36 note the diagram below, which shows a circuit created with a battery and three bulbs.
12 The diagram below represents one type of wave created on a guitar string when the string is plucked. The string has a length of 0.65 m and vibrates at a frequency of 880 Hz. a. In your Student Answer Booklet, copy the wave diagram and label the wavelength of the wave. b. Calculate the velocity of this wave on the string. 6. The diagram below shows a typical household circuit. The appliances (lights, television, toaster, etc.) are represented by boxes labeling 1, 2, 3, and so on. The fuse, or circuit breaker, shown in the diagram is a switch intended to shut off the circuit automatically if the wires become too hot because too much current is flowing in the circuit.
METHOD: Construct a series circuit with 1 cell, a resistor and the ammeter in series in the PhET simulation. Drag and drop each component to create the circuit. Connect the voltmeter in parallel with the cell. Record the readings in the table below. Add a second cell in series with the first cell.

Note the diagram below, which shows a circuit created with a battery and three bulbs.
Draw a diagram Of this circuit. Calculate the equiv-alcnt resistance of the circuit. Calculate the total power dissipated in the circuit. 10, In the space below, draw a diagram of an operating circuit that includes: a battery as a source of potential difference two resistors in parallel with each other The circuit in (Figure 1) has three batteries of emf ε in series. Part complete Assuming the wires are ideal, choose the correct graph of the potential as a function of distance traveled clockwise around the circuit, starting from V = 0 V at the negative terminal of the bottom battery. (Lecture 8) Parallel Circuit Example. In the circuit below, two light bulbs are connected in parallel to a battery power source. It can be seen that the top terminals of the two light bulbs are connected together and to the positive terminal of the battery. We know this because the three terminals or connection points have a node where they intersect.
Note the diagram below, which shows a circuit created with a battery and three bulbs.. 53. The diagram at the right shows three identical light bulbs wired in series. Several points along the circuit are labeled with letters. Compare the electric potential and the electric potential energy of the various points. For each comparison, use a greater than (>), less than (<), or approximately equal to (=) symbol. A simple circuit containing a battery and a light bulb is shown in the diagram at the right. Use this diagram to answer the next several questions. The current through the battery is ___. a. greater than that through the light bulb b. less than that through the light bulb c. the same as that through the light bulb d. greater than that through ... These energies must be equal, because there is no other source and no other destination for energy in the circuit. Thus, qV = qV 1 + qV 2 + qV 3.The charge q cancels, yielding V = V 1 + V 2 + V 3, as stated.(Note that the same amount of charge passes through the battery and each resistor in a given amount of time, since there is no capacitance to store charge, there is no place for charge to ... observations. A circuit diagram of two cells and two bulbs in series is shown below . Place . three bulbs in the circuit by connecting the bulb with another electrical lead. Unscrew one of the bulbs and record your observations. Vary the voltage within the circuit and record your observations. Sketch a diagram of the circuit. bulbs.
The circuit diagram below shows a $\quantity{6.0}{V}$ battery of negligible internal resistance connected in series to a light dependent resistor (LDR), a variable resistor and a fixed resistor, R. Figure 7: Circuit for the worked example. For a particular light intensity the resistance of the LDR is $\quantity{50}{kΩ}$. Batteries and Bulbs Figure 6 Two-bulb series circuit using two D-cell batteries, and both the round and long bulb. Above, the actual wiring is depicted. To the left, the circuit diagram corresponding to this circuit is displayed. Note that this is still a single-loop circuit (i.e., all components are connected in series. Question 6. SURVEY. 60 seconds. Q. Most cars have lights, power locks, radios and other equipment that uses electricity. Electric circuits power this equipment. Each circuit has a fuse that completes it. The picture shows one type of fuse a car may have. The circuit diagram above shows a circuit with three bulbs in series. The same 1-A current flows through each bulb, even if the bulbs are not identical. The following equation describes this relationship (T stands for total). I II I T 1 2 3 == = Current in a Parallel Circuit In a parallel circuit, the current splits at certain junctions and ...
The diagram below shows two light bulbs, X and Y, connected in series to a battery with negligible internal resistance If bulb X glows brighter than bulb Y then the…. A. current through bulb X is smaller than that through bulb Y B. resistance of bulb X is smaller than that of bulb Y C. resistance of bulb X is greater than that of bulb Y Circuit Problem (2) ÎThe light bulbs in the circuit shown below are identical. When the switch is closed, what happens to the intensity of the light bulbs? a) bulb A increases b) bulb A decreases c) bulb B increases d) bulb B decreases e) nothing changes (b) (a) Before switch closed: V a = 12V because of battery. V b =12 because equal resistance 9-volt battery of internal resistance 1 ohm is 3 amperes. The power dissipated in R 2 is 12 watts. (a) Determine the reading of voltmeter V in the diagram. (b) Determine the resistance of R 2. (c) Determine the resistance of R 1. 2. (1977-4) (a) In the space below draw a diagram, using the symbols described above, to show how you should The idea here is that the current must pass through one light bulb before it can pass through either of the two parallel bulbs. (Note: the bulbs may be on but be too dim to see.) Unscrew one bulb, describe the response 7. Diagram your circuit (both pictogram and schematic). Compare the behavior of the bulbs with the single bulb part 8.
The diagram below shows a circuit with one battery and 10 resistors; 5 on the left and 5 on the right. Determine… the current through; the voltage drop across; the power dissipated by each resistor; Given the circuit below… Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Calculate the current through the battery.
The Diagram Above Represents A Simple Electric Circuit Composed Of 5 Identical Light Bulbs And 2 Flashlight Cells Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Questions 14-15 refer to the following diagram that shows part of a closed electrical circuit. 14. The electrical resistance of the part of the circuit shown between point X and point Y is (A) 4/3 (B ) 2 (C) 4 (D) 6 15. When there is a steady current in the circuit, the amount of charge passing a point per unit of time is
10. The diagram below shows a parallel circuit with three resistors. For the questions below, apply the following values: V battery = 24 V, R 1 = 12 Ω, R 2 = 6 Ω and R 3 = 4 Ω. (Ignore the funny symbols for now) a. What is the net resistance of the circuit? R net = _____ b. What is the current leaving the battery?
of materials listed below: a. In a space below draw a diagram showing all the elements connected in one electrical circuit that can provide the maximum rate of heat produced. Use two meters in your circuit, they will help to measure the heat rate. The battery has an emf of 12 V and an internal resistance of 0.5 Ω and each heating
The diagram below shows the circuit for a small convector heater. Heater elements can be switched in and out of the circuit using switches X and Y. Each element has a resistance R and the power supply has an emf V. (a) The table shows the possible combinations of open and closed switches. When a switch is closed, charge can flow through it. 17
Note the diagram below, which shows a circuit created with a battery and three bulbs. Which of the circuit diagrams below represent the physical arrangement shown above? (Note: Select all that may apply.) Circuit diagram 1. Circuit diagram 2. Circuit diagram 3. Circuit diagram 4. Circuit diagram 5. None of these circuit diagrams
50. Three identical light bulbs (labeled X, Y and Z) are connected to a battery as shown at the right. Which adjustments could be made to the circuit below that would increase the current at point P? List all that apply. a. increase the resistance of one of the bulbs b. increase the resistance of two of the bulbs
Look at the diagram which shows how two light bulbs are connected in parallel. ... Connect another wire between the negative terminal of the first battery and the negative terminal of the second battery. Draw a circuit diagram of your circuit. ... Look at the circuit diagram below. Each light bulb is identical.
The bulbs in the circuit below are connected_____. A. in series ... The diagram below shows a circuit with two batteries and three ... D. 7.5 V E. There is not enough information to decide. Ω Slide 23-15 The diagram below shows a circuit with two batteries and three resistors. What is the potential difference across the 200 resistor?
1. The diagram below shows a segment of a circuit. What is the current in the 200 Ω resistor? A. 0.5 A B. 1.0 A C. 1.5 A D. 2.0 A E. There is not enough information to decide. Multiple choice questions 2. The diagram below shows a circuit with two batteries and three resistors. What is the potential difference across the 200 Ω resistor? A. 2 ...
Q. A string of light with small bubs is shown here. The bulbs are connected by wire that is covered with an insulator. When the lights are on, electricity travels in ---- (5.6B) answer choices. a complete circuit. a sound wave. a light ray. an incomplete path.
Parallel Circuit Example. In the circuit below, two light bulbs are connected in parallel to a battery power source. It can be seen that the top terminals of the two light bulbs are connected together and to the positive terminal of the battery. We know this because the three terminals or connection points have a node where they intersect.
The circuit in (Figure 1) has three batteries of emf ε in series. Part complete Assuming the wires are ideal, choose the correct graph of the potential as a function of distance traveled clockwise around the circuit, starting from V = 0 V at the negative terminal of the bottom battery. (Lecture 8)
Draw a diagram Of this circuit. Calculate the equiv-alcnt resistance of the circuit. Calculate the total power dissipated in the circuit. 10, In the space below, draw a diagram of an operating circuit that includes: a battery as a source of potential difference two resistors in parallel with each other

12v Led Light Bulb 7w 630lm Ac Dc 12 24volt Low Voltage E26 Base 2700k Warm White 40 60 Watt A19 Bulbs Equivalent Landscape Garden Yard 12volt Battery Power System Off Grid Solar Lighting 6 Pack

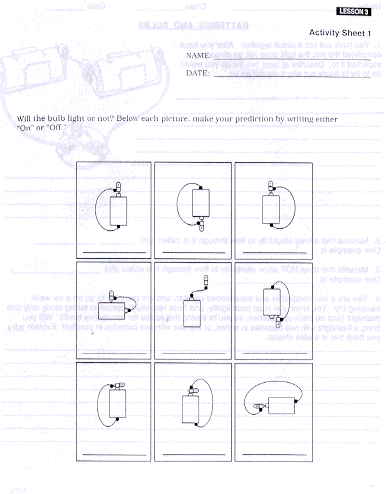














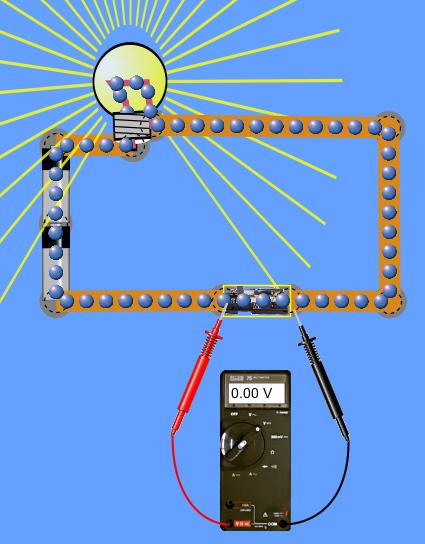
0 Response to "36 note the diagram below, which shows a circuit created with a battery and three bulbs."
Post a Comment