38 g protein coupled receptors diagram
As already stated earlier (slide 1.2.3), G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) form the largest class of drug targets in the human body. It is therefore appropriate to examine and understand them in some detail. The human genome contains genes for several hundred GPCRs. For a bit less than half of these, the ligands and physiological functions are not yet known. Once these …
by S Basith · 2018 · Cited by 68 — G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) belong to a large family of signaling proteins that mediate cellular responses to most hormones, metabolites ...
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), protein located in the cell membrane that binds extracellular substances and transmits signals from these substances to ...Key People: Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. KobilkaRelated Topics: receptor G-protein
G protein coupled receptors diagram
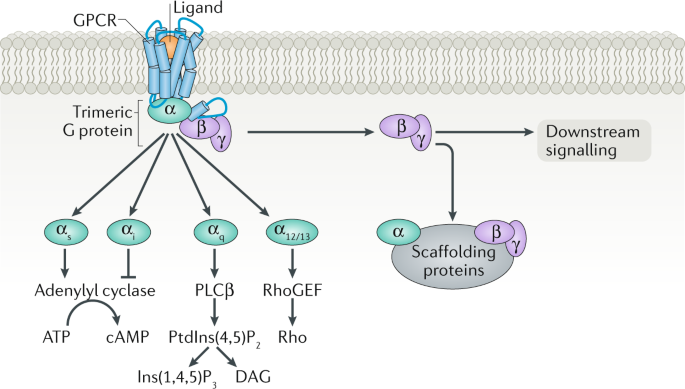
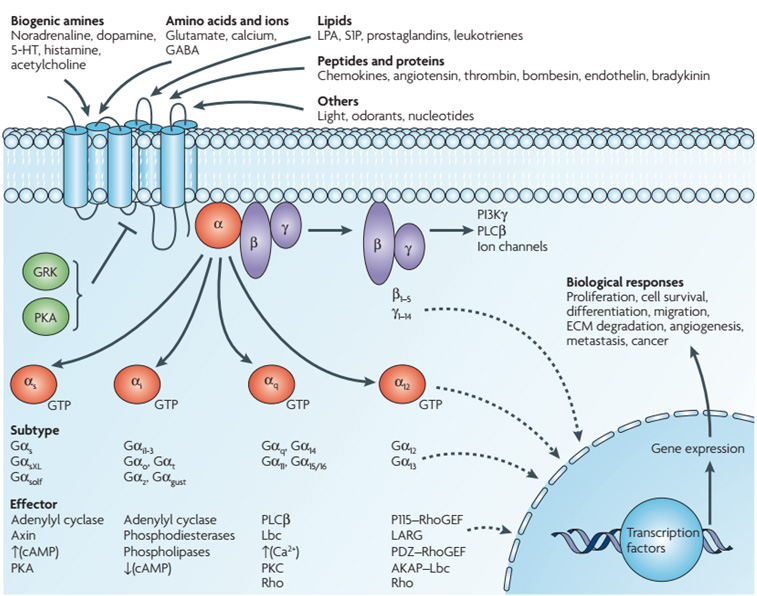
G q protein alpha subunit is a family of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits.This family is also commonly called the G q/11 (G q /G 11) family or G q/11/14/15 family to include closely related family members. G alpha subunits may be referred to as G q alpha, G αq, or G q α. G q proteins couple to G protein-coupled receptors to activate beta-type phospholipase C (PLC-β) …
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest and most diverse group of membrane receptors in eukaryotes. These cell surface receptors act like an ...
08.01.2021 · G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest protein family encoded by the human genome. Located on the cell membrane, they transduce extracellular signals into key physiological ...
G protein coupled receptors diagram.
