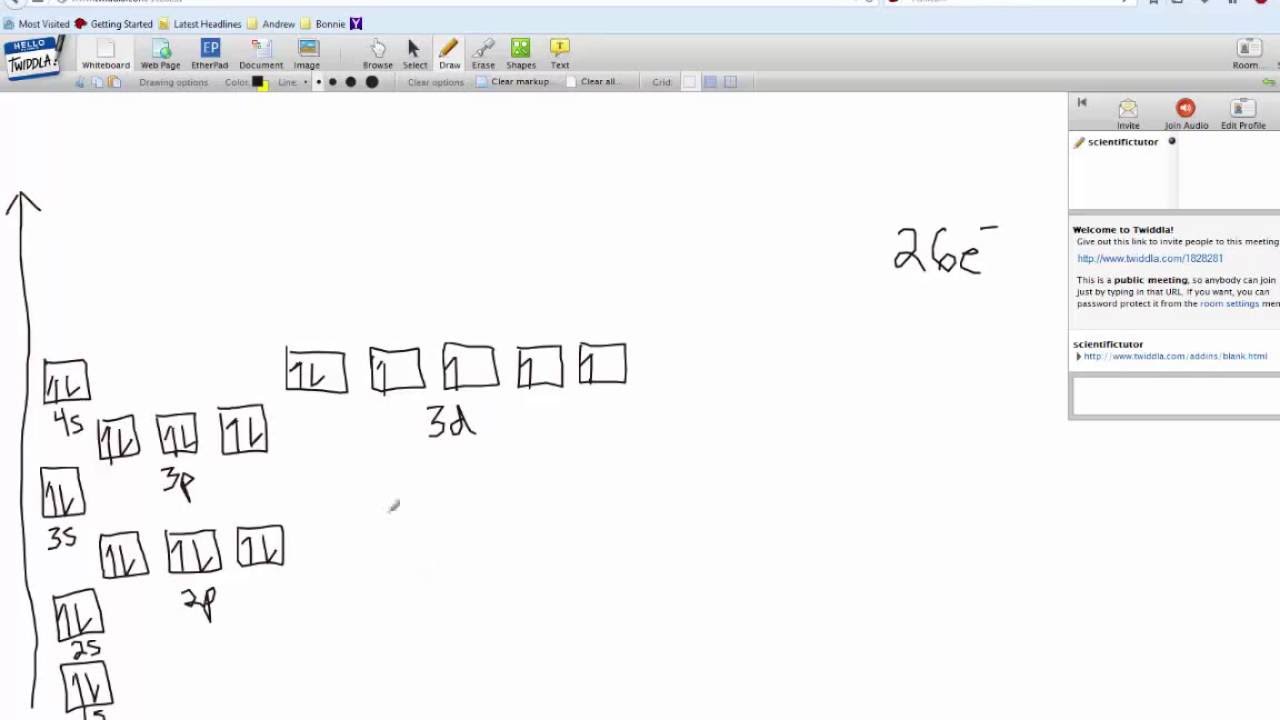
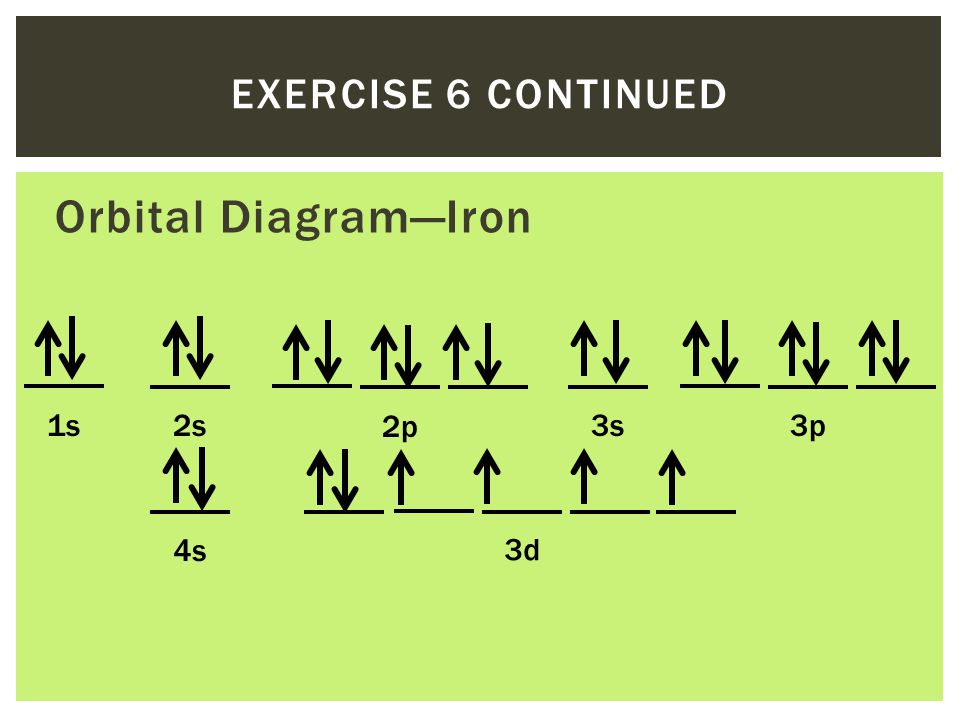
37 orbital diagram of fe
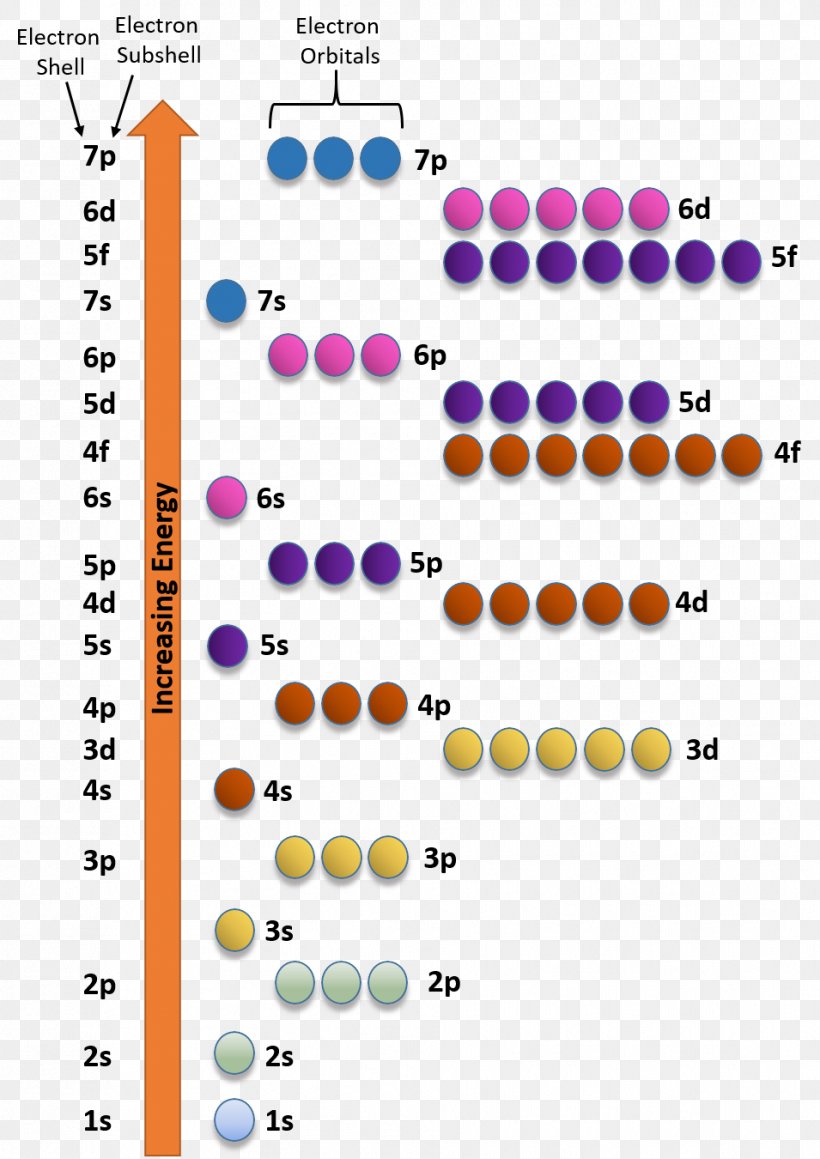
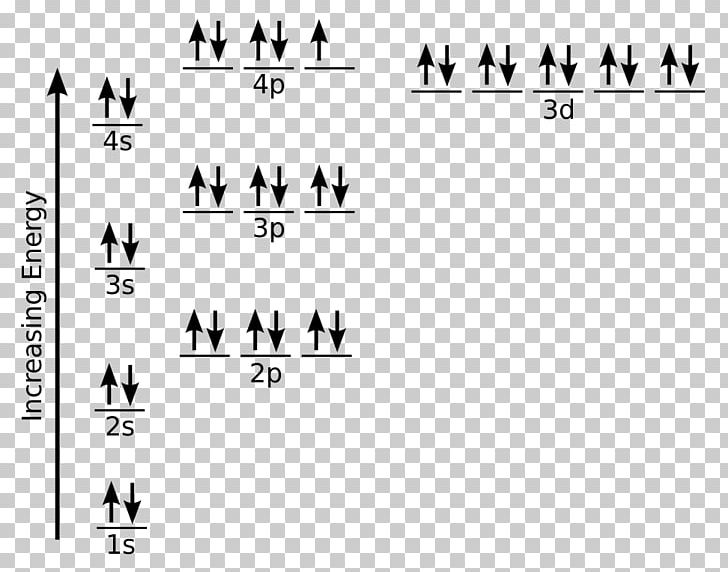
An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
This tells us that each subshell has double the electrons per orbital. The s subshell has 1 orbital that can hold up to 2 electrons, the p subshell has 3 orbitals that can hold up to 6 electrons, the d subshell has 5 orbitals that hold up to 10 electrons, and the f subshell has 7 orbitals with 14 electrons. Example 1: Hydrogen and Helium.
The ground state electron configuration for a neutral atom of iron is: … In an orbital (box) diagram a box represents each notation and an orbital diagram. Construct the orbital diagram for ni. Select the