38 diverging lens ray diagram
(a) An object is placed 10 cm from a lens of focal length 5 cm. Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of image if the lens is (i) converging, and (ii) diverging. (b) State one practical use each of convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens and concave lens.
The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature c of a concave mirror. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 30 cm tall object placed 100 cm from a converging lens having a focal length of 150 cm.
An object is placed in front of a converging lens and in front of a diverging lens as in fig. 5. (a) Complete the ray diagram to obtain an image. (b) Compare the nature of image formed by both the lenses in the above case.
Diverging lens ray diagram
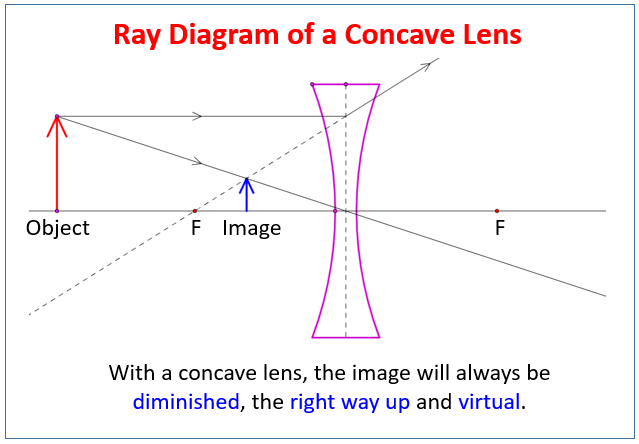
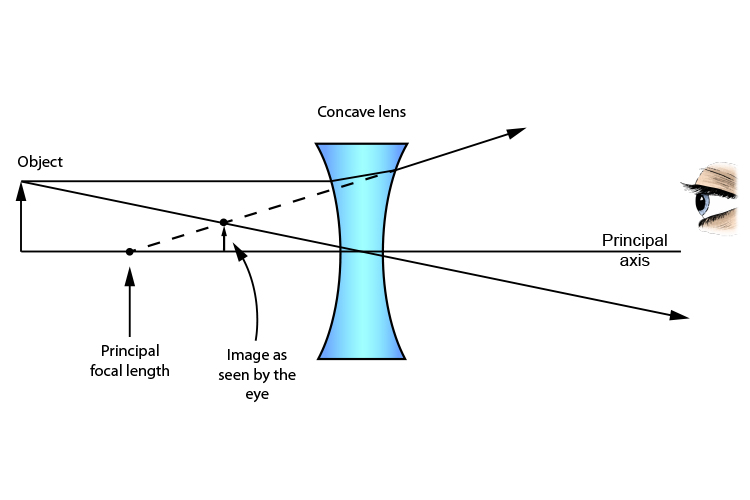
Imagine light rays coming into a concave lens and then shooting out in all directions. That's why a concave lens is sometimes called a diverging lens. It makes light rays shoot out (diverge). Concave lenses are used in movie projectors to make light from the film spread out and cover a bigger area when it hits the wall.
Convex lens for ms real image because of positive focal length and concave lens for ms virtual image because of negative focal length. In mirrors, images are for med through reflection but lens es for m images through refraction. This is explained with the help of ray diagram s as follows Convex & Concave Lens es. A lens is a piece of equipment that for ms an image by refracting light.
A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. 2 give me a thumbs up for this video. 11 draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of 108 cm when.
Diverging lens ray diagram.
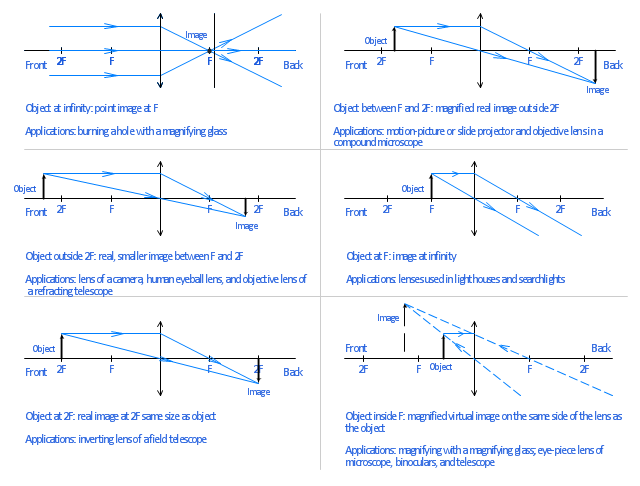
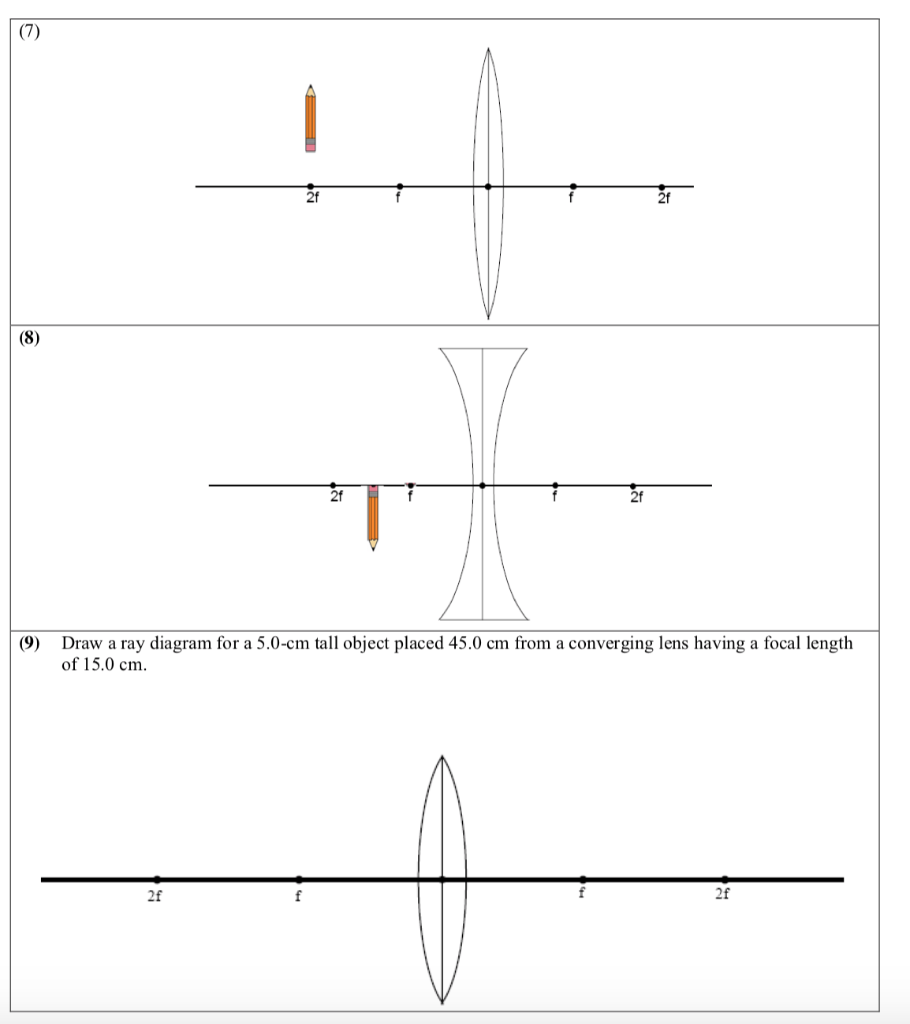
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens.
Related Doubts (a) Find the position and size of the virtual image formed when an object 2 cm tall is placed 20 cm from:(i) a diverging lens of focal length 40 cm.(ii) a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.(b) Draw labelled ray diagrams to show the formation of images in case (i) and (ii) above (The diagrams may not be according to scale).
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness or short-sightedness, is a defect of vision that can be corrected by using diverging or concave lenses. The following ray diagram clearly shows the correction of myopia using a concave lens. Fig. (a) It shows the parallel rays of light coming from a distant object form a blurred image, as the image is formed at a point in front of the retina.
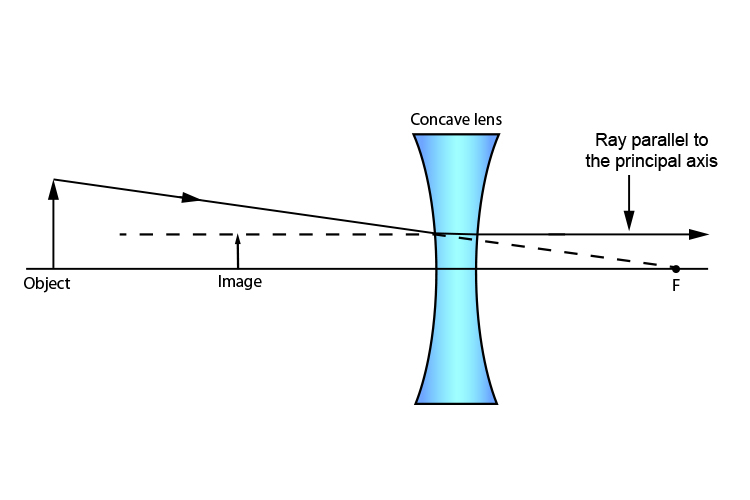
Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Draw a ray diagram for an object placed 60 cm from the surface of a convex lens with a focal length of 120 cm. Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results.
Show transcribed image text By using the principal rays, draw ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses with real objects placed inside, outside, and at the focal points. Use a focal length of 2 cm. For each case below Draw the ray diagram....
The diagram given below shows an object O and its image I. Without actually drawing the ray diagram, state the following : (i) Type of lens (Converging / Diverging) (ii) Name two optical instruments where such an image is obtained. (iii) List three characteristics of the image formed if this lens is replaced by a concave mirror of focal length 'f' and an object is placed at a distance 'f ...
Worksheets are ray diagrams for convex mirrors, converging diverging lenses ray diagrams, physics, concave mirrors, grade 8 science ray diagrams for convex mirrors, 1 1 1 h d i i in every problem draw a ray i o f h d o o, ray diagrams for concave mirrors, diverging converging lens work. Last, describe the image formed (inverted or upright ...
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results. Ray Diagrams 3 of 4 Concave and Convex Lenses and Mirrors. A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light converging or diverging the beam.
11 draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of 10 8 cm when an object is placed 32 4 cm from the lens s surface. Before the ray enters the lens it is parallel to the optical axis and it passes through the center of the lens. The following diagrams show the ray diagrams for convex lens.
Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Written By Pelvic Diagram Wednesday, May 26, 2021. Edit. Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Here are ray diagrams for the four cases from the video plus one more. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Solved: Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams DIRECTI ...
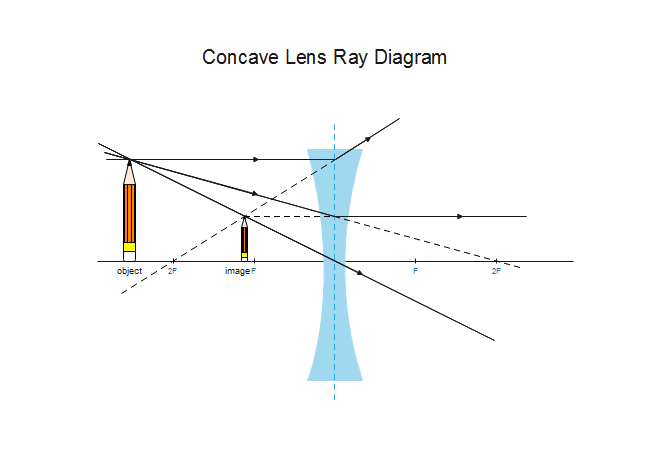
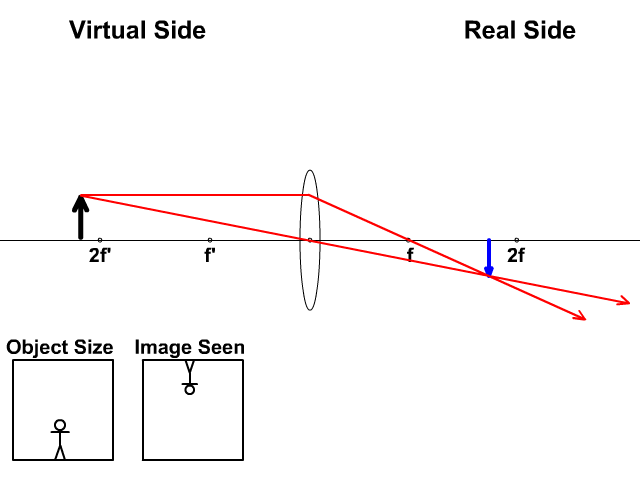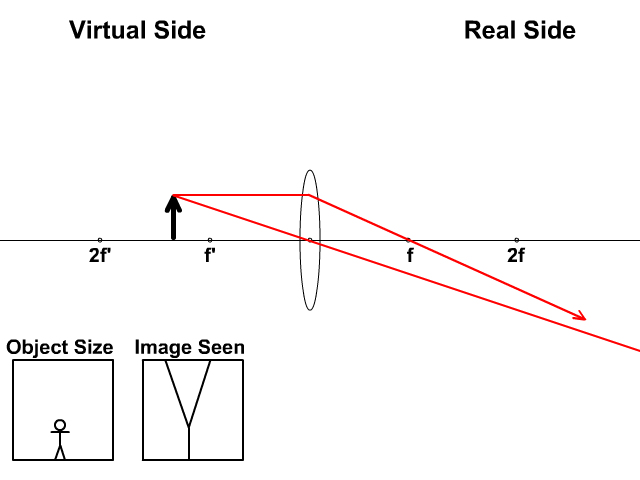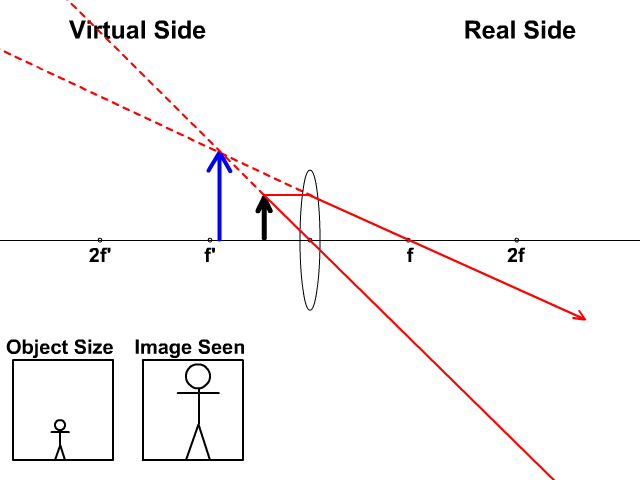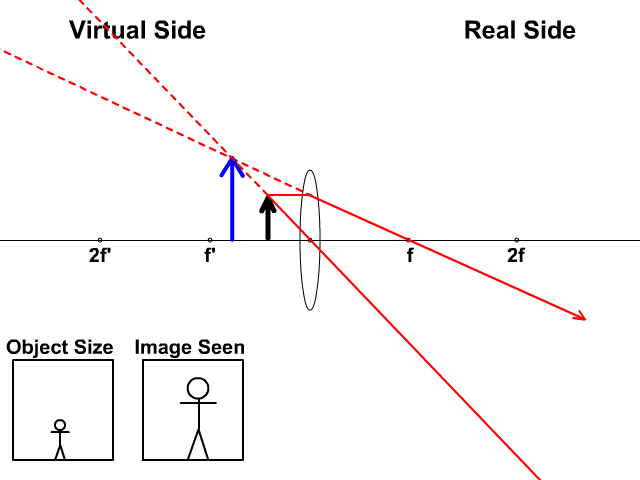
Here you have the ray diagram s used to find the image position for a diverging lens.A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagram s are constructed by taking the path of two distinct ray s from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will diverge as if he came from the ...
Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?Answer -While drawingray diagram, we follow these rulesA rayparallel tothe principalaxiswill pass through the principal focus.A raypassing throughthe principalfocuswill become parallel to the principal axis.A raypassin
(a) A thin diverging lens (b) A thin converging lens (c) A thick diverging mirror (d) A thick converging mirror. A real image of same size as that of object is formed by a convex lens. The object musty be at a distance of (a) υ < ƒ (b) υ = ƒ (c) ƒ < υ < 2ƒ (d) υ < 2ƒ
Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses). The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side ...
i) Construct a scaled ray diagram on a graph paper to obtain the position of the final image as would be observed by a person on the right hand side of L 2; ii) Determine the magnification obtained by the arrangement. The figure below represents and object O placed 10cm in front of a diverging lens. F is the focal point of the lens.
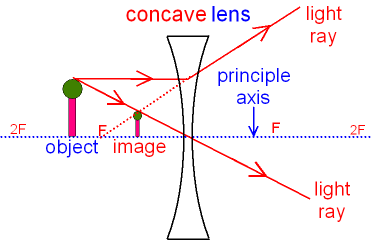
Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp.
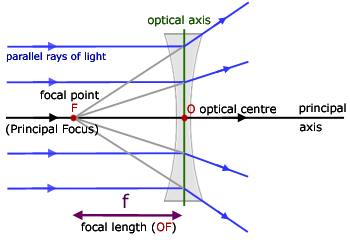
A spherical lens has two Centre of Curvature.. Focus (F): It is the point on the axis of a lens to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction. Focal length: Distance between Optical Centre and Focus. Concave lens: Diverging lens. Convex lens: Converging lens
A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak diverging lens is placed between the converging lens and the image, where is the new image ...15 pages
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the ...
In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror. Converging mirror ray diagram. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located […]
A diverging lens is a lens that diverges rays of light that are traveling parallel to ... The focal point is denoted by the letter F on the diagrams below.
Find Answer to MCQ A diverging lens always has the same ray diagram, which forms a - (a) curved image - (b) large image - (c) fat image - (d) smaller image - Geometrical Optics MCQs - MCQtimes.com
The above diagram shows the behavior of two incident rays approaching parallel to the principal axis of the double concave lens. Just like the double convex ...
13+ Convex Lens Ray Diagram. (draw in rays) this lens is called a concave or diverging lens. Beyond the lens, it will pass through the principal focal point. A point object at a distance of 20 cm on the axis of this combination has its image coinciding with itself.
One goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the double convex lens. Typically, this requires ...
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Three principal rays can be used to locate and size the image formed by a single lens, with examples for converging and diverging lenses. The three principal rays are:. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens.
, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses) ...
14+ Diverging Lens Ray Diagram. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. Ray tracing for concave or diverging lens draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were ...





















0 Response to "38 diverging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment