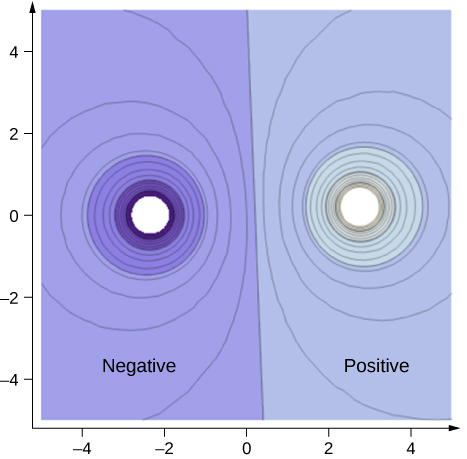
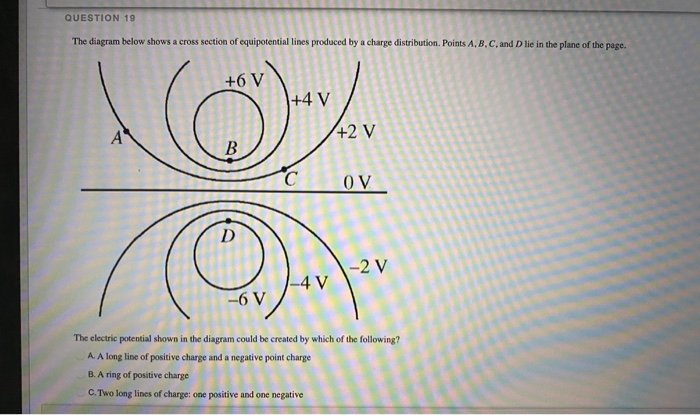
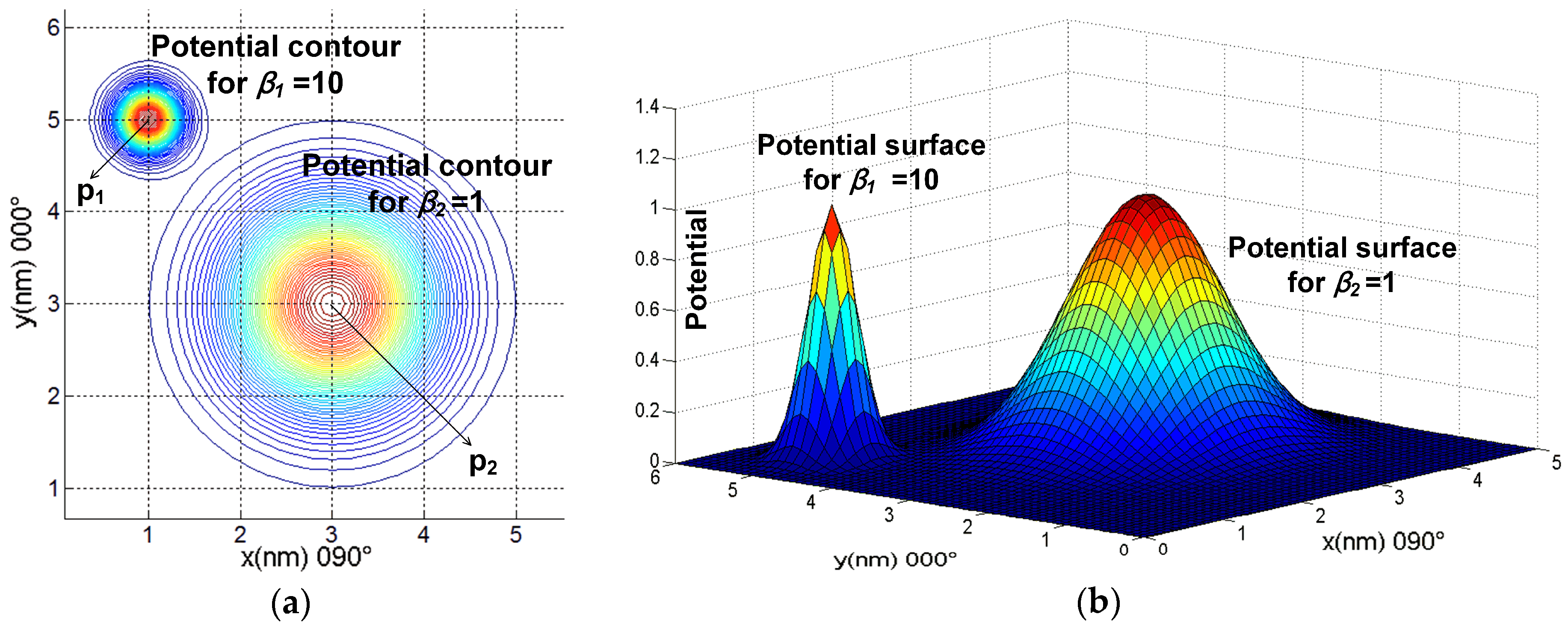
38 the same diagram could also represent the contours of the electric potential
Note that in this equation, E and F symbolize the magnitudes of the electric field and force, respectively. Neither q nor E is zero; d is also not zero. So must be 0, meaning must be .In other words, motion along an equipotential is perpendicular to E.. One of the rules for static electric fields and conductors is that the electric field must be perpendicular to the surface of any conductor.
