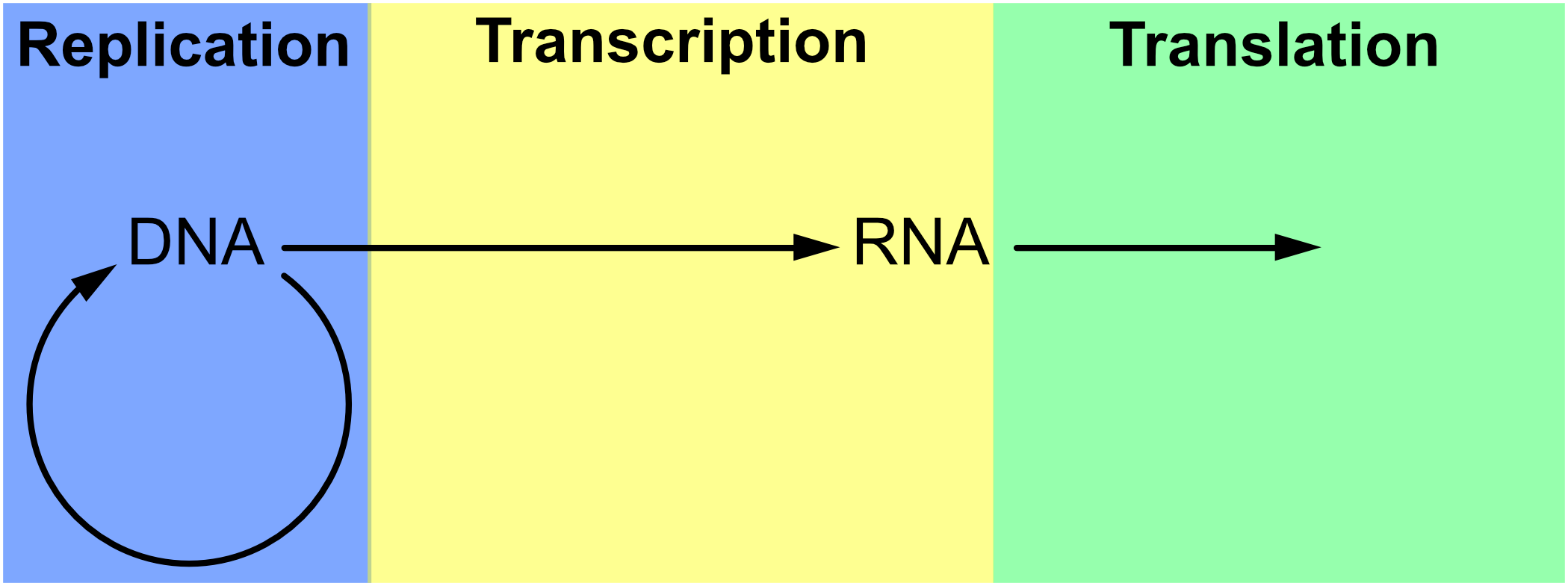
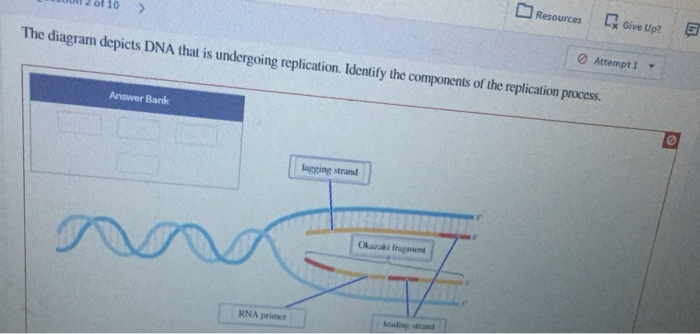
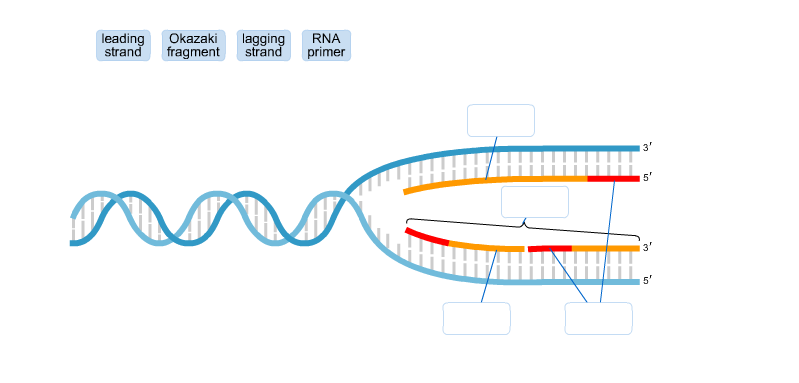
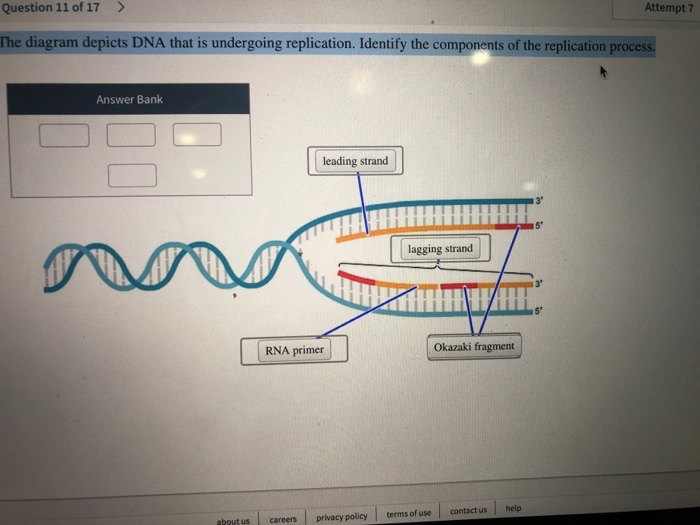
39 the diagram depicts dna that is undergoing replication
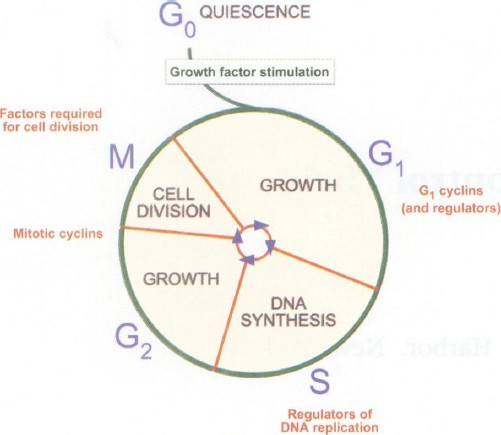
Protein synthesis is a continuous process in a cell while DNA replication occurs only when cell is undergoing division. Before cell division in interphase of the eukaryotic cell cycle that can be subdivided into the following three phases: Growth Phase 1 (G1): during this phase, the cell grows rapidly, while performing routine metabolic processes. So, for the parental strand of DNA that runs 3' to 5', replication occurs just like we always thought, with DNA polymerase working in an antiparallel direction, continuously adding the nucleotides.
The diagram below depicts a germinal cell in the gonads just before DNA replication has occurred (left) and the same cell in metaphase of meiosis | (right). Complete the diagram showing the cell in metaphase of meiosis I, knowing that the four gametes produced will be of the following genotypes: ABC, Abc, aBC, abc.

The diagram depicts dna that is undergoing replication
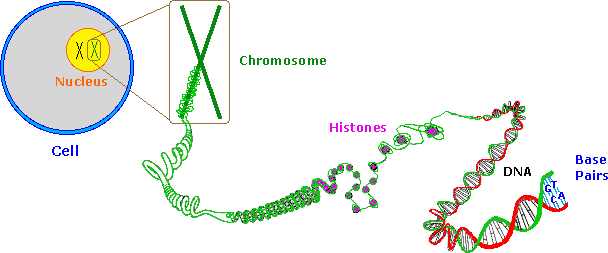
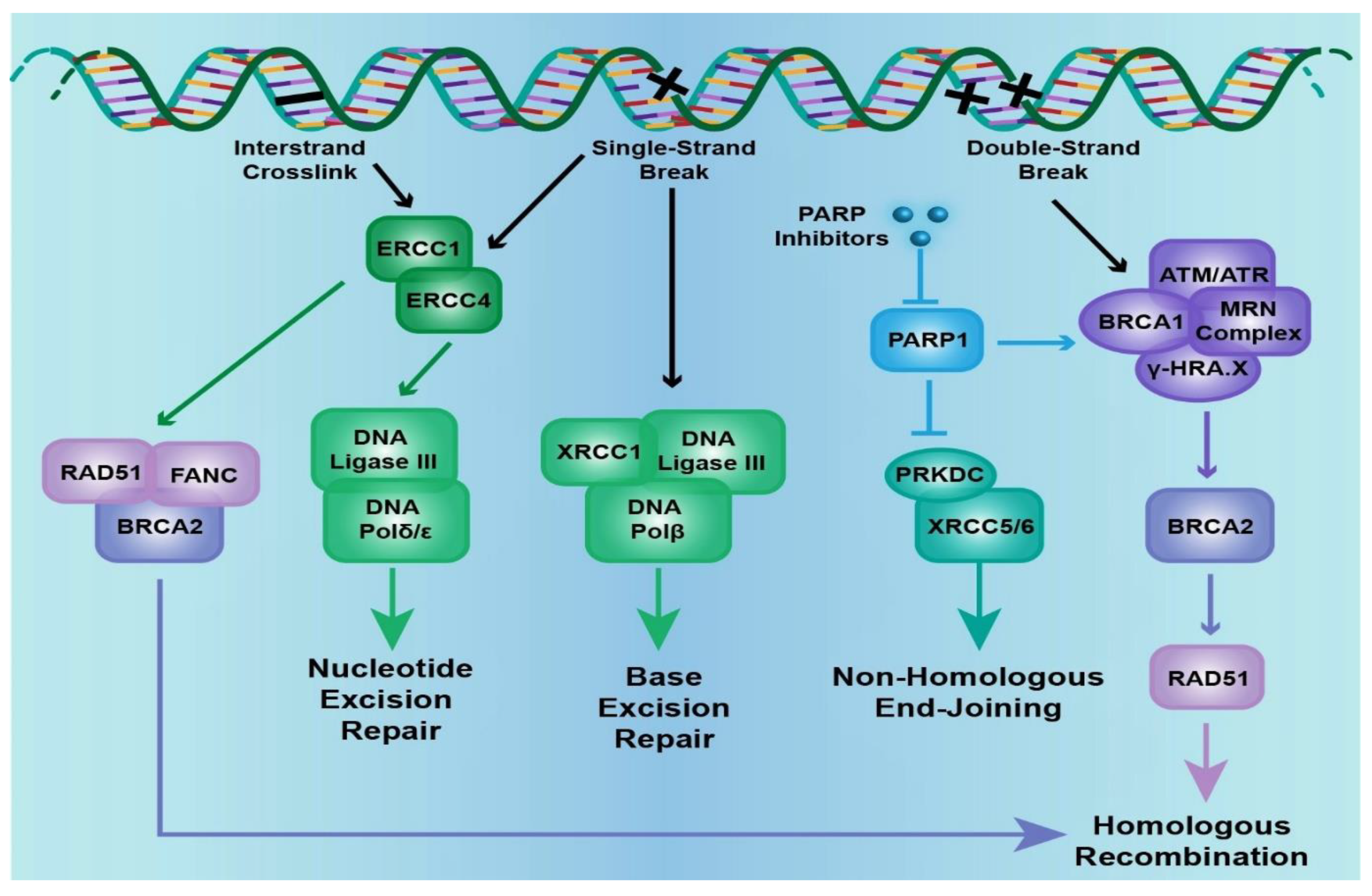
The genome is the most functional part of a cell, and genomic contents are organized in a compact three-dimensional (3D) structure. The genome contains millions of nucleotide bases organized in its proper frame. Rapid development in genome sequencing and advanced microscopy techniques have enabled us to understand the 3D spatial organization of the genome. Chromosome capture methods using a ... The second, homology-directed repair (HDR), uses homologous regions of DNA to facilitate repair in S/G2 after 5′-to-3′ nucleolytic resection of DSB ends. Beyond these high-level branches, however, descriptions of DSB repair as decision trees can oversimplify a complex mechanistic landscape (. Paull, 2021. Paull T.T. Eukaryotic DNA replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts DNA replication to once per cell cycle. Eukaryotic DNA replication of chromosomal DNA is central for the duplication of a cell and is necessary for the maintenance of the eukaryotic genome.. DNA replication is the action of DNA polymerases synthesizing a DNA strand complementary to the original template strand.
The diagram depicts dna that is undergoing replication. Nowadays, data are the most valuable content in the world. In the age of big data, we are generating quintillions of data daily in the form of text, image, video, etc. Among them, images are highly used in daily communications. Various types of images, e.g., medical images, military images, etc. are highly confidential. But, due to data vulnerabilities, transmitting such images in a secured ... Infections with viruses in the genus Flavivirus are a worldwide public health problem. These enveloped, positive sense single stranded RNA viruses use a small complement of only 10 encoded proteins and the RNA genome itself to remodel host cells to achieve conditions favoring viral replication. A consequence of the limited viral armamentarium is that each protein exerts multiple cellular ... We used DNA-content 17,18 for mapping the genome-wide replication-time (RT) profile in a single pre-B cell clone (E-5). We first identified SNPs by mapping sequencing results to the mm9 genome and ... The diagram below shows the structure of a DNA molecule undergoing replication. Based on your knowledge of DNA, which nitrogen base does label one indicate
The following diagram depicts the cell cycle. ... Question: Describe the events taking place in the various stages of karyokinesis of a cell undergoing mitosis. (Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology) Ans. a. Prophase ... The DNA synthesis and replication takes place. iii. G2 phase or second growth phase Interphase and the cell cycle. The interphase prepares the cell for the subsequent phases in cell division such as mitosis and cytokinesis. Since interphase is a preparation phase for the cell division processes, it enables the cell to grow, synthesizing organelles that allow the cell to function adequately ones it matures. a. diagram showing mutations present in spike plasmids used for cell entry PV experiments b. Single round infectivity on different cell targets by spike B.1.617.1 and B.1.617.1 versus WT (Wuhan-1 ... The essential property of a genetic material is that it should be able to replicate accurately in a process known as mitosis or meiosis for sex cells. An attractive feature of the Watson - Crick Model is that it provides us with a possible method of replication. It is not difficult to imagine the two chains separating from each other rather like undoing a zip-fastener.
Results. Although a number of studies have attempted to map DNA replication patterns on a genome-wide basis 12 - 15, it has not been possible to detect all regions that replicate asynchronously, especially in those cases where there is a random distribution, with some cells replicating the paternal allele early while in others it replicates late.These regions can be identified at individual ... Interphase: Cell division is a continual process in which daughters cells emerge, develop, and create their own daughter cells, and the cycle continues. Cell growth and cell division are two events that occur during the cell cycle, with the interphase defining the phase of cell expansion during which various metabolic responses occur. Mitotic cell division process. The cell cycle has two phases 1) Interphase and 2) Mitotic phase. The interphase is also called as resting phase.Though it is resting phase, it is the main phase during which the cell grows (G1), duplicates its DNA (S), and prepares for mitosis (G2) for later cell division by undergoing cell growth and DNA replication. It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. 14 best images of photosynthesis worksheets with answer key. Ionic bonds gizmo answers (3). Using a paper model, students make a mutation of their choice (substitution, insertion, or deletion) in a gene during dna replication. Ionic bonds gizmo answers (3).
In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis. Mitosis results in two new nuclei—which contain DNA—that eventually become two identical cells during cytokinesis. Mitosis occurs in eukaryotic (animal) cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell's ...

Sap1 Is A Replication Initiation Factor Essential For The Assembly Of Pre Replicative Complex In The Fission Yeast Schizosaccharomyces Pombe Journal Of Biological Chemistry
DNA replication, also known as semi-conservative replication, is the process by which DNA is doubled.This is an important process taking place within the dividing cell. In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the precise steps involved in replicating DNA (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.
Accurate and complete replication of the genome is essential not only for genome stability but also for cell viability. However, cells face constant threats to the replication process, such as spontaneous DNA modifications and DNA lesions from endogenous and external sources. Any obstacle that slows down replication forks or perturbs replication dynamics is generally considered to be a form of ...
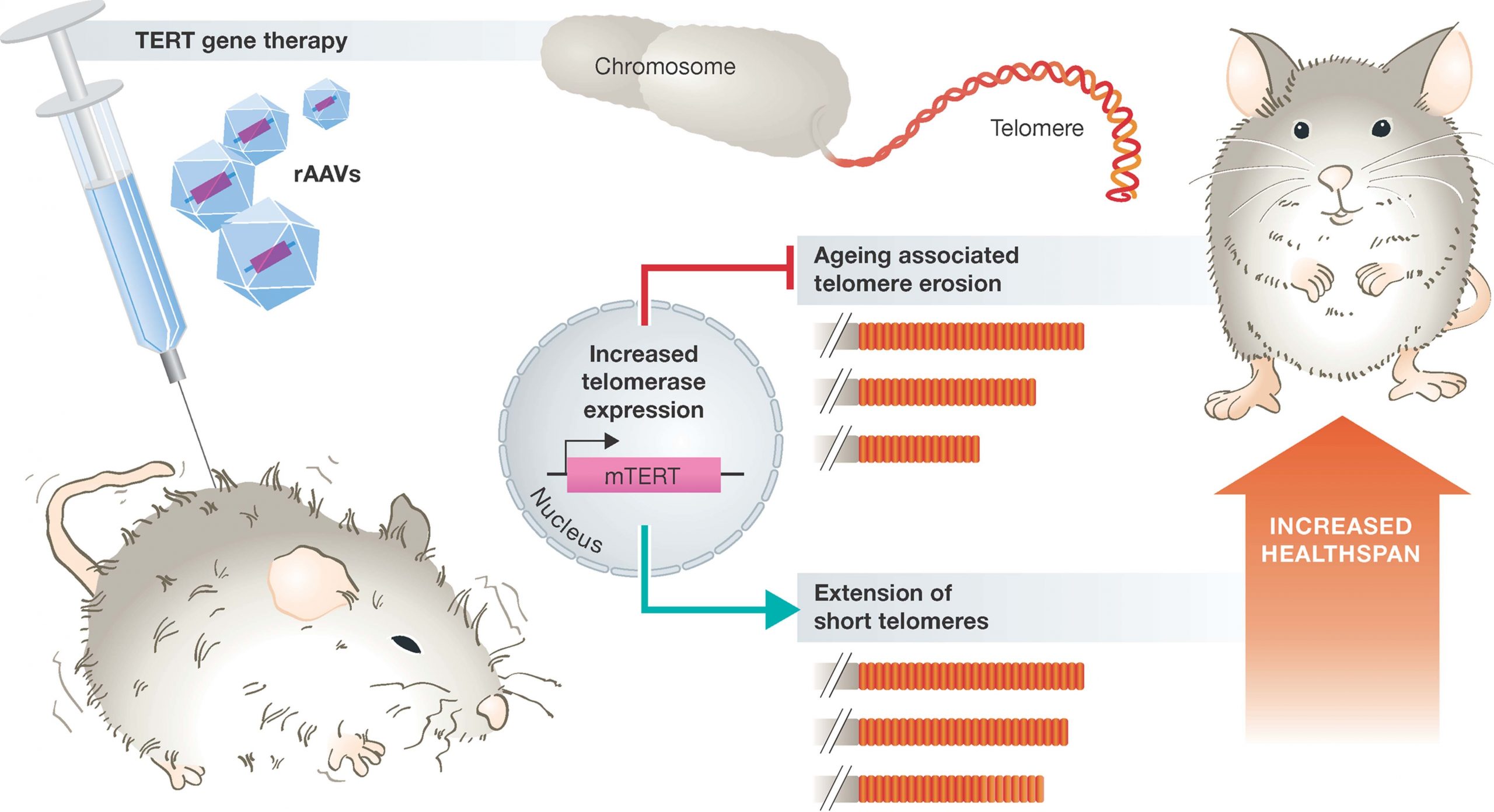
DNA replication proteins are those proteins which support the process of replication and are also reported to be important in drug design and discovery. This information depicts that DNA replication proteins have a very important role in human bodies, however, to study their mechanism, their identification is necessary.
The cell performs replication of its DNA in the S phase. Semiconservative replication occurs during this phase, in that the number of chromosomes remains constant during DNA doubling. Along with DNA duplication, the cell also duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure called the centrosome, which helps in separating the DNA during M phase.
The key difference between SF1 and SF2 is their ability to unwind nucleic acids.While SF1 only unwinds DNA, SF2 unwinds both DNA and RNA.. Helicase is one of the key enzymes that take part in the DNA replication process as well as in DNA repair processes. The primary role of helicase is to take part in the unwinding process in order to facilitate the separation of double-stranded DNA molecules.
A bacteria undergoing cell fission is seen in the diagram above. The mechanism of bacterial replication looks to be quick and easy, as illustrated. The steps of genomic replication, chromosomal segregation, and cytokinesis in a bacterial cell are as follows: (1) genomic replication, (2) chromosome segregation, and (3) cytokinesis.
Importantly, we show that high levels or unresolved DNA-RNA hybrids at the breaks interfere with their repair by homologous recombination. This interference is observed for both plasmid and chromosomal recombination and is independent of whether the DSB is generated by endonucleolytic cleavage or by DNA replication.'.
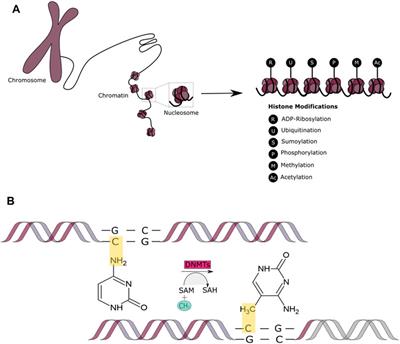
Frontiers Epigenetic Mechanisms In Dna Double Strand Break Repair A Clinical Review Molecular Biosciences
DNA replication is the process of synthesizing new DNA (choices A and D are incorrect). 3. Answer choice A is correct. The origin of replication describes where DNA replication starts. A break in the DNA must be made for replication to occur.
Both protein- and gene-based vaccines (including DNA and RNA) have been explored for COVID-19 and currently on clinical trials. There are several advantages of mRNA vaccines over the other platforms. The first advantage of mRNA vaccines is the easiness and fast speed for their manufacturing.
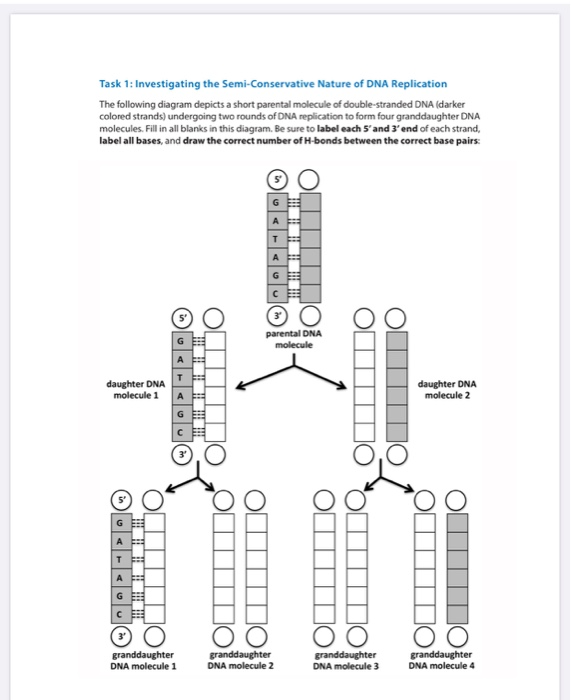
The term semiconservative replication refers to the fact that each new DNA molecule resulting from the replication process is "half-old, half-new." In the diagram, complete the replication required in the middle of the molecule by adding the required letters representing the missing nucleotide bases. Recall that ATP energy and the appropriate enzymes are actually required to complete this process.
Eukaryotic DNA replication is a conserved mechanism that restricts DNA replication to once per cell cycle. Eukaryotic DNA replication of chromosomal DNA is central for the duplication of a cell and is necessary for the maintenance of the eukaryotic genome.. DNA replication is the action of DNA polymerases synthesizing a DNA strand complementary to the original template strand.
The second, homology-directed repair (HDR), uses homologous regions of DNA to facilitate repair in S/G2 after 5′-to-3′ nucleolytic resection of DSB ends. Beyond these high-level branches, however, descriptions of DSB repair as decision trees can oversimplify a complex mechanistic landscape (. Paull, 2021. Paull T.T.

Sterilization Of Objects Products And Packaging Surfaces And Their Characterization In Different Fields Of Industry The Status In 2020 Jildeh 2021 Physica Status Solidi A Wiley Online Library
The genome is the most functional part of a cell, and genomic contents are organized in a compact three-dimensional (3D) structure. The genome contains millions of nucleotide bases organized in its proper frame. Rapid development in genome sequencing and advanced microscopy techniques have enabled us to understand the 3D spatial organization of the genome. Chromosome capture methods using a ...

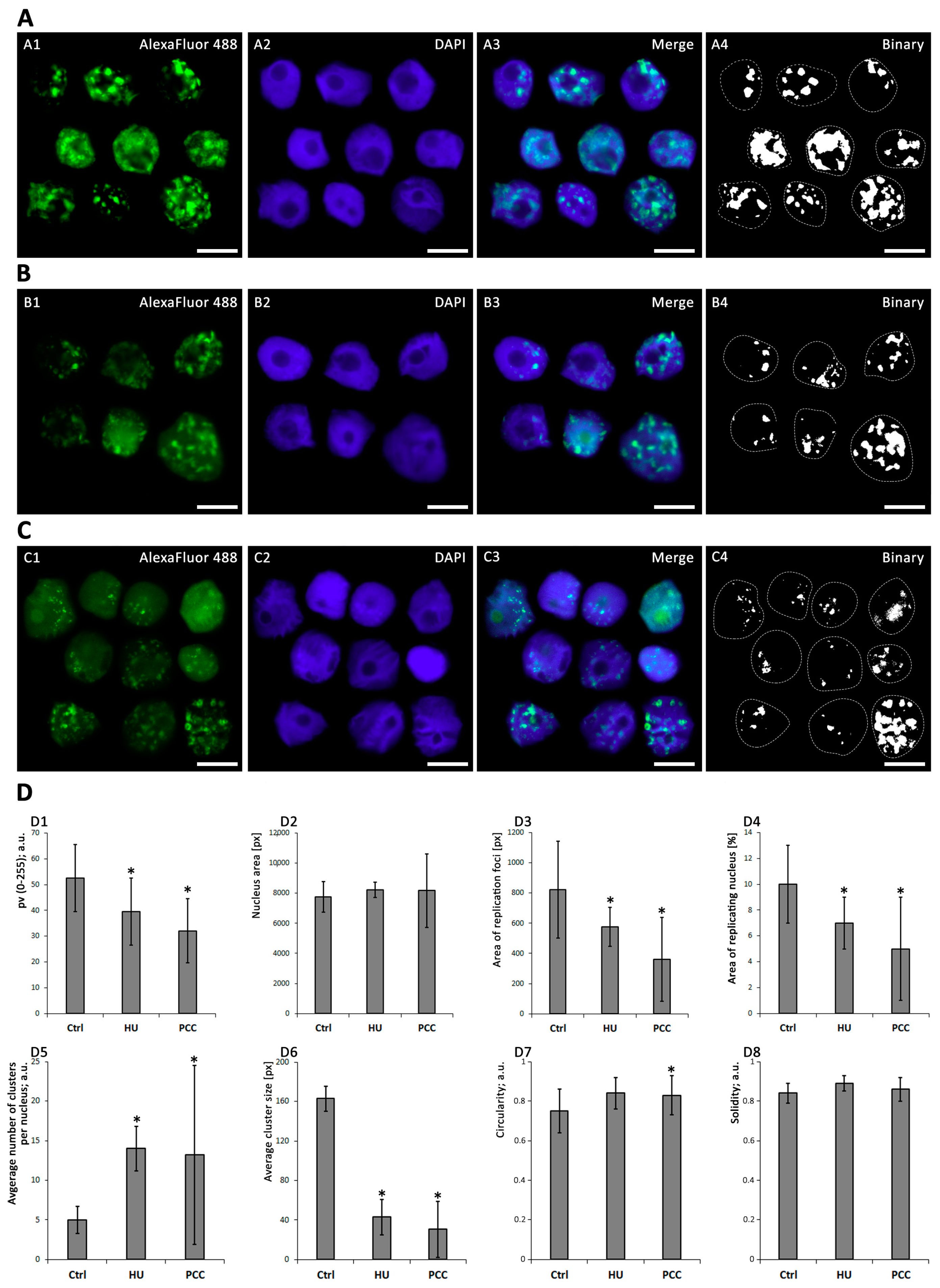
Cells Free Full Text Kinetics Of Dna Repair In Vicia Faba Meristem Regeneration Following Replication Stress Html

Draw A Diagram Showing A Portion Of A Chromosome Undergoing Replication Label The Leading And Lagging Homeworklib

High Prevalence Of Preexisting Hbv Polymerase Mutations In Pregnant Women Does Not Limit The Antiviral Therapy Efficacy

Dna Replication Replication The Process Before A Cell Divides It Duplicates And Copies Its Dna Dna Dna Remember Each Strand Can Be Used To Make Ppt Download

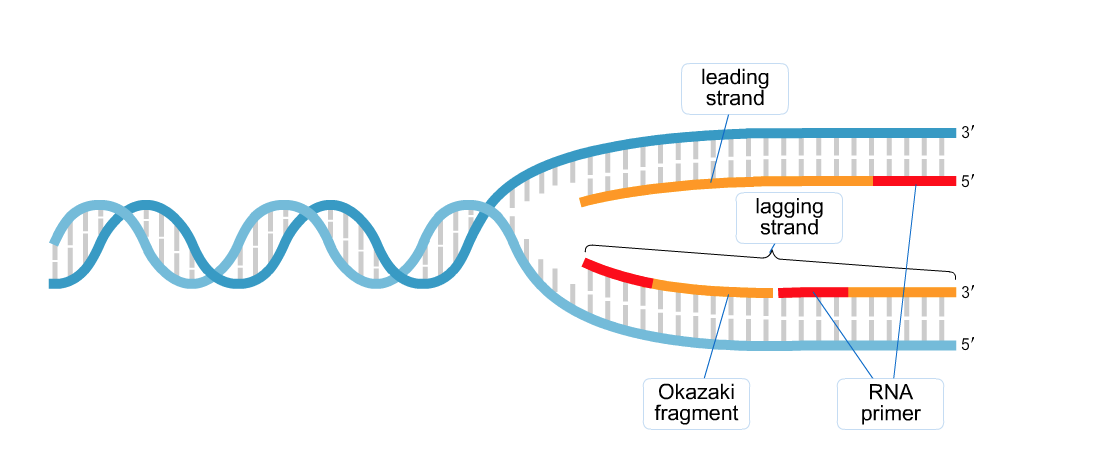


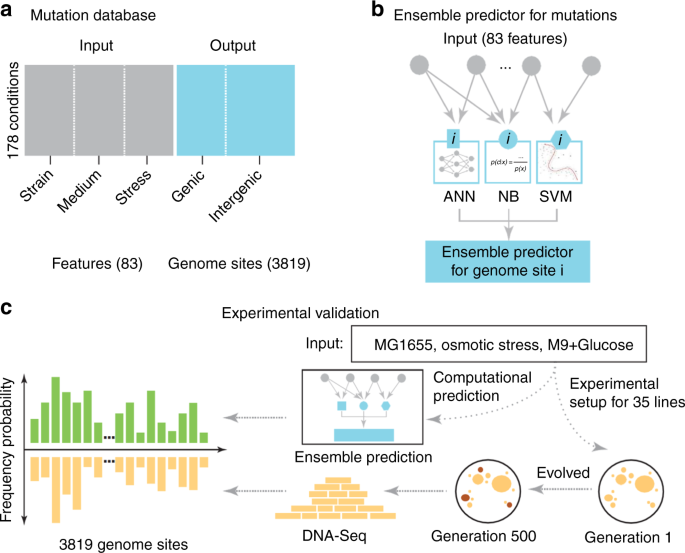
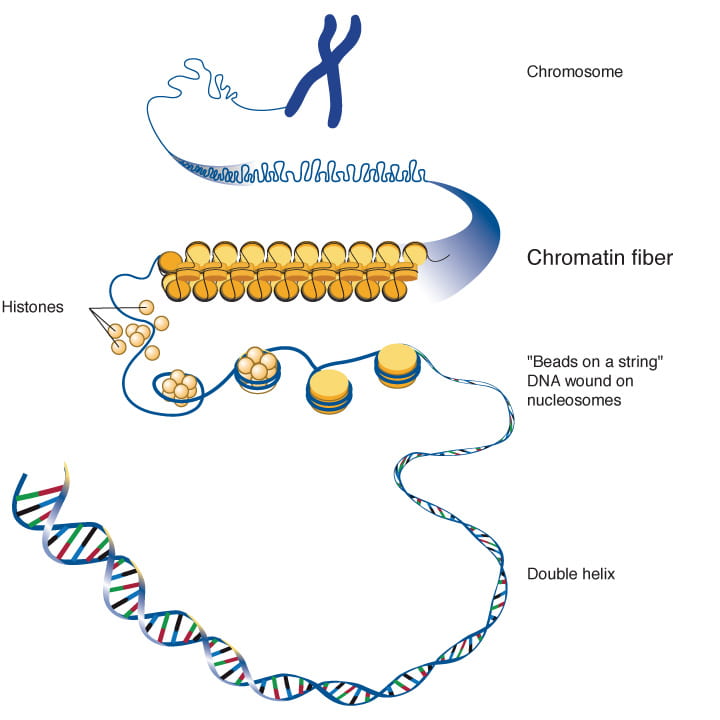











0 Response to "39 the diagram depicts dna that is undergoing replication"
Post a Comment