37 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
Molecular Orbital (MO) theory is a more accurate way to use calculations to predict molecular Note also that the bond order is essentially 1. The σ bond and σ* anti-bond cancel out, leaving the We can use these same diagrams for diatomic molecules or ions for any combination of n=2 elements...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms.
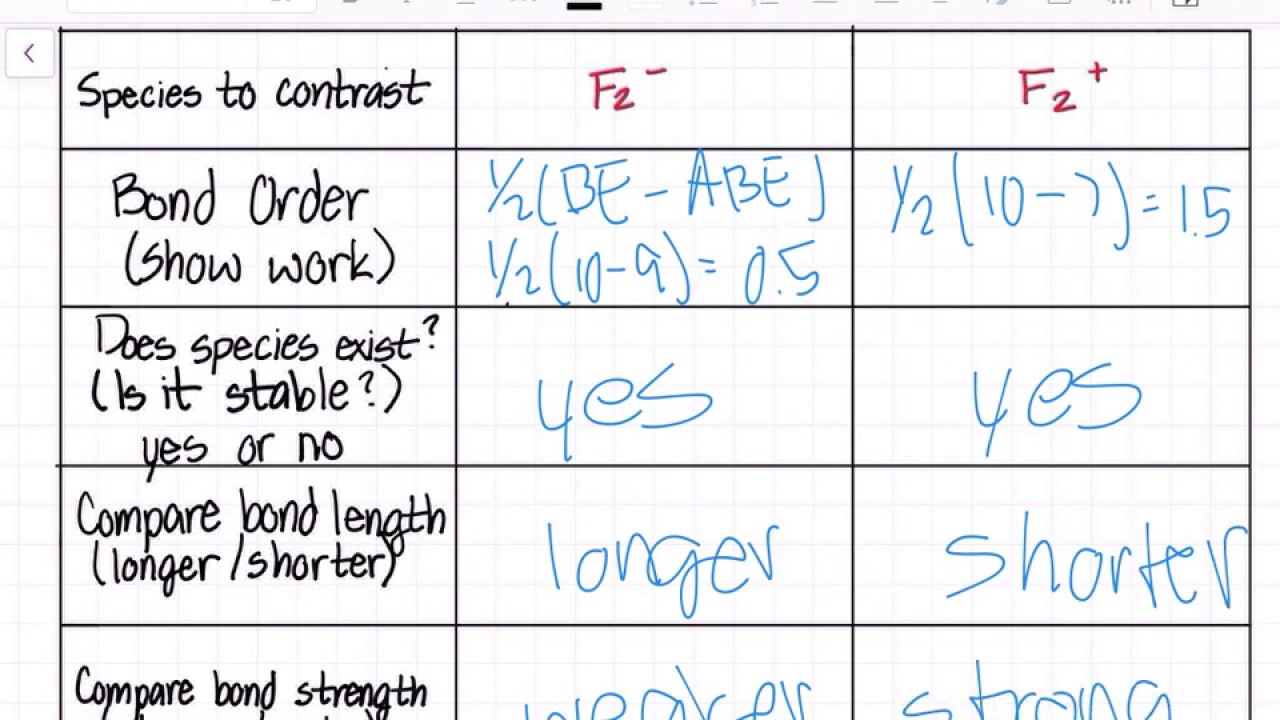
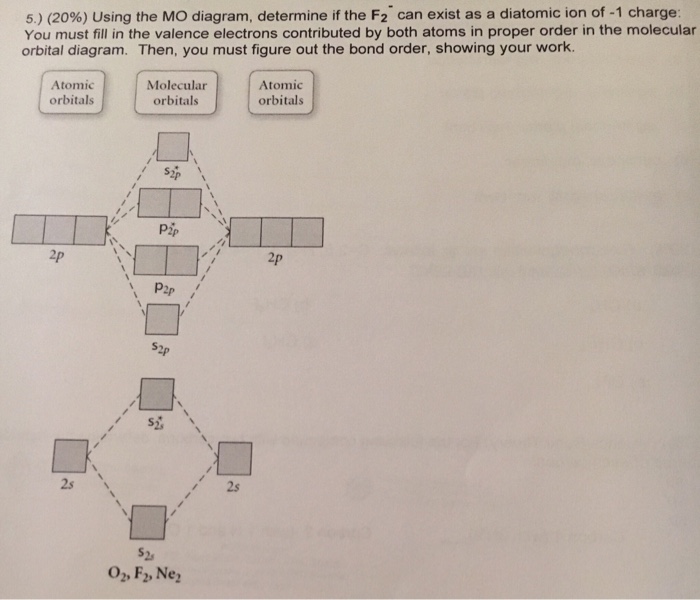
Transcribed image text: Determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of N_2, F_2, and Ne_2. Does the bond order calculated agree with what you would draw for the Lewis structures of these molecules? Explain your answer here in addition to providing the bond order values.
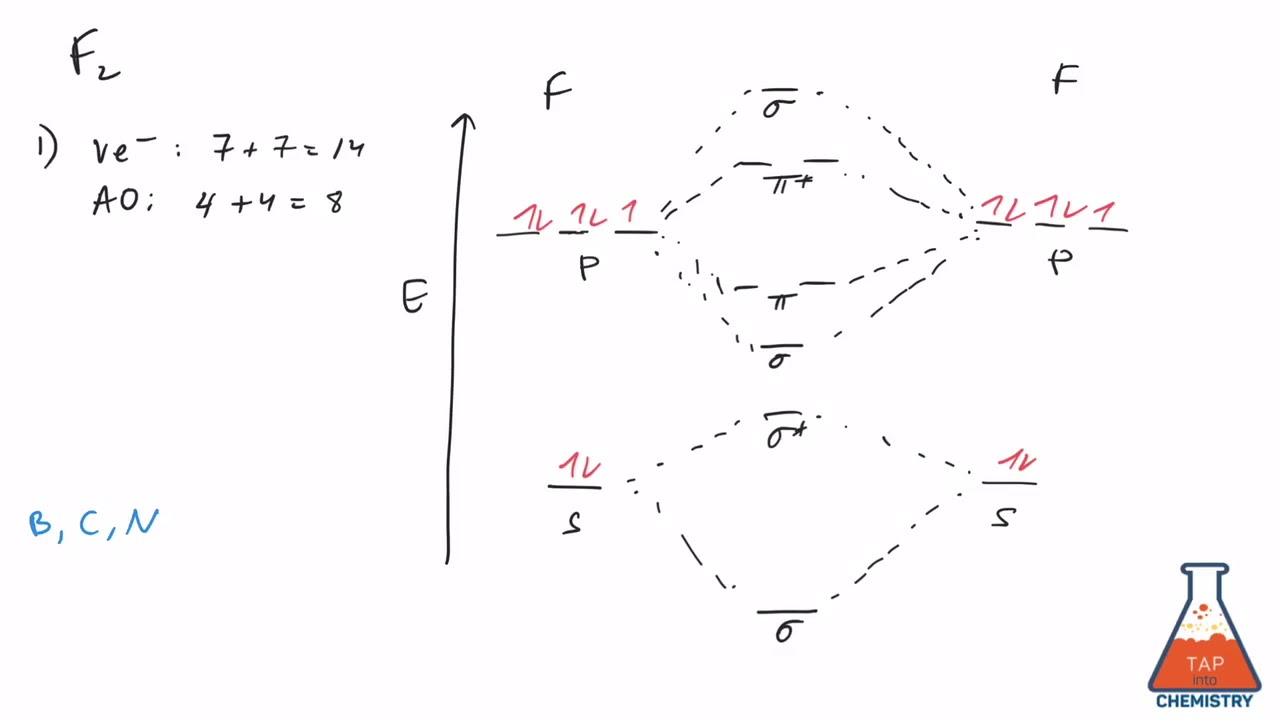
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. You can think of the molecule as the complex between Xe and F2, both of which are closed shell. The s-orbitals on each atom give a completely filled, low energy, net non-bonding set of...
Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. How would I determine bond length from these. How does valence electron configuration work (as in how do Alright, if all has gone well so far you should have an empty molecular orbital diagram with everything in the right order.
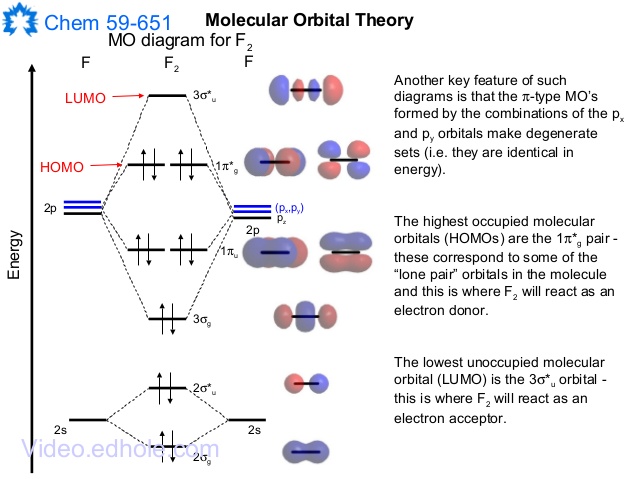
Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic. e.g. for CO - similar to N2 - but with different a.o. energies for C and O, i.e. O > C. Bond order = 1. F2s non-bonding - too low in energy F2px,2py non-bonding because of wrong symmetry.
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order.
In Molecular Orbital Theory, the greater the bond order, the more stable is the molecule or ion. Each bond contains one electron from each atom. These simple diagrams fail to properly account for the effective bond order of 2.5 predicted by molecular orbital theory and must be only considered as...
Describe the bond order of diatomic carbon, $\mathrm{C}_{2}$, with Lewis theory and molecular orbital theory, and explain why the results are different. In our discussion of bonding, we have not encountered a bond order higher than triple. Use the energy-level diagrams of Figure 11-26 to show...
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. The bond order decreases in the order is O 2 + >O 2 >O 2 - >O 2 2- so, we conclude stability is directly proportional to bond order.
33 Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 - Wiring Diagram Database PPT - Theories of Chemical Bonding PowerPoint Presentation ... A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. On the other hand, Molecular Orbital Theory visions the electrons of a...
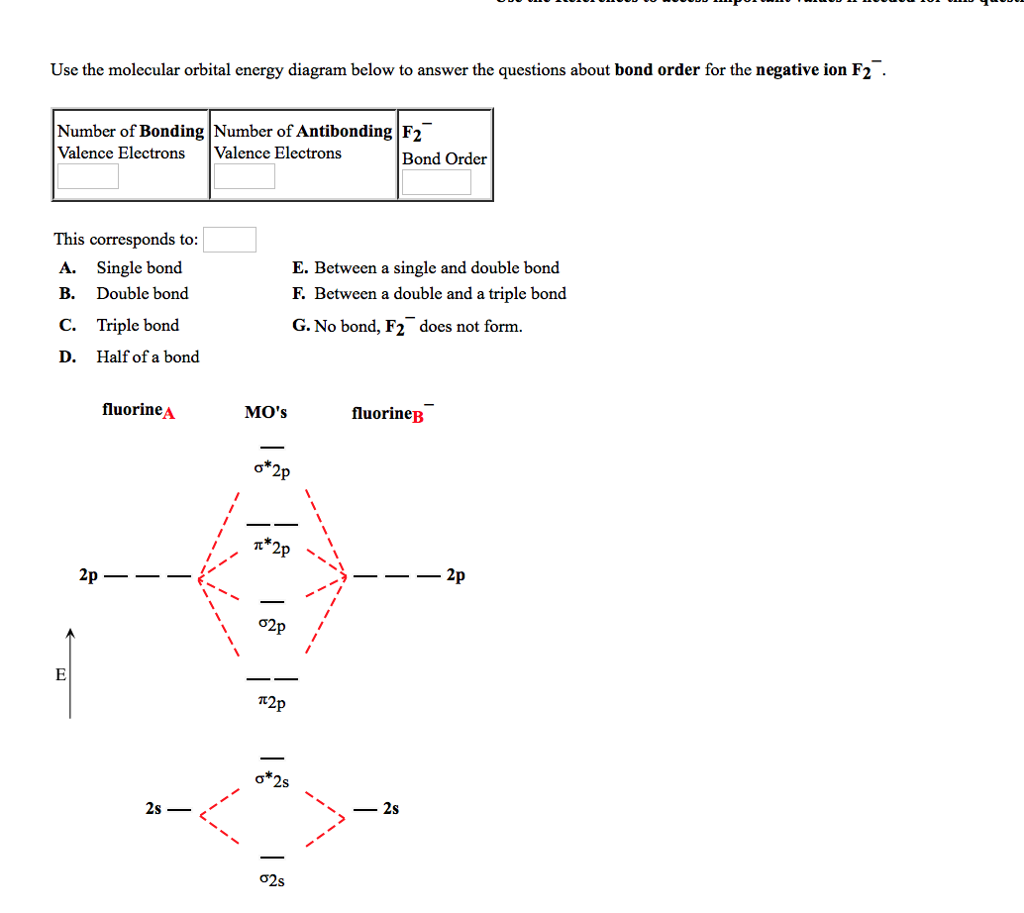
In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. For a straightforward answer: use this formula: Bond order = [(Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2.
The bonding mo wave function ψ psi can be squared ψ 2 psi squared to represent electron density. Molecular orbitals mo are constructed from...
2 Molecular orbital diagrams. Bond order is defined as the difference between the number of electron pairs occupying bonding and nonbonding orbitals in the molecule. Define bond order, and state its significance. Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a...
Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are...
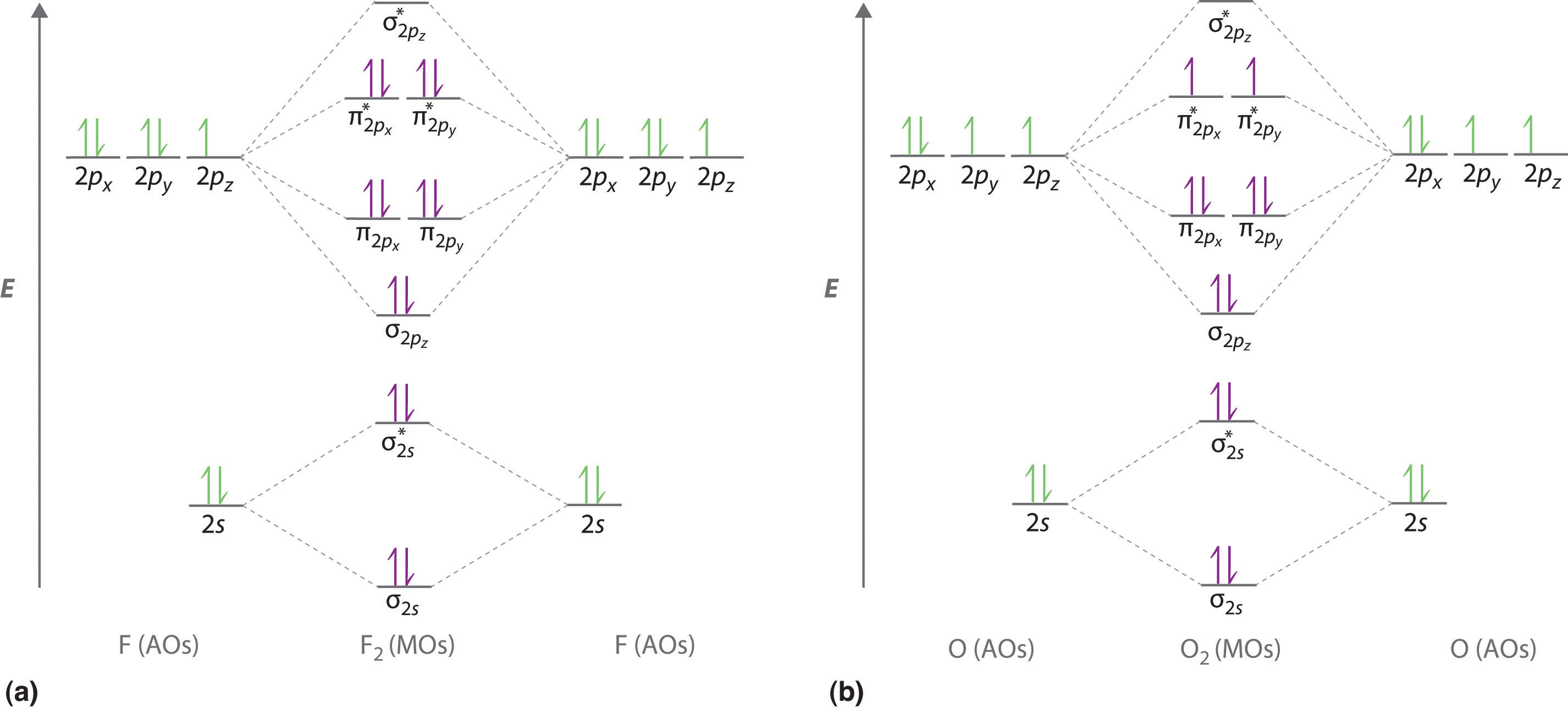
no two molecular orbitals for any molecule ever have the same energy. which of the following statements concerning the molecular orbital energy the diagram for O2, F2, and Ne2 molecules has the sigma2p orbital at a lower energy than the two pi2p orbitals. what is the bond order for a...
Use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram, such as those in Figure 9.20 "Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1", to predict the bond order in the He22+ ion. Is this a stable species? Given: chemical species.
Diagrams 9-3 Bond Order and Bond Stability 9-4 Homonuclear Diatomic. Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals (see Figure 9-5b).
>>Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure. >>Molecular Orbital Theory. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App.
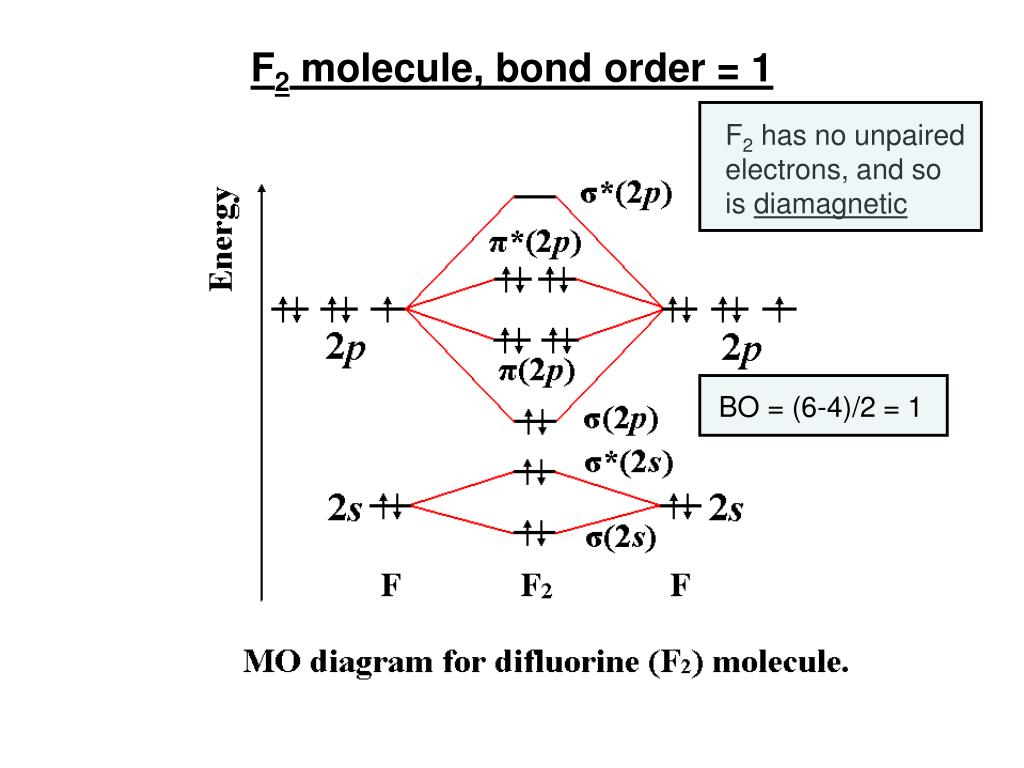
To determine what type of bonding the molecular orbital approach predicts F2 to have, we must calculate the bond order. According to our diagram, there are 8 bonding electrons and 6 antibonding electrons, giving a bond order of (8 − 6) ÷ 2 = 1. Thus F2 is predicted to have a stable F-F single...
• The bond order of a diatomic molecule is defined as one-half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding orbitals, nb, and the number of 3. For remainin g elements, molecular orbitals must also be formed usin g p orbitals. Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for.
Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory. Because arguments based on atomic orbitals One of these orbitals is called a bonding molecular orbital because electrons in this orbital spend This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms.
Single Bonds, Double Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams 20. Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 , A Bond Order Of 2 Is Stronger (But Not The first major step is understanding the difference between two major valence bond theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
The molecular orbital energy diagram for O 2 predicts two unpaired electrons. Determine its bond order and if it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F, Ne...
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
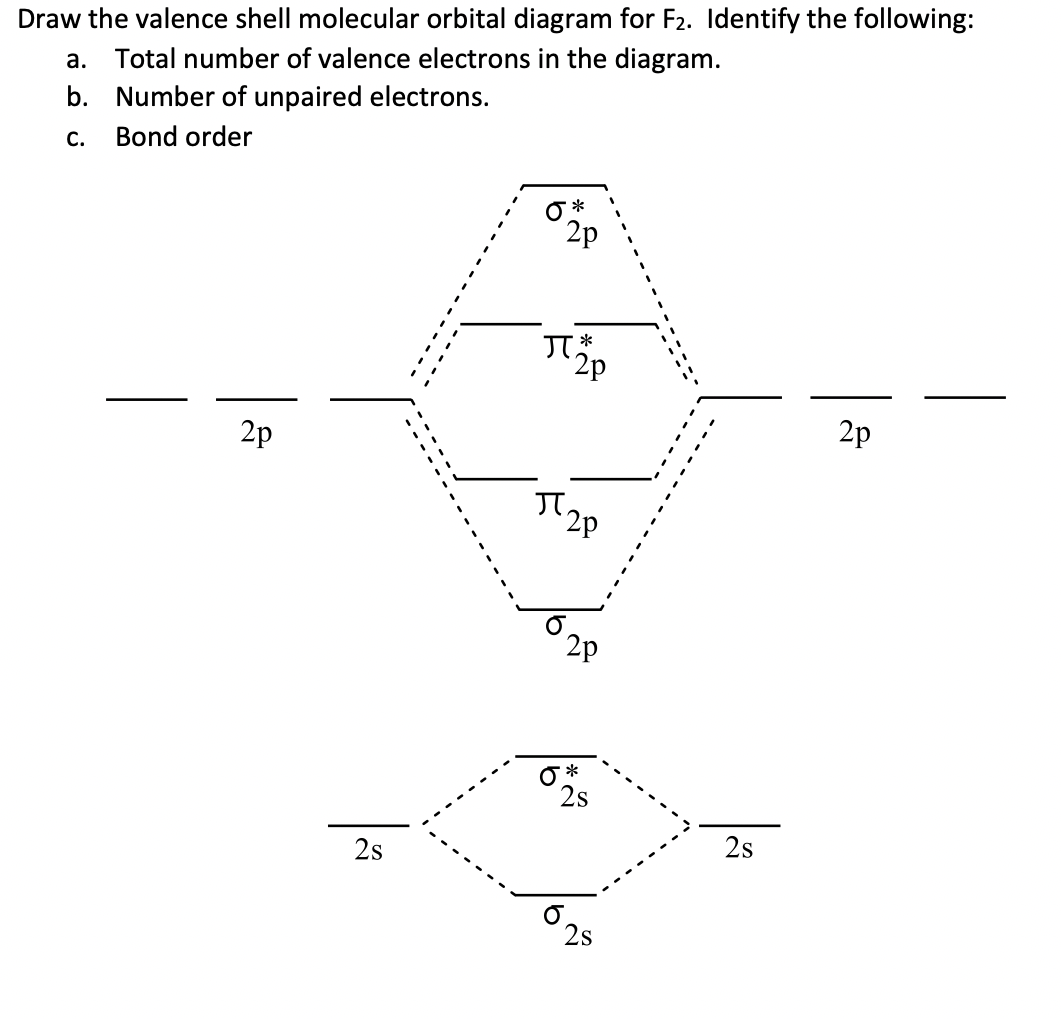
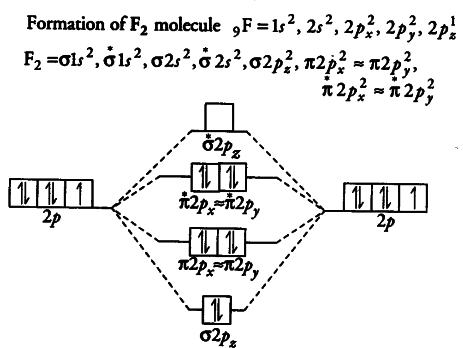
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and find out the bond order. These 18 electrons are filled in various molecular orbitals, in the increasing order of their energies (aufbau principle) and on the basis of Hund's rule and Pauli's exclusion principle as shown in the attachment.
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital.

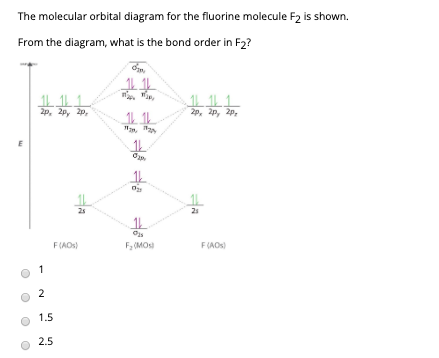
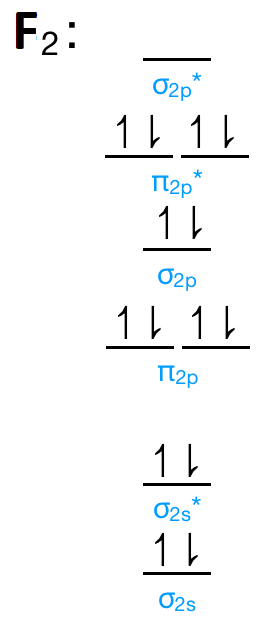

![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and find ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/dae/d7baa23a1d4a2ea2c90e0a703e2fd41d.jpg)

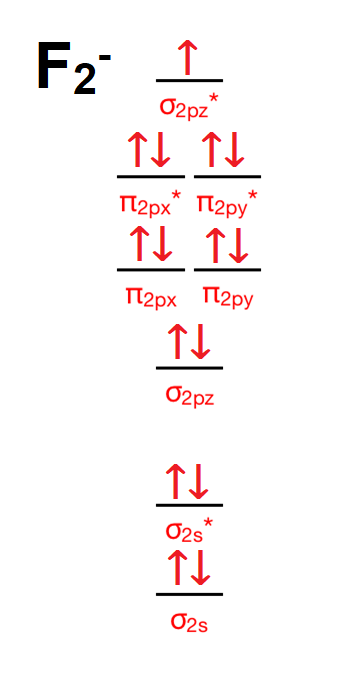



![SOLVED] Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2](https://toppr-doubts-media.s3.amazonaws.com/images/11548439/9a181915-044c-486d-a8de-e18b9373b6f5.jpg)





0 Response to "37 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment