39 nacl dissolved in water diagram
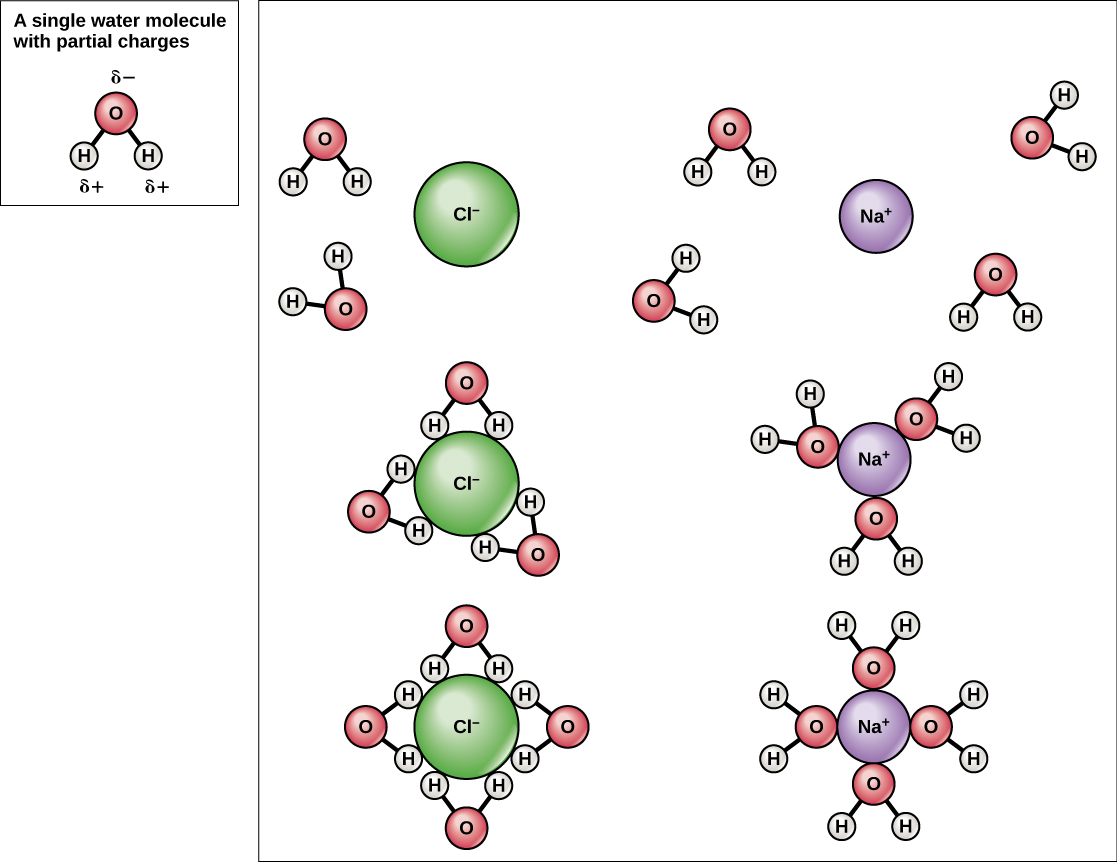
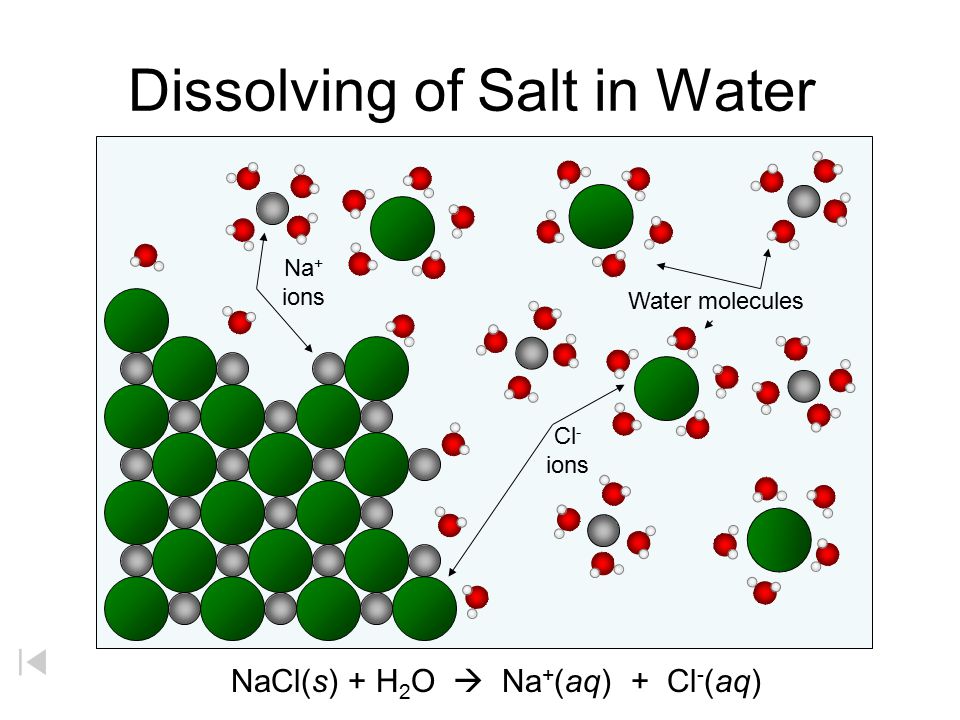
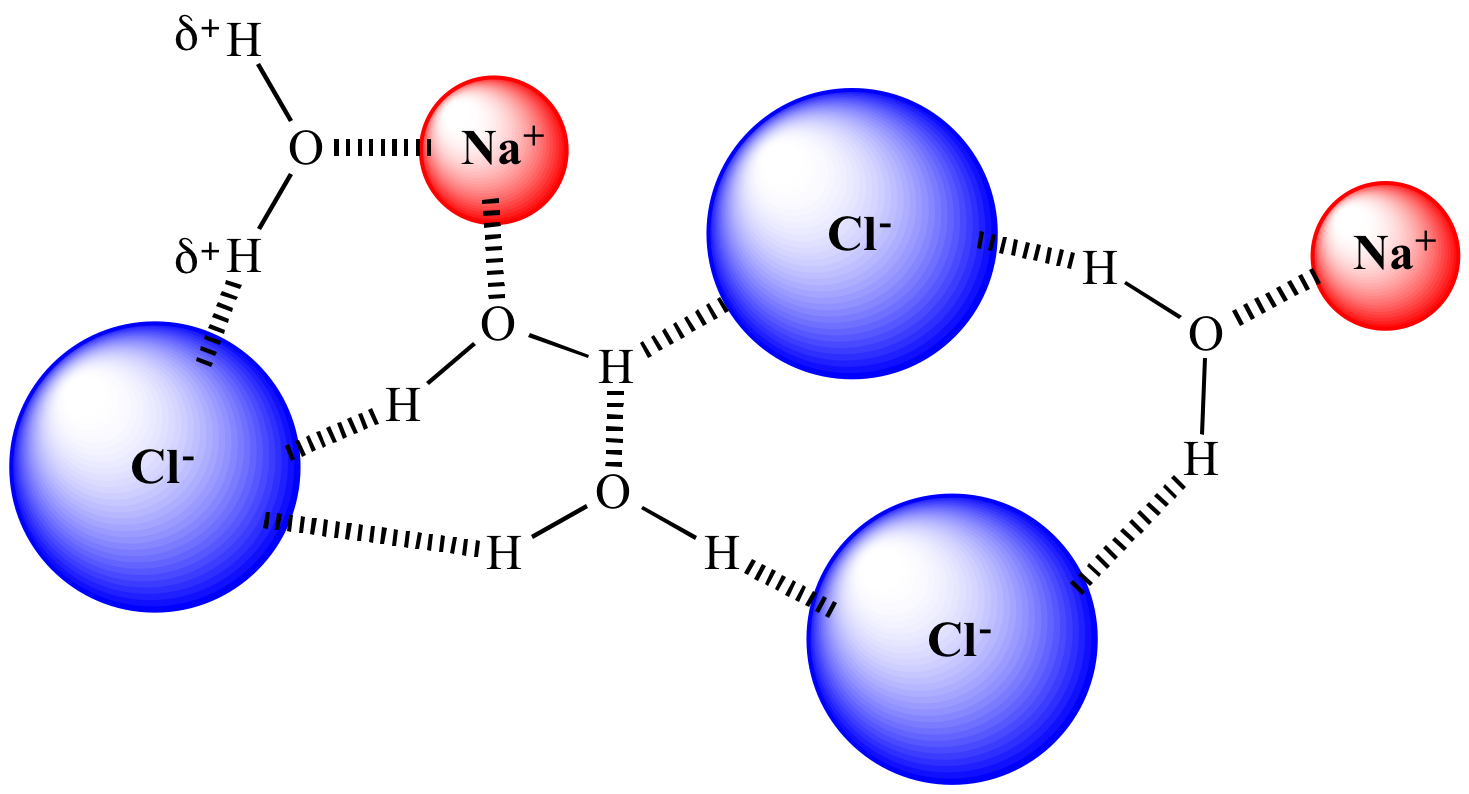
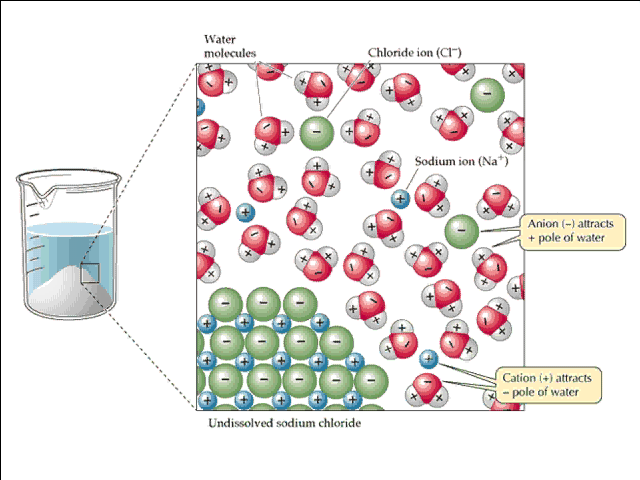
Dissociation of Sodium Chloride in Water. It is the polar nature of water that allows ionic compounds to dissolve in it. In the case of sodium chloride (\(\text{NaCl}\)) for example, the positive sodium ions (\(\text{Na}^{+}\)) are attracted to the negative pole of the water molecule, while the negative chloride ions (\(\text{Cl}^{-}\)) are attracted to the positive pole of the water molecule. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Since, NaCl is a strong electrolyte, …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Question 58 2 pts Which diagram represents sodium chloride, NaCl, dissolved in water? O NaCl Na a Nao N 70 Na+ 9 Na Na Naci Naci Naci NaCl.
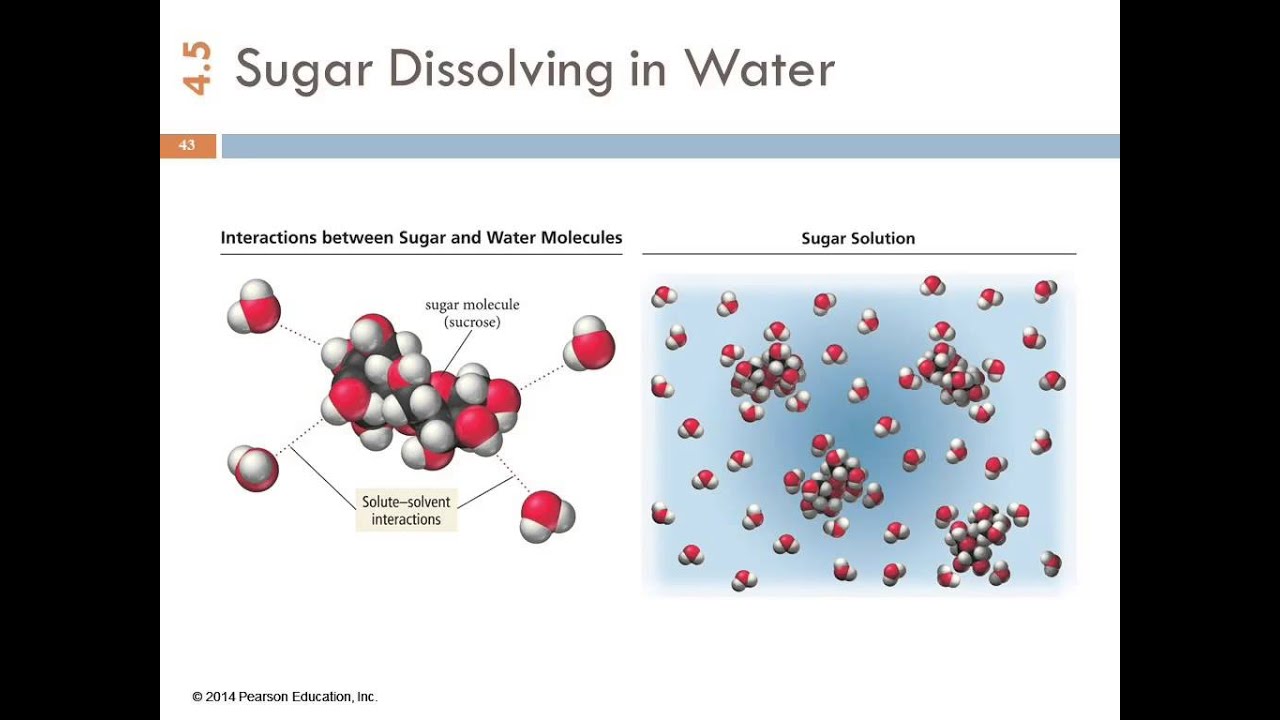
Sodium chloride dissolves in water because the water molecules have a sufficient attraction for the Na+ and Cl-ions to overcome the attraction of these two ions for one another in the ionic solid. To form an aqueous solution of NaCl, water molecules must also separate from one another to form
Nacl dissolved in water diagram
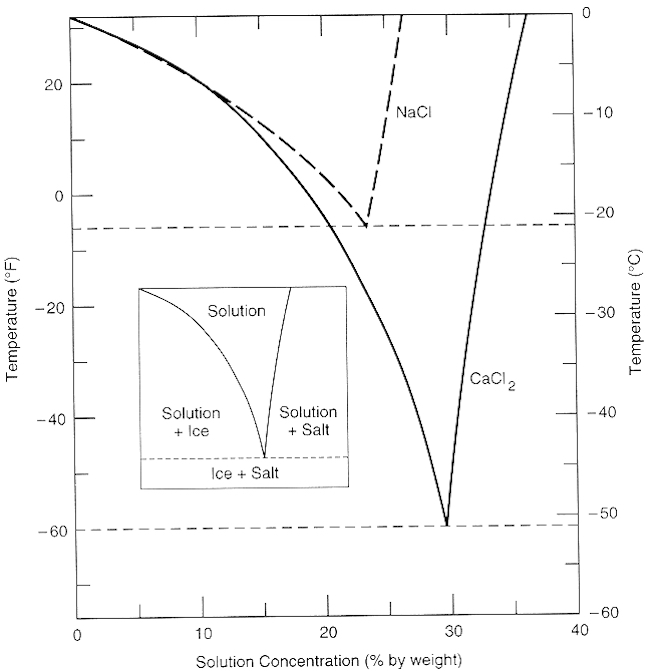
The average daily intake of sodium chloride from food-grade salt used in food processing and from salt added to cooking and at the table is from 4,960 to 6,230 mg sodium chloride. Salt is a requirement in the diet. The safe and adequate intake for adults is reported as 1,875 to 5,625 mg. These free ions in a salt-water solution allow electricity to flow through water. Ionic compounds such as sodium chloride, that dissolve in water and dissociate to form ions, are called electrolytes. Please Watch animation 10.3 on ionic solutions. At all temperatures above that marked on the graph (about 57°C), 100 g of water will dissolve more than 100 g of potassium nitrate. All the potassium nitrate will stay in solution. At 57°C, you hit the solubility curve. This is the temperature at which 100 g of water will dissolve 100 g of potassium nitrate to give a saturated solution.
Nacl dissolved in water diagram. 2. The diagram above represents a mixture of NO 2(g) and N 2O 4(g) in a 1.0 L container at a given temperature. The two gases are in equilibrium according to the equation 2 NO 2(g) N 2O 4(g) Which of the following must be true about the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction at this temperature? (A) K = 0 (B) 0 < K < 1 (C) K = 1 Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. The Enthalpy Change of Sodium Chloride Added to Water. When salt dissolves in water, sodium and chloride ions are pulled apart to form new weak bonds with water molecules. Pulling them apart takes energy, while forming new bonds with the water molecules releases energy. The net amount of energy released or absorbed is ... 1 What happens when sodium chloride dissolves in water? ... After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
Detailed Description. This diagram shows the positive and negative parts of a water molecule. It also depicts how a charge, such as on an ion (Na or Cl, for example) can interact with a water molecule. At the molecular level, salt dissolves in water due to electrical charges and due to the fact that both water and salt compounds are polar, with positive and negative charges on opposite sides in the molecule. If you mix two substances and the result is a homogeneous mixture, you are dealing with a solution. In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Water is a solvent. The reasons are electrostatic in nature. The cohesion of atoms and molecules derive from electrostatic links between particles ... Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal, pulling away the individual sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl –) ions. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. To understand this process at the molecular level, we must apply the three steps we previously discussed. Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
Reproduce the conductivity trace observed on the LabQuest when the NaCl was dissolved in the DI water. A rough sketch is sufficient, but label the x and y axes correctly. Describe in words what this graph shows. Conductivity Data Sample Concentration (NaCl, g/L) Conductivity (µS/cm) deionized water 0 original NaCl solution (C i) diluted NaCl ... In this video we will describe the equation NaCl + H2O and write what happens when NaCl is dissolved in water.When NaCl is dissolved in H2O (water) it will d... When you dissolve salt in water, the sodium chloride dissociates in Na + ions and Cl - ions, which may be written as a chemical equation : NaCl (s) → Na + (aq) + Cl - (aq) Therefore, dissolving salt in water is a chemical change. The reactant (sodium chloride, or NaCl) is different from the products (sodium cation and chlorine anion). Download for Mac (.mov) The positive area of the water molecules surround the negative Chloride ions. The negative area of the water molecules surround the positive sodium ions. As the attractions from the water molecules and their motion pulls the ions apart, the sodium chloride crystal dissolves. This video appears courtesy of Roy Tasker.
