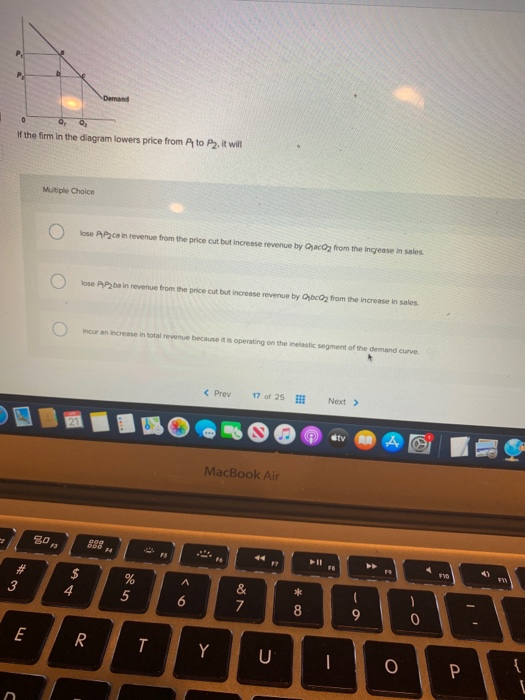
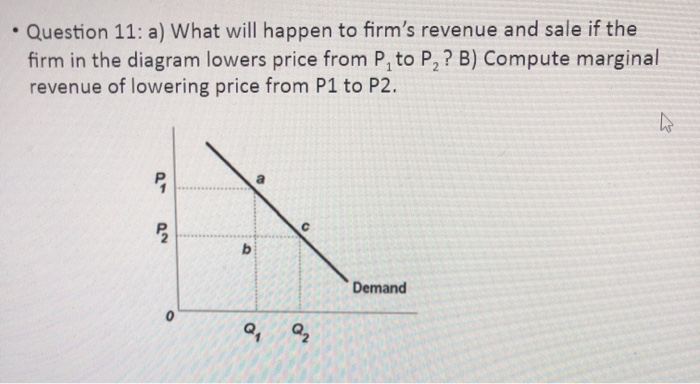
36 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
Econ Ch. 10-14 Flashcards | Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase ... MicroEconomics Final Flashcards - Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: ... If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P2, the monopolist would: produce output Q3 and realize a normal profit. Refer to the diagrams. With the industry structures represented by diagram:
Chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for for individual firms. Figure 1 pertains to: A purely competitive firm. in figure 2 the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are represented by: Lines B and C respectively. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will.

If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
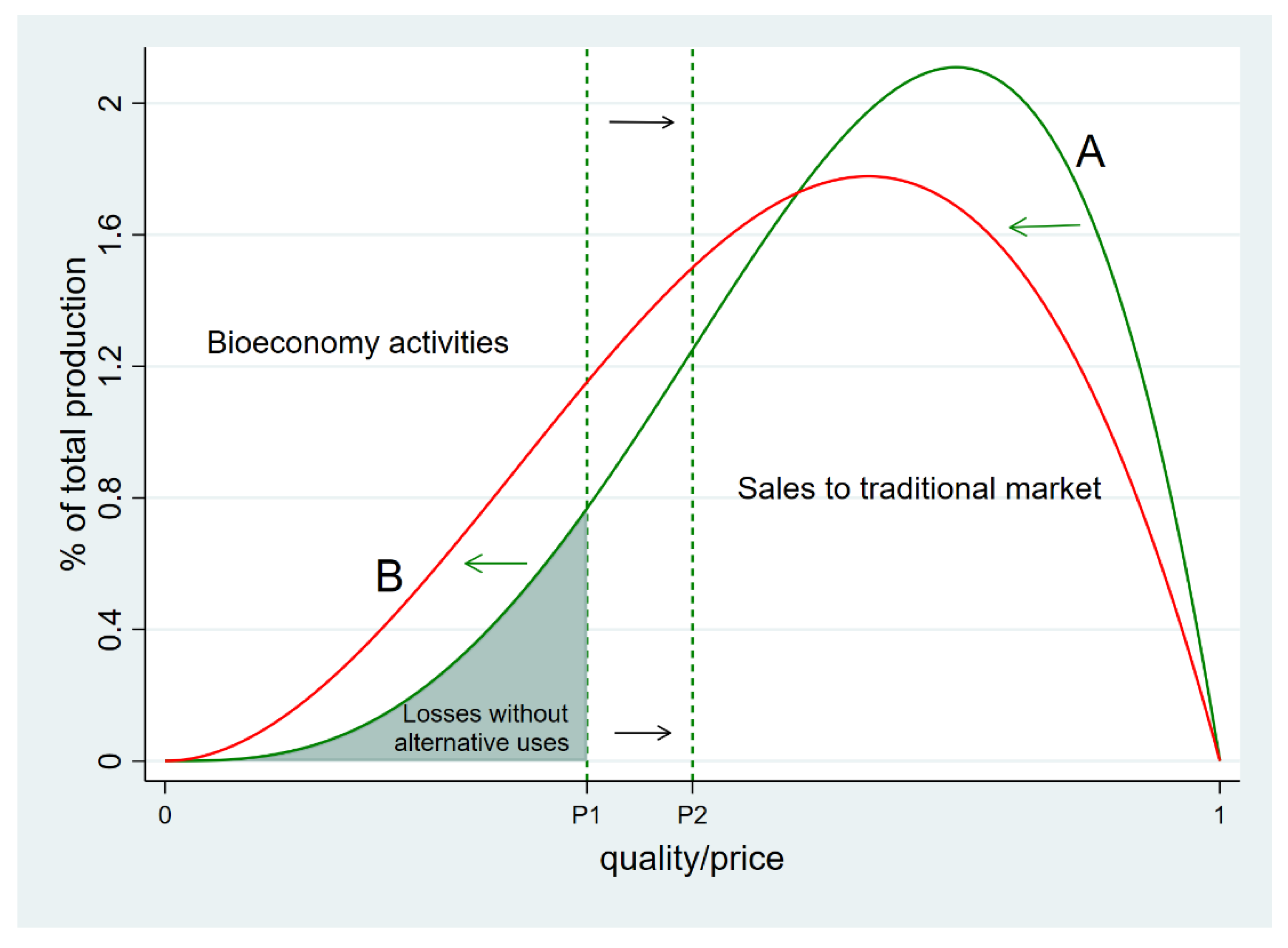
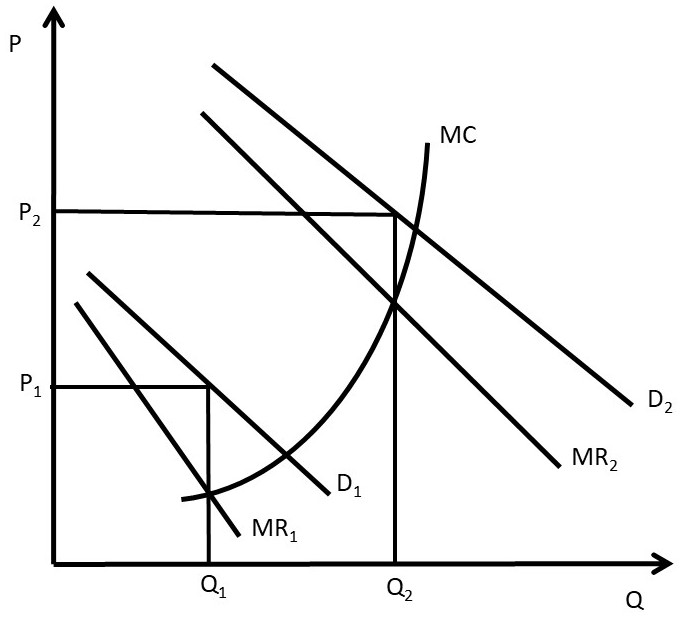
(PDF) Pump-Handbook.pdf | Prabir Datta - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet 17. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. Price Discrimination - A-level Economics Notes In this case to maximise profits, the firm produces quantity q2 and price p2. This price is below the original price p1 when there is no price discrimination. So the elastic group is better off under price discrimination – they face a lower price and higher consumer surplus. The right diagram shows the group with the more inelastic price ...