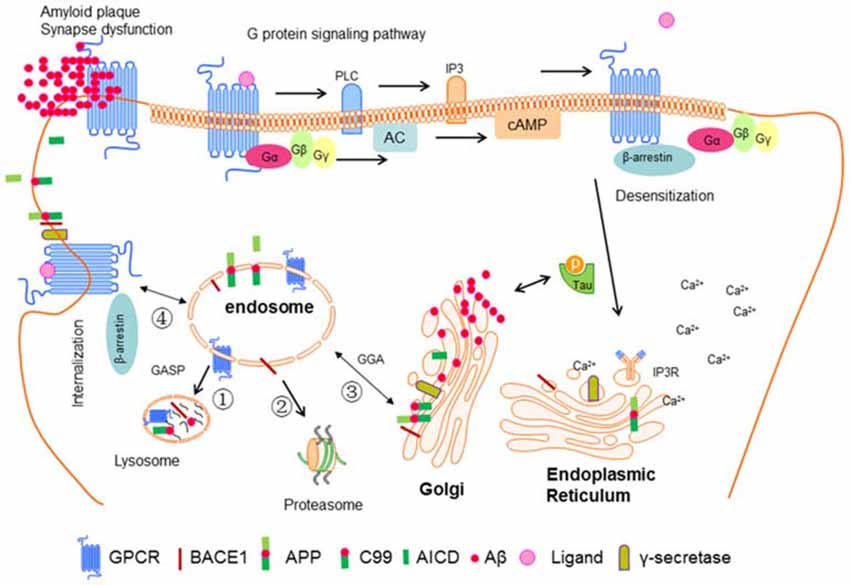
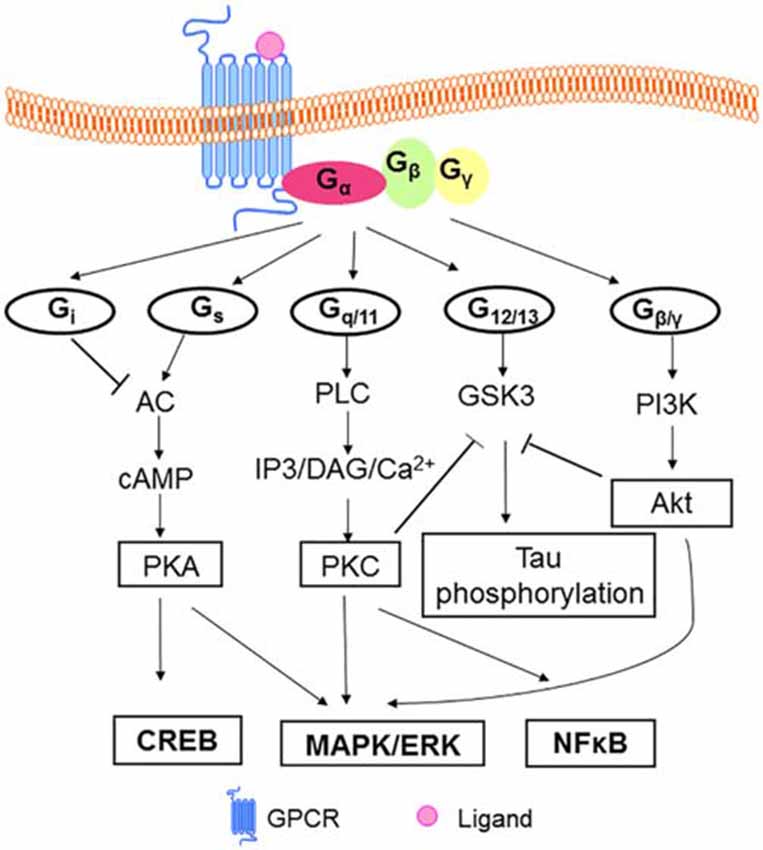
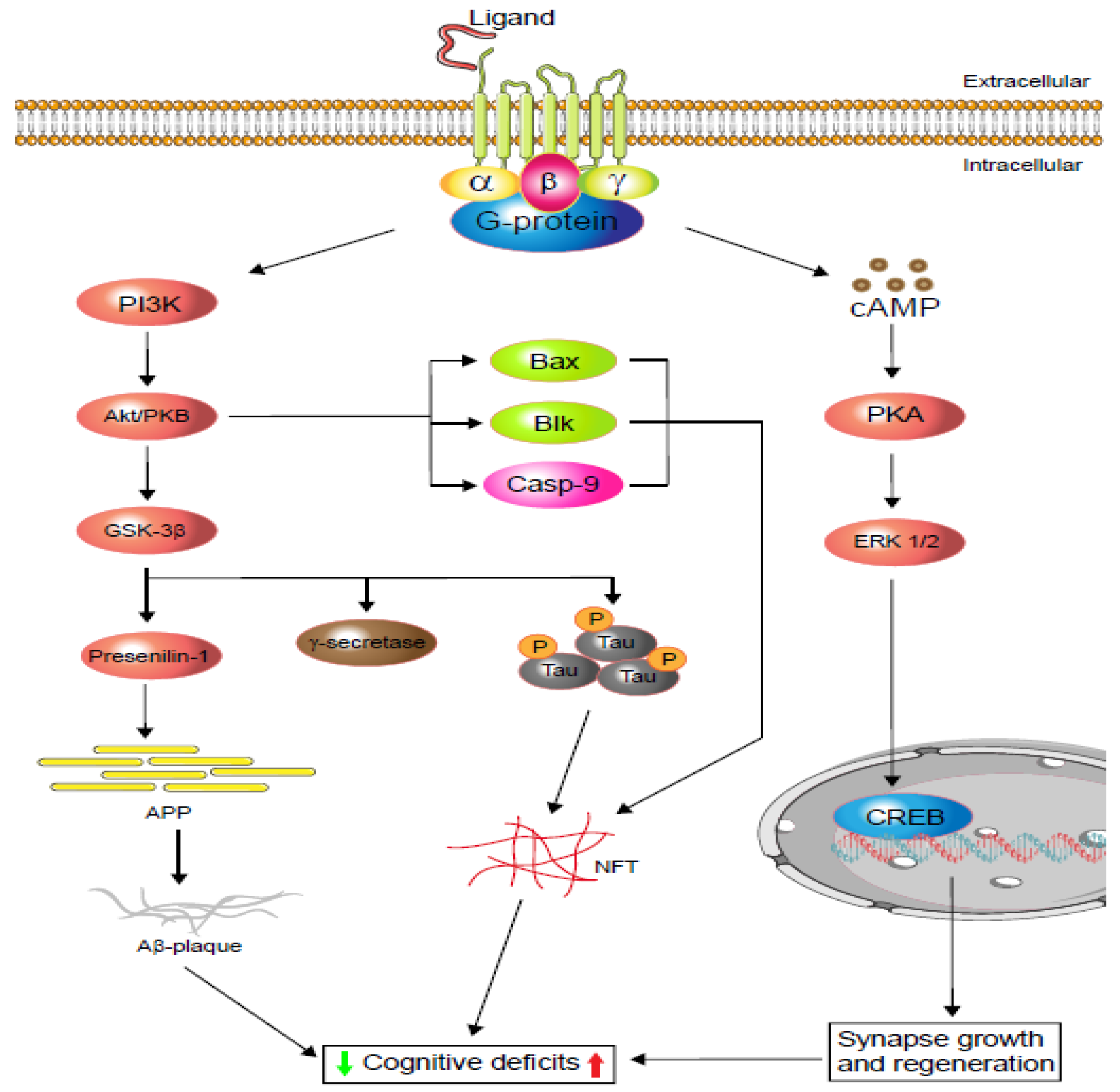
07.06.2021 · G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, can regulate vascular contraction by activating second messengers, including cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), inositol trisphosphate (IP 3), and Ca 2+ . It is known that 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), angiotensin II (Ang II), and urotensin II (UII) are strong …
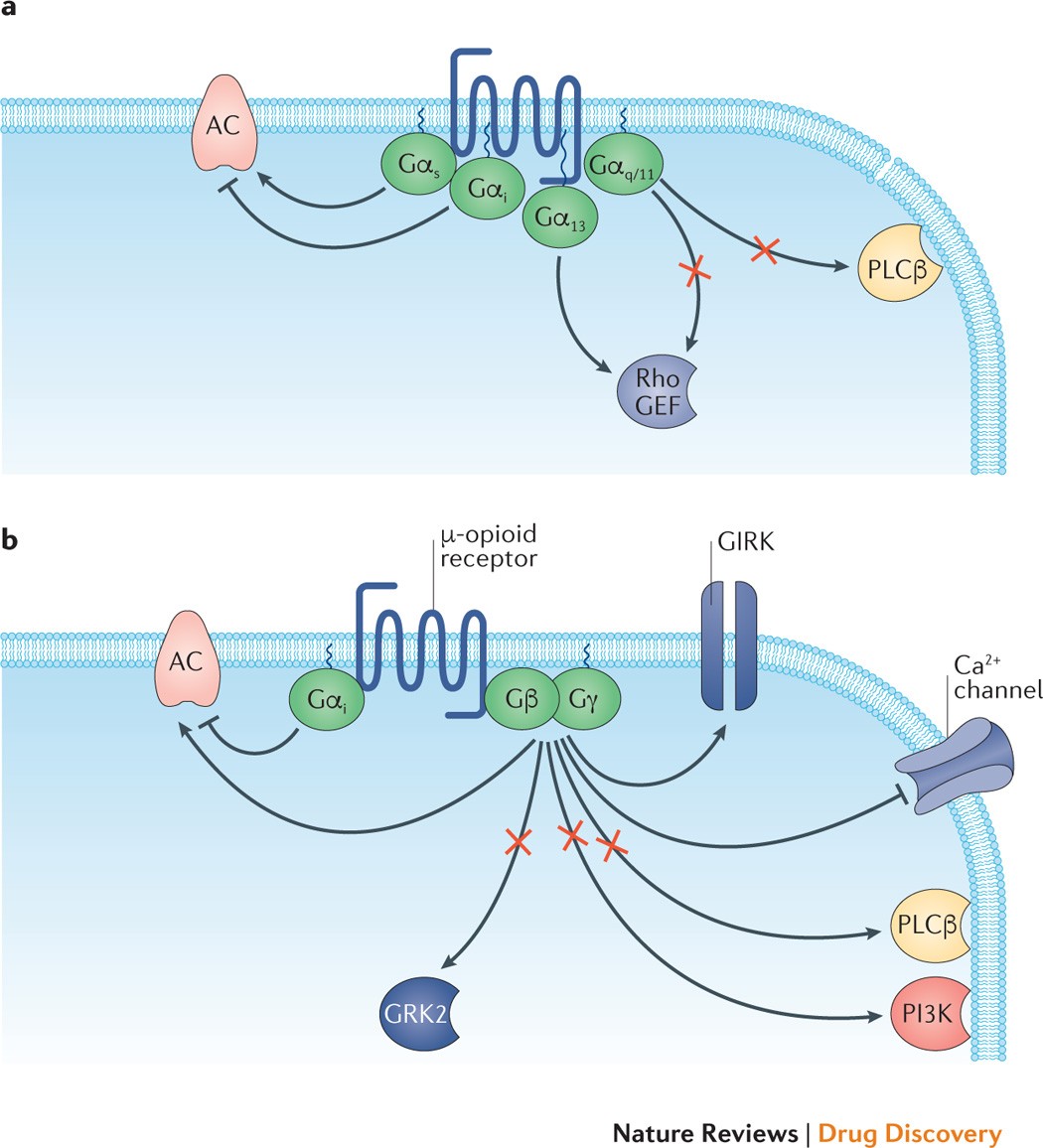
Diagram - G-protein coupled receptor common downstream activation pathways. In this diagram, lines ending in arrows (such as acting on adenylyl cyclase in Gs) indicate an increase in action, and lines ending in a 'T' shape (such as acting on adenyly cyclase in Gi) indicate a decrease in action. SimpleMed original by Thomas Burnell
Intracellular receptors, ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and receptor tyrosine kinases. Types of signaling molecules and the receptors they bind to on target cells. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on …
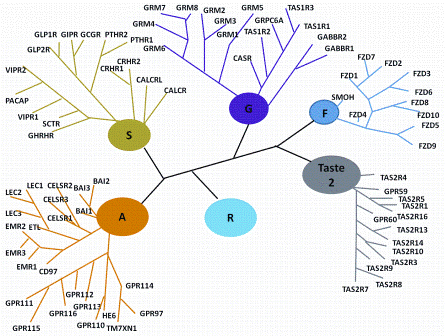
The G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) superfamily comprise similar proteins arranged into families or classes thus making it one of the largest in the mammalian genome. GPCRs take part in many vital physiological functions making them targets for numerous novel drugs. GPCRs share some distinctive features, such a 2020 Reviews in RSC Advances
05.10.2007 · Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptors constitute the largest family of eukaryotic signal transduction proteins that communicate across the membrane. We report the crystal structure of a human beta2-adrenergic receptor-T4 lysozyme fusion protein bound to the partial inverse agonist carazolol at 2.4 angstrom resolution. The …
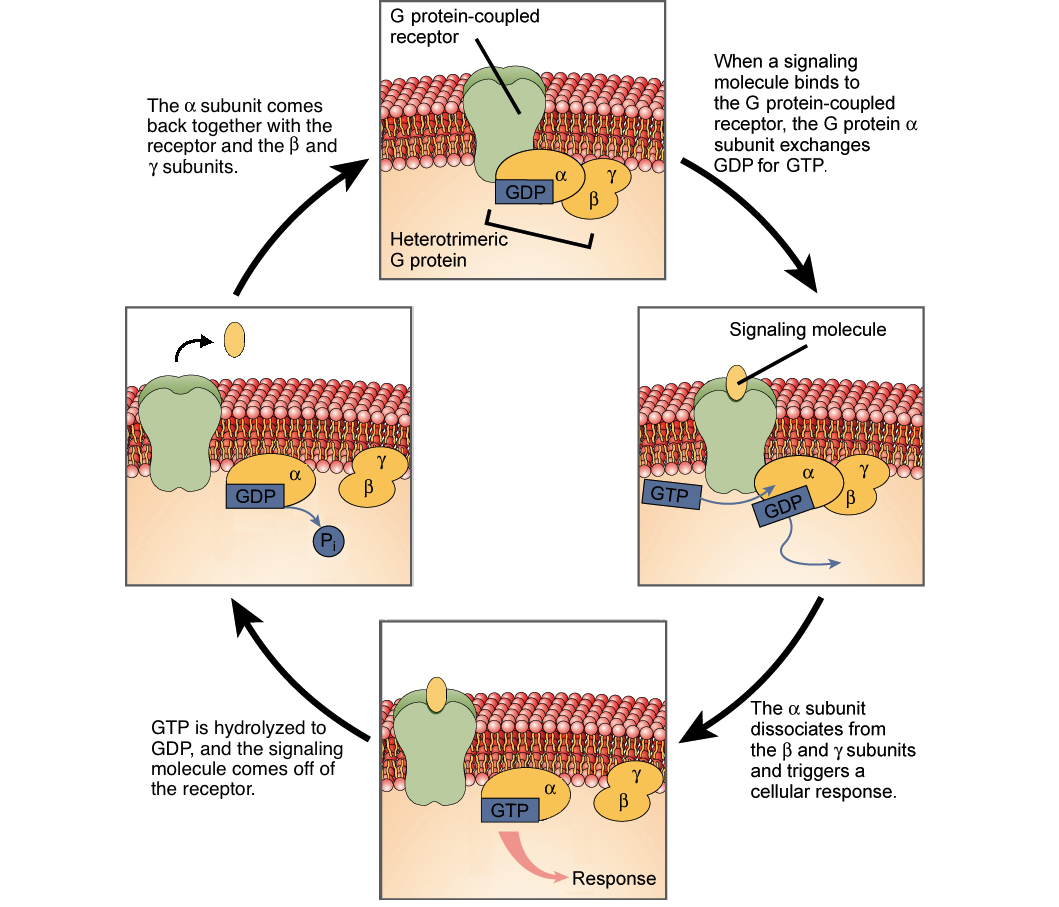
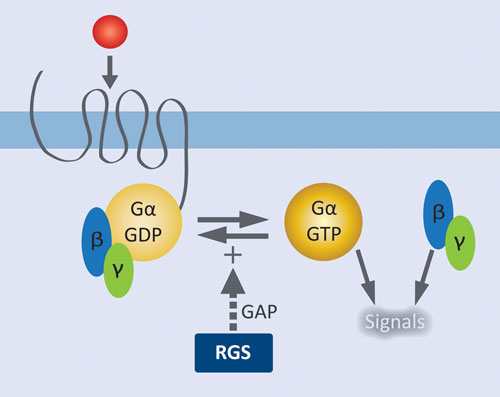
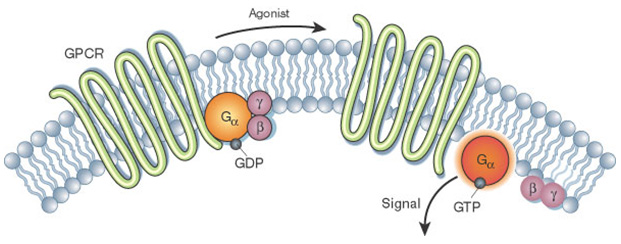
Once the G-protein binds to the receptor, the G-protein changes shape, becomes active, and splits into two different subunits. One or both of these subunits may be able to activate other proteins as a result. Figure 5 When a signaling molecule binds to a G-protein-coupled receptor in the plasma membrane, a GDP molecule associated with the G ...
