36 roller coaster free body diagram
Q. In which free-body diagram are the forces correct on a roller coaster car when it is upside down at the top of the . loop-de loop? answer choices . alternatives . answer explanation . Tags: Topics: Question 9 . SURVEY . Ungraded . 30 seconds ... Let's start with the roller coaster / water bucket example. As usual, begin with a free-body diagram. Follow this up with an appropriate choice of coordinate system. At rest, the free-body diagram is simple, with an upward normal force and a downward force of gravity. These are the only two forces in the system even when circular motion is ...
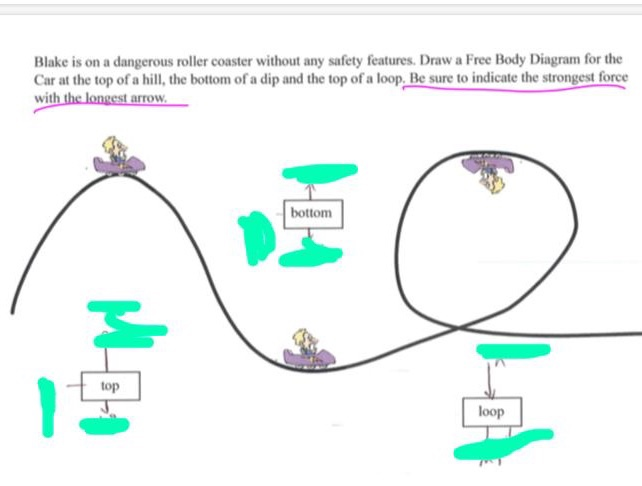
Physics Q&A Library Draw a free body diagram of the roller coaster car with all appropriate forces in three locations. At the bottom of the loop Halfway up the loop (or ¼ of the way around the entire thing) At the top of the loop Based only on your diagrams, where will the rider experience the greatest force?

Roller coaster free body diagram
Roller coaster loops assume a tear-dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as As depicted in the free body diagram, the magnitude of Fnorm is always. Energy conservation and forces on a train in a vertical roller coaster loop.. Figure 3 shows free-body diagrams for a rider in the front, middle and back of. The motion of objects along curved sections of roller coaster tracks (loops, turns, bumps and hills, etc.) can be analyzed using a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations. The Physics Classroom demonstrates how using numerous examples. 7,171. 509. souljaxd said: i researched about free body diagrams and roller coasters. all i have now for the straight away is , f-gravity, f-normal, f - applied, and f- friction. Other than when the coaster ( and passengers) are being pulled up the incline by a chain mechanism or other means, there is no applied force; otherwise you have ...
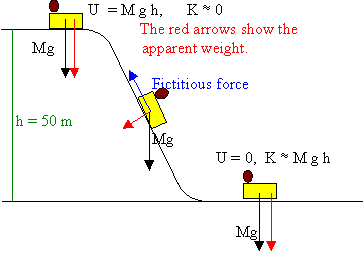
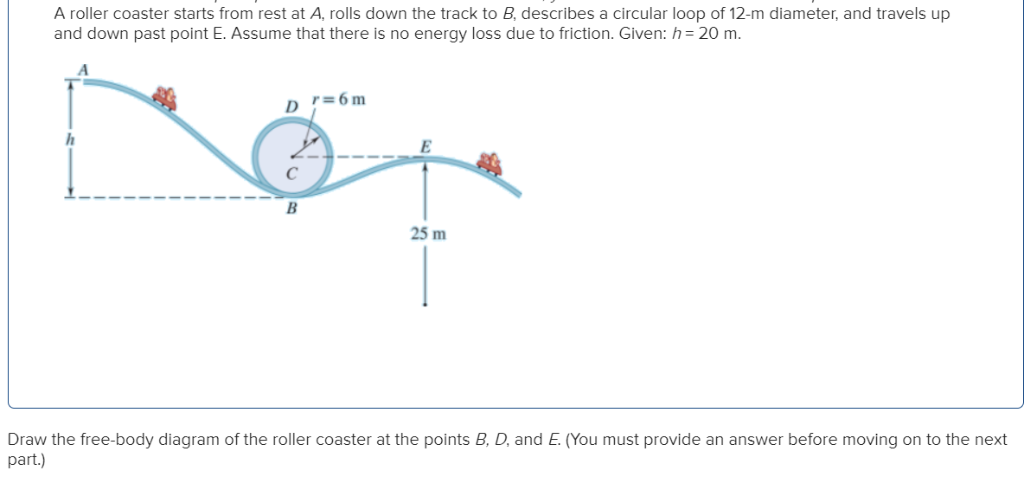
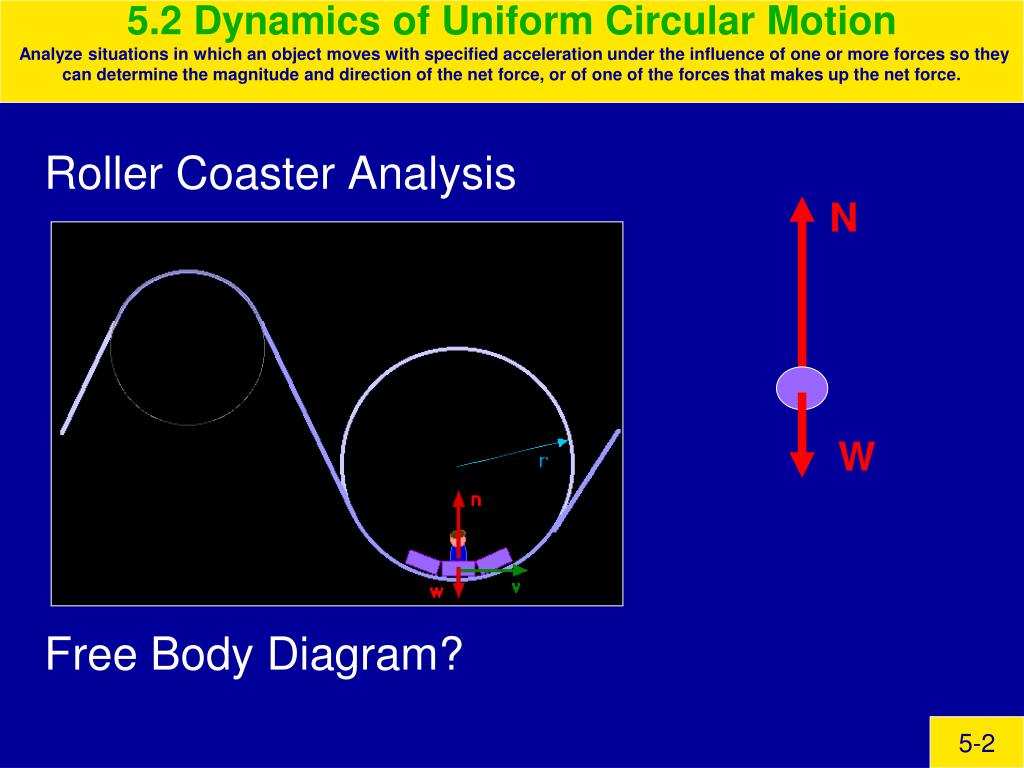
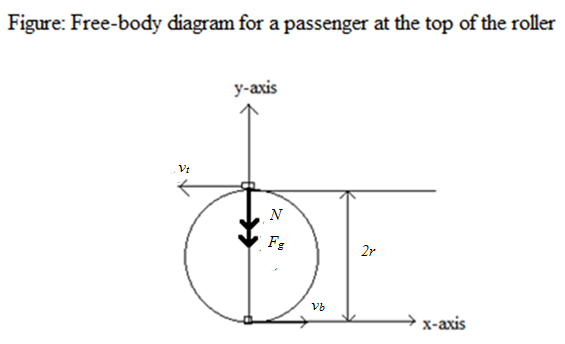
Roller coaster free body diagram. Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and ... a) See free-body diagram in attachment. b) Net force in the y-direction: [/tex] c) The velocity at which the roller coaster will fall is [/tex] d) The speed of the roller coaster must be 17.1 m/s. e) The roller coaster should start from a height of 90 m. f) The roller coaster should start from a height of 100 m. Explanation: a) Always draw good, detailed "free body diagrams"! ... We have described this with a diagram showing a guest on the top of a hill of a roller coaster.
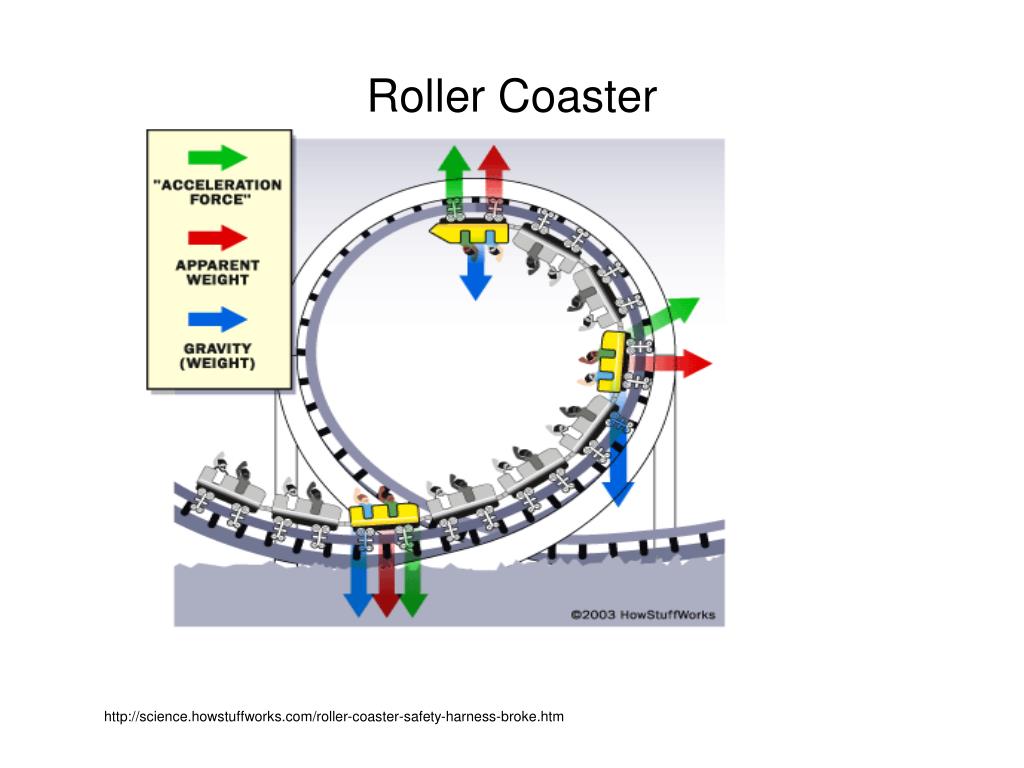
bucket and roller coaster turn completely upside down as they travel, ... We then draw a free-body diagram, although we have to decide whether.2 pages The figure shows the roller-coaster free-body diagram at the bottom of the loop. ! Since the net force is toward the center (upward at this point), n > F G .! This is why you “feel heavy” at the bottom of the valley on a roller coaster. ! The normal force at the bottom is larger than mg. Slide874$ CHAPTER8_LECTURE8.1$ 12 7,171. 509. souljaxd said: i researched about free body diagrams and roller coasters. all i have now for the straight away is , f-gravity, f-normal, f - applied, and f- friction. Other than when the coaster ( and passengers) are being pulled up the incline by a chain mechanism or other means, there is no applied force; otherwise you have ... The motion of objects along curved sections of roller coaster tracks (loops, turns, bumps and hills, etc.) can be analyzed using a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations. The Physics Classroom demonstrates how using numerous examples.
Roller coaster loops assume a tear-dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as As depicted in the free body diagram, the magnitude of Fnorm is always. Energy conservation and forces on a train in a vertical roller coaster loop.. Figure 3 shows free-body diagrams for a rider in the front, middle and back of.

Solved Problem Twoz Roller Coaster Roller Coaster Car Has Mass Of 400 Kg When Fully Loaded With Passengers Complete The Following Tasks Create Free Body Diagram For The Roller Coasters Point T0 The

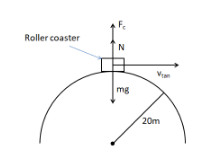
Normal Force On A Hill Centripetal Force Roller Coaster Problem Vertical Circular Motion Physics Youtube

A Roller Coaster Cart And Passenger Has A Capacity Of 2 000 Kg The Roller Coaster Needs To Be Designed Such That The Cart And Passengers Can Make It Around A Loop That

The Diagram Shows A Roller Coaster In Which The Car Going Over It Has A Mass Of 125 0 Kilograms A How Much Work Must Be Done To Get The Car To The

Consider A Roller Coaster As It Travels Near The Bottom Of Its Track As Sketched In The Figure Below At This Point The Normal Force On The Roller Coaster Is Three Times












0 Response to "36 roller coaster free body diagram"
Post a Comment