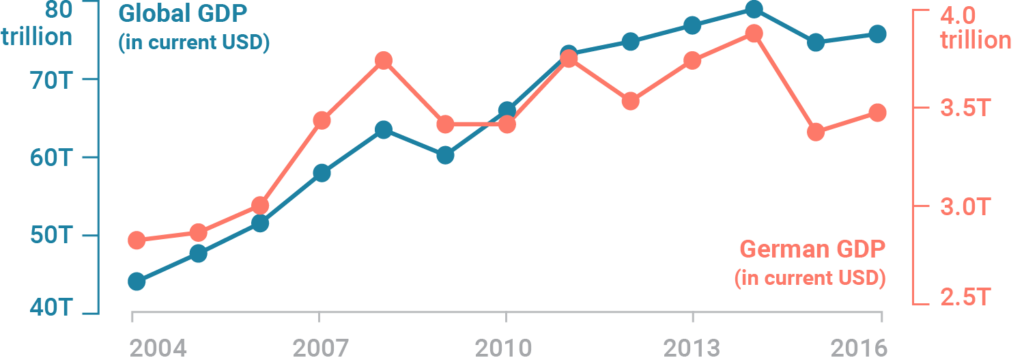









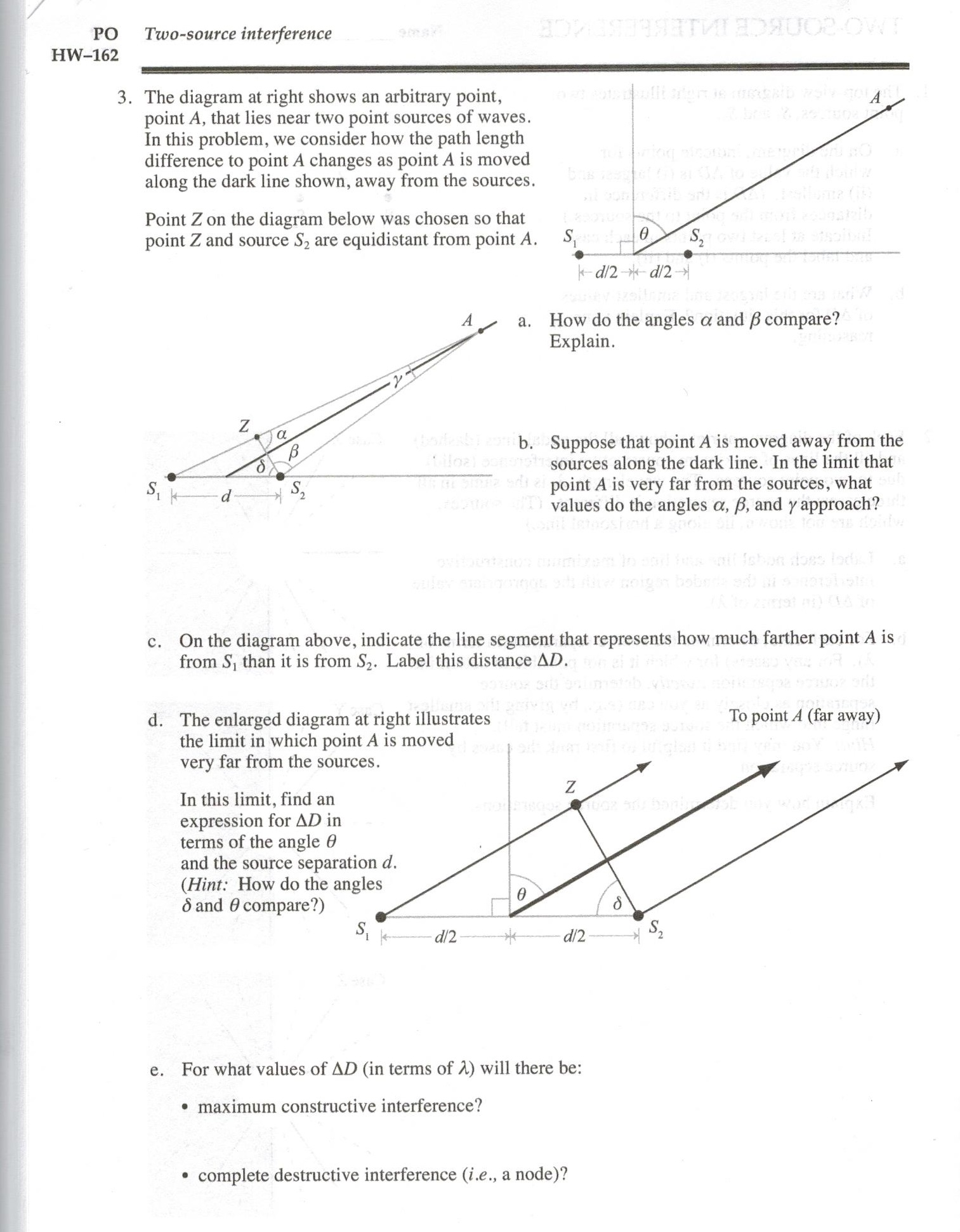
0 Response to "40 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point"
Post a Comment