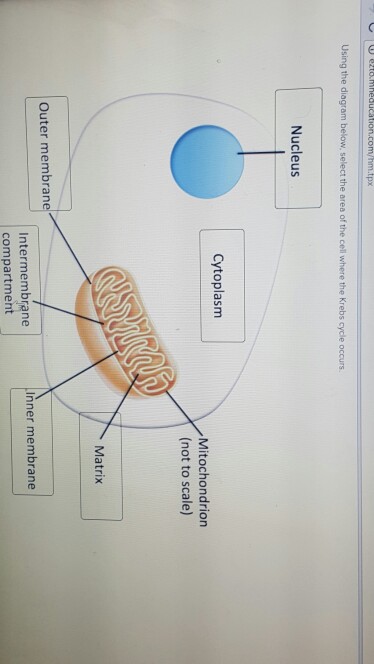
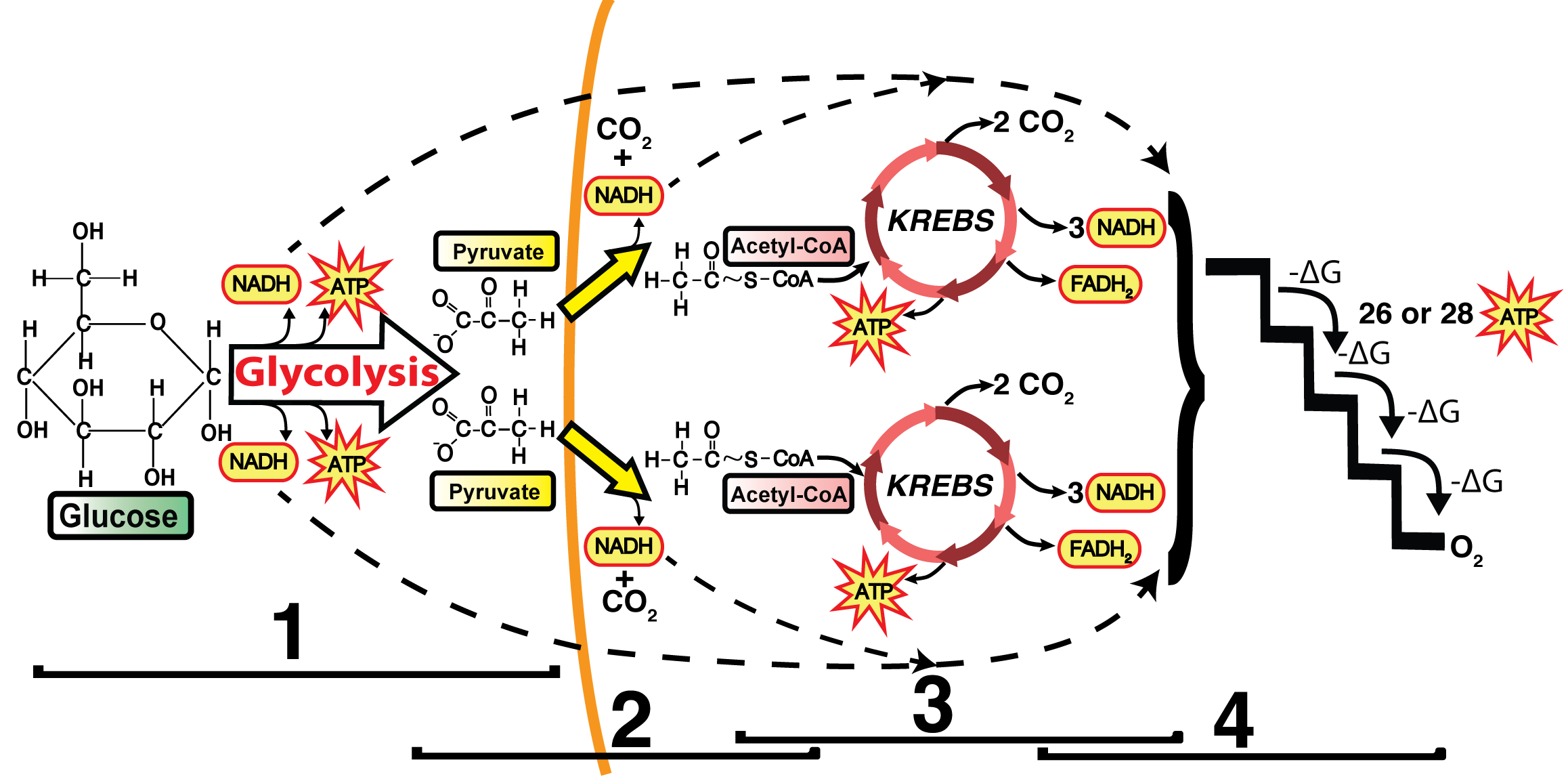
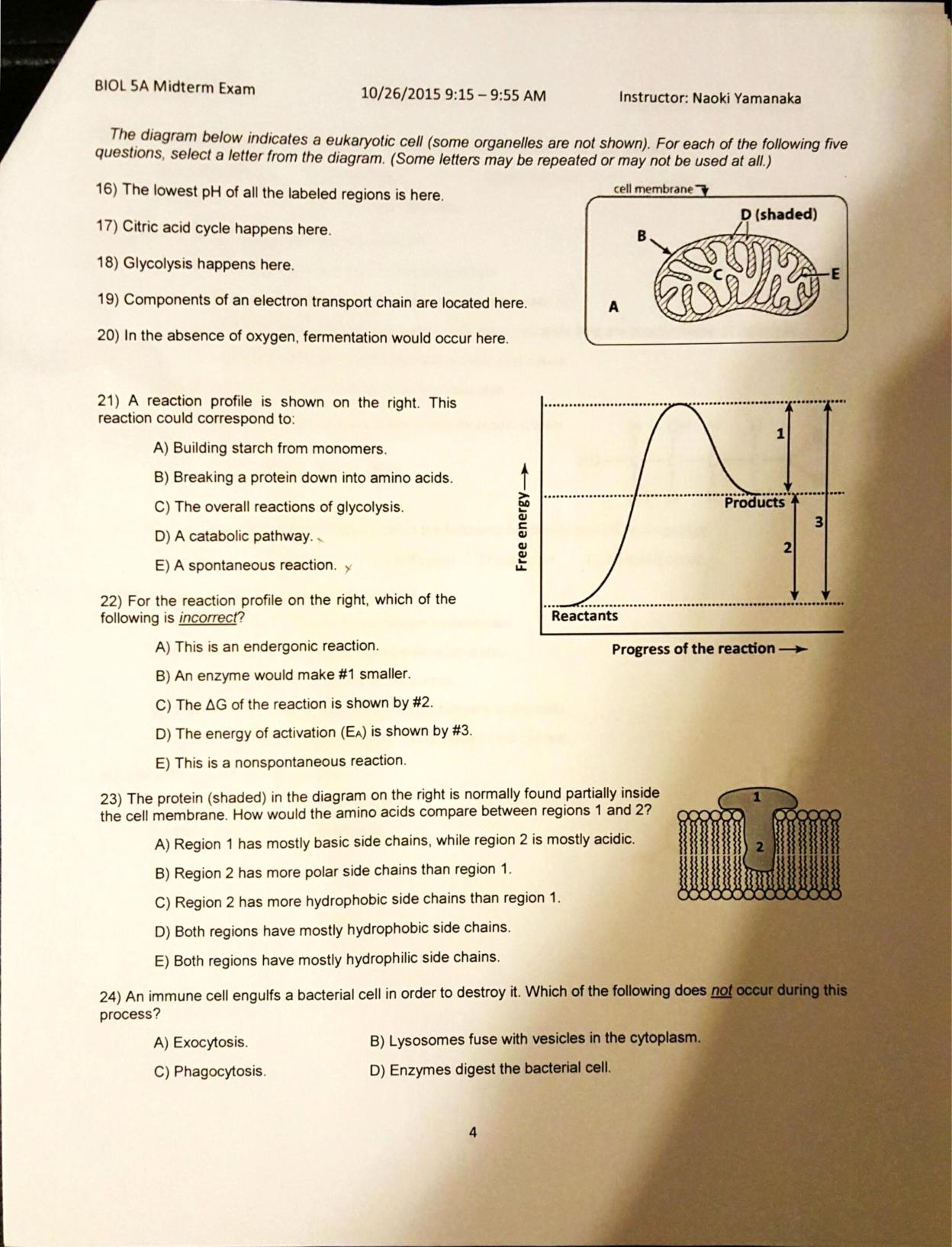
39 using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs.
Energy is used, converting ATP to ADP. Two, three-carbon molecules called PGAL are produced per glucose molecule. Electron carriers called NADH are produced that will be transferred into energy later in cellular respiration. A net of two ATP molecules per glucose are produced by substrate-level phosphorylation. Krebs Cycle ETC Arsenie Cyanide 0.25 mm 0.11 mM 0.17 mm + 0.50 mm 0.20 MM 0.07 mM + Glycolysis Healthy Muscle Ja … red's Muscle Cells Cells 2-Deoxyglucose Pyruvate 0.12 MM 0.12 MM 0.02 MM + NADH 0,30 mm 0,50 mM 0.08 MM + Intermembrane H 0.32 mm 0.05 mm 0.09 MM + Use the data to choose the poison you think was given to Jared.
Citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) 1. It is a linear pathway. 1. It is a cyclic pathway. 2. It occurs in the cell cytoplasm. 2. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. 3. It occurs in both aerobic as well as in anaerobic respiration. 3. It occurs in aerobic respiration only. 4.
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs.
If the cell has access to oxygen (aka is in an aerobic environment), then the 2 pyruvic acids will become Acetyl CoA and go inside the mitochondria to perform the Krebs cycle for more ATP Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (19 ratings) Kreb cycle is the second step of aerob …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the Krebs cycle occurs. Previous question Next question. What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle? The purpose of the Kreb's cycle is the complete oxidation of glucose, resulting in energy-rich molecules that later produce ATPs in the electron transport chain. Where does the Krebs cycle take place? Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria of eukaryote and in the cytoplasm of the prokaryotes.
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs.. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase ( Figure 6.3 ). During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. The diagram below summarises the pathways for the breakdown of fatty acid X and glucose. The number of molecules produced in each step is not shown. acetyl CoA Krebs Cycle electron transport chain lactic acid pyruvic acid fatty acid X glucose ADP ADP ADP ATP ATP ATP H2O O2 The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts (where would it occur in a prokaryote?). Carbon dioxide is captured by the chemical ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). RuBP is a 5-C chemical. Six molecules of carbon dioxide enter the Calvin Cycle, eventually producing one molecule of glucose. In the diagram below, click on the area of the cell where glycolysis occurs. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Glycolysis is process of oxida …. View the full answer.
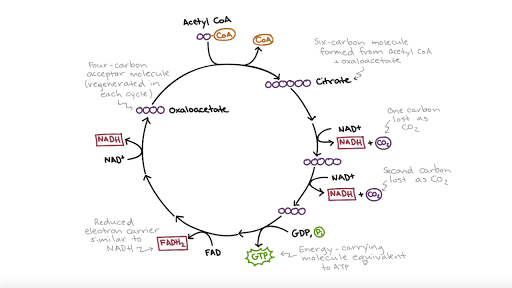
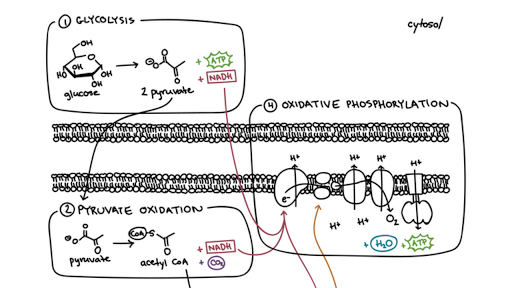
The acetyl group enters a cyclic sequence of reactions known collectively as the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid [TCA] cycle). The cyclical design of this complex series of reactions, which bring about the oxidation of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide and water, was first proposed by Hans Krebs in 1937. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate continues on to the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), where additional energy is extracted and passed on. Figure 24.2.2 - Glycolysis Overview: During the energy-consuming phase of glycolysis, two ATPs are consumed, transferring two phosphates to the glucose molecule. Drag and drop each item onto the proper area of the diagram. If an item describes more than one catenry, be sure to place it in the overlapping space. Viruses are tiny infectious pathogens that cause many different diseases, such as polio, and the flu. The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
Also known as the citric acid cycle, the Krebs cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells produce energy in aerobic respiration. It uses oxygen and gives out water and carbon dioxide as products. Here, ADP is converted into ATP. Cell Biology Bio 1310 debelica chapter 5&6 STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity pruvyate Click card to see definition 👆 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to Click again to see term 👆 1/22 THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... bio exam 5 & 6 106 terms lindsey_pearson4 BIO1320 Ch3 Pt2 24 terms ImBigDumbDumb BIO1320 Ch4 Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle produce the molecules that shuttle electrons to the electron transport chain. When carbon atoms are removed from organic molecules during the transition step and the Krebs cycle, the carbon atoms are released as carbon dioxide. Cell Communication and Cell Cycle (Cell Signaling) Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can activate an action potential in a postsynaptic neuron (Figures 1 and 2). A researcher is investigating the effect of a particular neurotoxin that causes the amount of acetylcholine released from presynaptic neurons to increase.
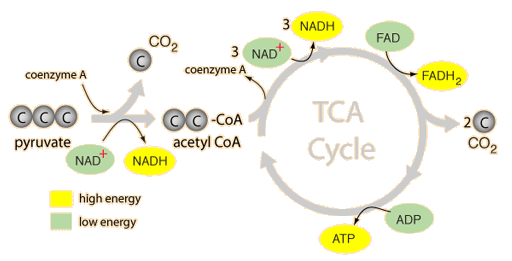
In the matrix, pyruvate is modified in a series of steps: More detailed diagram of the mechanism of pyruvate oxidation. A carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The two-carbon molecule from the first step is oxidized, and NAD+ accepts the electrons to form NADH.
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that cycles twice, one for each molecule of pyruvate. One of the first few chemicals produced in the cycle is citric acid, which explains why the Krebs Cycle is also called the citric acid cycle. The Krebs Cycle completely dismantles the remaining 2 pyruvates and transfers energy from them into ATP energy, energy carrier molecules, and CO 2 (the carbon and oxygen atoms originally in glucose). The Krebs Cycle produces: 2 ATP molecules; 8 NADH; 2 FADH 2
step by step sequences where the product of one reaction becomes the reactant of the next reaction catalyzed by an enzyme cellular respiration and photosynthesis example of a metabolic pathway Energy the capacity to do work Kinetic energy the energy of motion Potential Energy stored energy the transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy
5 Mar 2021 — Each small circle in the diagram represents one carbon atom. For example, citric acid is a six carbon molecule, and OAA (oxaloacetate) is a four ...
answer. answered. The diagram below shows the energy conversions of the Krebs cycle, which is part of cellular respiration. The U-shaped arrows that show changes for NAD, FAD, and ADP molecules represent energy conversions. From each glucose. molecule, two acetyl-CoA molecules are made for the Krebs cycle. NADH.
6. Below is an outline diagram of the Krebs cycle. A two carbon acetyl group enters the cycle by combining with a molecule of oxaloacetate. A molecule of citrate is formed which is decarboxylated and dehydrogenated to regenerate the oxaloacetate. citrate (6C) CoA intermediate (4C) intermediate (5C) P Q S R T V oxaloacetate (4C) fatty acids acetyl (2C) CoA NAD
Why is cellular respiration important? It generates ATP, which cells can use to do work. 13. Oxygen is a product of the electron transport chain. FALSE 14. The electrons that are transferred through the electron transport system initially belonged to NADH and FADH2 15. In the diagram below, click on the area of the cell where glycolysis occurs ...
Multiple Choice - Choose the best and most complete answer. 1. Which type of energy transformation occurs in photosynthesis? A. heat to electrical. B. light to chemical. C. mechanical to electrical. D. chemical to mechanical. 2. The potential energy of organic molecules is most readily available to cells in the form of. A. ribonucleic acid. B. ATP. C. water.
Below is an image of the light reactions in the thylakoid membrane. Drag the descriptions of events that occur during the light reactions to their correct location in the diagram. during the light reactions 1. Light energy is captured at a peak wavelength of 680nm 2. Water donates electrons to replace electrons ejected from the reaction center 3.
Total energy production per glucose of ONLY the Krebs cycle (before electron transport chain) Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 8 NADH, 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Describe the Pre-Krebs Cycle. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆.
called Krebs cycle. 2. In the absence of o xygen, pyruvic acid breaks into ethyl alcohol or ethanol (2-carbon molecule), CO 2 and releases energy. It is called anaerobic respiration. 3. In lack (deficiency) of oxygen in muscles, pyruvic acid breaks into lactic acid (3-carbon molecule) and energy, is released. Respiration in plants occurs ...
The Kreb's cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule. The protein complexes are arranged on the inner mitochondrial matrix so that the electrons pass from one reacting molecule to the other. This is known as the electron transport chain. ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate; Also Read: Difference between Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle
1 Jun 2020 — This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, and it occurs in ... The Krebs cycle uses a 2-carbon molecule (acetyl-CoA) derived from ...
Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where pyruvate is transported after glycolysis occurs. Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondrion (not to scale) Matrix Outer membrane Intermembrane compartment Inner membrane. Question: Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where pyruvate is transported after glycolysis occurs.
Krebs Cycle Steps. It is an eight-step process. The Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria under aerobic conditions. Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate (4C) to form citrate (6C), coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase. Step 2: Citrate is turned to its isomer, isocitrate
The Krebs Cycle (Source: Wikimedia). Also called as the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle, or simply the Citric Acid cycle, the Krebs cycle (identified by Hans Adolf Krebs) is an 8-step process that involves 18 different enzymes. The Krebs cycle, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion, includes a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that result in the oxidation of the acetyl group to ...
Before entering the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA. Three "turns" of the Krebs cycle will yield 3 ATP, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH 2 . In glycolysis, glucose is converted to Pyruvate. In muscle cells deprived of oxygen, the end product of glycolysis is converted to lactic acid.
This acetyl-CoA reacts in the first step of the eight step sequence of reactions that comprise the Krebs cycle, all of which occur inside mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. While the Krebs cycle does produce carbon dioxide, this cycle does not produce significant chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) directly, and this reaction sequence does not require any oxygen.
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle? The purpose of the Kreb's cycle is the complete oxidation of glucose, resulting in energy-rich molecules that later produce ATPs in the electron transport chain. Where does the Krebs cycle take place? Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria of eukaryote and in the cytoplasm of the prokaryotes.
Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (19 ratings) Kreb cycle is the second step of aerob …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the Krebs cycle occurs. Previous question Next question.
If the cell has access to oxygen (aka is in an aerobic environment), then the 2 pyruvic acids will become Acetyl CoA and go inside the mitochondria to perform the Krebs cycle for more ATP






















0 Response to "39 using the diagram below, select the area of the cell where the krebs cycle occurs."
Post a Comment