correct answer and click on the "Finish" button Check your score and answers at the end of the … Fe, or iron, has an atomic number of 26.

Orbital diagram of fe
An orbital diagram is used to show how the orbitals of a subshell areoccupied by electrons. Complexes with zero to two unpaired electrons are considered low-spin and those with four or five are considered high-spin. Electron Configurations The electron configuration of an atom is a shorthand method of writing the location of electrons in the ...
How many d electrons are in FE? From the periodic table, iron has atomic number 26 , meaning that there are 26 electrons in each ground state iron atom. 2⋅5=10 electron in each d orbital, and so on so forth. Electron orbitals fill according to the Aufbau (Build-up) Principle. Why Fe2+ is easily oxidized to Fe3+?
The Fe-Cp distance for ferrocene is 1.66 Å; for ferrocenium, it's 1.68 Å. [c] Given that the removal of an electron from the HOMO a'1g orbital resulted in the lengthening of Fe-Cp distance, it should have bonding character. So what is going on here? Why is there this discrepancy? How are these orbitals actually interacting with each other?
Orbital diagram of fe.
The magnetic and electronic phase diagram of a model for the quasi-one-dimensional alkali-metal iron selenide compound Na 2 FeSe 2 is presented. The novelty of this material is that the valence of iron is Fe 2+, contrary to most other iron-chain compounds with valence Fe 3+.Using first-principles techniques, we developed a three-orbital tight-binding model that reproduces the ab initio band ...
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for (ce {O2}), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure (PageIndex {1}). We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
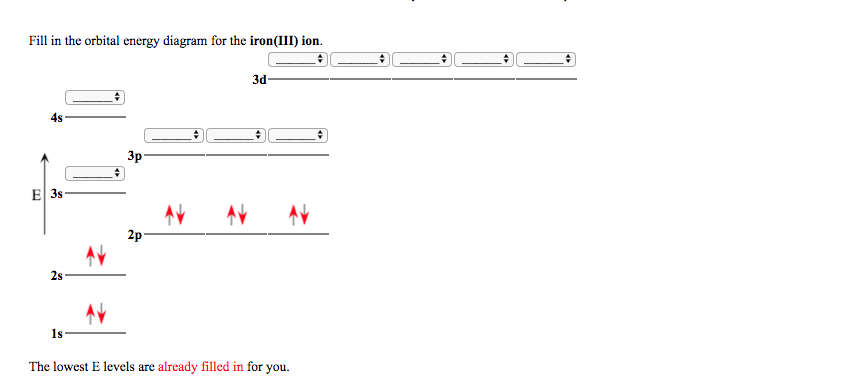
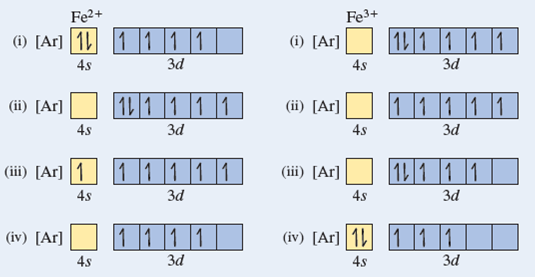
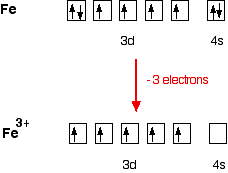
STEP 2 The ion has a 3+ charge so three electrons are removed. Two are taken from the 4s sub-shell, the other from the 3d sub-shell. So the electron configuration of Fe3+ is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5.. How many electrons are in an Fe3+ ion?, We've established that Fe3+ has 26 - 23 = 26 electrons. Furthermore, What is the electron configuration of the iron ion in fecl3?, Its electron ...
CH2F2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. CH2F2 or difluoromethane or difluoromethylene is an organic compound of the haloalkane family. Haloalkanes or alkyl halides are organic compounds, which contain at least one halogen atom bonded to the carbon atom. It is a colorless gas at standard temperature and pressure.
In the hole-doping region, two different interesting orbital-selective Mott phases were found: OSMP1 (with one localized orbital and two itinerant orbitals) and OSMP2 (with two localized orbitals and one itinerant orbital). Moreover, charge disproportionation phenomena were found in special doping regions.
The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how chemical bond formation is taking place. Also, it helps with figuring out how mixing and overlapping have taken place to produce four new hybrid orbitals. The mixing and overlapping occur in the orbitals of similar energy, whereas the bonding electrons contribute to the formation of ...
This is the actual shift er for 18 speed eaton fuller transmission. Direct aftermarket replacement for oe a 69 18 a 5013 shift the transmission between the top two gears. Buy eaton fuller 4300764 diagram.And above and gcws over 90000lbs. Are parts in shift ing knob worn. Eaton fuller 18 speed shift knob diagram.
36 construct the orbital diagram of the f- ion. Written By Christine J. Bell Tuesday, November 16, 2021 Add Comment. Edit. Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion. In writing the electron configurat ion for fluorine the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. The 24 electrons of a.
Draw the orbital diagram for the valence shell of each of the following atoms: (a) C (b) P (c) V (d) Sb (e) Ru. Use an orbital diagram to describe the electron configuration of the valence shell of each of the following atoms: (a) N (b) Si (c) Fe (d) Te (e) Mo
Fe 13 CHe1 14 Ni2 15. Electron configuration pdf worksheet. Electron configuration worksheet answer key chemistry. The electron configurations in this worksheet assume that lanthanum La is the first element in the 4f block and that actinium Ac is the first element in the 5f block. 2 State the difference between a subshell and an orbital.