Explanation: NaCl is an ionic compound that occurs naturally as white crystalline solid in NaCl unit has cubic …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 28: Explain all important intermolecular forces that occur in when NaCl is dissolved in water. (5 points) Diagram: Explanation: Previous question Next question.
Which diagram but illustrate the ion-molecule attractions that occur when the ions of NaCl(s) are added to water? A) H2O+Na and Cl+H2O B) OH2+Na and Cl+OH2 C) H2O+Na and Cl+OH2 D) OH2+Na and Cl+H2O. A. What happens when NaCl(s) is dissolved in water? A) Cl- ions are attracted to the oxygen atoms of the water. B) Cl- ions are attracted to the ...
For example, the ionic or polar solute, NaCl, dissolves in water, a polar solvent. The phase "like dissolves like" has often been used to explain this. As the water molecules collide with the ionic compound (NaCl), the charged ends of the water molecule become attracted to the positive sodium ions and negative chloride ions.
What Happens When Nacl Is Dissolved In Water? Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a ...
Sodium chloride, a common salt, dissolves in water due to the attraction between the negative part of the water (oxygen) and the positive part of the salt (sodium). Similarly, there is also an attraction between the positively charged part of water molecules (hydrogen) and the negative chloride atoms.
Maddy. Mar 29, 2021. We can draw diagrams on this site. Solid NaCl dissolves in water because the polar water molecules are attracted to the Na^+ and Cl^- and that attractions is enough to break the Na-Cl bond. Google this and you will get some good diagrams and explanations to explain just what is happening. 👍.
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
Deionized water fails to light the light bulb in the conductivity tester. A light bulb conductivity tester does not light up at all when the electrodes are inserted into either solid granular sodium chloride or solid granular sucrose. However, when solid NaCl dissolves in water, the sodium chloride solution lights the bulb brightly.
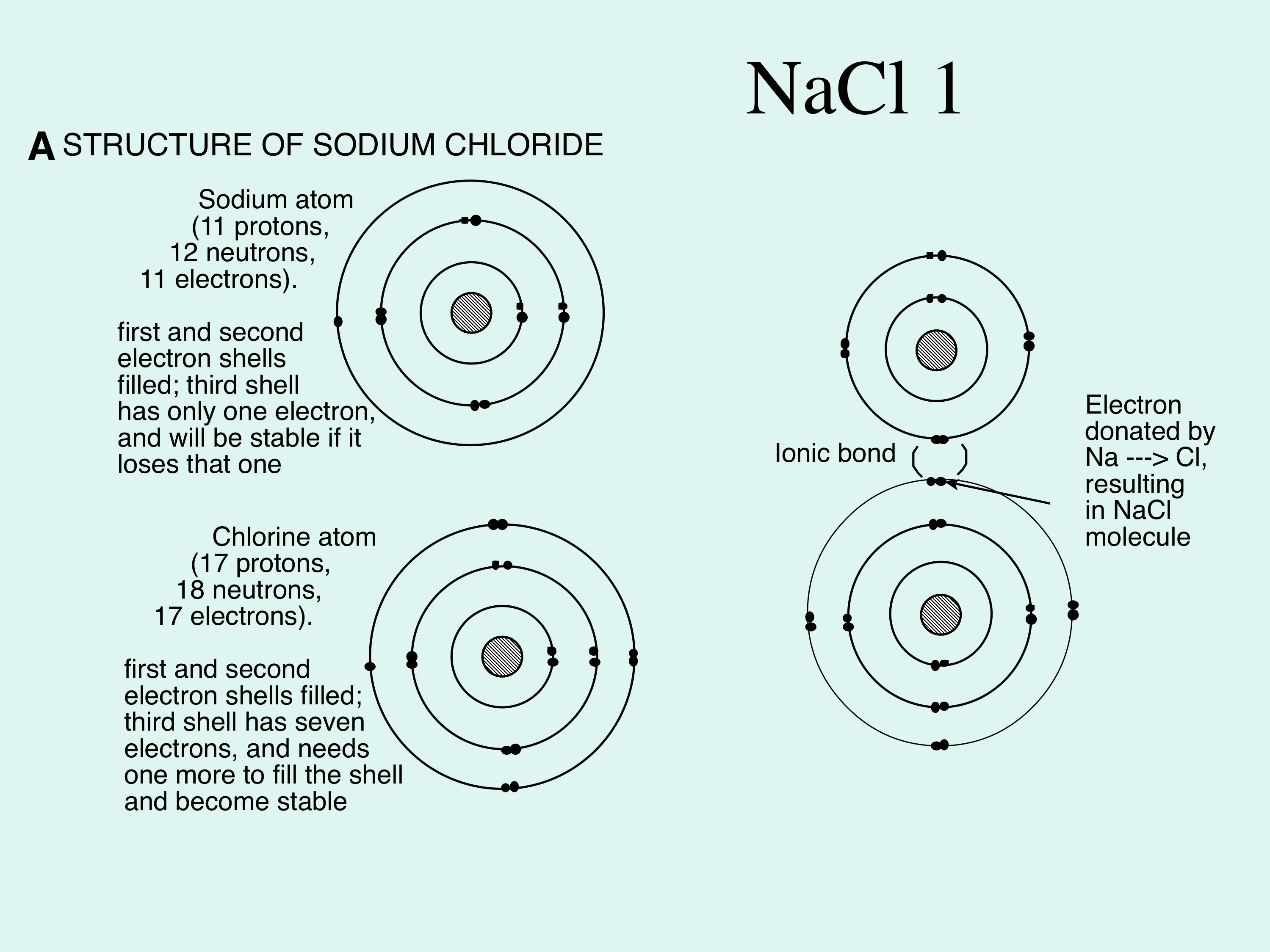
we can easily draw a diagram of sodium chloride dissolved in water. Let's just do some quick review, though. Sodium chloride is in a C l. And remember, sodium has a positive charge because it has one extra proton in the nucleus than electrons in the outer cloud. And chloride has one extra electrons in the outer plowed compared to the neutrons, protons that are in the nucleus with you and sodium chloride that's held together with an ionic bond to a polar solvent such as water, which is held ...
Step 1. 1 of 2. Explanation:- \textbf {\color {#c34632}Explanation:-} Explanation:-. ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ Water molecules ionize NaCl molecules and convert them into positive sodium ions and negative chlorine ions. ⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ The negative end of water molecules \textbf {The negative end of water molecules} The negative end of water ...
In the post-laboratory you were to write a chemical equation describing what happens when a soluble ionic compound dissolves in water. For example, sodium chloride dissolves in water. The chemical equation that can be written to describe the solubility of sodium chloride is, NaCl (s)---H 2 O--> Na + (aq) + Cl-(aq)
Diagram 1 represents NaCl; it has a lower melting point than MgS because the coulombic attractions between its singly charged Na+Na+ ions and the Cl− ions are weaker than those between the ions in MgS. ... and a .10 mol sample of KCL(s) are dissolved in water and diluted to 500mL what is the concentration of Cl-1 in the solution? D. 1.0 M. At ...
At all temperatures above that marked on the graph (about 57°C), 100 g of water will dissolve more than 100 g of potassium nitrate. All the potassium nitrate will stay in solution. At 57°C, you hit the solubility curve. This is the temperature at which 100 g of water will dissolve 100 g of potassium nitrate to give a saturated solution.
These free ions in a salt-water solution allow electricity to flow through water. Ionic compounds such as sodium chloride, that dissolve in water and dissociate to form ions, are called electrolytes. Please Watch animation 10.3 on ionic solutions.
The average daily intake of sodium chloride from food-grade salt used in food processing and from salt added to cooking and at the table is from 4,960 to 6,230 mg sodium chloride. Salt is a requirement in the diet. The safe and adequate intake for adults is reported as 1,875 to 5,625 mg.

















0 Response to "39 nacl dissolved in water diagram"
Post a Comment