If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will. Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 41. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. Solved > 13.2 How a Monopolistically Competitive Firm ... Figure 13-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. 8) Refer to Figure 13-4. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged? A) P0. B) P1. C) P2. D) P3. 9) ... Ch 6 Elasticity - Subjecto.com March 5, 2020 - Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: D. that demand is ... (PDF) N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Economic | marta ... Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
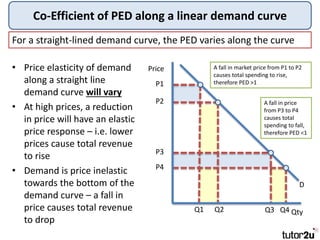
Ch8-11 Flashcards | Quizlet B. the firm does not have sufficient time to change the size of its plant. ... If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: X04 Cost Volume Profit Relationships - StuDocu A. P1,600,000 C. P1,350, B. P1,150,000 D. P1,630,000 Bobadilla; 76. Tactless Manufacturing Company produces two products for which the following data have been tabulated. Fixed manufacturing cost is applied at a rate of P1 per machine hour. Per Unit XY-7 BD- Selling price P4 P3. Variable manufacturing cost P2 P1. Fixed manufacturing cost P0 P0. [Solved] (a) An oligopolistic firm, estimates the ... (a) An oligopolistic firm, estimates the following demand functions as: P1 = 9 - 0.3Q for price increase. P2 = 10 - 0.4Q for price decrease. The firm's total cost function is: TC = 25 =+1.5q + 0.05Q2. i) Define price rigidity. ii) Prove the price is rigid. iii) Define third degree price ... Refer to the above diagram The decline in price from P1 to ... 7. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A. 8. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: A. that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes.
Solved Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from ... demand if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will lose p1 p2 ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by q1bcq 2 from the increase in sales. lose p1 p2 ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by q 1 acq2 from the increase in sales. o incur a decline in total revenue because it is operating on the … Cross Elasticity of Demand Questions and Answers - Study.com Assume that utility over two goods is given by U(x1,x2) = 0.3lnx1 +0.7lnx2. The price of good x1 is equal to p1 and the price of good x2 is p2. The total income of the individual is given by I. a W... OneClass: The diagram below shows the market demand curve and the ... Î =P1Q1+P2 (Q2-Q1)+P3 (Q3-Q2)-mQ3 Where P1 is the high price charged on the first Q1 units (first block), p2 is a lower price charged on the next Q2-Q1 units, p3 is the lowest price charged on the Q3-Q2 remaining units, Q3 is the total number of units actually purchased, and m=$30 is the firmâ s ... ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet In the accompanying diagram, if price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: Increase by C − A. ... When a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. ... Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC3, then the firm is: ...
Solved Suppose the typical catfish farmer was incurring an ... P1 P2 P3 (b) What forces would raise the price? Question: Suppose the typical catfish farmer was incurring an economic loss. (a) What price level illustrates these losses on the firm in the above diagram? P1 P2 P3 (b) What forces would raise the price?
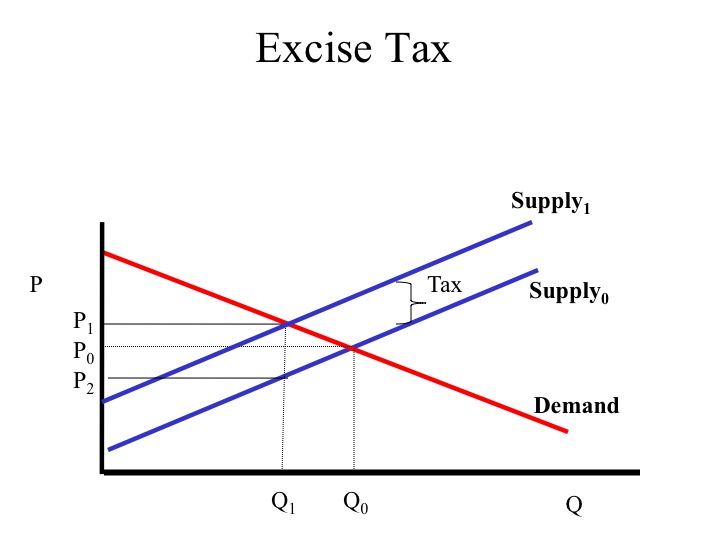
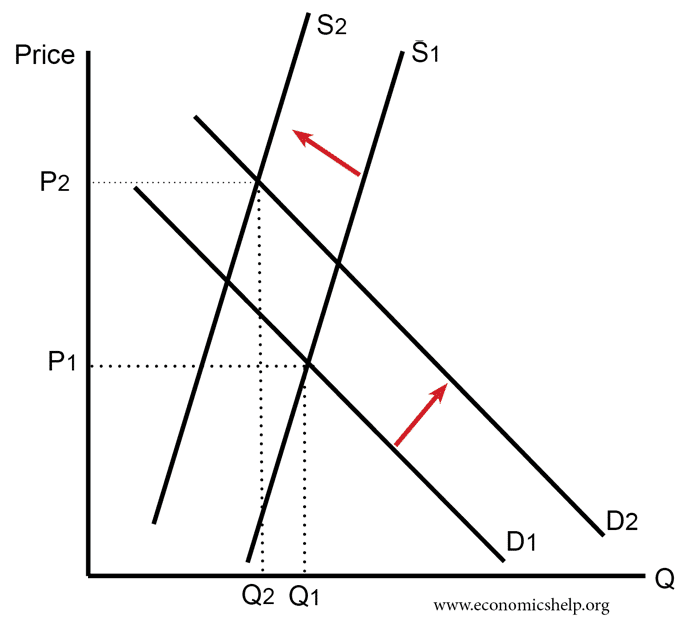
Equilibrium levels of real national output - Edexcel Economics ... August 12, 2018 - A decrease in costs of production causes SRAS to increase (SRAS1 to SRAS2) resulting in an increase in real GDP (Y1 to Y2) and a decrease in the price level (P1 to P2). This is due to the fall in the price of key inputs allowing firms to sell their goods/services at a lower price.
182 Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms Figure ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: ANSWER: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. 195. Refer to the diagram. The quantitative difference between areas Q1bcQ2 and P1P2ba in the diagram measures: ANSWER: marginal revenue. 196.
16 consumers benefit from monopolistic ... - Course Hero Figure 13-4 Figure 13-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. 17) Refer to Figure 13-4. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged? A) P0 B) P1 C) P2 D) P3
PERFECT COMPETITION DIAGRAM - Course Hero LONG RUN (LR) PERFECT COMPETITION Price Quantity 0 S 1 P1 D 1 MARKET SUPPLY/DEMAND (A) Price Quantity 0 AC P1 D 1 =MR 1 =AR 1 INDVIDUAL FIRM’S SUPPLY/DEMAND (B) MC Q1 The entry of new firms shifts the market supply curve in diagram A from S1 to S2, equilibrium price falls from P1-P2.
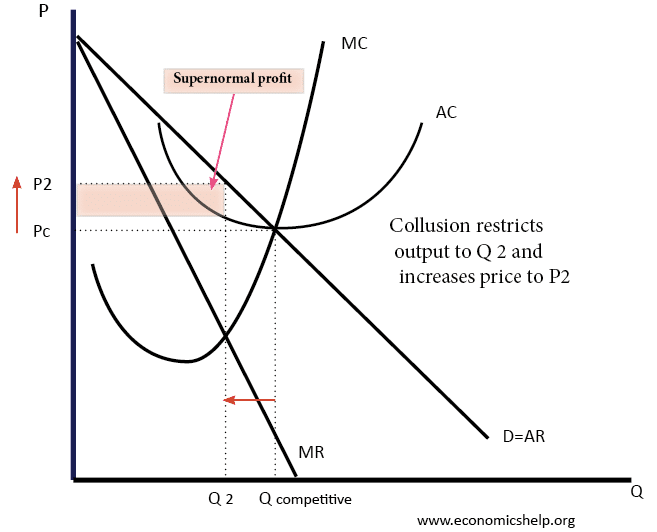
Chapter 12- Monopolies Flashcards | Quizlet a.) selling the product at the highest possible price at which a positive quantity will be demanded. b.) producing Q1 units and charging a price of P1. c.) producing Q3 units and charging a price of P3. d.) producing Q2 units and charging a price of P2.
15 The more elastic the demand facing a firm A the higher ... 19) Refer to Figure 2. Suppose that the government decides to limit monopoly power with price regulation. If the government sets the price at the competitive level, it will set the price at _____. A) P1 B) P2 C) P3 D) P4
Econ Final Flashcards | Quizlet P2. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: will be less than $35. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.
PDF Diagram A. Shut Down Point of a Firm in Perfect Price MC ... This would be any price lower than p1. If the firm does not cover its variable costs of production it will close down in the short run- see p 23 on diagram A 2. Shut downs occur most frequently in primary producing industries. Note that it may only be a temporary shut down. 3. It can afford not to cover its fixed costs in the short run only ...
Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A) lose P1P 2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. ... a higher price and produce a smaller output than a competitive firm. D) a lower price and produce a smaller output than a competitive firm . C . 125. An important ...
CHAP 12 Flashcards - Quizlet marginal revenue is positive when total revenue is increasing, but marginal revenue becomes negative when total revenue is decreasing. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist
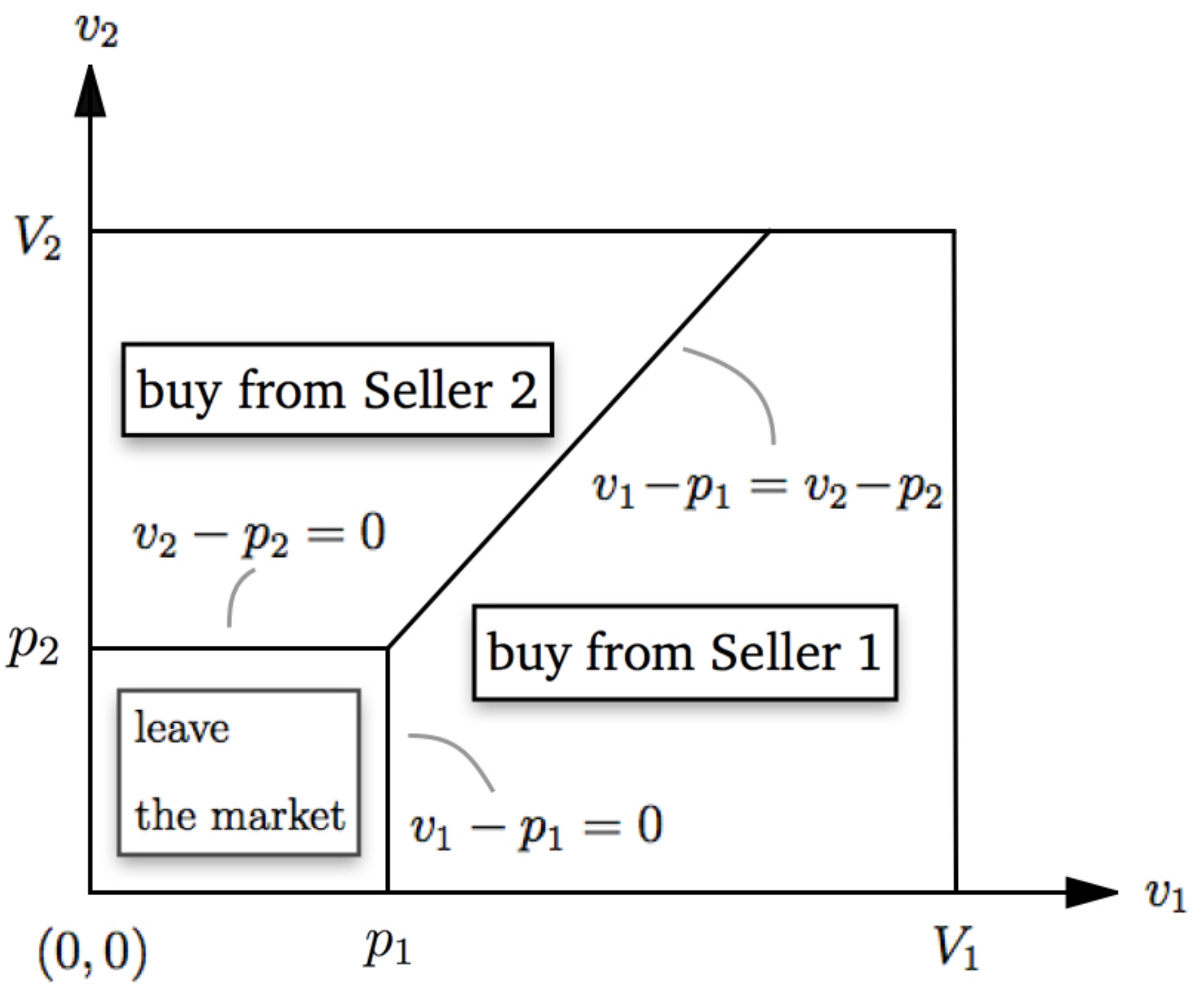
General Equilibrium Theory - Washington State University Firms demand capital and ... Edgeworth Box Diagram. 6/4/2014 16 Edgeworth Box Diagram 31 32 Edgeworth Box Diagram. 6/4/2014 17 ... Person A’s consumption choices are measured from the lower left hand corner, Person B’s consumption choices are measured from the upper right hand ...
10 Flashcards | Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will incur an increase in total revenue because it is operating on the inelastic segment of the demand curve. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.Correct
ECON Module 9A Flashcards | Chegg.com Refer to the above diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, ... The quantitative difference between areas A and C for reducing the price from P1 to P2 measures: marginal revenue. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: an imperfectly competitive market. Refer to the above diagram. Demand is relatively elastic:
Diagram A. Shut Down Point of a Firm in Perfect Price MC ... Shut Down Point for a firm in Perfect Competition 1. Shut-down occurs where P is lower than where mr = mc = avc (see X in diagram). This would be any price lower than p1. If the firm does not cover its variable costs of production it will close down in the short run- see p 23 on diagram A 2.
Price Discrimination - A-level Economics Notes In this case to maximise profits, the firm produces quantity q2 and price p2. This price is below the original price p1 when there is no price discrimination. So the elastic group is better off under price discrimination – they face a lower price and higher consumer surplus. The right diagram shows the group with the more inelastic price ...
Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet 17. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales.
(PDF) Pump-Handbook.pdf | Prabir Datta - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.




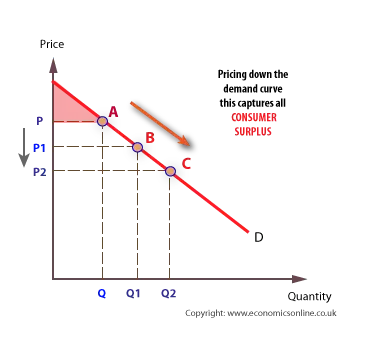


/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)
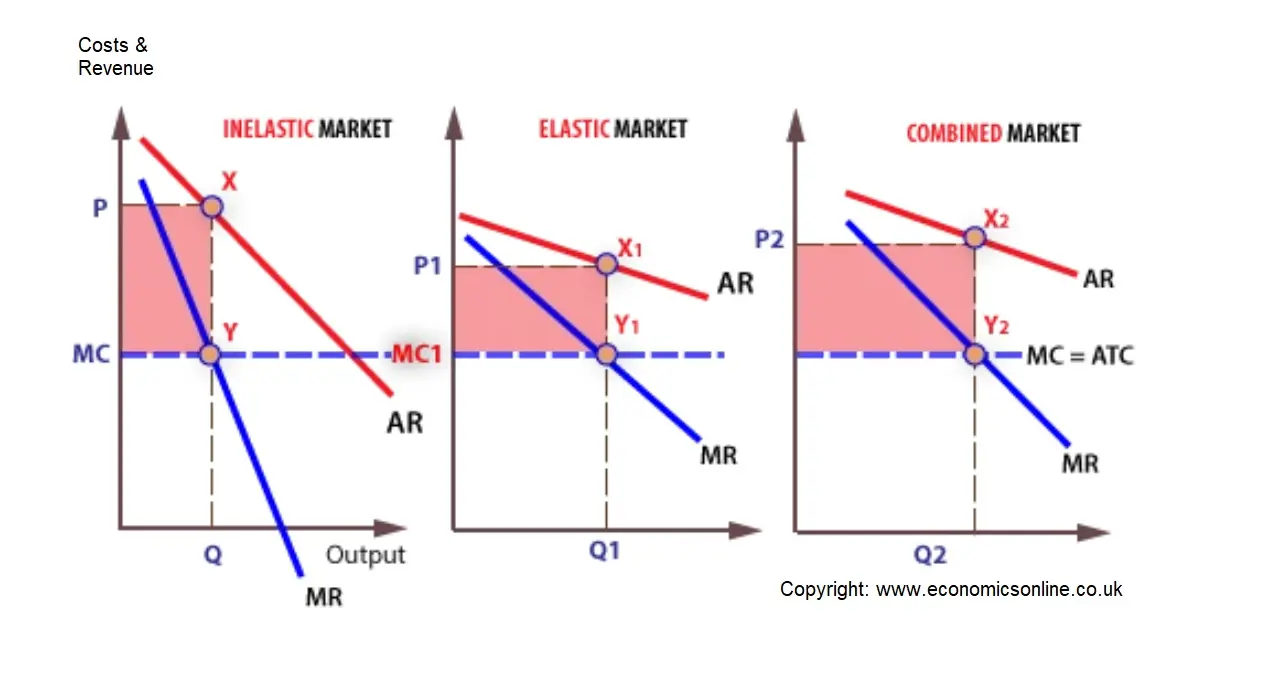





0 Response to "36 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will"
Post a Comment