Ground State Electron Configuration For Nitrogen. When we talk about the electronic configuration, then the ground state Nitrogen Electron Configuration is written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3.Below you can get the full image representation which will help you to understand the topic more easily.
Schematic illustration of orbital interactions between adsorbed CO (5σ and 2π*) and 3d orbital (d z 2, d xz /d yz) of Fe site in a Fe-SAC and b NiFe-DASC. Differential charge density on c Fe-SAC ...
Draw a molecular orbital diagram for (a) H2, (b) H2 O, (c) BHs, (d) CH4, and (e) [Fe (H)ol by performing the following steps i. Determine the point group of the molecule. Do not descend in symmetry ii. Determine the reducible representation (THIs) using the hydrogen 1s orbital s as your basis set. 111, Express the reducible representation as a ...
The calculated Fe 3 d orbital contributions is imposed on (c). (d) The BZ of Fe 5 − x GeTe 2 with the high-symmetry points and lines indicated. (e)-(f) and (g)-(h): The photoemission intensity and their second derivative of the intensity plots along the Γ - K-M direction and the K-M-K direction, respectively.
Another strength of this model is that the electron correlation depends on the orbital, and the \(d_{xy}\) orbital plays a crucial role. This is consistent with the present results for SC1 and SC3.
Formation of π-back Bond. The π-bond in metal carbonyls is formed by overlapping filled dπ orbitals or hybrid dpπ orbitals of a metal atom with low-lying empty (LUMO) orbitals of C O molecule. i.e., M → C O π bonding. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) of C O is ( π 2 P x = π 2 P y) which can accept the electron density ...
Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As) 34: Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se) 35: Orbital diagram of Bromine ...
The protons in the nucleus do not change during normal chemical reactions. Only the outer electrons move. Positive charges form when electrons are lost. Iron (III) sulfate [Fe 2 (SO 4) 3] is composed of Fe 3+ and \ (\ce {SO4^2-}\) ions. Explain why a sample of iron (III) sulfate is uncharged.
Cobalt is within the first row of the d-block of parts. The 4s orbital is stuffed. Equally one might ask, what number of orbitals are in cobalt? Cobalt is a transition metallic within the fourth interval that's slowly filling up its third shell with electrons. Cobalt has fifteen electrons in its third shell that holds a most of eighteen ...
The atomic number of fe (iron) is 26. The electron configuration of iron, atomic number 26, is [ar]3d64s2. Fe (26 electron) = 1s2, 2s2,2p6, 3s2,4s2,3p6,3d6. An electron shell is the set of allowed states that share the same principal quantum number, n (the number before the letter in the orbital label), that electrons may occupy.
Orbital diagram for cr3+. The electronic configuration of Cr having atomic number of 24 is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 3d 5 which is half-filled d-orbital.. Cr3+ has 3 electrons removed from the outermost shell. Therefore, the electronic configuration comes out to be [Ar]3d3.
41 orbital diagram for titanium. The electron configuration for titanium is 1s22s22p63s23p63d24s2, according to the Jefferson Lab website. The element's 22 electrons are arranged in four energy levels surrounding the nucleus of the atom. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels, which are also called shells.
Electron Configuration Chart of All Elements (Full Chart) June 10, 2021 March 7, 2021 by Admin. Electron configuration chart of all Elements is mentioned in the table below. The Shorthand electron configuration (or Noble gas configuration) as well as Full electron configuration is also mentioned in the table. Atomic no.

Write the orbital diagram corresponding to the ground state of nb whose configuration is leftmathrmk















![Figure 11 from Fe L-edge XAS studies of K4[Fe(CN)6] and K3[Fe(CN)6 ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/b07e10a3ee9d48f935dd9354cc632f2dfd4b8861/9-Figure11-1.png)








/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)
0 Response to "37 orbital diagram of fe"
Post a Comment