G Protein-Coupled Receptors Examples: Beta-adrenergic receptors that bind epinephrine; prostaglandin E2 receptors that bind inflammatory compounds called prostaglandins; and rhodopsin, which contains a photoreactive molecule called retinal that responds to light signals received by rod cells in the eye, are all examples of GPCRs.
G protein can refer to two distinct families of proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, sometimes referred to as the "large"; G proteins, are activated by G protein-coupled receptors and are made up of alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) subunits. "Small"; G proteins (20-25kDa) belong to the Ras superfamily of small GTPases.
Receptor-G protein interactions (chimeras, mutagenesis, peptide blocking etc): 1. efficacy and selectivity of G-protein interactions probably depend on the proper combination of multiple specific cytoplasmic receptor regions 2. residues at cytoplasmic ends of all helices and nearby loops have been implicated for
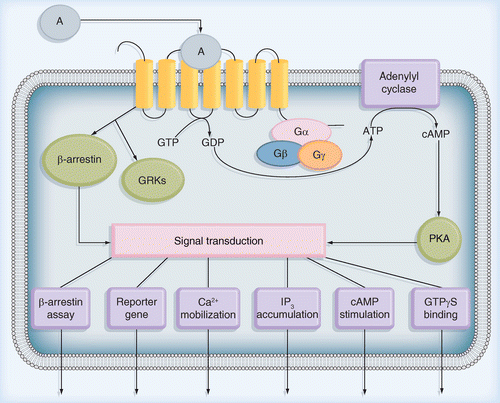
These receptors are coupled to intracellular GTP-binding proteins (G-proteins). Once activated, G-proteins trigger the production of a variety of second messengers (e.g. cyclic AMP [cAMP], inositol triphosphate [IP3], diacylglycerol [DAG], etc.) helping to regulate a number of body functions ranging from sensation to growth to hormone release.
G-protein coupled receptors are only found in eukaryotes and they comprise of the largest known class of membrane receptors. In fact humans have more than 1,000 known different types of GPCRs, and each one is specific to a particular function. They are a very unique membrane receptor and they are the target of around 30 to 50% of all modern ...
The past two years have seen remarkable advances in the structural biology of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Highlights have included solving the first crystal structures of ligand-activated GPCRs—the human β 2 adrenergic receptor (β 2 AR), the avian β 1 AR and the human A 2A adenosine receptor—as well as the structures of opsin and an active form of rhodopsin.
08.11.2017 · Based on their canonical structure, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are sometimes termed heptahelical or 7-transmembrane receptors, are the largest family of membrane receptors in humans and numerous other species. In addition, GPCRs are considered the largest family of targets for approved drugs Allen and Roth, 2011; Rask-Andersen et al., …
G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors ...OPM protein: 1gzmSymbol: 7tm_1OPM superfamily: 6
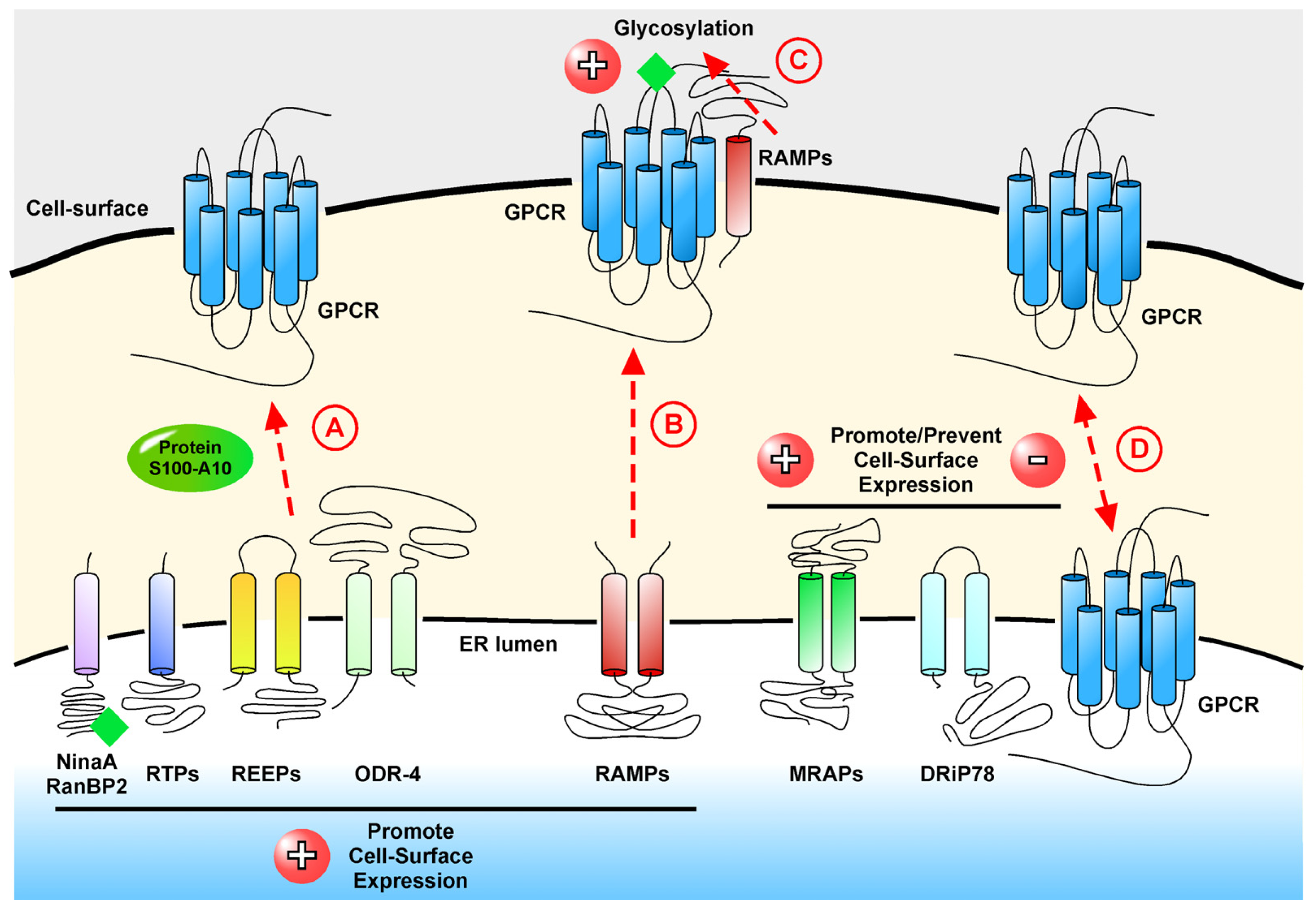
Introduction. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the largest protein family encoded by the human genome. Located on the cell membrane, they transduce extracellular signals into key physiological effects. 1 Their endogenous ligands include odors, hormones, neurotransmitters, chemokines, etc., varying from photons, amines, carbohydrates, lipids, peptides to proteins.



















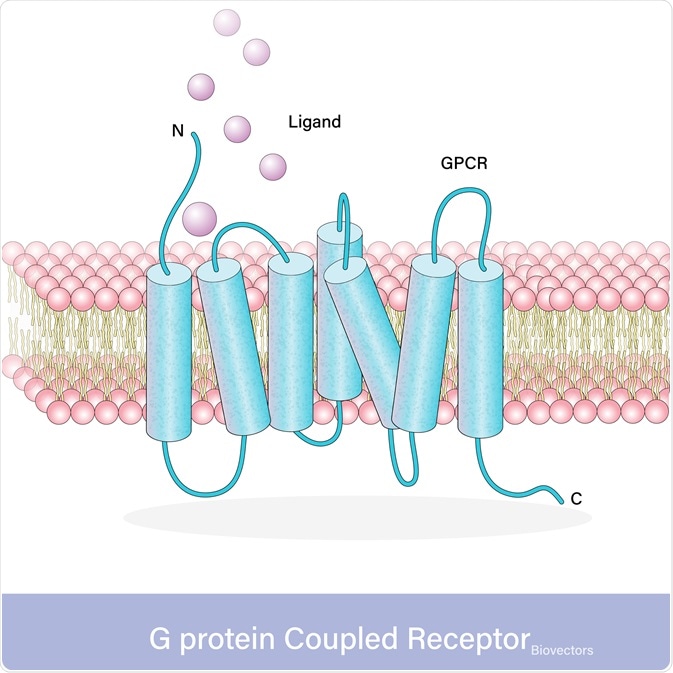

0 Response to "38 g protein coupled receptors diagram"
Post a Comment