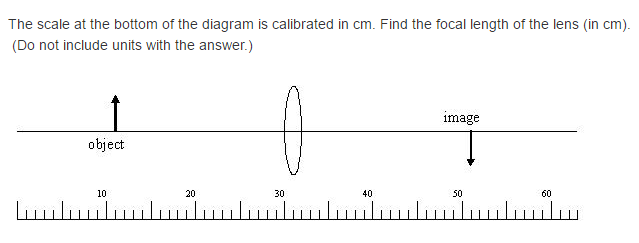
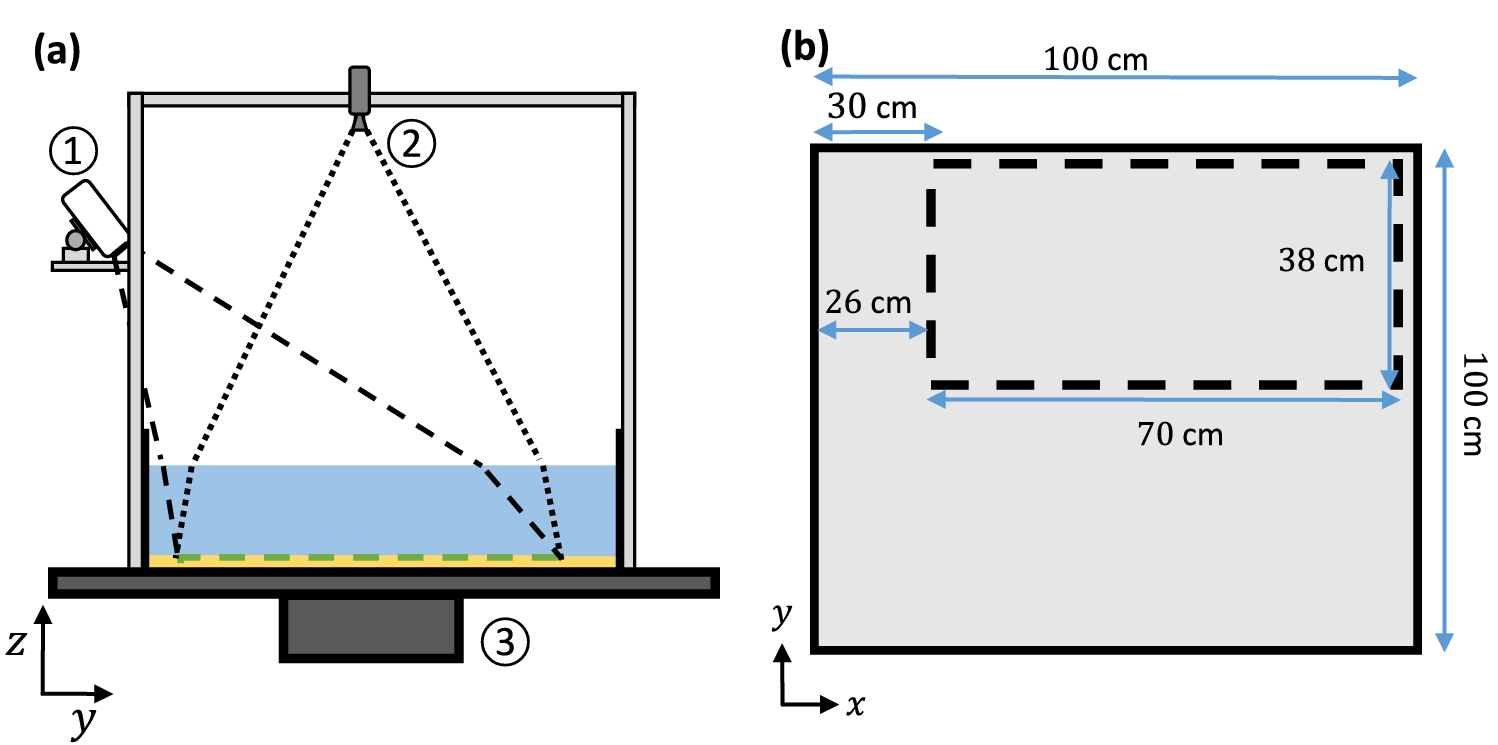
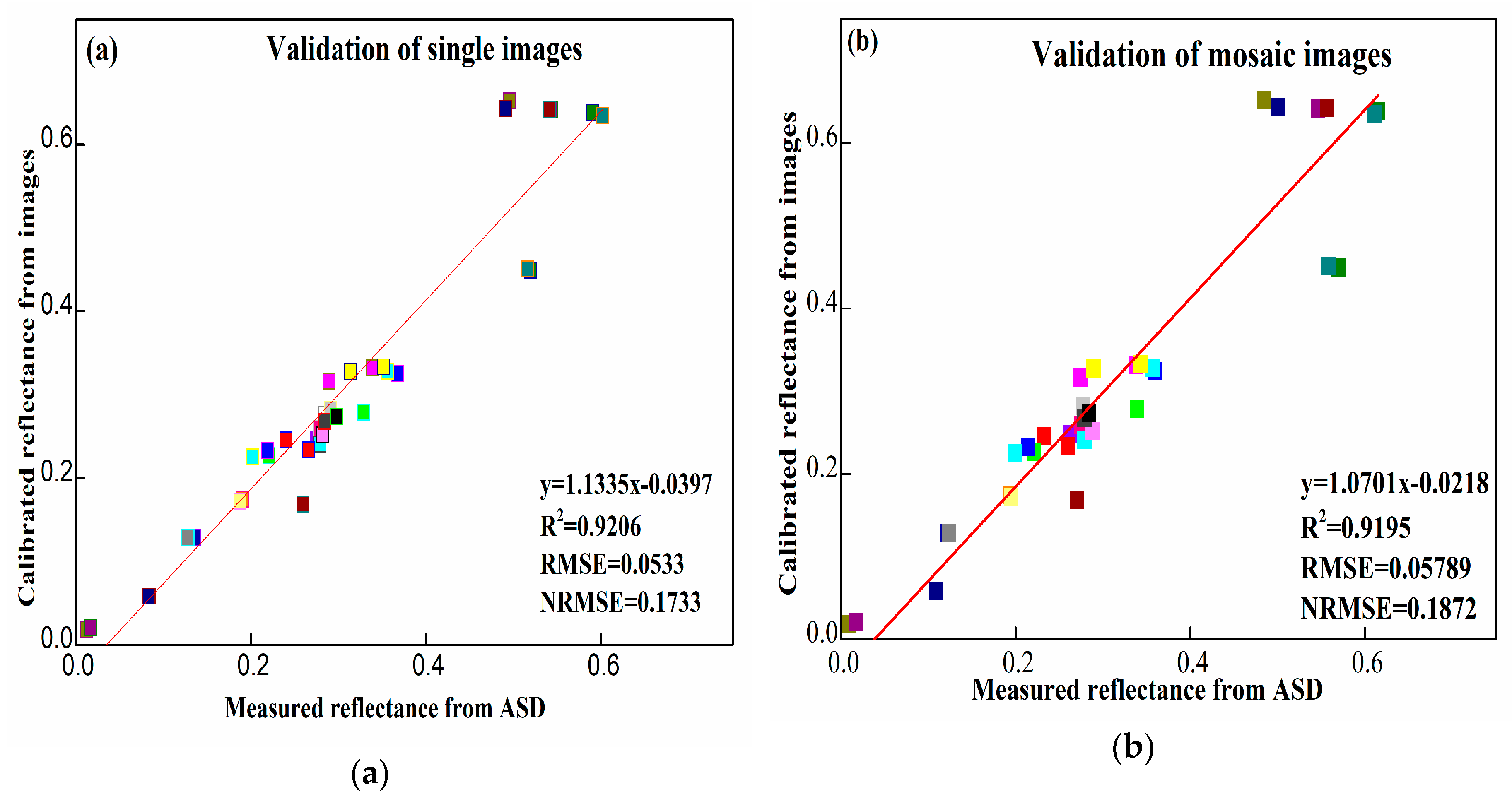
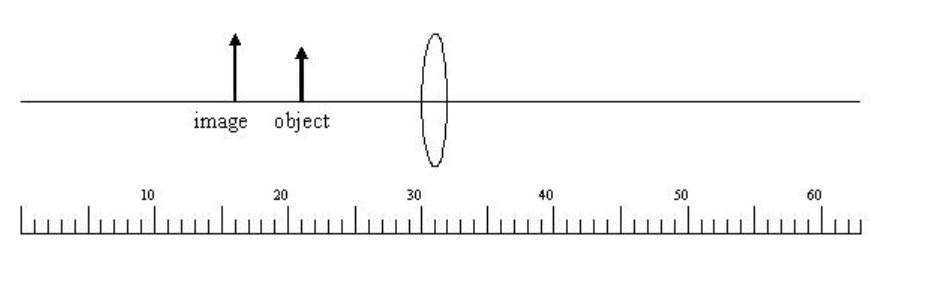
40 the scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. find the focal length of the lens
100% (7 ratings) According to the question we need to …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). (Do not include units with the answer.) The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). ANSWER: 3.8|4.2 Hire a professional writer to help you with your home work.
What is Lens Focal Length. Focal length, usually represented in millimeters (mm), is the basic description of a photographic lens. It is not a measurement of the actual length of a lens, but a calculation of an optical distance from the point where light rays converge to form a sharp image of an object to the digital sensor or 35mm film at the focal plane in the camera.

The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. find the focal length of the lens
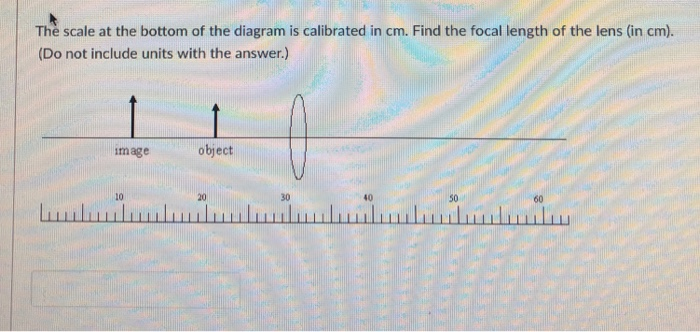
2.When using the Lens Equation, a virtual image has a a. positive object distance b. negative image distance c. positive image distance 3.The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed. If the bottom half of a diverging lens is covered, then the bottom half of the image will not be visible. Diverging lenses only produce virtual images. Diverging lenses can produce images which are both magnified and reduced in size. Diverging lenses only produce upright images. Diverging lenses have a - focal length.
The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. find the focal length of the lens. Buku kumpulan soal fisika Canada ini bakalan bikin kamu makin seneng deh sama fisika. Answer 2: Correct! virtual Question 7 0 / 1 pts The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). (Do not include units with the answer.) You Answered Correct Answers Between 14.25 and 15.75 TG-Prelab Due Apr 14 at 7am Points 5 Questions 7 20.0000 32.The size of the image of an object, which is at infinity, as formed by a convex lens of focal length 30 cm is 2 cm. If a concave lens of focal length 20 cm is placed between the covex lens and the image at a distance of 26 cm from the convex lens,calculate the new size of the image[2003-2 marks] a) 1.25 cm b) 2.5 cm c) 1.05 cm d) 2 cm Ans. Ans. Focal length: the distance from the middle of the camera lens to the focal plane (i.e. the film). As focal length increases, image distortion decreases. The focal length is precisely measured when the camera is calibrated. Scale: the ratio of the distance between two points on a photo to the actual distance between the same two points on the ...
Practice Scale Computation Example: Aerial imagery was acquired with a digital aerial camera with lens focal length of 50 mm and CCD size of 0.020 mm (or 20 microns). The resulting imagery had a ground resolution of 60 cm (2 ft). Determine the scale of the resulting imagery. Solution. Scale = 0.020 mm 60 cm x 10 mm/cm = 0.020 600 = 1 30, 000 centimeters. The two terms on the right must have the same units before you can add them! f = 2.096 cm 2.1 cm For (c), the object distance is do= 25 cm f = 1.94 cm 26.5 An object sits 35 cm to the left of a converging lens with focal length of 20 cm. 75 cm to the right is a second converging lens with focal length of 15 cm. A. An object is 1.0 cm tall and its erect image is 4.0 cm tall. What is the exact magnification? B. When using the Lens Equation, a virtual image has a a. positive object distance b. negative image distance C. The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). Problem Giancoli 33-42 (II) Reading glasses of what power are needed for a person whose near point is 105cm, so that he can read a computer screen at 55cm?Assume a lens-eye distance of 1:8cm. Solution: The screen placed 55cm from the eye, or 53:2cm from the lens, is to produce a virtual image 105cm from the eye, or 103:2cm from the lens. Find the power of the lens from Eqs 33-1 and 33-2.
convex mirror with a "15.0-cm focal length. Find the image position using both a scale diagram and the mirror equation.! d 1 o! #! d 1 i!!! 1 f! so d i!! d o d o " f f! !!!! "8.57 cm 18. A convex mirror has a focal length of "13.0 cm. A lightbulb with a diameter of 6.0 cm is placed 60.0 cm from the mirror. By factoring the ratio, the photo scale is 1 in. = x ft. 6.2.2.1 Engineers' Scale When using a 6-in. focal length camera flying at a height of 1200 ft above mean ground elevation, the engineers' scale of the photograph is: which translates to an engineers' scale of 1 in. = 200 ft. 6.2.2.2 Representative Fraction An object is placed 20.0 cm from a converging lens with focal length 15 cm. A concave mirror with focal length 10 cm is located 75 cm to the right of the lens as shown in the figure. Note: The figure is not drawn to scale. Determine the location of the final image. example, if the object distance is four times the focal length, the magnitude of the magnification is 1/3, regardless of the exact values of the object distance and focal length. Hint C.2 Object at the focal point If an object is located exactly at the focal point, the image is "infinitely" large.
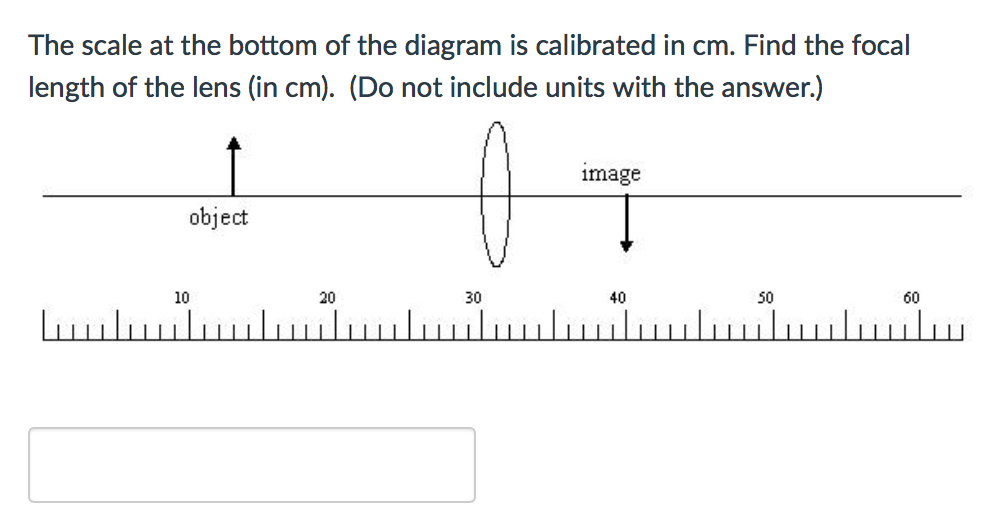
1 / 1 pts Question 7 The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). (Do not include units with the answer.) 15.0000 Correct! Between 14.25 and 15.75
The positive meniscus lens (Figure 1(c)) has an asymmetric structure with one face shaped as a convex radius, while the opposite face is slightly concave. Meniscus lenses are often employed in conjunction with another lens to produce an optical system having either a longer or shorter focal length than the original lens.
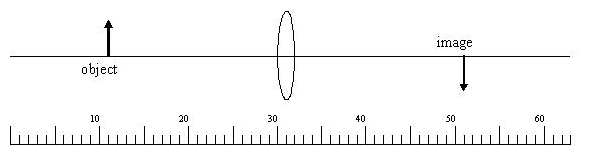
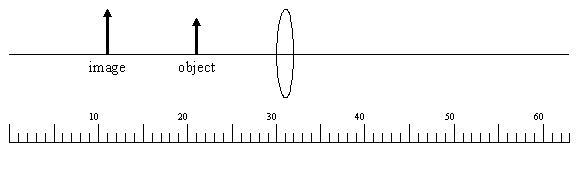
When using the Lens Equation, a virtual image has a a. positive object distance b. negative image distance C. The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). (Do not include units with the answer.) image object 20 10 30 40 50 60 ulu
192 No links please Q Find the focal length of the projector-lens which projects the image of size 60×60 cm of a slide on a screen 2 4 m away, the slide being of the size 3×3 cm Light enters a prism of angle A at a grazing incidence to emerge at an angle θ with the normal Show that the refractive index of the material of the prism is given ...
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed 10 cm apart with their principal axes coinciding. A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis and having a beam diameter 5.0 mm, is incident on the combination. Show that the emergent beam is parallel to the incident one.
The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm). Question: The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm).
the object, what is the mirror's focal length? (a) 12.0 cm (b) 20.0 cm (c) 70.0 cm (d) 90.0 cm (e) none of those answers 7. Two thin lenses of focal lengths 1 5 15.0 and 2 5f f 10.0 cm, respectively, are separated by 35.0 cm along a common axis. The f 1 lens is located to the left of the f 2 lens. An object is now placed 50.0 cm to the left ...
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. If the eye is placed 60 cm to the right of the lens at a distance h below the principal axis, then the maximum value of h to see the image will be [MP PMT 1999]
A second converging lens, this one having a focal length of 60.0 cmcm , is located 300 cmcm to the right of the first lens along the same optic axis. Find the location and height of the image (call it I1I1) formed by the lens with a focal length of 40.0 cm
15. A 2.25-cm-tall object is 8.5 cm to the left of a convex lens of 5.5-cm focal length. Find the image position and height.! &! d i! ! ! 15.6 cm, or 16 cm m! ! h i! ! ! "4.1 cm 16. An object near a convex lens produces a 1.8-cm-tall real image that is 10.4 cm from the lens and inverted. If the focal length of the lens is 6.8 cm, what are the ...
Listings 47151 - 47200 (out of 312082) Improve your grade with ScholarOn's Physics expert answers, textbook solutions, flashcards, essays, study resources & learning aids now.
If the bottom half of a diverging lens is covered, then the bottom half of the image will not be visible. Diverging lenses only produce virtual images. Diverging lenses can produce images which are both magnified and reduced in size. Diverging lenses only produce upright images. Diverging lenses have a - focal length.
Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed.

ğŸâ€Â´ If you want to use this image Please Follow me on insta ►►👉 https://tinyurl.com/y7fsmkjz
2.When using the Lens Equation, a virtual image has a a. positive object distance b. negative image distance c. positive image distance 3.The scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. Find the focal length of the lens (in cm).
























0 Response to "40 the scale at the bottom of the diagram is calibrated in cm. find the focal length of the lens"
Post a Comment