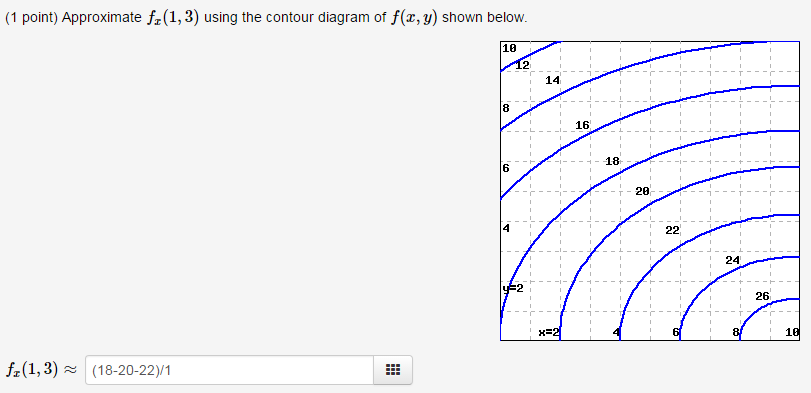
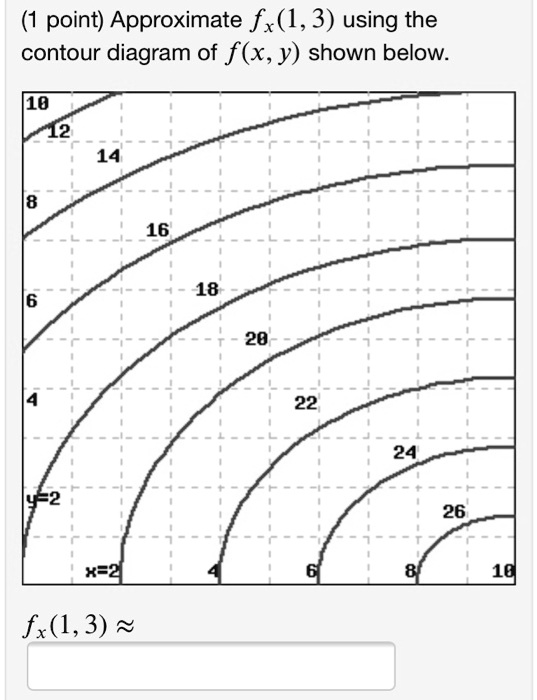
35 approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
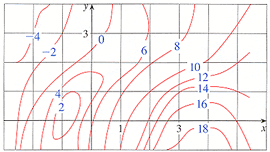
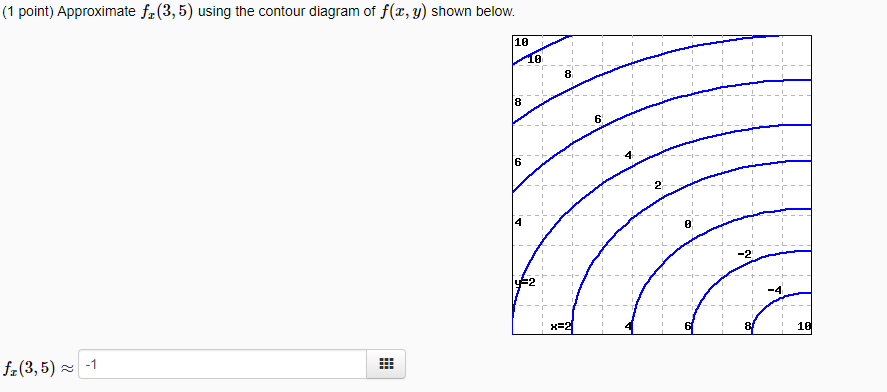
Answer to 16. (1 point) Approximate fr(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 14 12 10 2 *=2 of 10 fx (3, 5) ~ See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings)
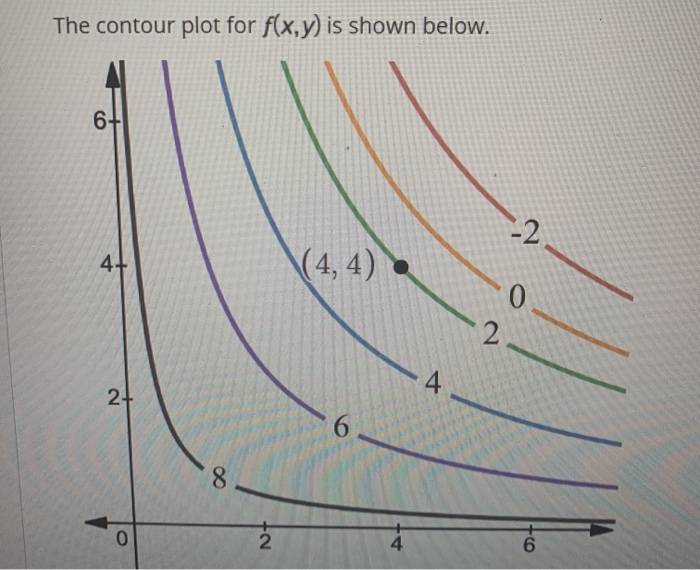
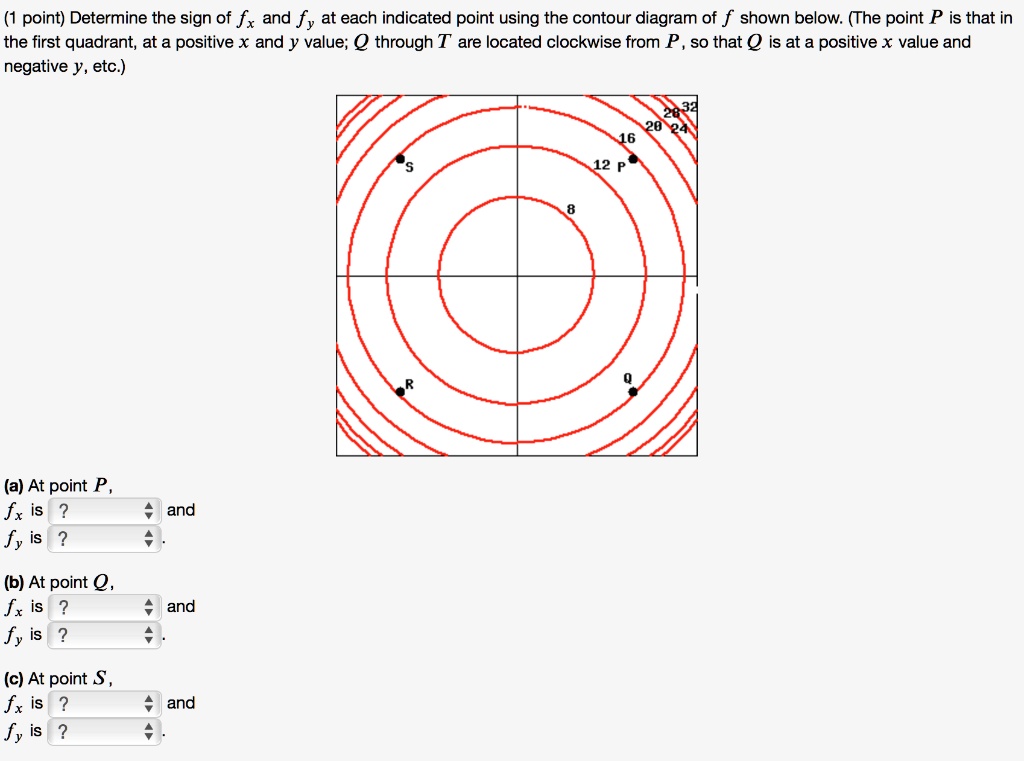
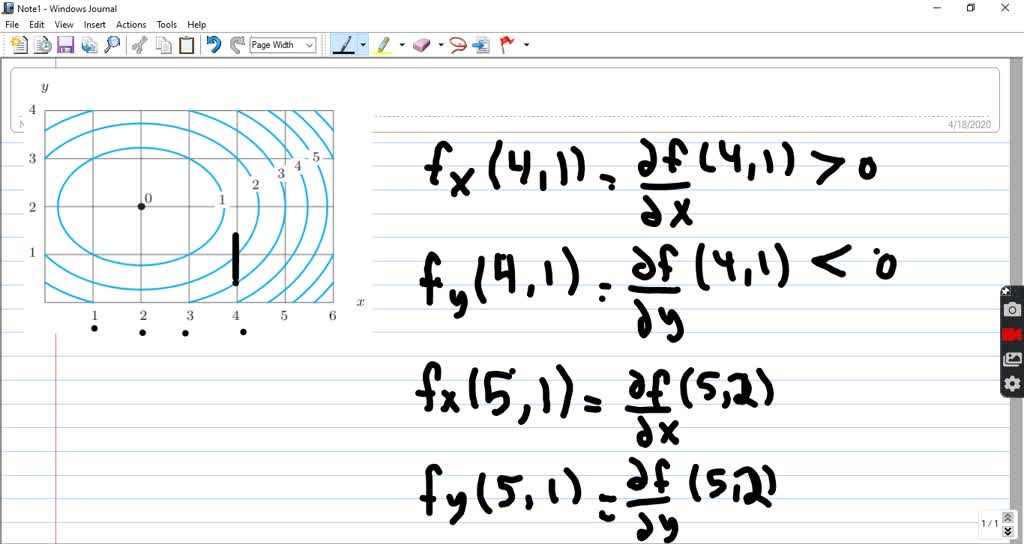
Math 205 HWK 11 Solns continued §14.7 p687 Problem 19, §14.7, p687. Use the given level curves of the function z = f(x,y) to decide the sign (positive, negative, or zero) of each of the following partial derivatives at the point P indicated
Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
a function f(x,y), recall that the gradient is hfx(x,y),fy(x,y)i, a vector that depends on (is a function of) x and y. We usually picture the gradient vector with its tail at (x,y), pointing in the direction of maximum increase. Vector fields that are gradients have some particularly nice properties, as we will see. An important example is F ... Solution for Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables.
Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.. 1 Answer to Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com Learning Objectives. 5.1.1 Recognize when a function of two variables is integrable over a rectangular region.; 5.1.2 Recognize and use some of the properties of double integrals.; 5.1.3 Evaluate a double integral over a rectangular region by writing it as an iterated integral.; 5.1.4 Use a double integral to calculate the area of a region, volume under a surface, or average value of a ... ASSIGNMENT 6 SOLUTION JAMES MCIVOR 1. Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f
F(x,y,z) = k at the point (a,b,c) is ∇F(a,b,c). The surface x2+xy2+xyz = 4 can be rewritten as F(x,y,z) = x2+xy2+xyz = 4, ∇F(x,y,z) = h2x+y2 +yz,2xy +xz,xyi and ∇F(1,1,2) = h5,4,1i Thus the equation of the tangent plane to the surface x 2+xy +xyz = 4 at the point (1,1,2) is h5,4,1i·hx−1,y −1,z −2i = 0 which yields 5x−5+4y −4+z ... 27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉. sponding point (1;0) is one of the corners, and we will consider it separately below. the line y= 0: f(x;0) = x2 2x: Computing the derivative and setting it to 0 we find 2x 2 = 0 =)x= 1. This gives the corner (1;0) as before. the line y= 2: f(x;2) = x2 +2x+4 with critical point x= 1 which is again a corner. Finally, we check the four corners (1 pt) Approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. For both parts of this problem, be sure you can explain what • negative • negative • negative 4. (1 pt) Approximate f y (1, 3) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. f y (1, 3) ≈ Correct Answers: • (16 - 18)/2.5
c. (G) (III) - Identical reasoning as the other two ex-amples. 12.Below is the contour diagram of f(x;y). x y 1 2 31 1 2 3 2 2 1 1 0 0-1-1-2-2 Sketch the contour ... Desmos offers best-in-class calculators, digital math activities, and curriculum to help every student love math and love learning math. If n →∞, R.H.S of the expression approaches the definite integral \(\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx\) Solved Examples. Go through the below given Trapezoidal Rule example. Example 1: Approximate the area under the curve y = f(x) between x =0 and x=8 using Trapezoidal Rule with n = 4 subintervals. A function f(x) is given in the table of values. Front Door - Valencia College
Free Riemann sum calculator - approximate the area of a curve using Riemann sum step-by-step This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy.
fullscreen Expand. Transcribed Image Text. Approximate f (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. 18 12 10 6 X=2 10. check_circle.
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of fx(x,y). I am very confused full credit for right answer. Show transcribed image text (1 point) Approximate fx(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below.
f(x+u1h,y)− f(x,y) h = fy. Example 1.3. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, ... Drawing a vector out from the point (1,1) in the direction of ~u =~i+~j, we can use a difference quotient to approximate the rate of change. Specifically, the vector ~u ...
Section 14.5 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview: The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x- and y-directions.Rates of change in other directions are given by directional
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text : (1 point) Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. fx(1,3) ^
(c) fxx ˘ @x (fx), so if we fix y and allow x to vary, fxx is the rate of change of fx as x increases.Note that at points to the right of P the level curves are closer together (in the x-direction) than at points to the left of P, demonstrating that f increases more quickly with respect to x to the right of P.So as we move through P in the positive x-direction the (positive) value
3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below.
Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 1 Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables.
Solution for Approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below.
a function f(x,y), recall that the gradient is hfx(x,y),fy(x,y)i, a vector that depends on (is a function of) x and y. We usually picture the gradient vector with its tail at (x,y), pointing in the direction of maximum increase. Vector fields that are gradients have some particularly nice properties, as we will see. An important example is F ...


















0 Response to "35 approximate fx(1,3) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment