38 free body diagram inclined
Jul 24, 2013 — Free Body Diagrams. Representation of all the forces acting on an object. Free-body diagram. The free-body diagram of the entire beam is shown in Figure 3.11b. Computation of reactions. Observe that the distributed loading in the beam is triangular. The distributed load is first replaced with a single resultant force, as shown in Figure 3.11c. The magnitude of the single resultant force is equal to the area under the ...
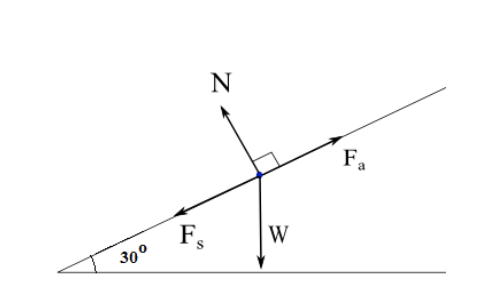
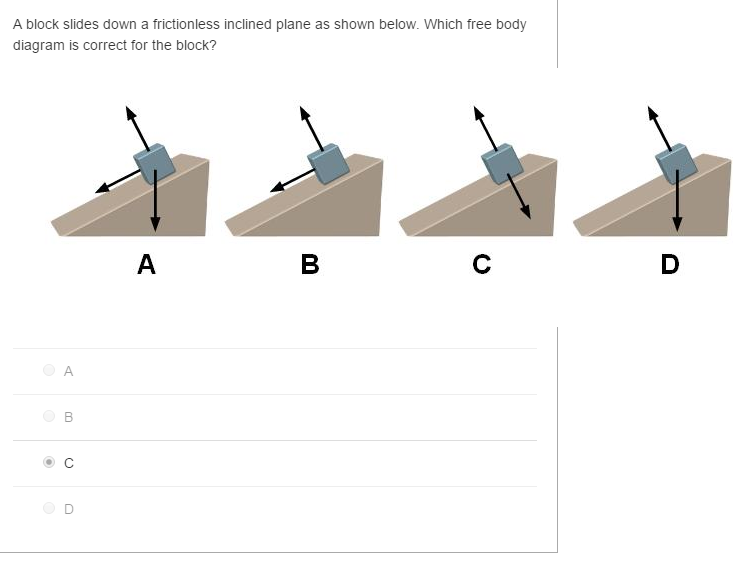
The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The ...

Free body diagram inclined
For T₂, its free-body diagram shows us it is only responsible for the mass of m₂, we can say that T₂ = a * m₂. With that said, T₂ = (2.4 m/s²) * (2 kg) = 4.8 N . On the other hand, T₁ is the tension force that pulls both the weight of m₁ and m₂. A free-body diagram is a picture that represents one or more objects, along with the forces acting on those objects. In a force diagram, or free-body diagram, the pointy-end of the arrow tells you this about the force: answer choices. relative strength. The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving ... Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In Figure 6.8. 1 a, a sled is pulled by force P → at an angle of 30°. In part (b), we show a free-body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem-solving strategy. In part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x- and y ...
Free body diagram inclined. Free Body Diagram of an Inclined Plane in TikZ. April 21, 2021 February 9, 2021 by admin. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a triangle to represent the inclined plane, a rectangle for the load, then add arrows with labels to ... These forces are illustrated in the free-body diagram. Diagram showing the frictional force on an inclined plane. Therefore, the net force in the parallel direction is given by by W Moebs · 2016 — Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in (Figure). Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in ... A free - body diagram, isolated - body diagram, or force diagram is a diagram in which the forces acting on a body are represented by arrows. Be sure to include in the diagram all the forces acting on the object, and since it is a vector quantity, the arrow is responsible for pointing out its direction and direction, while the length of the arrow gives …
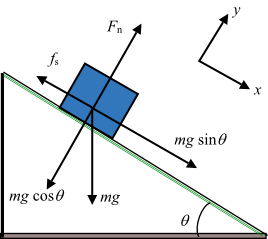
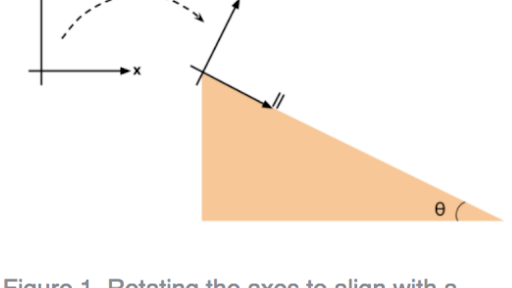
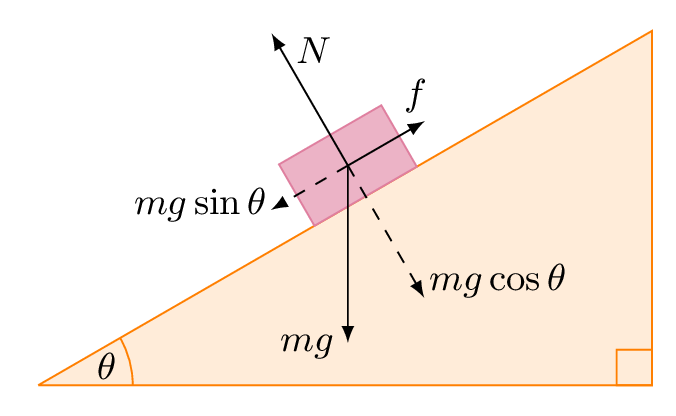
Let's, first of all, focus on the motion of the smaller block placed on the inclined surface. Its free body diagram is as shown below. Assume that the force applied on the incline and surface produces an acceleration 'a' so that there is a pseudo force (of magnitude 'ma') acting on the smaller block. The magnitude of normal reaction is equal to ... Confused how to approach problem after making a free body diagram and finding the length of the inclined plane . Reply. Answers and Replies Mar 24, 2021 #2 Doc Al. Mentor. 45,210 1,550. So you made a free body diagram? ... Related Threads on Inclined plane problem without mass or coefficient of friction given Two masses on an inclined plane ... block on block fricton , and inclined plane in elevator Relevant Equations: f=ma ... of this block above block problems. i did a free body diagram , its very long but if you can or someone to see if i did it correct and if i understand what happens in each case.(if i do the free body diagram correctly than all question of this kind would be ... Free body diagram for a log being pulled up an inclined plane. Rotated coordinate axes are shown. Note that I have defined \(+x\) to point up the ramp this time; it is generally most convenient to define \(+x\) in the direction of motion.
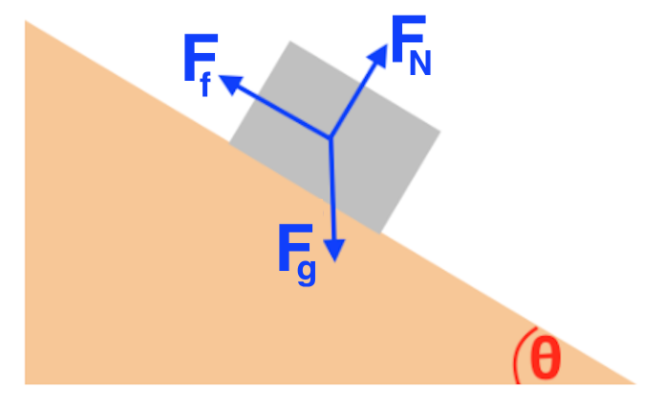
Free Body Diagram of an Inclined Plane in TikZ. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a triangle to represent the inclined plane, a rectangle for the load, then add arrows with labels to highlight different forces. 1. Figure a shows two objects on an inclined plane, sloping down to the left. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body ...Definition of weight, vector form: →w=m→gw...Net external force: →Fnet=∑→F=→F1+→F2+...Newton’s second law, vector form: →Fnet=∑...Newton’s second law, component form: ∑→Fx... Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\): (a) A snowboarder glides down a slope inclined at 13° to the horizontal. (b) The free-body diagram of the snowboarder. Strategy. The forces acting on the snowboarder are her weight and the contact force of the slope, which has a component normal to the incline and a component along the incline (force of kinetic friction). What magnitude must the static friction force f s have for the box in the figure to remain at rest in the middle of the inclined plane at an angle α of 37º? The mass of the box is m = 8 kg. Free-body diagram for an object at rest on an inclined plane. Solution. The figure shows the free-body diagram of the box on the plane.
The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. draw and label a free body diagram for the airplane write the equilibrium equation of motion for the vertical direction; solve for the tension in the string in terms of m ...
Example 2 Normal reaction = 12 N Block Figure 1.20 shows the free body diagram of a block sliding down a smooth inclined plane. Weight, (a) Sketch the component of the weight of the block parallel to the W = 24 N 60° inclined plane and the component of the weight of the block Figure 1.20 perpendicular to the inclined plane.
Forces on a dynamics trolley on an inclined plane (GCSE level analysis) Next we place a dynamics trolley on a horizontal table top. We observe that it is is equilibrium. This is easy to explain if we draw a free body diagram to show the forces on the trolley.
A shopper pushes her 25 kg grocery cart by a force of 225 N inclined at an angle of 60° with the horizontal through a distance of 7.5 m as shown in the free body diagram. Find the work done by (a) the 225 N force and (b) friction. Assume that the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.32.
In diagram C, the the apple and scales are in an elevator that is accelerating downwards at 1.00 metres per second per second. The resultant upward force must therefore be smaller than the downward weight as shown in the free body diagram. The scales show a reading of 0.881/9.81 - 0.089 806 kg = 89.806 g.
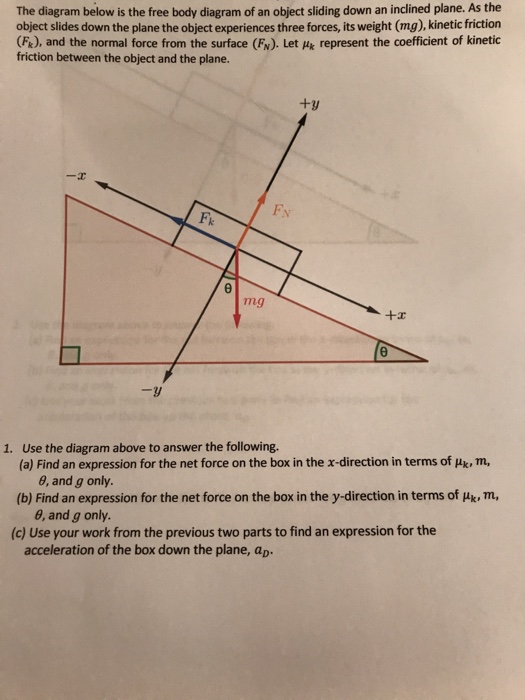
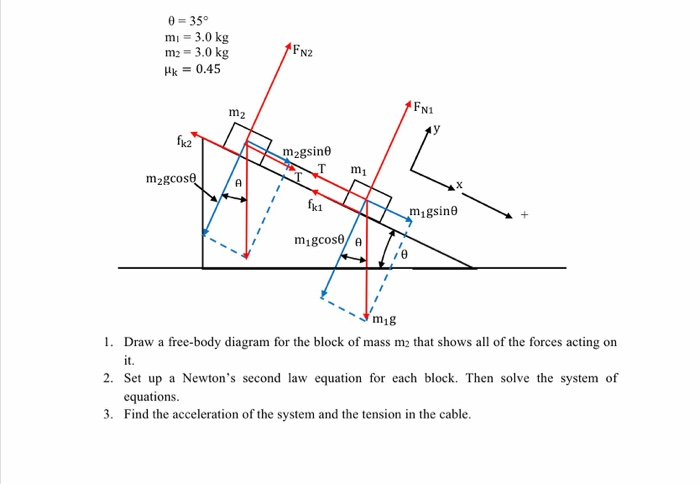
#2. Dynamic (in motion): The block is moving downward on the inclined surface. Refer to the Free Body diagram. Since there is a motion, we have kinetic friction f k between the block and the surface which is opposite to the direction of motion. Depending on the acceleration in the motion (then F net in x-axis), we may have kinetic friction alone or both kinetic friction f k and tension force T ...
The free-body diagram of the entire arch is shown in Figure 6.5b, ... Taking B as the origin and denoting the tensile horizontal force at this origin as T 0 and denoting the tensile inclined force at C as T, as shown in Figure 6.10b, suggests the following: Fig. 6.10. Suspended cable.
A box sits at rest on a rough 33° inclined plane. Draw the free-body diagram, showing all the forces acting on the box. (b) How would the diagram change if the box were sliding down the plane? (c) How would it change if the box were sliding up the plane after an initial shove? A 25.0-kg box is...
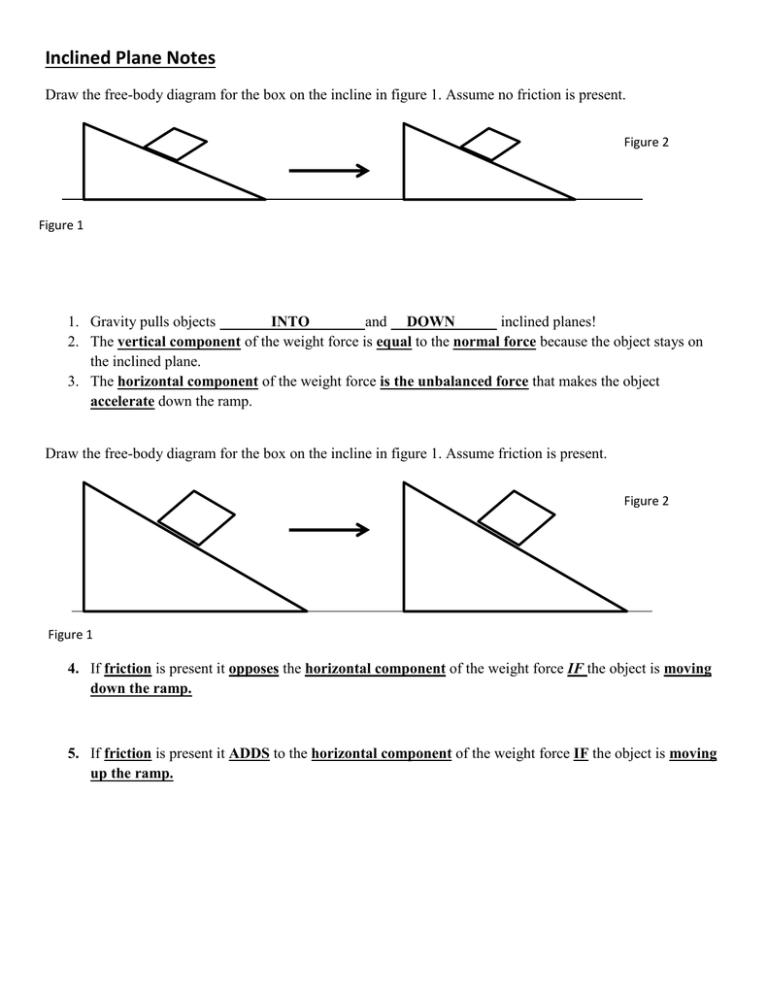
Inclined Plane - Simple Machine Answer Key Vocabulary: coefficient of friction, efficiency, force, free-body diagram, friction, inclined plane, mechanical advantage, mechanical energy, normal force, resultant force, simple machine, vector, work, work-energy theorem Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) [Note: The purpose of these questions is to activate prior ...
4.3.2 Draw a free-body diagram showing ALL forces acting on the box while moving from B to C. (3) 4.3.3 Use the energy principles to calculate the kinetic frictional force between B and C if the speed of the box at position C, the bottom of the plane is 3 m•s-1. (5) 4.4 The angle between the incline and the horizontal is decreased.
Investigate how an inclined plane redirects and reduces the force pulling a brick downward with or without friction. Jan is moving to a new apartment. Coefficient of friction efficiency force free-body diagram friction inclined plane mechanical advantage mechanical energy normal force resultant force simple.
Using free body diagram. R − mg = 0 (where R is the normal reaction force) ... A block slides down an inclined surface of inclination 30° with the horizontal. Starting from rest it covers 8 m in the first two seconds. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two.
How to write Newton's second law for forces on an incline. 1) Draw a free body diagram for the object (see Figure 3). Remember to rotate the coordinate axes to ...
Draw a free body diagram of the body coming in contact with the surface of interest and identify all the forces acting on it. ... The case described by the previous image is a typical problem in physics, called an inclined plane or ramp. You will usually have a body with a known mass sitting on top of the ramp.
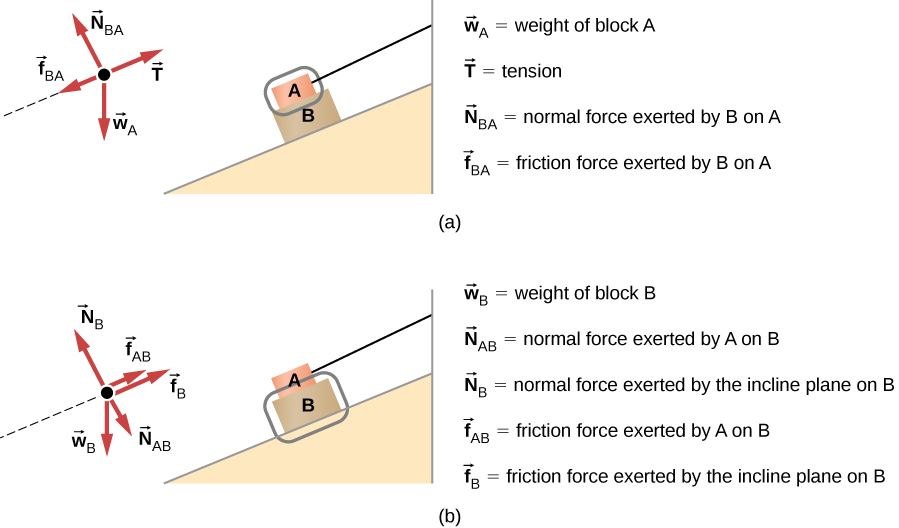
Free body diagram for two masses on inclined plane with frictions. 1. Frictional force on an inclined plane with applied force = Mgsinx - Mgcos x? 0. Body falling off a smooth hemisphere - simple but I'm missing something. What is it? 1. Confusion on Normal force and its resolution on inclined plane.
1. Observe: Select the FREE-BODY DIAGRAM tab. Make sure Magnitude is on. A free-body. diagram is a picture that uses vectors to show the different forces acting on an object. What does the purple arrow pointing down represent? The weight of the brick. The inclined plane breaks this force down into two components: one parallel to the inclined
Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In Figure 6.8. 1 a, a sled is pulled by force P → at an angle of 30°. In part (b), we show a free-body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem-solving strategy. In part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x- and y ...
A free-body diagram is a picture that represents one or more objects, along with the forces acting on those objects. In a force diagram, or free-body diagram, the pointy-end of the arrow tells you this about the force: answer choices. relative strength. The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving ...
For T₂, its free-body diagram shows us it is only responsible for the mass of m₂, we can say that T₂ = a * m₂. With that said, T₂ = (2.4 m/s²) * (2 kg) = 4.8 N . On the other hand, T₁ is the tension force that pulls both the weight of m₁ and m₂.





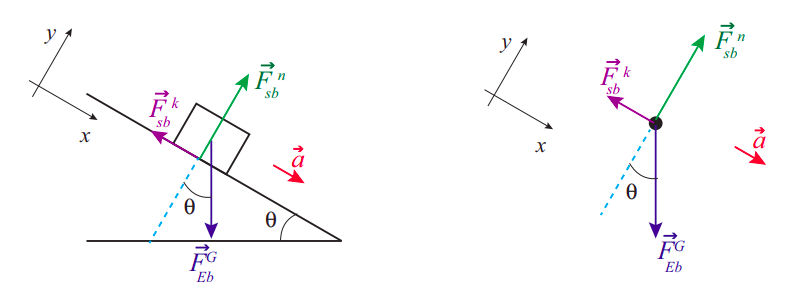
















0 Response to "38 free body diagram inclined"
Post a Comment