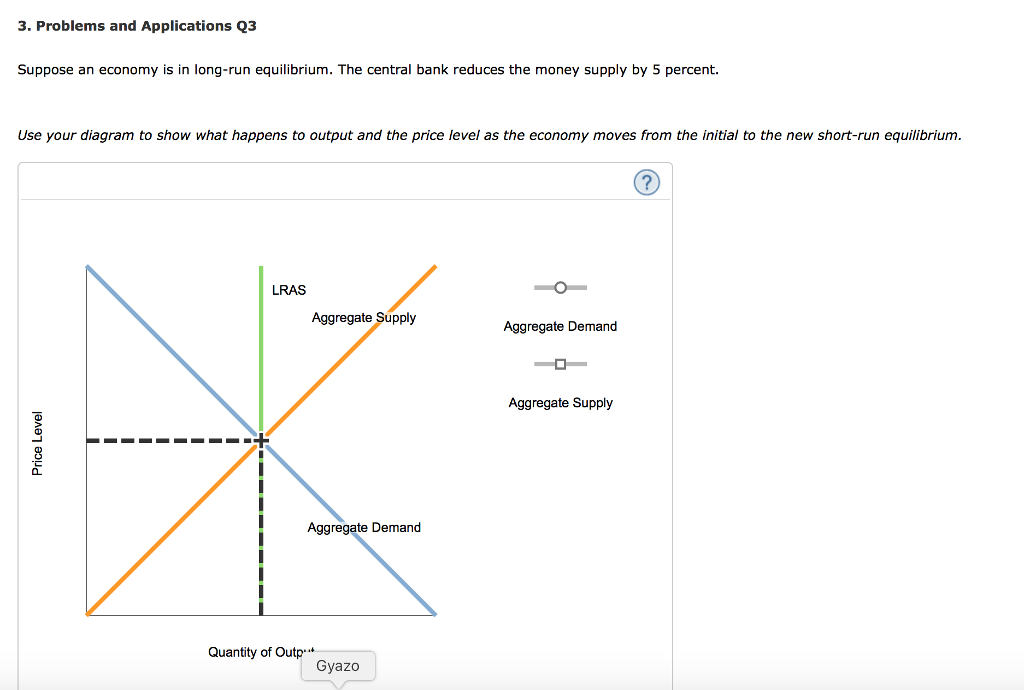
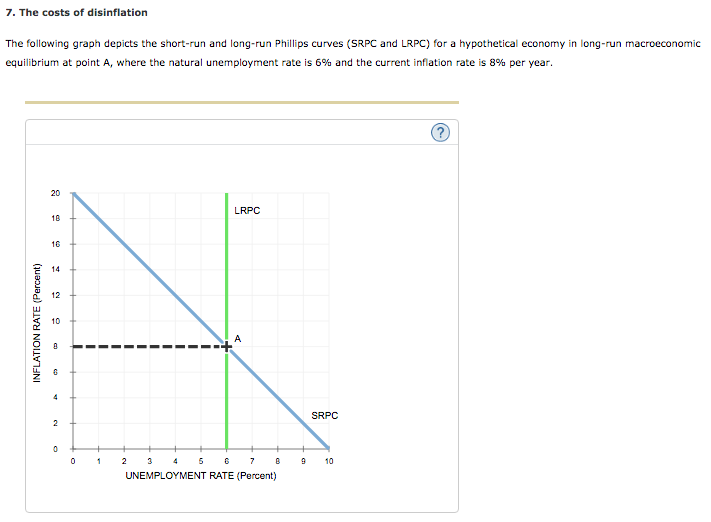
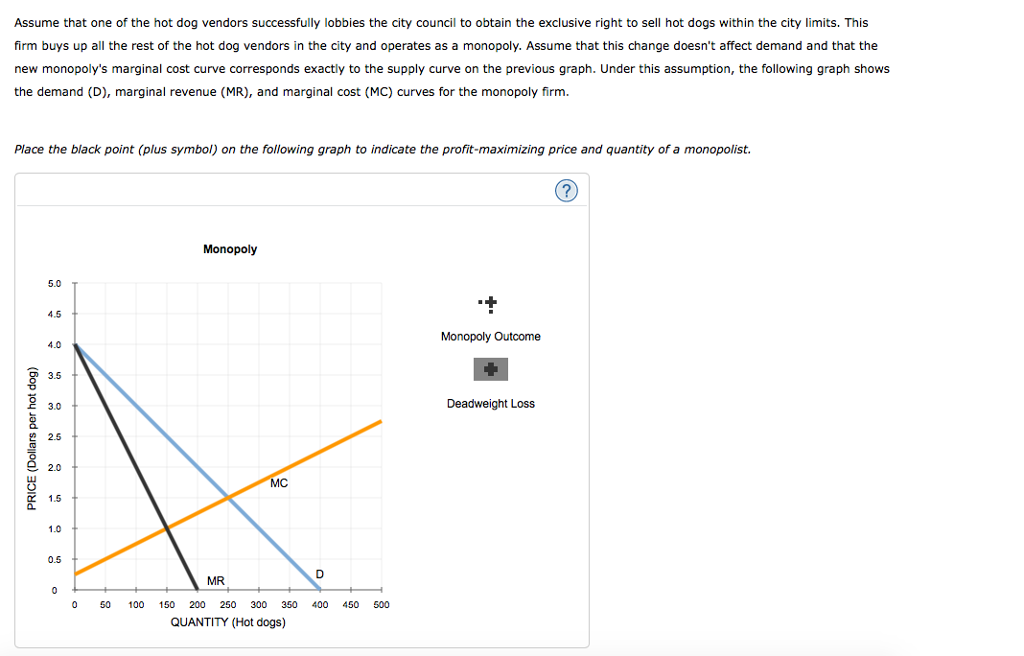
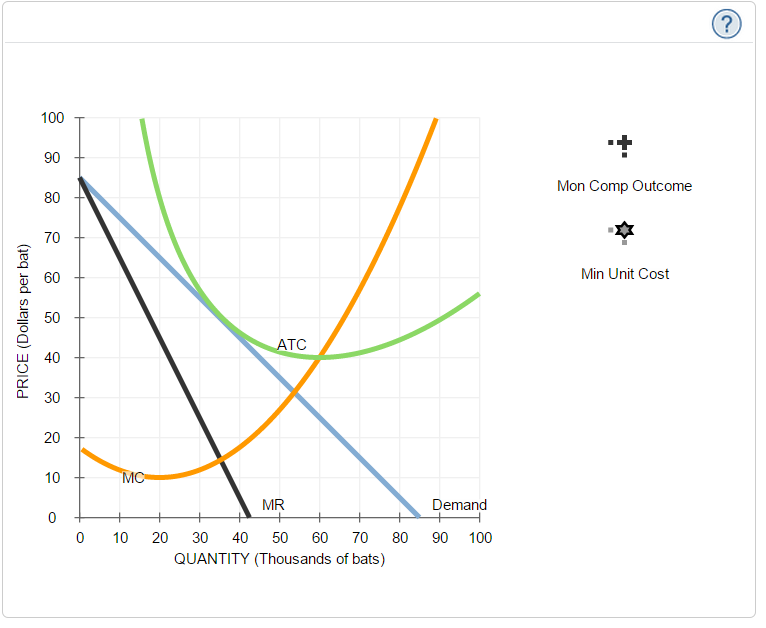
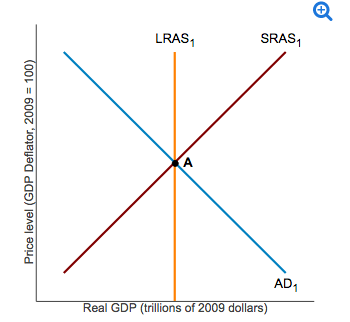
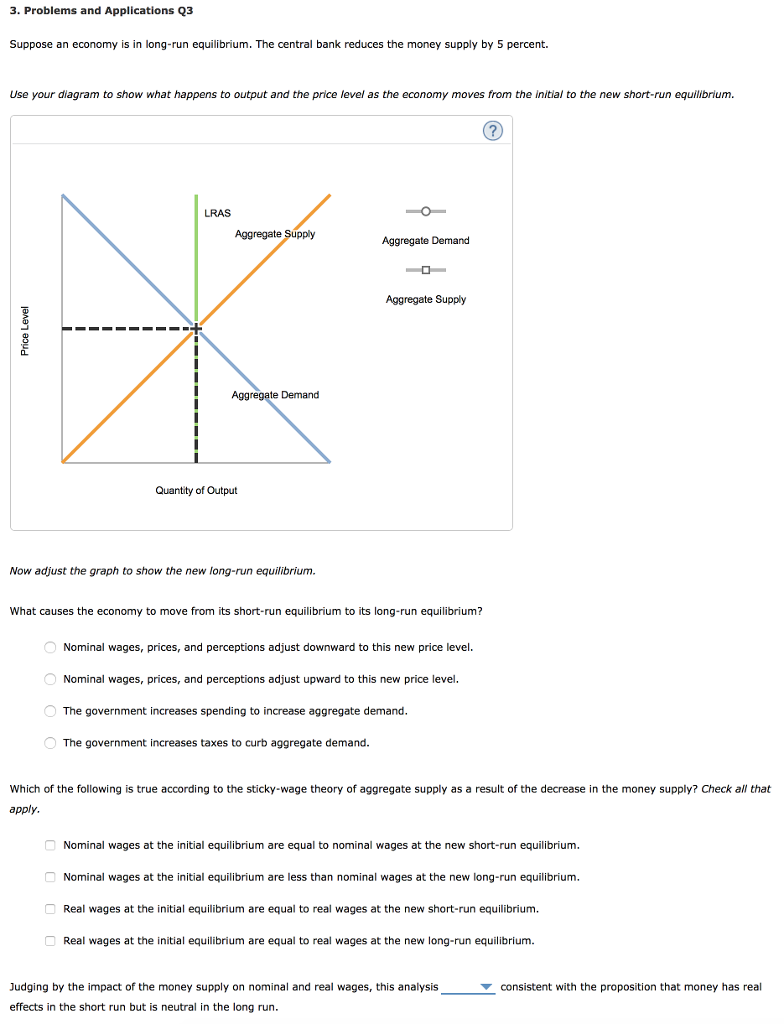
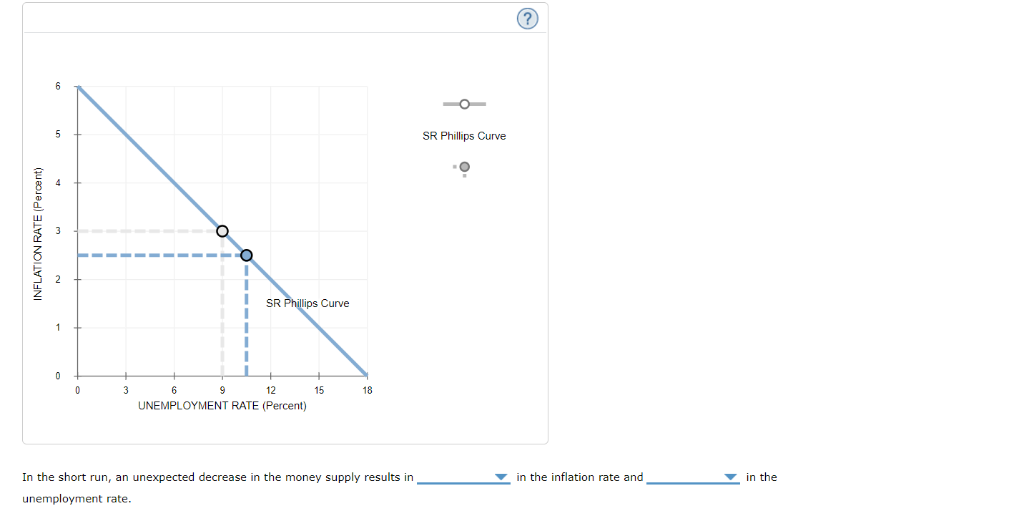
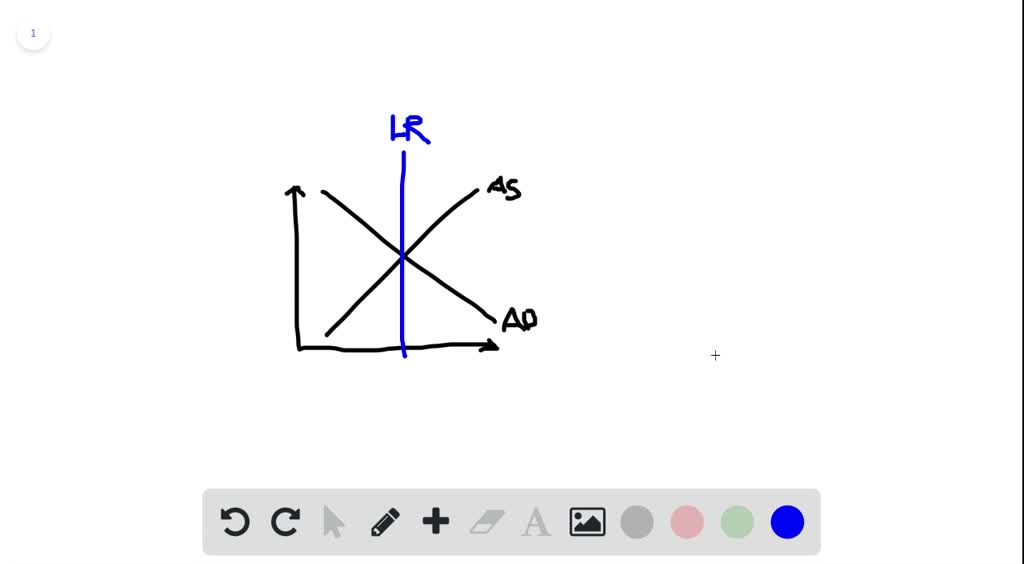
37 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
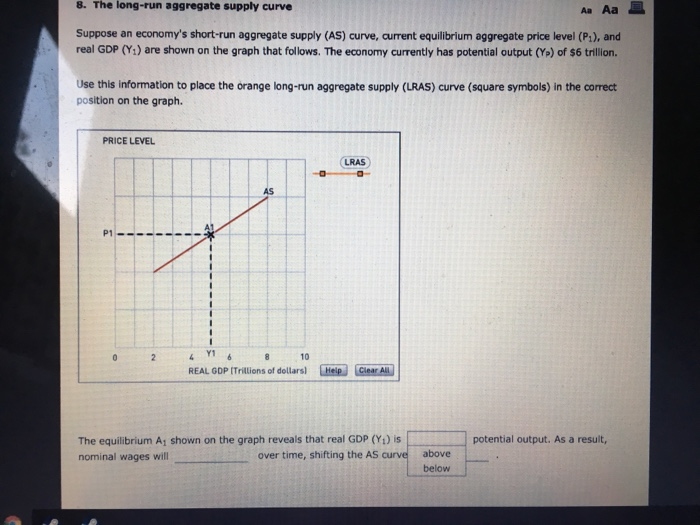
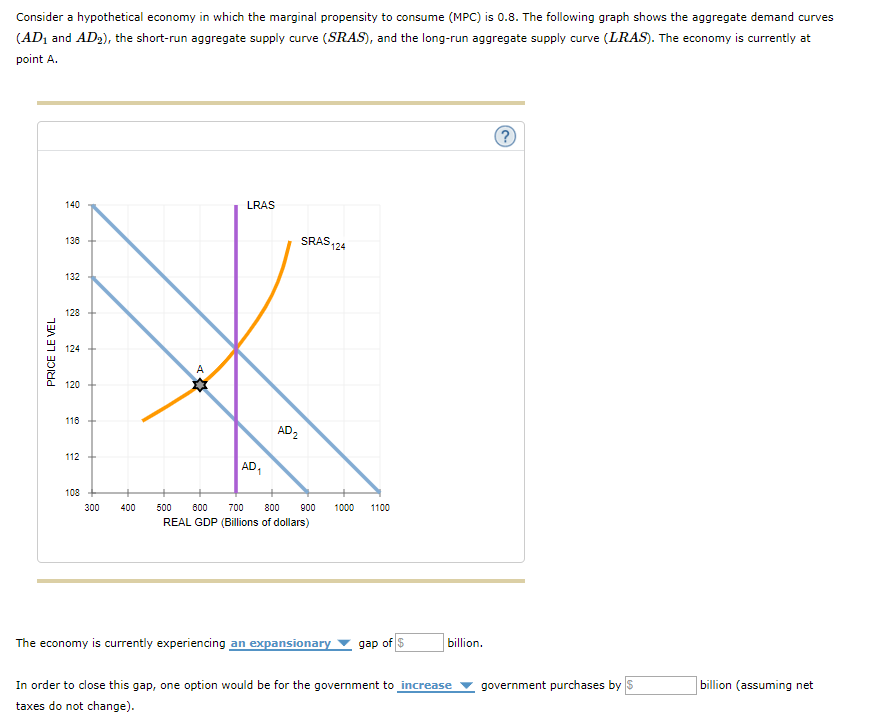
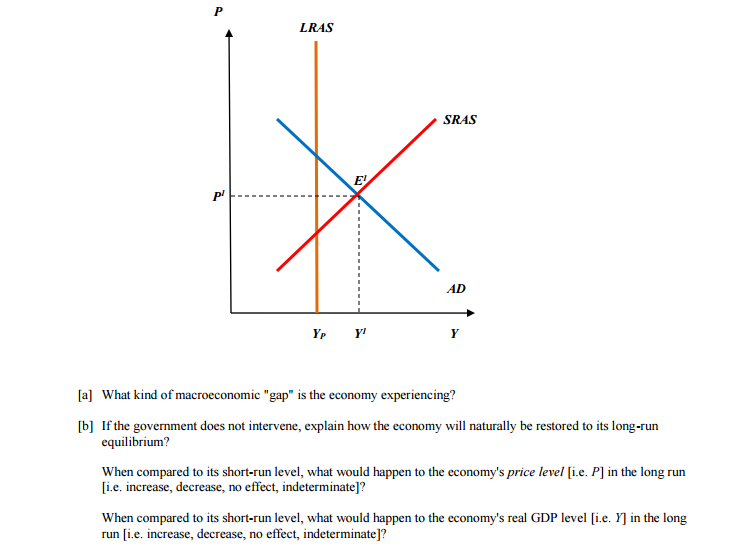
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap . LRAS SRAS If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $0.1 trillion. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has an inflationary gap. b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.5 , to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $.58. 8 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. (This is my answer, I think it's right). If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20, calculate the change in governemtn spending that could eliminate the gap. $ ____ trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal
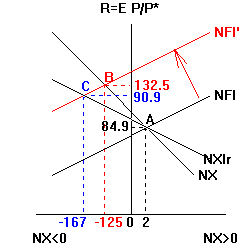
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has _____. b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.5 , to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $____ trillion. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $.25 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places. )... Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has (an expectation gap / an inflationary gap / a recessionary gap) . If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap.
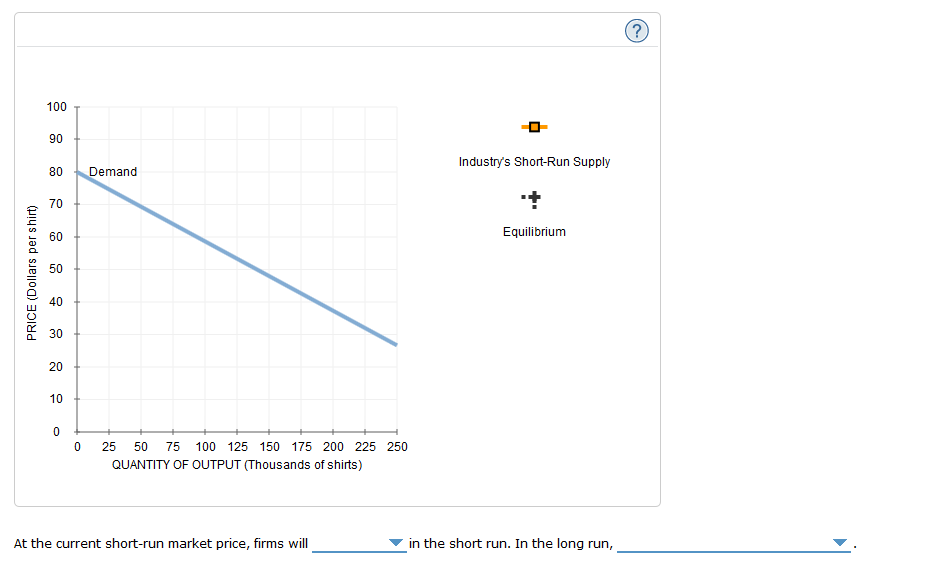
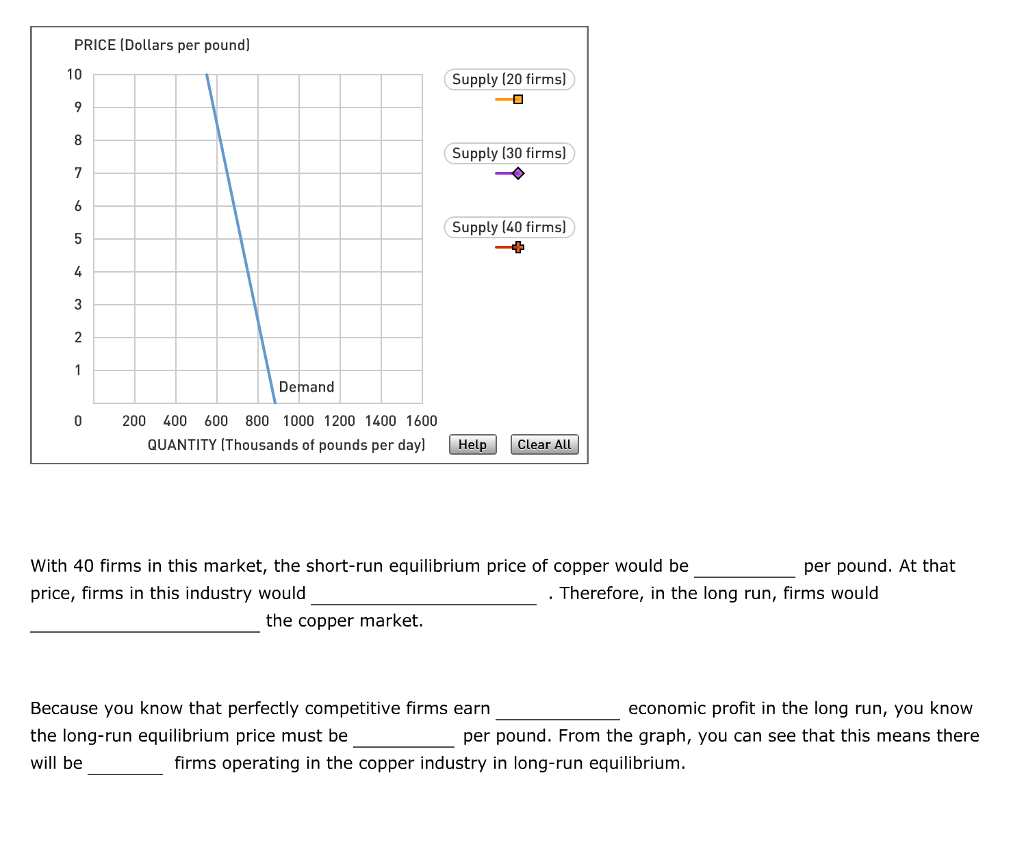
Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a.. A purely competitive firm is currently in short-run equilibrium and its MC exceeds its ATC at its current output level. It can be concluded that. A. Firms will leave the industry in the long run. B. The firm is realizing an economic profit. C. The firm is suffering an economic loss. D. The firm will shut down in the short run. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has (an expectation gap / an inflationary gap / a recessionary gap) . If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.20 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. At point A, the economy has a recessionary gap. If the marginal propensity to save equals 0.25 , calculate the change in government spending that could eliminate the gap. $.25 trillion. (Round your answer to two decimal places. )... Consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point A. a. At point A, the economy has _____. b. If the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.5 , to eliminate the gap, the government should decrease spending by $____ trillion.
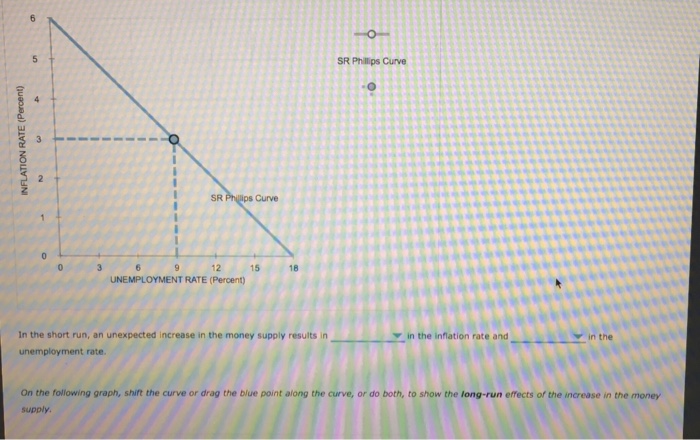














0 Response to "37 consider the following diagram, in which the current short-run equilibrium is at point a."
Post a Comment