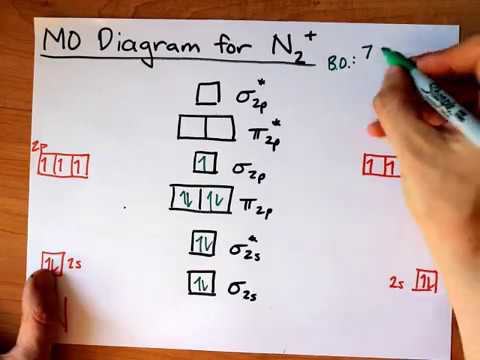
39 n2+ molecular orbital diagram
N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram General Wiring Diagram Answer to draw an mo energy diagram and predict the bond order of be2 and be2−. do you expect these molecules to exist in the. even rather simple molecular orbital (mo) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how mo diagrams are ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of N2 Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
Molecular orbital theory. How to draw Molecular orbital Diagram for Fluorine. How to draw molecular orbital diagram for oxygen atom / ion . How to draw molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen. How to draw molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen and helium. Difference between the Molecular orbital structure of ethene and ethyne

N2+ molecular orbital diagram
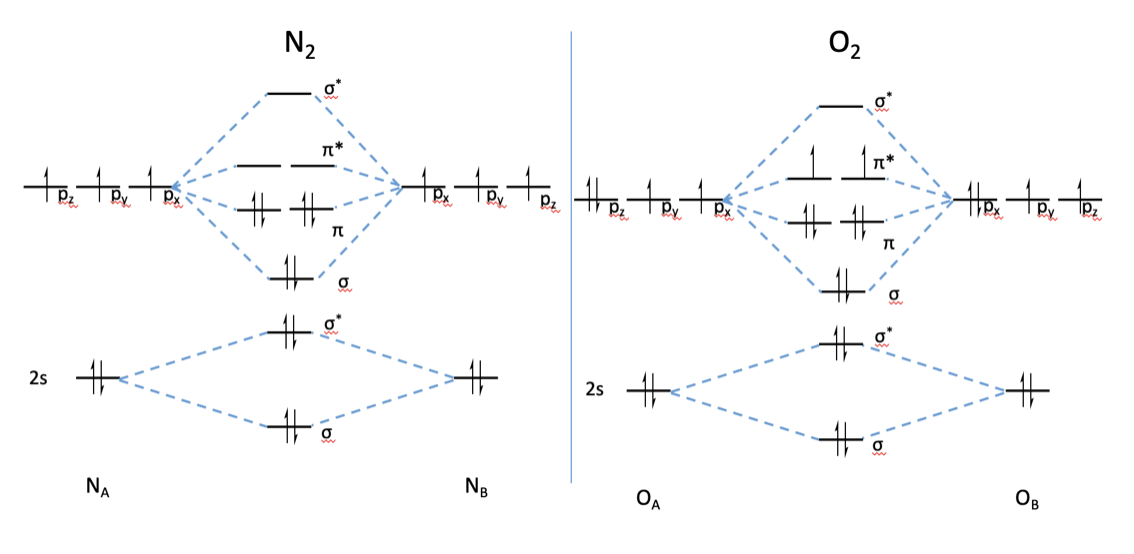
How many molecular orbital will be formed in the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atom? 10 molecular orbitals. How many electrons are in bonding orbitals in O2? Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for O2. Now we add the 12 electrons, 6 from each oxygen atom. Why mot of O2 is different from N2? O2 and N2 have different number of electrons.
Bond order is outlined because the variety of covalent bonds in a covalent molecule.It is the same as one half of the distinction between the variety of electrons within the bonding & antibonding molecular orbitals. Therefore, the bond order of oxygen molecule is 2. Which of the next has the very best bond order N2 N2 N2?
