38 flat mirror ray diagram
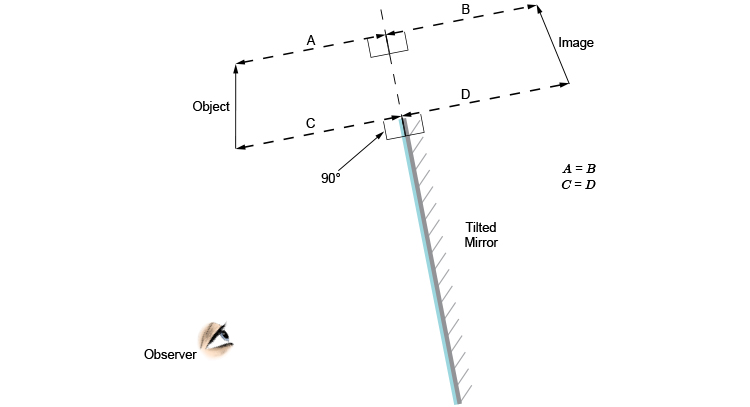
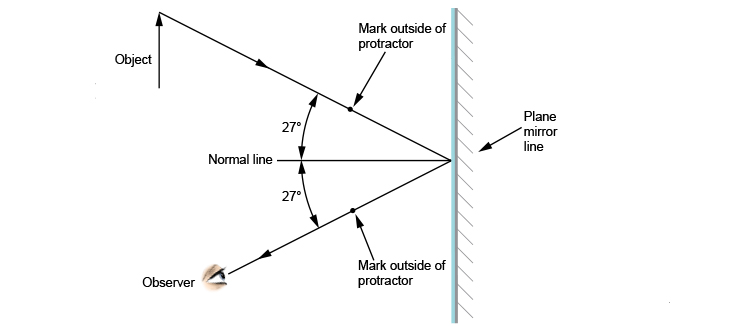
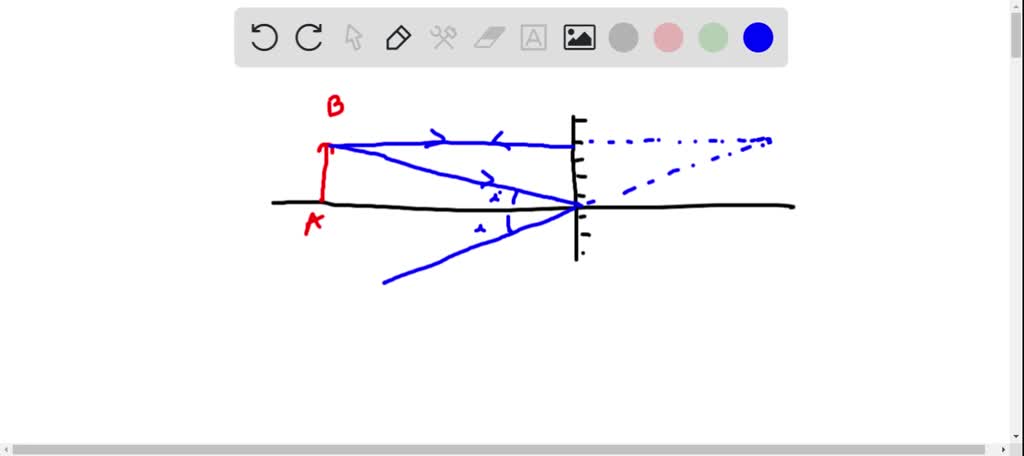
Flat Mirror Ray Diagram - 4Physics.com How to draw a light ray diagram for a flat mirror and locate the looking glass' virtual image. Locating Flat Mirror Virtual Images Top » Consulting » Tutorials » Flat Mirror Images: Flat Mirror Ray Diagram. Translatable page. Shop for neat science stuff. ... Using flat mirrors ray diagram rules - Mammoth Memory Using flat mirrors ray diagram rules How do we draw the ray diagram for a flat mirror, an object and an observer using flat mirror ray diagram rules? See below: The first stage is to draw an image on the other side of the mirror perpendicular (at 90°) to the mirror. Behind the mirror Equal distance The same size
Drawing Plane (Flat) Mirror Ray Diagrams - YouTube How to draw a ray diagram for a plane (flat) mirror.Please visit
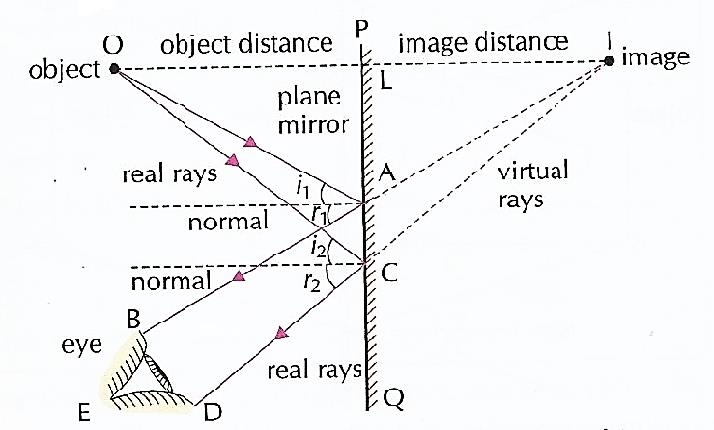
Flat mirror ray diagram
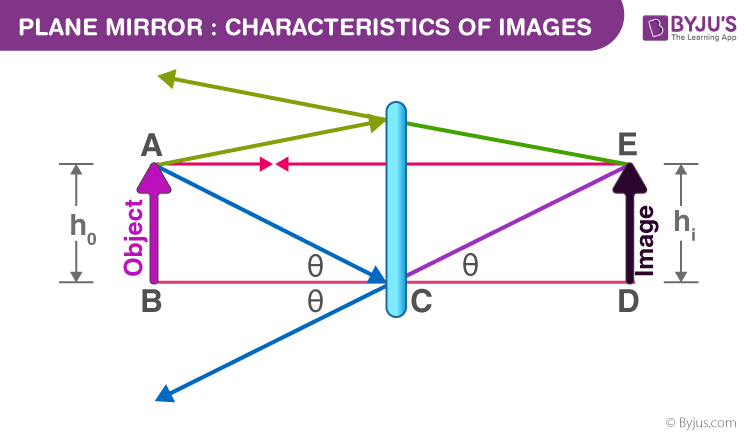
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror Flat Mirror Diagrams - Beyond the Classroom Flat Mirror Diagrams . Overall Information In this diagram you can see how an image is formed. 1. Light leaves the object and hits the mirror ... Drawing Ray Diagrams •For our ray diagrams you will need to determine the location of the top of the object and the location of the bottom of the object. Use the following steps to do that. Step 1 ... Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics ... Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
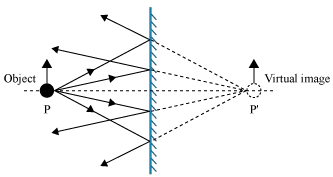
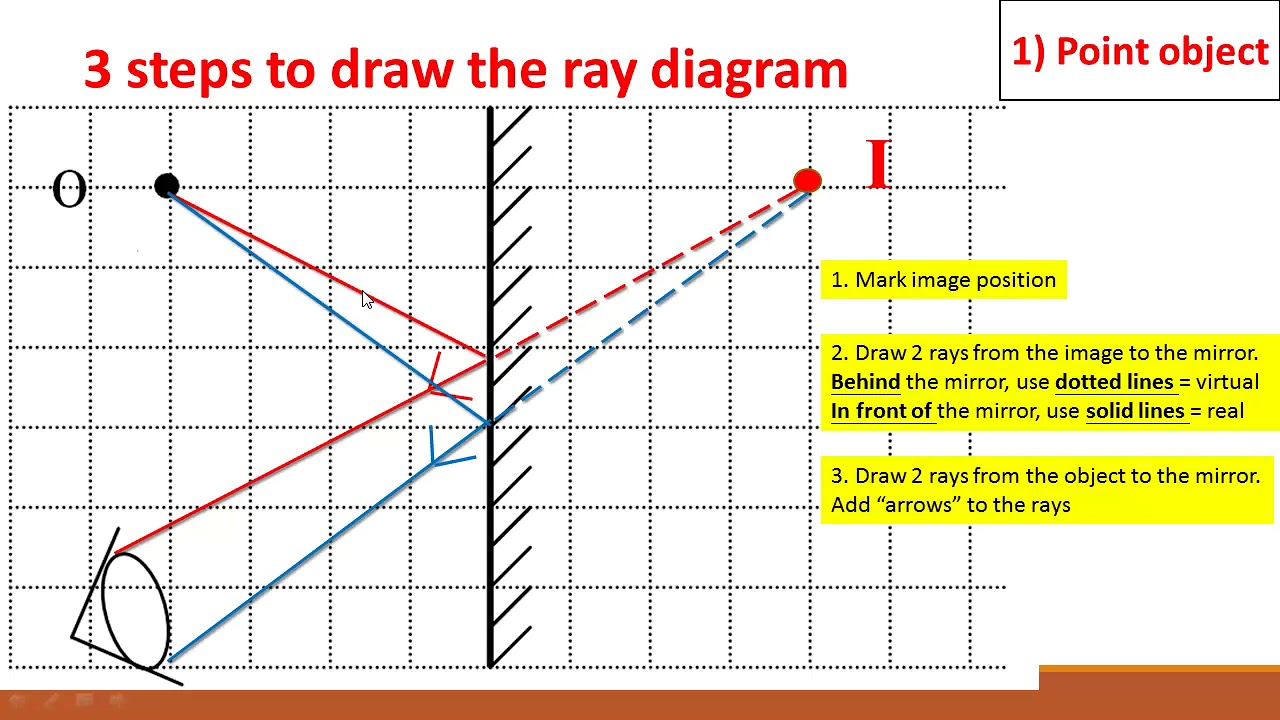
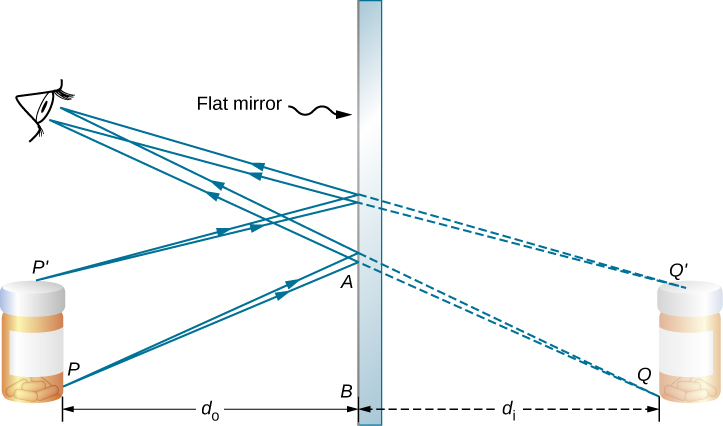
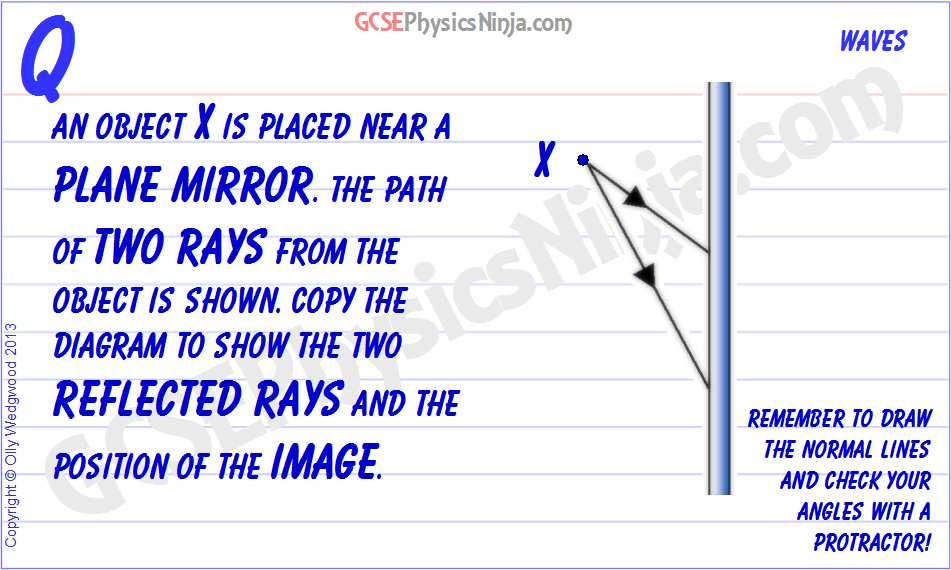
Flat mirror ray diagram. Solved Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat ... Solved Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat | Chegg.com. Science. Physics. Physics questions and answers. Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 178 cm tall can see his or her full image. (Suggestion: Drawing a ray diagram would be helpful) Question: Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat ... Ray diagrams and curved mirrors (practice) | Khan Academy Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Practice: Ray diagrams. Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation . Cartesian sign conventions mirrors . Practice: Sign convention. PDF Mirrors and Reflection - Boyertown Area School District Drawing plane mirror ray diagrams: 1. Draw the object and the mirror 2. Draw two incident rays from the object to the mirror 3. Construct the reflected rays -- solid line in front of the mirror, dashed line behind to represent the fact that no light actually reaches the image. 4. Locate the image where reflected rays intersect behind the mirror. Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram. Mirrors are defined as one side-polished surface that can reflect the light rays. Plane mirrors in physics are the ones that have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. In this tutorial, we review the most important topics in the plane (flat) mirrors in physics ...
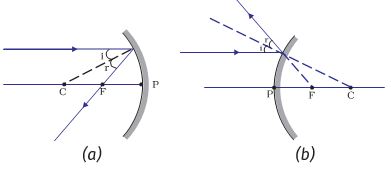
Physics Tutorial: The Anatomy of a Curved Mirror Thus far in this unit, our focus has been the reflection of light off flat surfaces and the formation of images by plane mirrors. In Lessons 3 and 4 we will turn our attention to the topic of curved mirrors, and specifically curved mirrors that have a spherical shape. Such mirrors are called spherical mirrors.The two types of spherical mirrors are shown in the diagram on the right. PDF Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams R R, from the ... Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p. Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors Uses of Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams can be particularly useful for determining and explaining why only a portion of the image of an object can be seen from a given location. The ray diagram at the right shows the lines of sight used by the eye in order to see a portion of the image in the mirror. Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors - Physics Classroom • Ray diagrams are based on the premise that to view an object in a mirror, one must sight along a line at the image of the object. When one does, light travels along that line to your eye. • Ray diagrams can be drawn for all types of mirrors. This video focuses on plane mirrors. Proceure for Drawing Ray Diagram Step 1 Locate the Image:
Flat mirror, tilted, ray diagram - Mammoth Memory The way to draw the ray diagram for this situation is to carry out the three stages as we have previously learnt as follows: The first stage is to draw an image behind the mirror by marking either end of the image as being equal-distance and perpendicular (at 90°) from the mirror. Behind the mirror Equal distance The same size Matrix methods for mirrors - University of Tennessee Mirror details. A flat mirror. Let us trace a ray across a singe, flat reflecting surface at the origin. Let the index of refraction of the surrounding material be n = 1. For a flat mirror R = infinite and . Let the ray leave position (x 1, z 1) = (1 cm, -4 cm) making an angle θ 1 = 0.1 radians with the z axis. Lecture 34 - University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 5' 10" in height can see his or her full image. (A ray diagram would be helpful). A. 2' 11" B. 3' 9" C. 5' 10" D. Depends on distance to mirror. Answer klm In what location will the image form? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Answer klm Which ray is correct? ray A ray B ray C ray D ... Concave and Convex Mirrors | Ray Diagram for Convex and ... The convex mirror is the curved mirror where the reflective surface bulges out towards the position of the light source. The convex mirrors tend to reflect light in the outwards direction, diverging light rays, and hence they are not used for focusing light. The image is erect, virtual, and smaller than the object, however gets larger as the ...
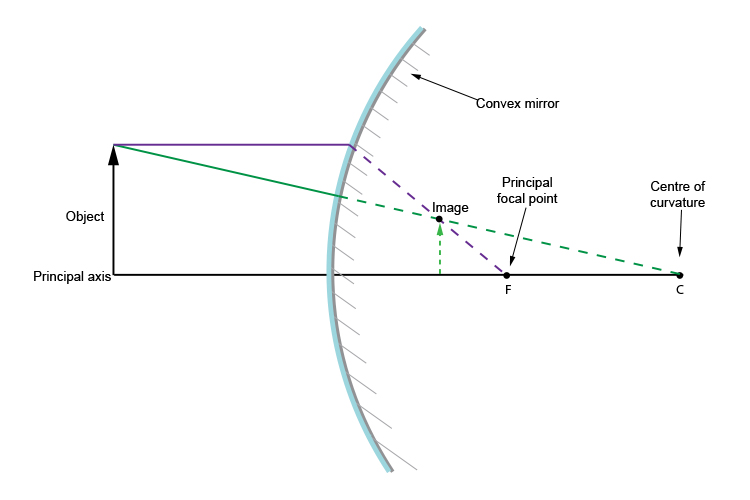
PDF Image formation - University of Wisconsin-Madison Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror ¥ The object is in front of a convex mirror ¥ The image is Ðvirtual Ðupright Ðsmaller than the object (reduced) Notes on Images ¥With a concave mirror, the image may be either real or virtual ¥With a convex mirror, the image is always virtual and upright ¥An image is real when the rays are passing through,
Mirrors | Boundless Physics - Lumen Learning Ray Diagrams. The way that we can predict how a reflection will look is by drawing a ray diagram. These diagrams can be used to find the position and size of the image and whether that image is real or virtual. These are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: Draw the plane mirror as a straight line on a principal axis.
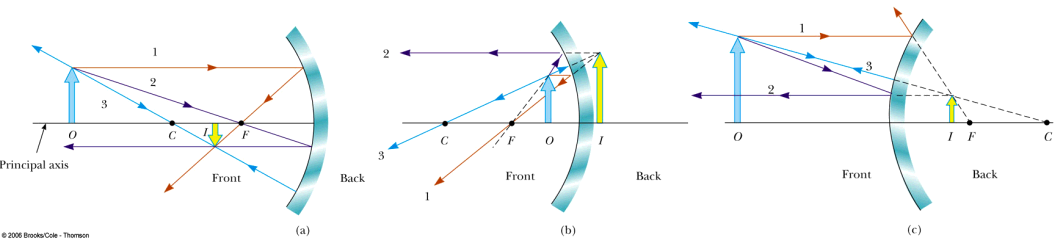
PDF Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors Concave Mirror Ray Diagrams For mirrors, the following set of rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Ray # 1 The flrst ray starts at the top of the object, parallel to the optical axis and is re°ected through the focus of the mirror just as is shown in Figure 3. In Figure 2, the dotted line with the \1" above it is an example of this kind of ray.
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
How Do Mirrors Work? - AZoOptics.com The ray diagram below uses three reflected rays to illustrate how the image can appear to be enlarged and upright. The image formed is a virtual image. Figure 6 .
Ray Diagrams for Mirrors - Georgia State University Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
The reflection and refraction of light - Boston University As the ray diagram shows, the image for a convex mirror is virtual, and upright compared to the object. A convex mirror is the kind of mirror used for security in stores, and is also the kind of mirror used on the passenger side of many cars ("Objects in mirror are closer than they appear."). A convex mirror will reflect a set of parallel rays in all directions; conversely, it will …
Simple Ray Diagram for Mirrors JavaScript HTML5 Applet ... The simple ray diagram maker shows one principal ray leaving a candle of height h and striking a flat mirror. This ray strikes the mirror a distance h below the flame. The angle between the reflected ray and the surface normal is the same as that between the incident ray and the normal in accord with the principles of geometric optics. Drag the ...
HOLDEN - Car PDF Manual, Wiring Diagram & Fault Codes DTC looking for 2007 fiat grande punto 1.2 8v left hand power door mirror wiring diagram #482. Uzair Hassan (Tuesday, 01 March 2022 19:51) Wiring diagram suzuki cultus 2021 model at gear #481. Dante Razeto (Sunday, 27 February 2022 11:22) Excellent tool to repair and find faults in our cars thank you very much #480. Name mugala suwilanji (Friday, 25 February 2022 15:15) Fault …
Drawing Ray Diagrams for a Plane Mirror - YouTube How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror. How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror.
Answered: An angle's terminal ray sweeps out 198… | bartleby 15.03.2022 · (a) Suppose your car has a flat passenger-side rearview mirror, 1.55 m from your eyes. How far from your eyes is the image of the car following you? (b) What angle does the image subtend in your field of view? (c) What If? Now suppose your car has a convex rearview mirror with a radius of curvature ofmagnitude 2.00 m (as suggested as shown). How far from …
Ray Diagrams | National Schools' Observatory Ray Diagrams. The example ray diagram above shows three imaginary "rays" of light being reflected off a mirror and then going through a lens. You can see where the focus is by looking where the "rays" cross each other. It is the lens that is making the light focus. If you want to use a mirror to focus light, then it needs to have a curved surface.
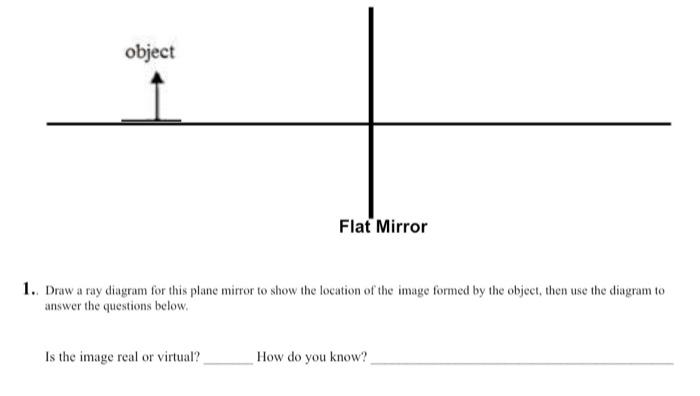
PDF Sub Objectives Teaching Strategies Active Student ... Students experiment with mirrors and make observations about what the "mirror image" of an object is. Students work with tables to come up with scientific definition of image, then class shares the agreed-upon definitions. 3. SWBAT identify the location and size of an image in a flat mirror by drawing ray diagrams (application) 15 min 3.
Lens and Mirror Lab - SimBucket Lens and Mirror Lab. Category. Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick! Recommended Lab:
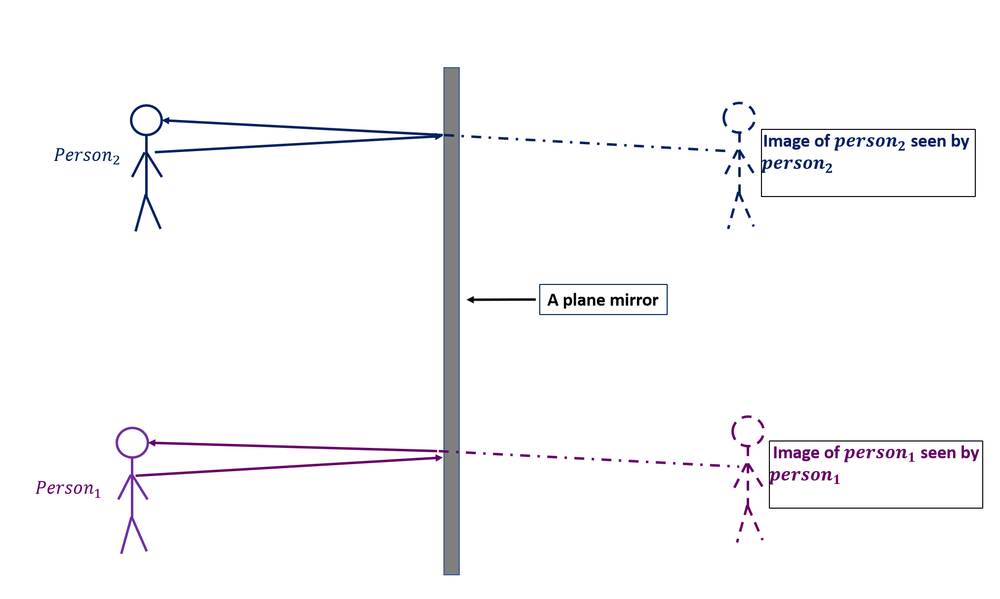
Images Formed by Plane Mirrors - University Physics Volume 3 Construct a ray diagram as in (Figure) to show how many images are formed. Consider a pair of flat mirrors that are positioned so that they form an angle of 60. An object is placed on the bisector between the mirrors. Construct a ray diagram as in (Figure) to show how many images are formed.
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics ... Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
Flat Mirror Diagrams - Beyond the Classroom Flat Mirror Diagrams . Overall Information In this diagram you can see how an image is formed. 1. Light leaves the object and hits the mirror ... Drawing Ray Diagrams •For our ray diagrams you will need to determine the location of the top of the object and the location of the bottom of the object. Use the following steps to do that. Step 1 ...
Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror














0 Response to "38 flat mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment