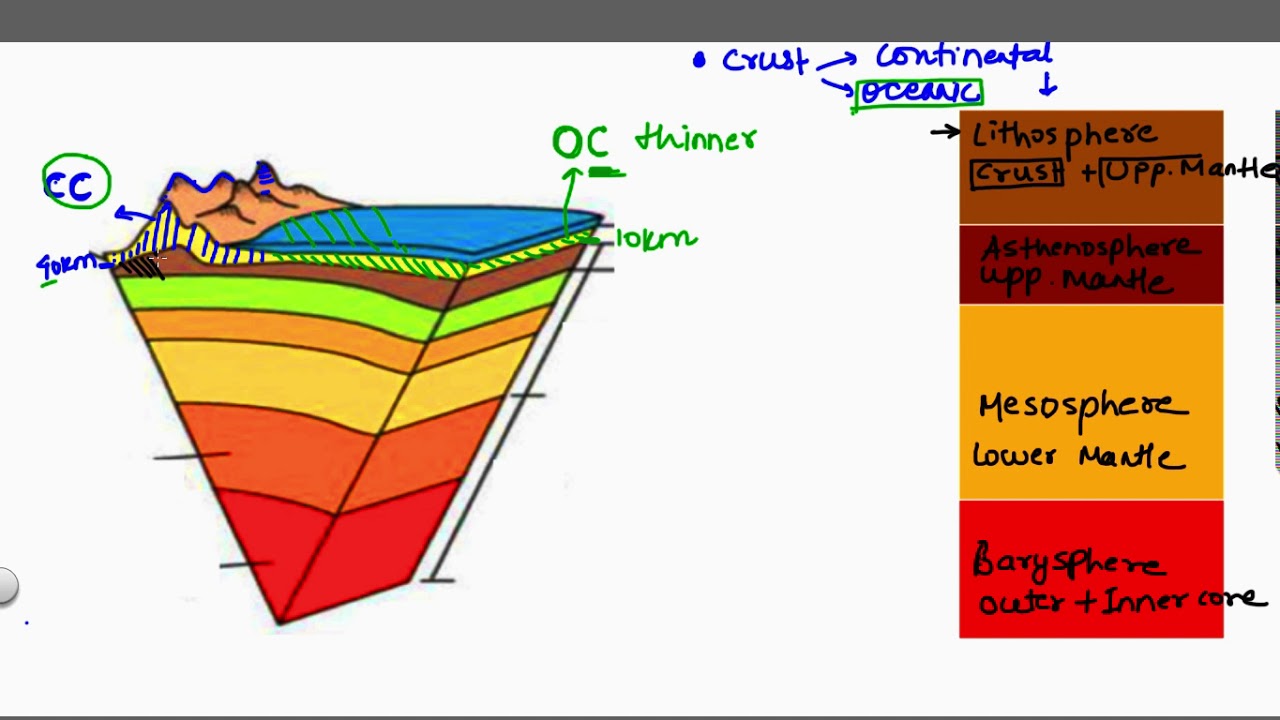
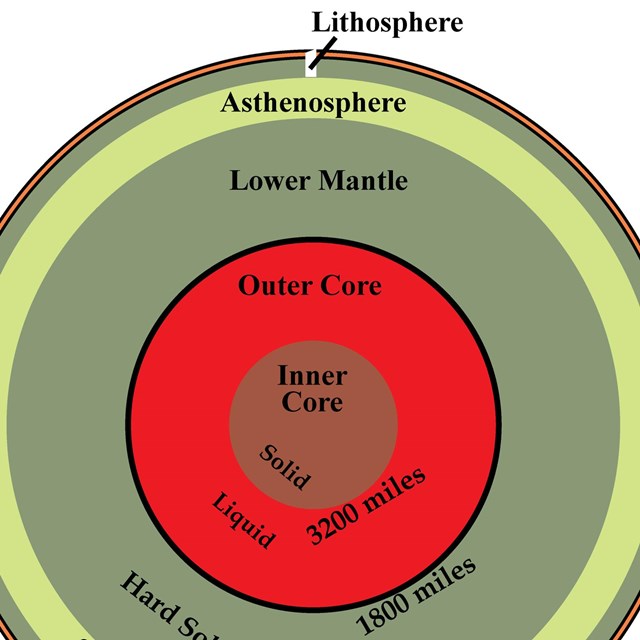
38 lithosphere and asthenosphere diagram
Lithosphere - Composition, Types, Importance and MCQ Earth's lithosphere composition varies greatly depending on whether it lies under oceans or on land. Nevertheless, chief components for this layer as a A lithospheric plate, or more commonly known as a tectonic plate, is a giant and irregular slab of solid rock that usually comprises both the oceanic well... Lithosphere and Asthenosphere ( Read ) | Earth... | CK-12 Foundation Lithosphere and Asthenosphere. Can you think of a solid that can flow? You use one twice a day! The asthenosphere is solid upper mantle material that is so hot that it behaves plastically and can flow. The lithosphere rides on the asthenosphere.
Structure of the Earth | Lithosphere and Asthenosphere This diagram is from the DINOSAURS AND THE HISTORY OF Life - GEOLOGY V1001x site - Professor Paul Eric Olsen. Lithosphere and Asthenosphere. Lithosphere - The lithosphere (from the Greek, λίθος, lithos, stone) is the rigid outermost layer of the geosphere.

Lithosphere and asthenosphere diagram
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Geo108_lec04_structure_origins.ppt The Lithosphere is rigid, or brittle, and consists of the crust and uppermost mantle. The Aesthenosphere is ductile, or plastic, and can flow. the Asthenosphere and Lithosphere can accommodate changes in the redistribution of load (ice sheets, volcanoes, mountains, erosion). Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Hydrosphere (With Diagram) Return to Content. Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Hydrosphere (With Diagram). The lithosphere comprises the solid components, i.e., the rocky substances of the continents. The soil component of the lithosphere has been called pedosphere by Odum. PDF 5. Stress Coupling Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Underlying the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer of higher temperature and thus lower average viscosity. Dehydration at the ridge generates a column of dehydrated material, hdry, which advances with the plate, leading to an additional viscosity stratification [Hirth and Kohlstedt, 1996; Lee...
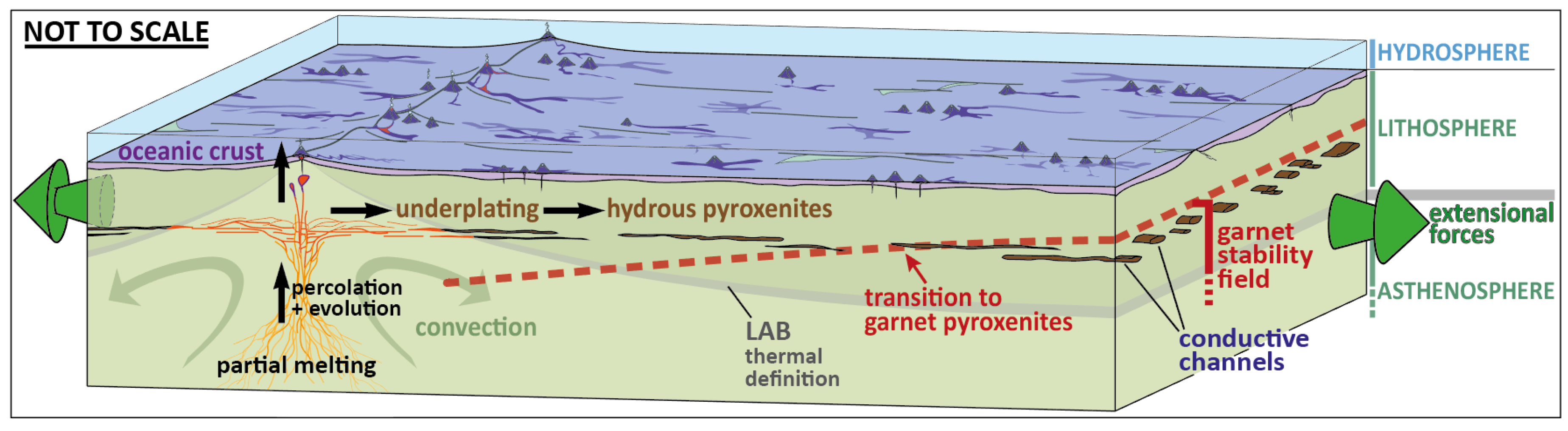
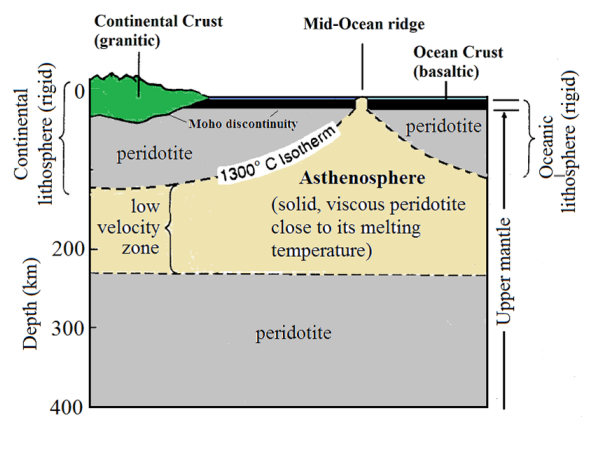
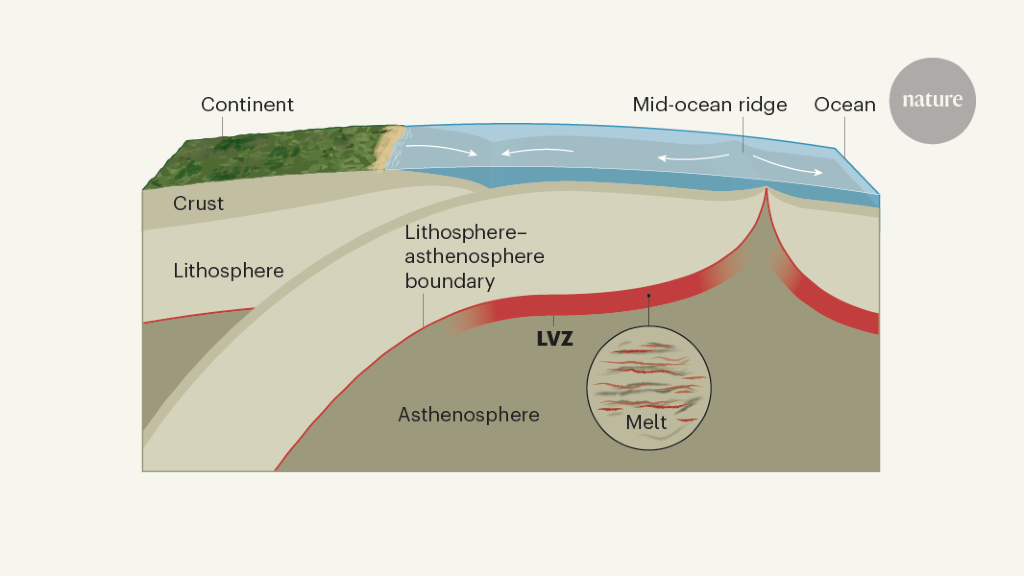
Lithosphere and asthenosphere diagram. › earths-crust-elements-mineralsEarth's Crust: Elements, Minerals and Rocks - ClearIAS May 22, 2017 · Asthenosphere, which is just below the upper mantle, a region beneath Lithosphere is the main source of magma. They might be formed directly by cooling of magma from the interior of the earth itself or by cooling of lava from the surface of the earth. › earth520 › contentWhere Does Volcanic Activity Occur? | Earth 520: Plate ... The schematic diagram below shows their model, which they call "petit-spot" volcanism. A conceptual model of petit-spot volcanism. Magmas from the asthenosphere escape to the shallow depths because of the extensional environment of the lower lithosphere and migrate up through the brittle compressed upper lithosphere by exploiting fractures ... › ~sanelson › eens212Earth's Interior & Formation of Magmas - Tulane University Asthenosphere - about 250 km thick - solid rock, but soft and flows easily (ductile). The top of the asthenosphere is called the Low Velocity Zone (LVZ) because the velocities of both P- and S-waves are lower than the in the lithosphere above. But, not that neither P- nor S-wave velocities go to zero, so the LVZ is not completely liquid. PDF Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, and Perisphere Lithosphere, asthenosphere, and perisphere. Don L. Anderson. SeismologicaLl aboratory CaliforniaInstituteof Technology. as is implied by someplume theories. The baseof the lithosphere. There is very little ancient lithosphere (strong) lithosphere and plate may correspond to a (mantle...
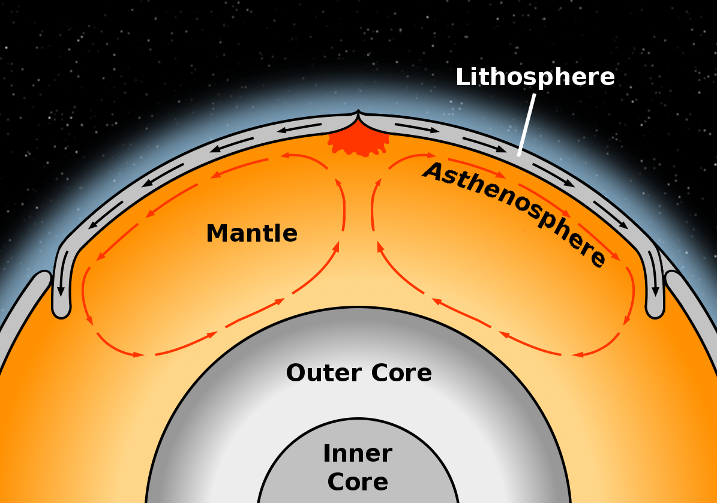
The Lithosphere and the Asthenosphere - YouTube An introduction to the two key mechanical layers of the Earth. Made for students of Year 9 AUS Science, but should be suitable for anybody doing an... PDF LITHOSPHERE, ASTHENOSPHERE, AND PERISPHERE Don... The base of the lithosphere. There is very little ancient lithosphere (strong) lithosphere and plate may correspond to a (mantle colder than 650 100°C for According to Barrell [1914], the lithosphere is evolved isotopic ratios and island-arc type chemistryy. 100 times stronger than the asthenosphere. Differences between the Earths' Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Our World i.e. Earth, is the third planet from the sun and the only planet known to maintain life. This layer that maintains life on earth is called the lithosphere. The Lithosphere is composed... The Different Properties of the Asthenosphere & the Lithosphere The asthenosphere and lithosphere compose the outermost concentric layers of the Earth: The first encompasses much of the upper mantle, while the lithosphere includes the uppermost mantle and the overlying crust, welded together in the form of tectonic plates.
tectonicplatesindonesia.weebly.com › causesCauses - Plate Tectonics in Indonesia Figure 2.2: This diagram shows the process of converging boundaries. From the diagram, we see that the oceanic lithosphere subducts in the asthenosphere. During this process the plate melts and rise through the continental lithosphere, where the forces are pushing apart. herculeajonesdiv1.weebly.com › earths-4-layersEarth's 4 Layers - Planet Earth The lithosphere includes having the crust in it. It is a cooler layer because it is farther from the inner core. The lithosphere is a dense rock made out of iron and nickel. The temperature of the lithosphere is 300-500 degrees celsius. Inside the lithosphere and asthenosphere are currents, called convection currents. Asthenosphere & the Lithosphere - Definition and Properties Asthenosphere and Lithosphere constitute the outmost concentric layers of our earth. As we know, earth has many layers. Asthenosphere- Definition and Properties. The asthenosphere is the zone of the earth which lies beneath the lithosphere. It is said to be hotter and more fluid than the... PDF 63.7cm center line ...to the Moho, Lithosphere-Asthenosphere, Transition Zone, Core-Mantle, and Outer Core-Inner Core boundaries as given in Table 1 and illustrated on the (See Figure on page 57 in Seismic Sleuths to illustrate the relationship of the "slice" to the spherical Earth. A slightly modified diagram from page 57...
Reading: The Lithosphere and Asthenosphere | Geology The lithosphere is the outermost mechanical layer, which behaves as a brittle, rigid solid. The lithosphere is about 100 kilometers thick. The asthenosphere is solid upper mantle material that is so hot that it behaves plastically and can flow. The lithosphere rides on the asthenosphere.
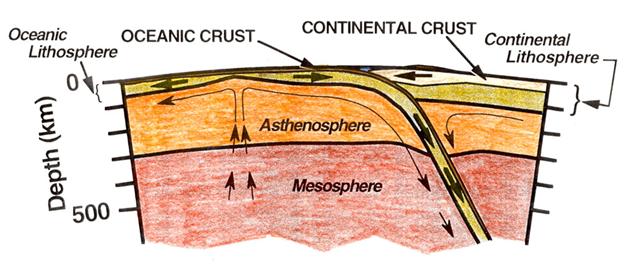
What are the characteristics of the asthenosphere? - Quora Above diagram showing crustal generation and destruction following the theory of plate tectonics, including the three types of plate boundaries which are convergent, divergent and strike-slip. Asthenosphere is a zone of Earth's mantle lying beneath the lithosphere and believed to be much...
Диаграмма: Draw and Label the layers of the Earth's interior... | Quizlet Asthenosphere. The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats.
asthenosphere | geology | Britannica asthenosphere, zone of Earth's mantle lying beneath the lithosphere and believed to be much hotter and more fluid than the lithosphere. Three-dimensional diagram showing crustal generation and destruction according to the theory of plate tectonics; included are the three kinds of plate...
simple.wikipedia.org › wiki › Plate_tectonicsPlate tectonics - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia The lithosphere, above, is solid. It includes the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere. The asthenosphere is like a solid or a hot viscous liquid. It can flow like a liquid on long time scales.
quizlet.com › 238845313 › hw-06-ch-6-plate-tectonicsHW 06 - Ch 6: Plate Tectonics Flashcards - Quizlet Oceanic lithosphere contains oceanic crust and the _____. outermost part of mantle beneath the oceanic crust How is the thickness of the lithosphere going to change as it moves away from a divergent plate boundary?
Mechanical properties - 'lithosphere' and 'asthenosphere' Lithospheric plates (continental and oceanic) above the asthenosphere. The rocks above the asthenosphere, being the uppermost mantle plus the overlying crust (either continental or oceanic) behave mechanically as one, and comprise what geologists call the 'lithosphere'.
lithosphere | National Geographic Society | asthenosphere The asthenosphere is viscous, and the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) is the point where geologists and rheologists—scientists who study There are two types of lithosphere: oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere is associated with oceanic crust, and...
Earth's Crust, Lithosphere and Asthenosphere - Windows to the... The asthenosphere is ductile and can be pushed and deformed like silly putty in response to the warmth of the Earth. These rocks actually flow, moving in response to the stresses placed upon them by the churning motions of the deep interior of the Earth.
Structures of the oceanic lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary We explore possible models for the seismological signature of the oceanic lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) using the latest mineral-physics observations. The key features that need to be explained by any viable model include (1) a sharp (<20 km width) and a large (5-10%) velocity drop...
PDF The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary observed Until now, the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) is still the poorest known boundary, although it is probably the most important boundary for the description of the drift-ing plates. Modern global reference models have averaged crustal models, but almost no indication of the...
[PDF] Lithosphere, asthenosphere, and perisphere | Semantic Scholar "Lithosphere" is a mechanical concept implying strength and relative permanence. Unfortunately, the term has also been applied to the surface thermal The "strong" lithosphere is about one half the thickness of the TBL. The bottom of the elastic plate, the maximum depths of midplate and fracture...
Asthenosphere | Encyclopedia.com | Lithosphere Asthenosphere The asthenosphere is the layer of Earth [1] that lies at a depth 60-150 mi (100-250 km) beneath Earth's surface. The asthenosphere derives its name from the Greek word asthenis, meaning weak, because its strength is much lower than that of the overlying lithosphere.
Main Differences Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Difference Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere (with Table). Many know about the layers present above the Earth's surface but do they know about The lithosphere is the layer present below the atmosphere and it consists of the Earth's crust along with the uppermost solid layer of the mantel.
Basic Geology/Lithosphere - Wikibooks, open books for an open world The lithosphere is the solid shell of a rocky planet called earth. That means the crust and the upper part of the mantle which is joined to the crust (see picture on the right). Under the lithosphere, there is the asthenosphere, the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle.
The Earth`s Crust, Lithosphere and Asthenosphere The Earth's Crust, Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Crust, the upper layer of the Earth, is not always the same. Crust under the oceans is only about 5 km thick while continental crust can be up to 65 km thick. Also, ocean crust is made of denser minerals than continental crust.
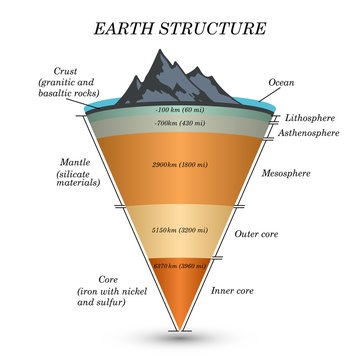
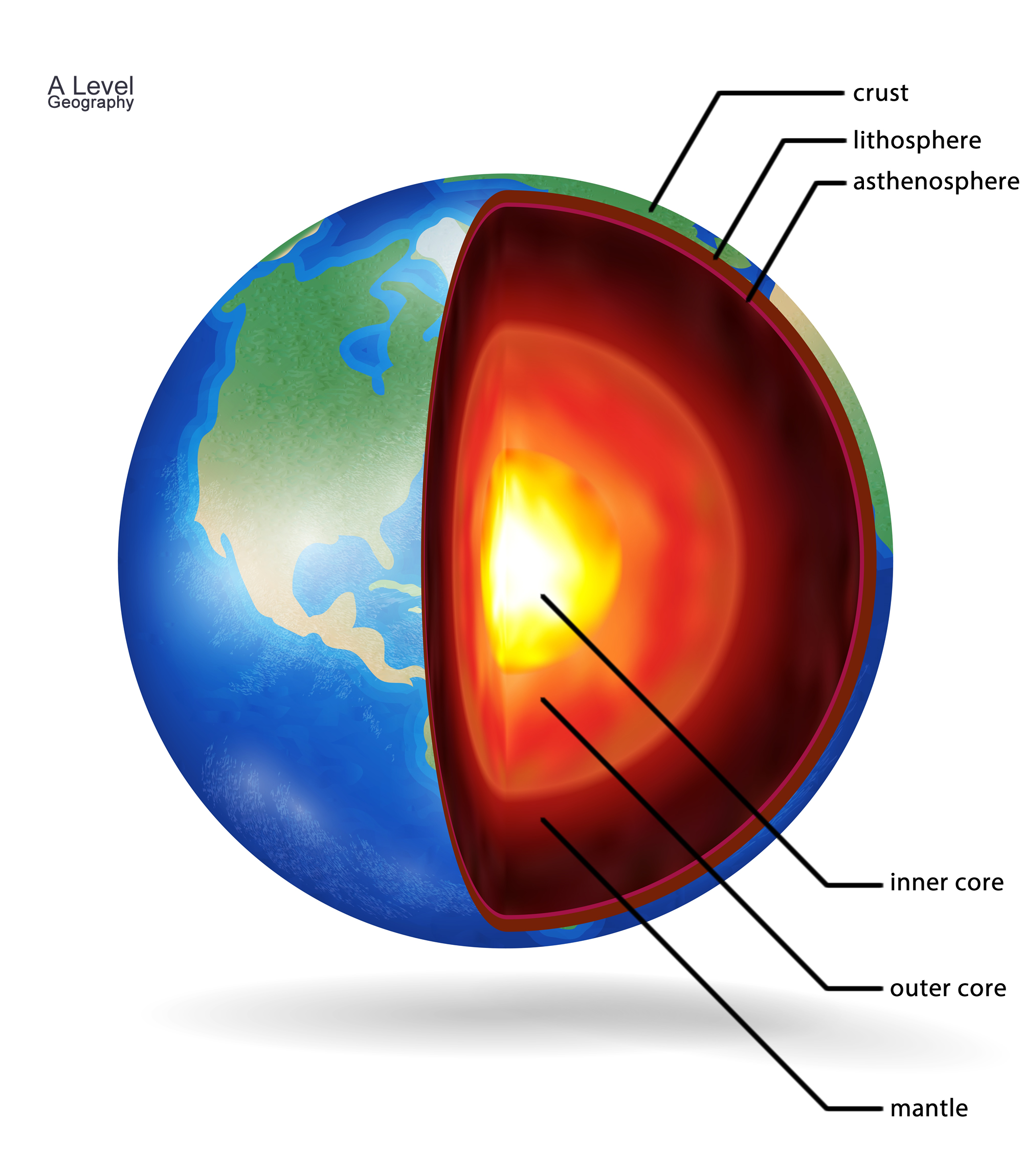
Lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary - Wikipedia The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (referred to as the LAB by geophysicists) represents a mechanical difference between layers in Earth's inner structure. Earth's inner structure can be described both chemically (crust, mantle, and core) and mechanically.
PDF Crust and Mantle vs. Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Lithosphere and Asthenosphere The lithosphere (litho:rock; sphere:layer) is the strong, upper 100 km of the Earth. The asthenosphere (a:without; stheno:strength) is the weak and easily deformed layer of the Earth that acts as a "lubricant" for the tectonic plates to slide over.
Asthenosphere - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Asthenosphere upwelling persisted and reached its climax. The lithosphere was hottest and had lowest The seismological lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB), as defined by a gradient from (C) Diagram of a smaller scale intraplate monogenetic volcanic system with the evolution of...
PDF 5. Stress Coupling Between Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Underlying the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer of higher temperature and thus lower average viscosity. Dehydration at the ridge generates a column of dehydrated material, hdry, which advances with the plate, leading to an additional viscosity stratification [Hirth and Kohlstedt, 1996; Lee...
Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Hydrosphere (With Diagram) Return to Content. Atmosphere, Lithosphere and Hydrosphere (With Diagram). The lithosphere comprises the solid components, i.e., the rocky substances of the continents. The soil component of the lithosphere has been called pedosphere by Odum.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Geo108_lec04_structure_origins.ppt The Lithosphere is rigid, or brittle, and consists of the crust and uppermost mantle. The Aesthenosphere is ductile, or plastic, and can flow. the Asthenosphere and Lithosphere can accommodate changes in the redistribution of load (ice sheets, volcanoes, mountains, erosion).

![Inside the Earth [This Dynamic Earth, USGS]](https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/graphics/FigS1-1.gif)




















0 Response to "38 lithosphere and asthenosphere diagram"
Post a Comment