a) Both charges experience the same net force directed away from each other. 1. If a negatively charged particle is placed at rest in an electric potential field that increases in the positive x-direction, the particle will. (a) accelerate in the positive x-direction. (b) accelerate in the negative x-direction.
a) Both charges have the same sign, equal magnitude, and the grass seeds representation is the electric field. b) Both charges have the same sign, equal magnitude, and the grass seeds representation is the electric potential. c) The charges have opposite signs, equal magnitude, and the grass seeds representation is the electric field.
The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electric potential
Equipotential Lines. Equipotential lines are like contour lines on a map which trace lines of equal altitude. In this case the "altitude" is electric potential or voltage.Equipotential lines are always perpendicular to the electric field.In three dimensions, the lines form equipotential surfaces.
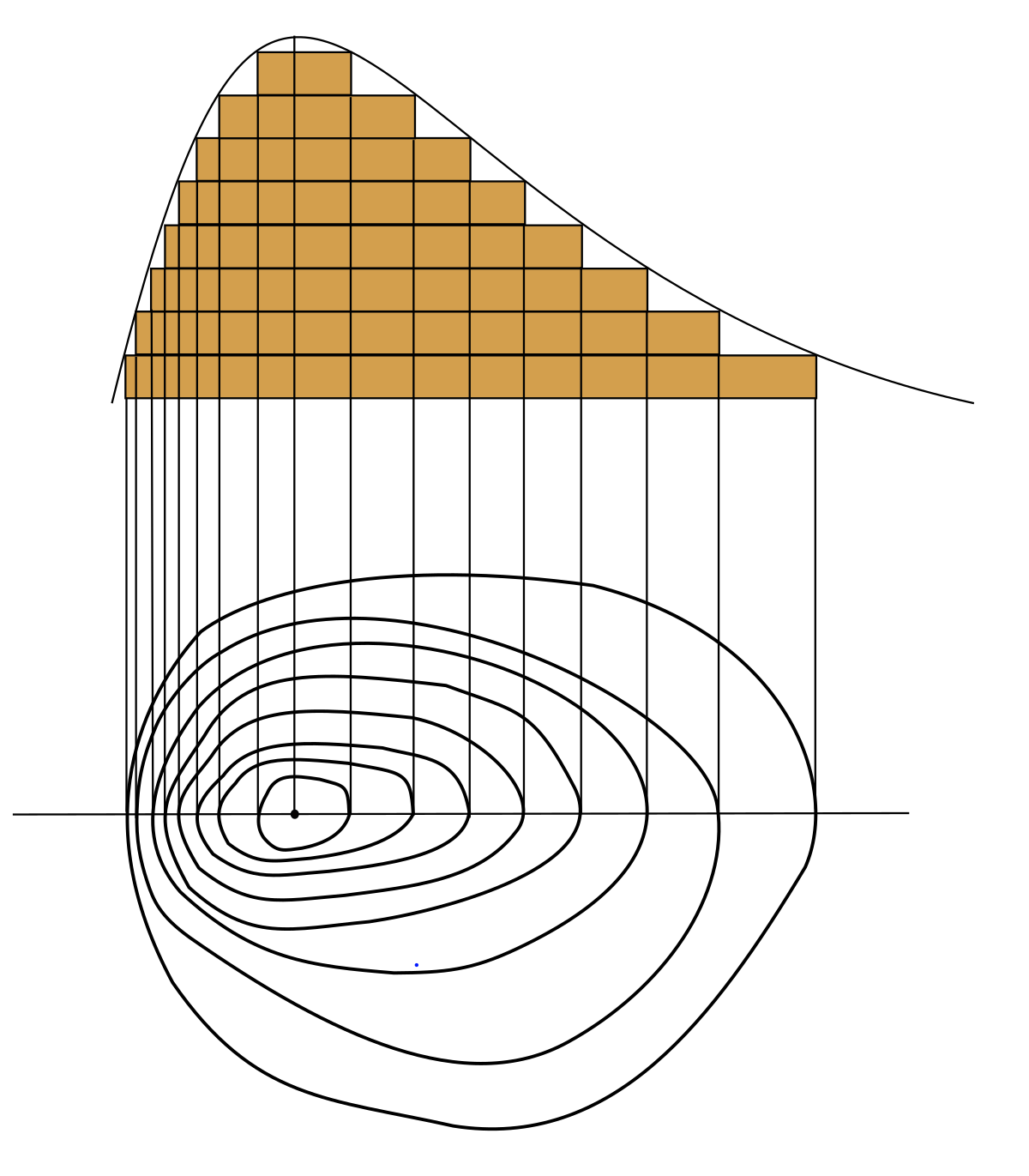
Each contour line going towards the center represents an equipotential surface with a potential 5 V greater than the previous contour. a) Where is the electric ...
Calculate the electric potential associated with the proton's electric field at this distance. Solution The potential of the proton, at the position of the electron (both of which may be regarded as point-charge atomic constituents) is (Equation 25-4) V = ke=a 0, where a 0 is the Bohr radius. Numerically, V = (9 ×10 9 N ⋅ m2/C2) × (1.6 × 10
The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electric potential.
A book held 1 meter above the floor has potential energy. The book is dropped and hits the floor. ... The diagram represents the ear of a human. ... Jamaican sprinter Usain Bolt, also known as "Lightning Bolt," is considered to be the fastest person to date. The 94.0-kg Bolt set an Olympic record by running the 100-meter dash in 9.63 seconds.
points of the same electric potential. All electric field lines cross all equipotential lines perpendicularly. 4. a. The work along an electric field line depends on the magnitude of the charge and the potential difference through which the charge is moved. b. No work is required to move a charge along an equipotential line because no force is
Diagrams of equipotential lines give us information about the gravitational field in much the same way as contour maps give us information about geographical heights. What does it mean on a contour map if the contours are very close together? (On a contour map, the contours may be marked off at, say, 5 m intervals. Therefore, if they are close ...
Potential Lines Lines of constant ! are called potential lines of the flow. In two dimensions ! d"= #" #x dx+ #" #y dy d"=udx+vdy Since ! d"=0 along a potential line, we have ! dy dx =" u v (4.4) Recall that streamlines are lines everywhere tangent to the velocity, ! dy dx = v u, so potential lines are perpendicular to the streamlines. For ...
The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electrical potential of two positively charged objects with irregular shapes (for example charges stored on a rubber sheet). Assume that the outer part of the figure is at zero potential. Each contour line
The diagram shows an electric circuit containing a potentiometer of maximum resistance R. The potentiometer is connected in series with a resistor also of resistance R. The electromotive force (emf) of the battery is 6 V and its internal resistance is negligible. The slider on the potentiometer is moved from P 1 to P 2.
Chapter 28 The Electric Potential Chapter Goal: To calculate and use the electric potential and electric potential energy. ... They have the same potential energy. D. Both have zero potential energy. Slide 28-26 Increasing PE ... diagram for a positively charged particle in a uniform electric field. The potential
densities to be at the same potential. Also electric field is larger for the small sphere and at right angles to the surface. The electron-volt as an energy unit Explain why an electron-volt (eV) is a unit of energy, not a voltage. Which is larger, a gigaelectron-volt or a
i. Both plates have the same electric potential ii. There is a uniform electric field iii. It would take the same external work to move a positive particle from A to B as it would to move it from B to A. A. i B. ii C. ii and iii D. i and iii E. i, ii and iii 6. What is the electric potential at point c if each side of the triangle has a length s?
Electric potential Today, we focus on electric potential, which is related to potential energy in the same way electric field is related to force. Electric potential, like field, is a way to visualize how a charged object, or a set of charged objects, affects the region around it. A voltage is essentially a difference in electric potential, which
The distance between any two contour lines in the diagram represents the horizontal distance between points on the two different countours. North is up. The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electrical potential of two positively charged objects with irregular shapes (for example charges stored on a rubber sheet).
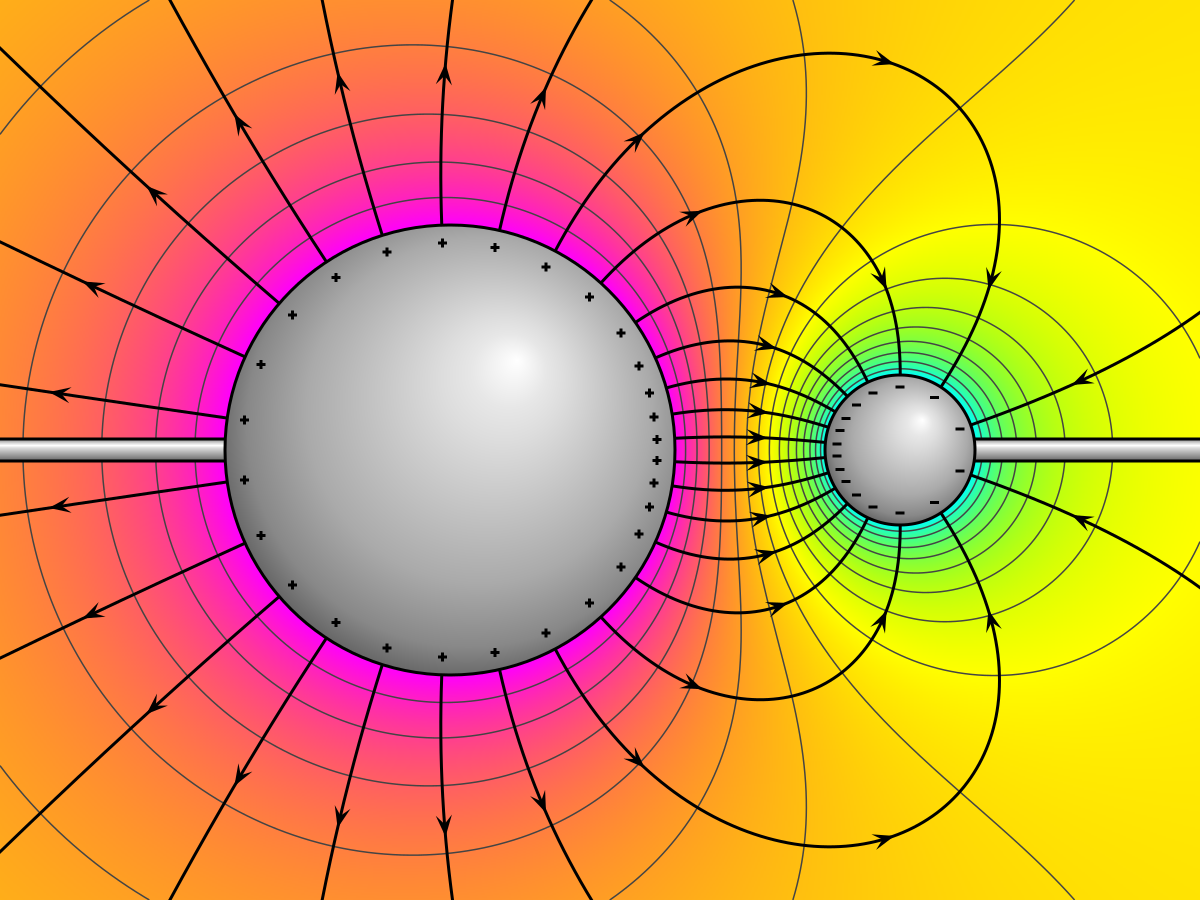
Potential from a charged sphere • The electric field of the charged sphere has spherical symmetry. • The potential depends only on the distance from the center of the sphere, as is expected from spherical symmetry. • Therefore, the potential is constant on a sphere which is concentric with the charged sphere. These surfaces are called
A potential difference of 8 000 V is applied across two parallel plates set 5.0 mm apart. What is the acceleration on an electron placed in the field. a Example 2 The electric field strength between two parallel plates is 930 V/m when the plates are 7.0 cm apart What is the electric field strength when the plates are moved to a point
The electric potential, , at a particular point can be defined in terms of the electric potential energy, , associated with an object of charge q being placed at that point:, or . (Eq. 17.3: Connecting electric potential and potential energy) The unit for electric potential is the volt (V). 1 V = 1 J/C.
A moving electron is deflected by two oppositely charged parallel plates, as shown in the diagram below. Electron The electric field between the plates is directed from (C) CtoD (D) DtoC (B) 13toA The diagram below represents a source of potential difference connected to two large, parallel metal plates separated by a distance of 4.0 x 10 meter.
The bottom part of the diagram shows some contour lines with a straight line running through the location of the maximum value. The curve at the top represents ...
12.Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents an electric circuit consisting of four resistors and a 12-volt battery. A)72 B)18 C)3.0 D)0.33 What is the equivalent resistance of this circuit? A)1 B)2 C)8 D)4 13.Two identical resistors connected in series have an
We can represent electric potentials (voltages) pictorially, ... The term equipotential is also used as a noun, referring to an equipotential line or ...
The free electron model of metals has been used to explain the photo-electric effect (see section 1.2.2).This model assumes that electrons are free to move within the metal but are confined to the metal by potential barriers as illustrated by Figure 2.3.1.The minimum energy needed to extract an electron from the metal equals qF M, where F M is the workfunction.
A useful means of visually representing the vector nature of an electric field is through the use of electric field lines of force. A pattern of several lines are drawn that extend between infinity and the source charge or from a source charge to a second nearby charge. The pattern of lines, sometimes referred to as electric field lines, point in the direction that a positive test charge would ...
(A) the same everywhere in the circuit (C) greater at point X than at point Y (B) greater in the 1 resistor than in the 2 resistor (D) greater in the 2 resistor than in the 3 resistor 16. Two concentric circular loops of radii b and 2b, made of the same type of wire, lie in the plane of the page, as shown above.
The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electrical potential of two positively charged objects with irregular shapes (for example charges ...
The same diagram could also represent the contours of the electrical potential of two positively charged objects with irregular shapes (for example charges stored on a rubber sheet). Assume that the outer part of the figure is at zero potential.
In the same way, we can define a potential which is created by a particle (gravitational potential is created by mass, electric potential by charge) and which then gives to other particles a potential energy. So, we define electric potential, V, and given the potential can calculate the field: ∆= ∫ G VV B G dV BA−V=−Es⋅d ⇒ in 1D E ...
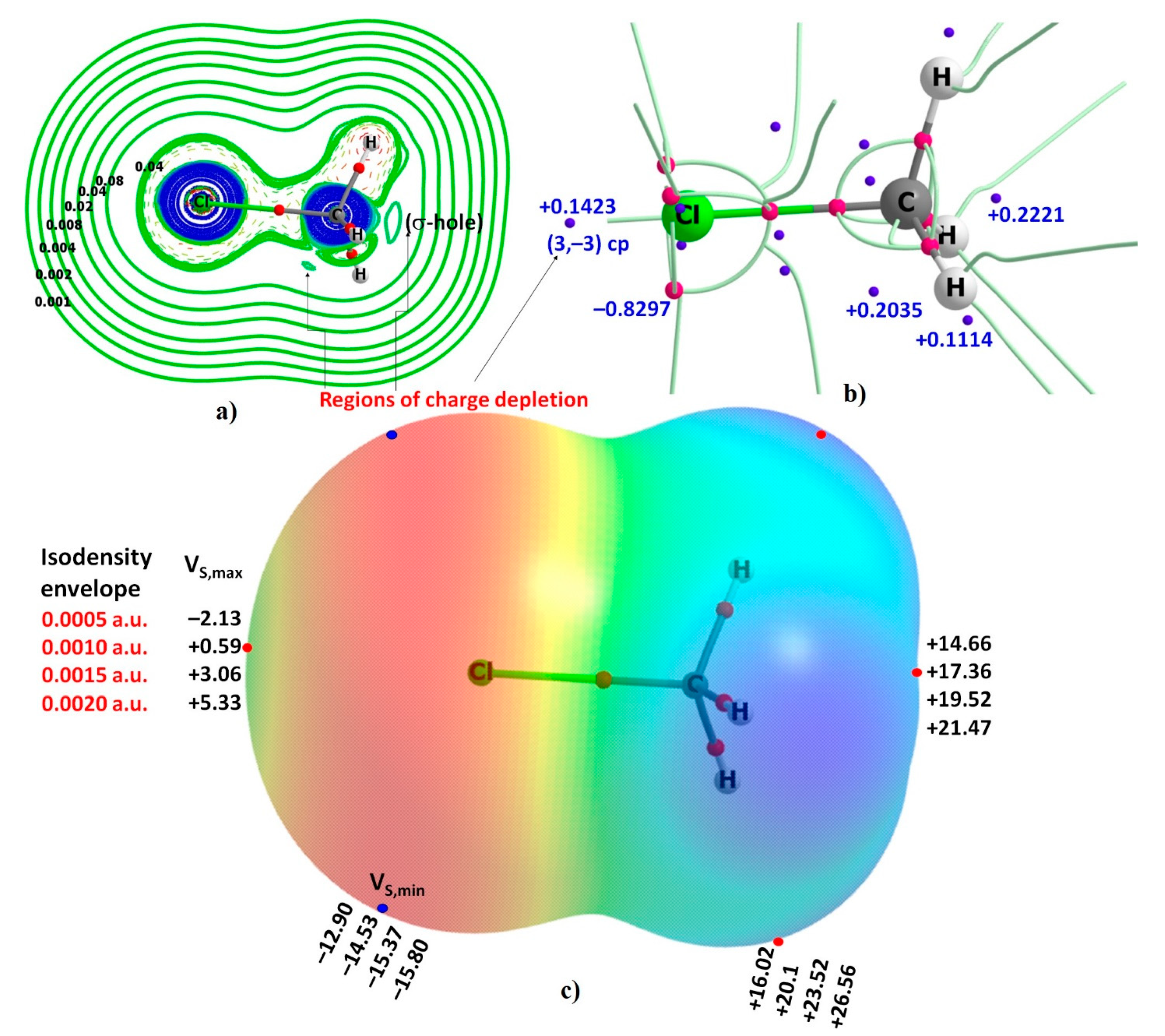
Aug 15, 2020 — Electrostatic potential maps, also known as electrostatic potential energy maps, or molecular electrical potential surfaces, illustrate the ...
Electric Potential Diagrams. An electric potential diagram is a convenient tool for representing the electric potential differences between various locations in an electric circuit. Two simple circuits and their corresponding electric potential diagrams are shown below. In Circuit A, there is a 1.5-volt D-cell and a single light bulb.
Using the diagram to the left, rank each of the given paths on the basis of the change in electric potential. Rank the largest-magnitude positive change (increase in electric potential) as largest and the largest-magnitude negative change (decrease in electric potential) as smallest. from b to a from f to e from c to d from c to e from c to b ...
In the same way, we can define a potential which is created by a particle (gravitational potential is created by mass, electric potential by charge) and which then gives to other particles a potential energy. So, we define electric potential, V, and given the potential can calculate the field: ()in 1D B BAA dV VVV d E dz ∆=−=−∫ Es⋅ ...



















0 Response to "38 the same diagram could also represent the contours of the electric potential"
Post a Comment