37 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Plant biologists strenuously argue whether the cell wall is an integral part of the cell and, hence whether the term ‘extra’ cellular matrix 1 is appropriate. Considering that the cytoskeleton-ECM is a continuum vital to cell development 2, the term extracellular matrix is perhaps an unfortunate one for animal cells, too.In this article, we refer to the plant cell wall or outer cell matrix ... I cant find one, thank you!
The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below: It provides shape and support to the cell. It helps in the formation of vacuoles. It holds different cell organelles in place. It assists in cell signalling. It supports intracellular movements like the migration of cell organelles, transportation of vesicles in and out of the cell, etc.
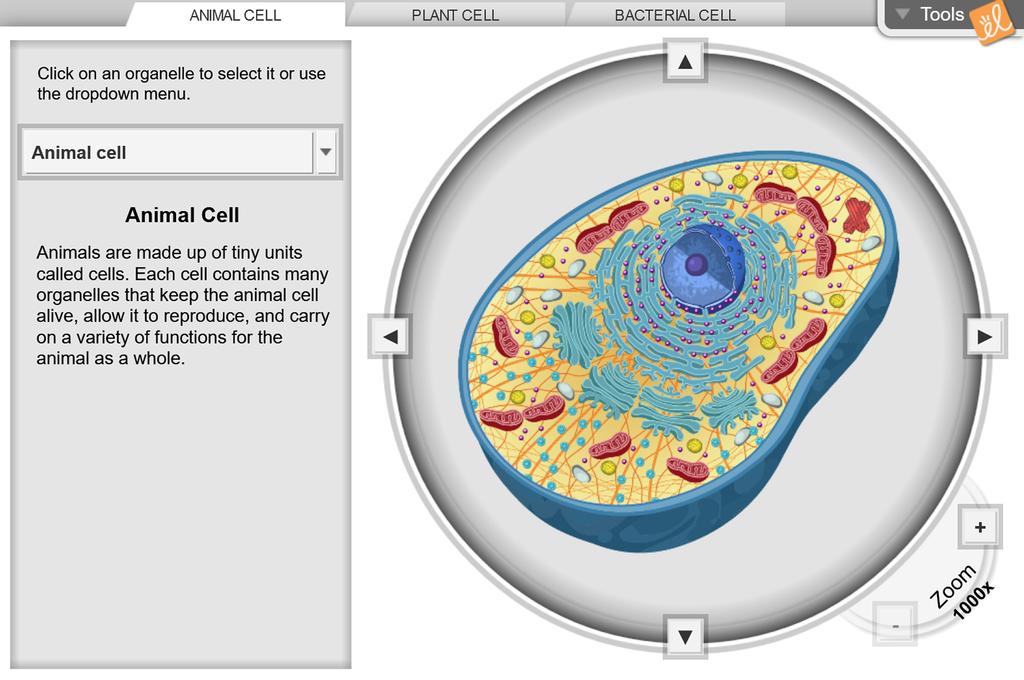
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. While animal and plant cells have many common characteristics, they are also different. Plant cell ribosome definition. This is the organelle responsible for protein synthesis of the cell. Its found in the cell cytoplasm in large numbers and a few of them called functional ribosomes can be found in the nucleus, mitochondria, and the cell chloroplast. Its made up of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and cell proteins. Transcribed image text: Note: Character counts include spaces 20 Worth I po 7 Imagine that you are looking through a microscope at plant cells, specifically, epidermal cells. How does this cell differ from the one you drew in Activity 4? (Hint: Consider numbers and types of organelles, cell-cell junctions, etc.) Type answer here rachitha 20 Worth I point 8 Imagine that you are looking through ...
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram. Tap again to see term 👆. list the three parts of the cell theory. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 1. all living things are made of cells. 2. all cells come from other living cells. 3. the cell is the most basic unit of life. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Structure of Cell: Cell is the basic functional unit that makes up all living organisms.All organisms, including ourselves, start life as a single cell called the egg. Cells are small microscopic units that perform all essential functions of life and are capable of independent existence. Functionally, you can say the cytoskeleton network is equal to a cell’s muscle, bone, blood vessel, and nervous systems in combination. [In this figure] Left: A diagram of a cell showing the network of cytoskeleton consisting of three types of filament proteins – actin, intermediate filament, and microtubule. Blank Plant Cell Diagram - Color. 4. Blank Plant Cell Diagram - Black & White. 5. Unlabeled Plant Cell Illustration - Color. 6. Unlabeled Plant Cell Illustration - Black & White. You can hand page 1 or 2 to your kids to help them memorize the organelles. Then present them with page 3 and 4 as a quiz.
Plant cells. Get the Gizmo ready: Select the PLANT CELL tab, and click Sample. Question: What functions do the organelles in a plant cell perform? Label : Locate each organelle in the plant cell. Label the organelles in the diagram below. Compare : What structures are present in an animal cell, but no t in a plant cell? Transcribed image text: Note: Character counts include spaces 20 Worth I po 7 Imagine that you are looking through a microscope at plant cells, specifically, epidermal cells. How does this cell differ from the one you drew in Activity 4? (Hint: Consider numbers and types of organelles, cell-cell junctions, etc.) Type answer here rachitha 20 Worth I point 8 Imagine that you are looking through ... Plant cell ribosome definition. This is the organelle responsible for protein synthesis of the cell. Its found in the cell cytoplasm in large numbers and a few of them called functional ribosomes can be found in the nucleus, mitochondria, and the cell chloroplast. Its made up of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and cell proteins. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. While animal and plant cells have many common characteristics, they are also different.

0 Response to "37 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram"
Post a Comment