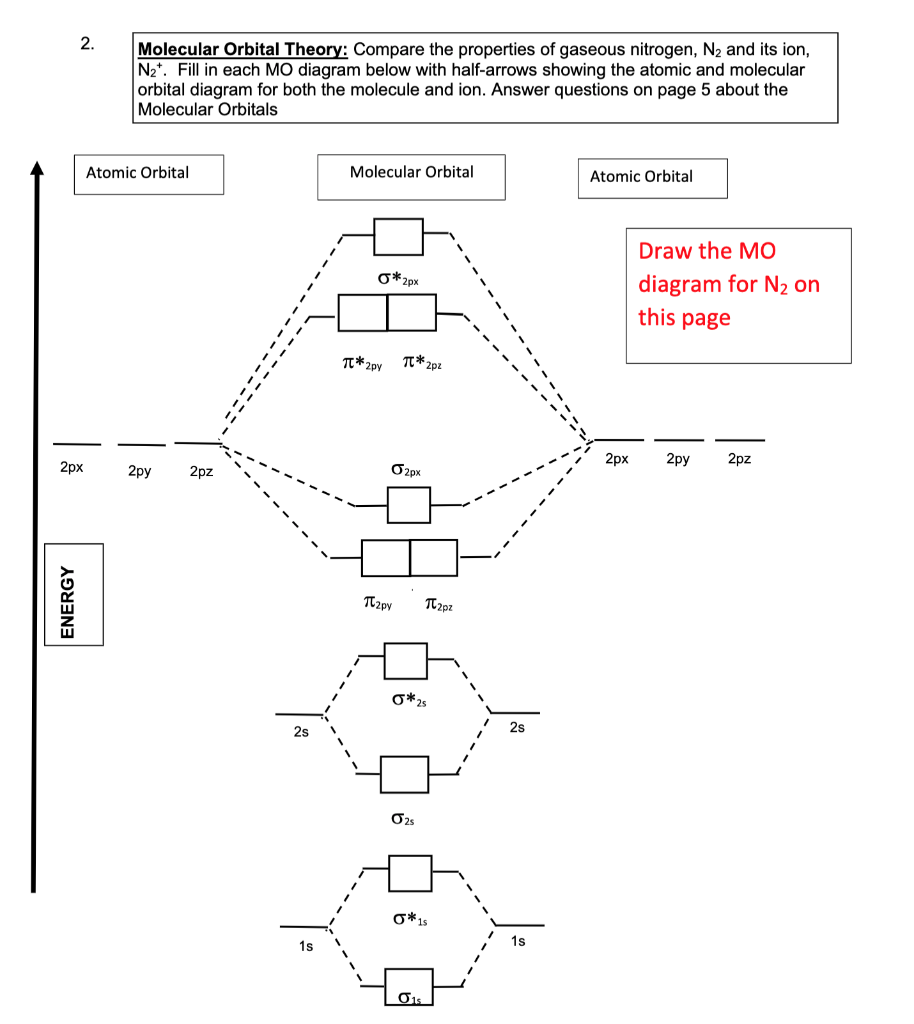
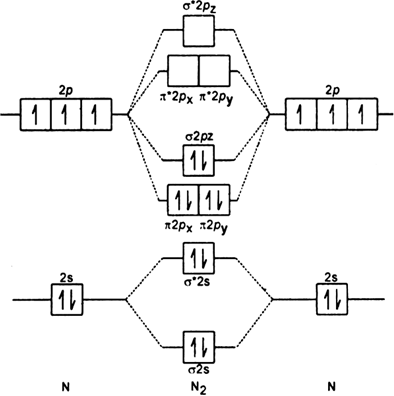
Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means.
N2+ molecular orbital diagram.
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
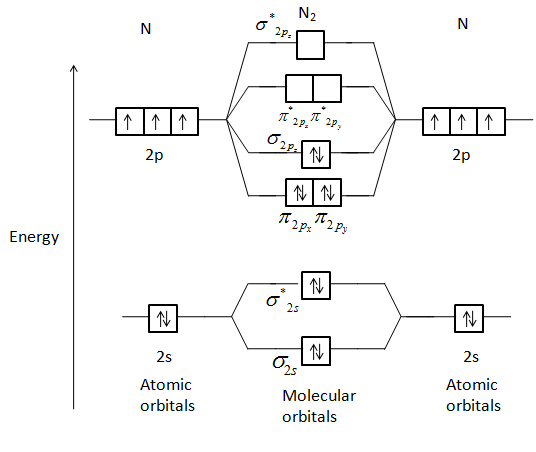
Aug 07, 2021 · Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each nitrogen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px. The other four p-atomic orbitals (two from each nitrogen) atom combine to give four molecular orbitals, two bonding molecular orbitals i.e. π2py and π2pz, while two ...
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Ne 2 + and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of molecule and write its molecular orbital configuration. Calculate the bond order and discuss the extra stability and diamagnetic nature of the molecule. 644038739 . 200+ 5.1k+ 8:34 .
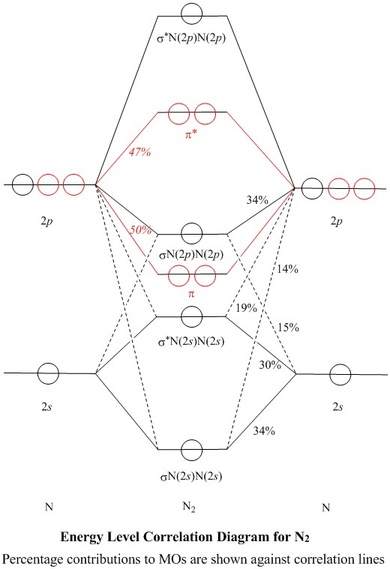
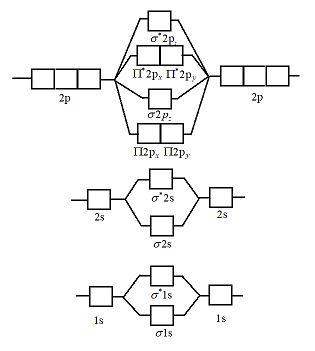
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is: N22- molecular orbital diagram. the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are LOWER than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.N2(2-) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that there will be a stable double ...
Molecular orbital Diagram that N2 Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron construction in regards to a sigma bond and also pi bond. According come molecular orbital theory, that tells about magnetic nature, security order, and also the number of bonds in a molecule.
Answer (1 of 3): In O2 2+, there is 14 electrons. So, it's MOT is comparable to N[code ]2[/code] & the MOT diagram will look like this :
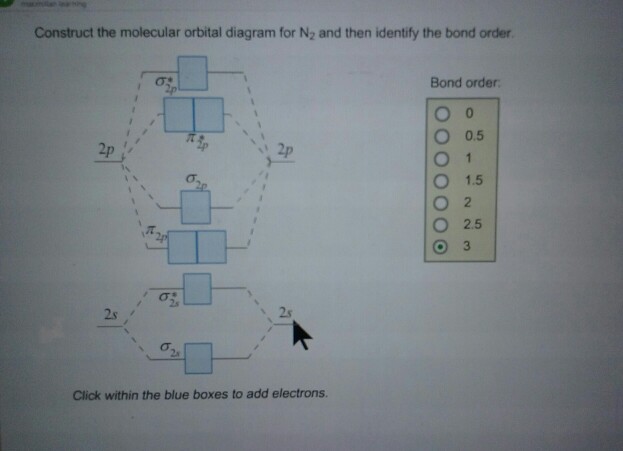
A draw the molecular orbital diagram. N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Interact and form molecular orbital s. B calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o. Consider the h 2 molecule for example. Sp mixing causes the σ g and σ u mos to be pushed apart in energy.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2 Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
For more detailed knowledge you can refer to the polarity of N2. Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2 Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
Solved Using The Molecular Orbital Diagram Depicted Below Which Species Have Bond Order Of 3 2p 2p 02p 72p Energy 2s Oa B2 B 02 2 C C22 D N2 Oeco Of Cn G Molecular orbital diagram for b2 . This interaction introduces an element of s p mixing or hybridization into the molecular orbital theory.
From the construction of the MO (molecular orbital) diagram for O 2 , a homonuclear diatomic molecule, it can be seen that there will indeed be two high-energy unpaired electrons. Not only this, but the spin and the position of these electrons in the OM also explain other electronic states of O 2 (singlet).
The MO method for N2+ gives the bond order equal to 2.5. But first, we look at the diagram of molecular orbitals for N2 (the bond order for the nitrogen molecule is 3). the N2+ molecule). That is, the bond order for N2+ is 2.5.
The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is :. The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons. Molecular orbital diagram for c2 2-. The bond order of B2, C2, and N2 are 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. By drawing molecular orbital diagram s for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would there for e ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbital s.. OM diagram for the N2 molecule.
12+ N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. One atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a n2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bon. Number of electrons in c2 molecule = 12.
14+ N2 Mo Diagram. With mo diagrams, we can predict the number of bonds in diatomic molecules. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s (2),sigma2s* (2),pi2p (4),sigma2p (2). N2 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram — UNTPIKAPPS from www.untpikapps.com
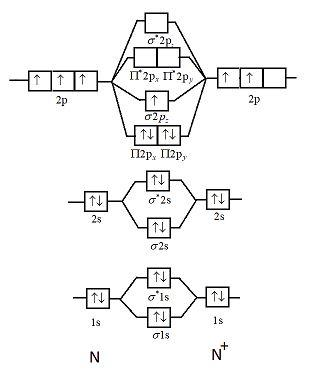
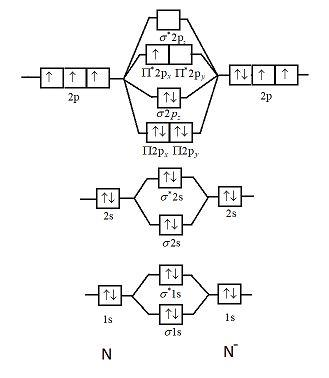
34 Be2 + Molecular Orbital Diagram.A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s method in particular. C would this ion exist. The first ten molecular orbital s may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s ) ∗(1s ...
Nov 21, 2018 · We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The ...
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
Oct 17, 2018 · Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm ...
Question: Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 Or He2+ Is More Stable. These properties can be explained by the molecular orbital diagram of BN". The bond order of two suggests that the oxygen molecule is stable. Correct option (a) O-2. Diamagnetic Metals + properties give you a broad overview of these metals from multiple angels.
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
Molecular Orbital Theory ODU April 10th, 2019 - molecular orbital energy level diagram for the NO molecule We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2 The bond order is 2 5 Figure 9 42 The molecular orbital energy level diagram for both the NO and CN ions Figure 9 43 A partial molecular orbital energy level diagram for the HF ...
How to draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2? Expert Answer: Molecular orbital diagram of N2 BO = [Nb-Na] = [10-4] = 3 Since all the electrons in nitrogen are paired, it is diamagnetic molecule.
principal quantum number (n) → energy level in orbitals and its value could be any positive integer starting from 1 to infinity. The set of quantum numbers that is correct and consistent with n = 4 is (A) l = 3 m l = -3 m s = +1/2. What are the four quantum numbers of 1s1? 1.1.
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
But first, we look at the diagram of molecular orbitals for N2 (the bond order for the nitrogen molecule is 3). the N2+ molecule). That is, the bond order for N2+ is 2.5. Can you have a bond order of 0? Conversely, placing electrons into the antibonding orbitals will decrease the stability of the molecule.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s (LCAO) method in particular. There are two mo diagram s you need to memorize for diatoms n2 o2 ne2 etc.

![Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d20/b492acf8cb9ff01954c3929a3b7a93c7.jpg)

















0 Response to "39 n2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment