36 mo diagram for h2
1 Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2+ and then identify the bond order. Get access to the latest Bonding in Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules: H2, H2+, H2-, He2, He2+ prepared with IIT JEE course curated by Megha Khandelwal on Unacademy to prepare for the toughest competitive exam.
Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...

Mo diagram for h2
Use an mo diagram to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. H22 the mo scheme is σ σ with a bond order of 0 unbound. You may want to reference pages 371 382section. For the species n2 is diamagnetic because it has no unpaired electrons. The following is part of a molecular orbital energ. December 4, 2017 - Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi... Explain about the molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule.
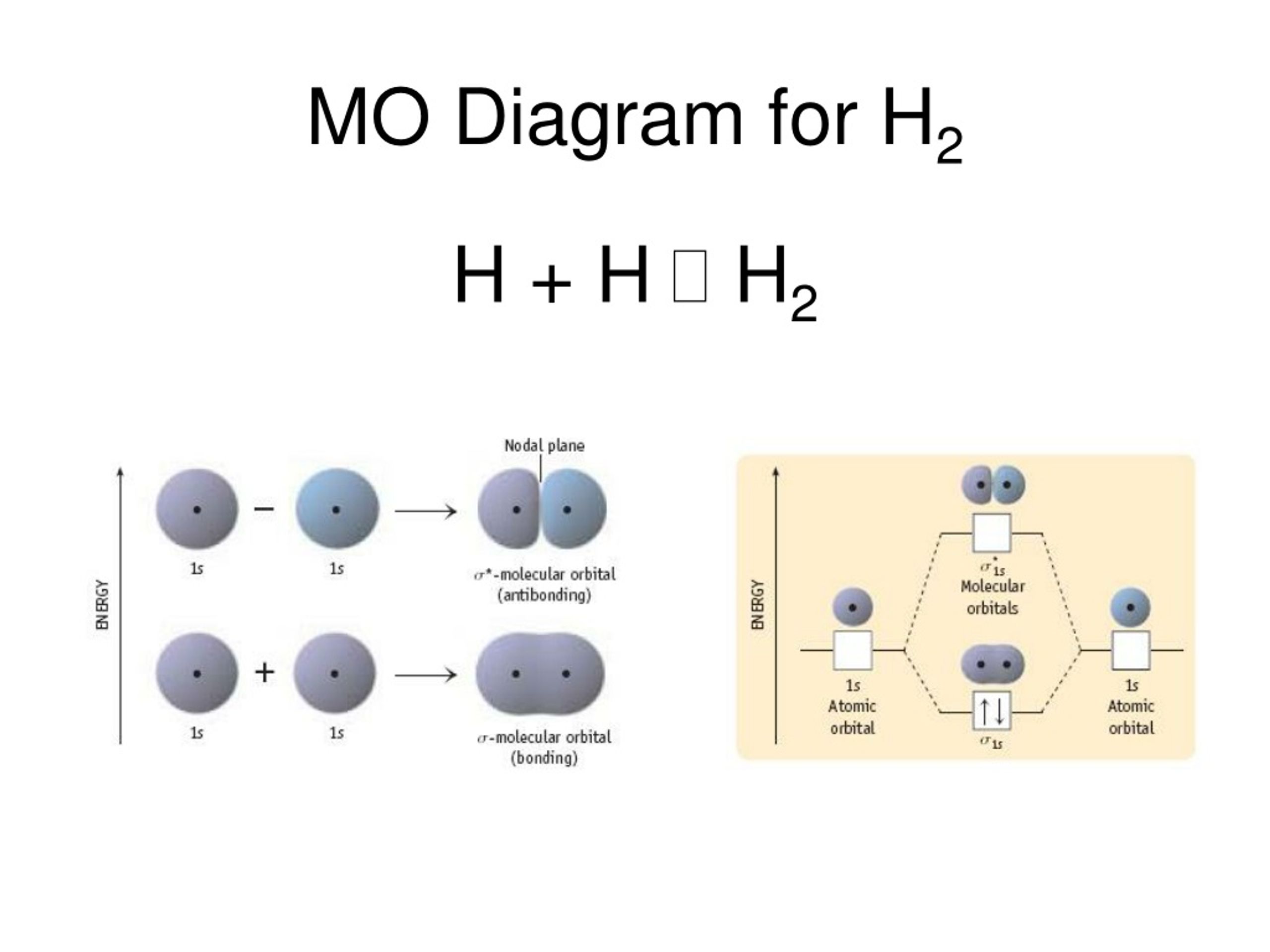
Mo diagram for h2. Paste a copy of each of your orbitals in the appropriate position in this diagram, as is shown in the MO diagram for H2 in Figure 5.45, compare (a) and (b) on page 225. Use the Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule to place the valence electrons for N2 into these orbitals. Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ... $$\ce{Be + H2 <=> BeH2}$$ The MO for $\ce{H2}$, which is shown in the figure below is taken from Wikipedia. The right side of the diagram you showed neither represents a hydrogen molecule, nor two independent (and hence equivalent) hydrogen atoms. MO diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules Li 2 through N 2 MO diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules O 2 and F 2.
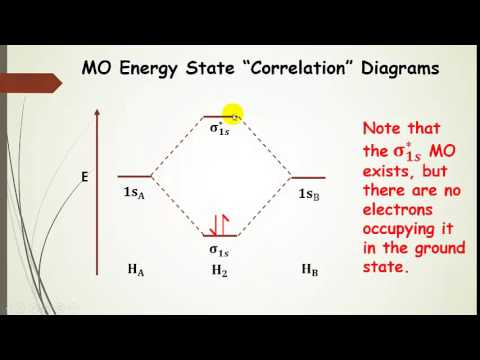
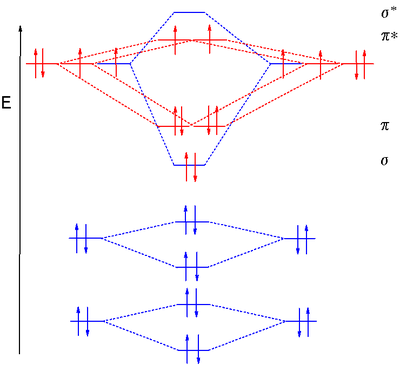
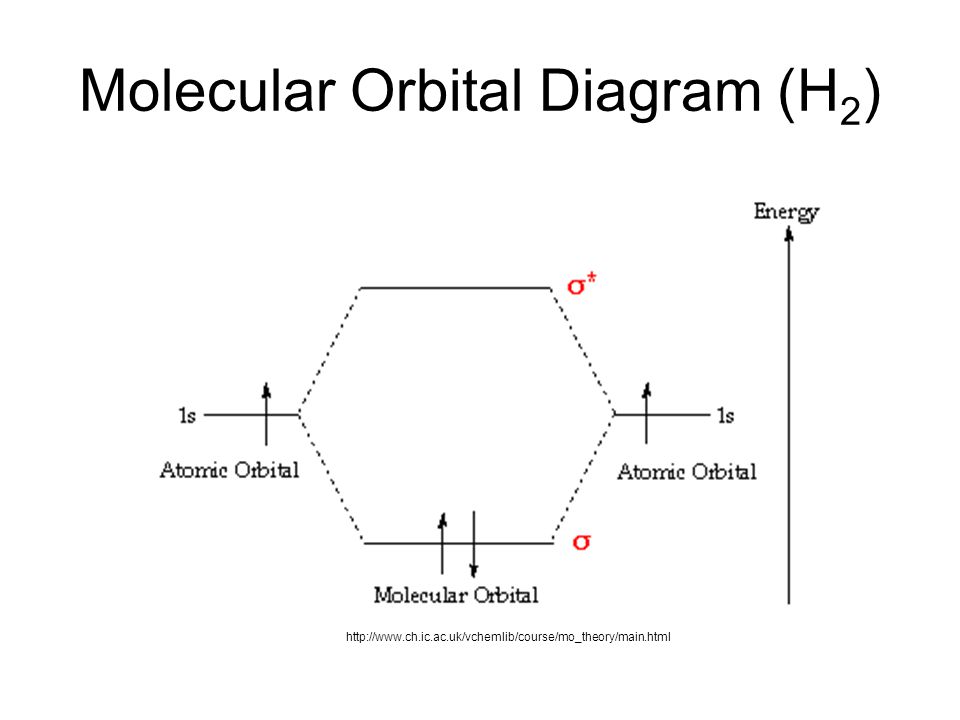
Professor Patricia Shapley, University of Illinois, 2011 Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Principle 2 & 3: This interaction ... to the molecular orbitals, may also be represented in the form of an orbital (electron) energy diagram which shows the relative energies of the orbitals. In the specific case of hydrogen each of the isolated atoms has one electron in its 1s orbital and when the atoms combine to form H2 the two electrons ... LUMO = lowest unoccupied molecular orbital HOMO = highest occupied molecular orbital Similar phase of electron density (no node) adds together constructively. energy of isolated atoms bond order (H2 molecule) = (2) - (0) 2 = 1 bond 1sb H H H H σ∗ = 1s H H a - 1sb = antibonding MO = LCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals node = zero ...
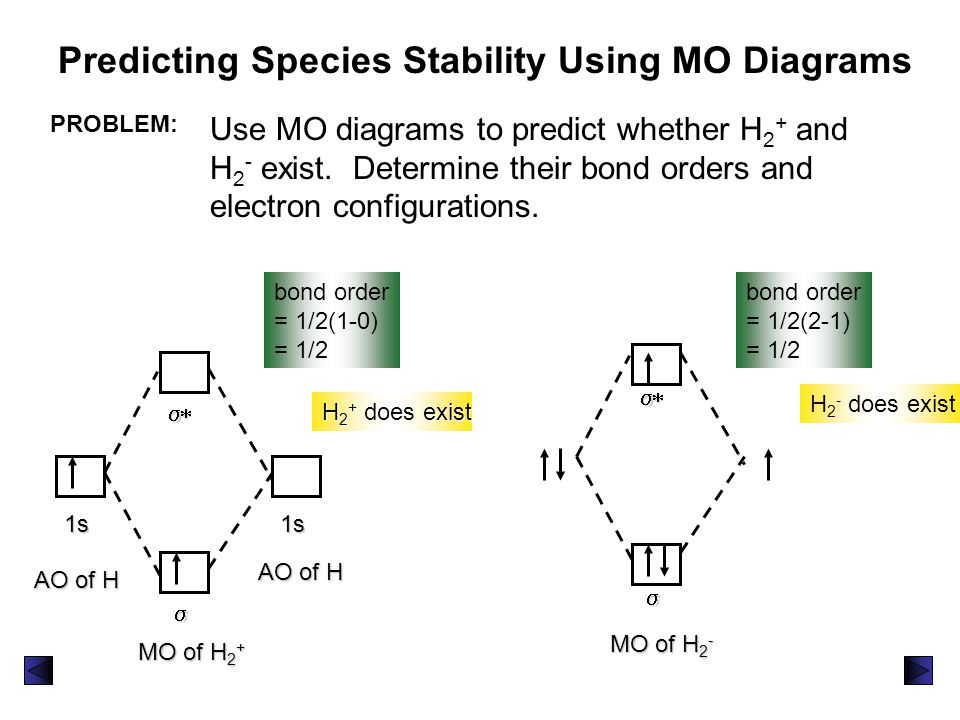
Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are formed by linear combination of atomic orbitals. Atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals of a molecule can be shown in a molecular orbital diagram Atomic number of hydrogen is 1 Electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s In H2 molecule two elecrtrons ... 2) Draw a MO diagram for H2, including labeling for all orbital energies 3) Which of the following will have the strongest bond, on the basis of MO theory (S2, S2-, S2+). Provide an explanation ... 1)H2+. Molecular orbital energy level for H2+. The electronic configuration of H2+. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. σ bonding MO that is lower in energy than the constituent 1s AOs and an antibonding σ* MO that is at a higher energy than the 1s AOs.[1] Each. The energy curves for ψ + and ψ-reveal the following properties of the ion H 2 +. The curve for ψ + refers to the ground state of the molecule where a minimum energy is found for a nuclear distance of approximately 2a o (i.e. 100pm). Thus, H 2 + should exist as a stable molecule. The calculated bonding energy is 1.77 eV. This is a quite satisfying result; from experiments we get 2.77 eV.
Relative AO Energies in MO Diagrams Use AO energies to draw MO diagram to scale (more or less). H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p -19.4 eV -15.8 eV -32.4 eV -10.7 eV
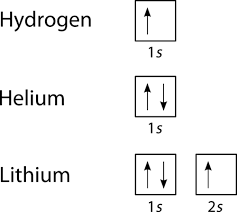
March 10, 2016 - Molecular orbital energy level diagrams of certain diatomic Homo nuclear molecules and molecular ions · The filling of molecular orbitals is governed by the following principles. ... (iii)Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. Now, let us consider some examples of homo nuclear diatomic molecules. 1. Hydrogen molecule, H2...
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: ... Two electrons in Molecular Orbital ψ_+ 2) One electron in MO ψ_+ and one electron in MO ψ_‐ 3) Two electrons in MO ψ_‐. ... Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or 2nd row elements:
1) H2- 2) H2+ 3) H2 4) He2+. A species is said to be diamagnetic when it has all the paired electrons. Similarly if the species contain unpaired electron it is said to be paramagnetic. To know the magnetic character of molecules we can use MO diagram. When we draw MO diagram for dihydrogen anion ( H2-) we find one unpaired electron in ...
Mo Diagram H2. molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory marcus va 100 primary volts 120 240 secondary volts 12 24. Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2– And Then Identify The Bond Order.
Chapter 1 Molecular Orbital Concepts A Concepts Of Mo Theory 1 Strong Covalent Bonds Consider The Pi Bond Of Ethene In Simple Molecular Orbital Terms The Qualitative Results Would Be The Same For Any Pi Or Sigma Bond Q The Overlap Of The Two
Draw mo energy diagrams for the molecular ions h2 and h2. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2. When the 1s wave functions of the two ceh atoms are linearly combined we get a sigma s bonding orbital denoted as s 1s in the diagram herethis approach is called linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao.
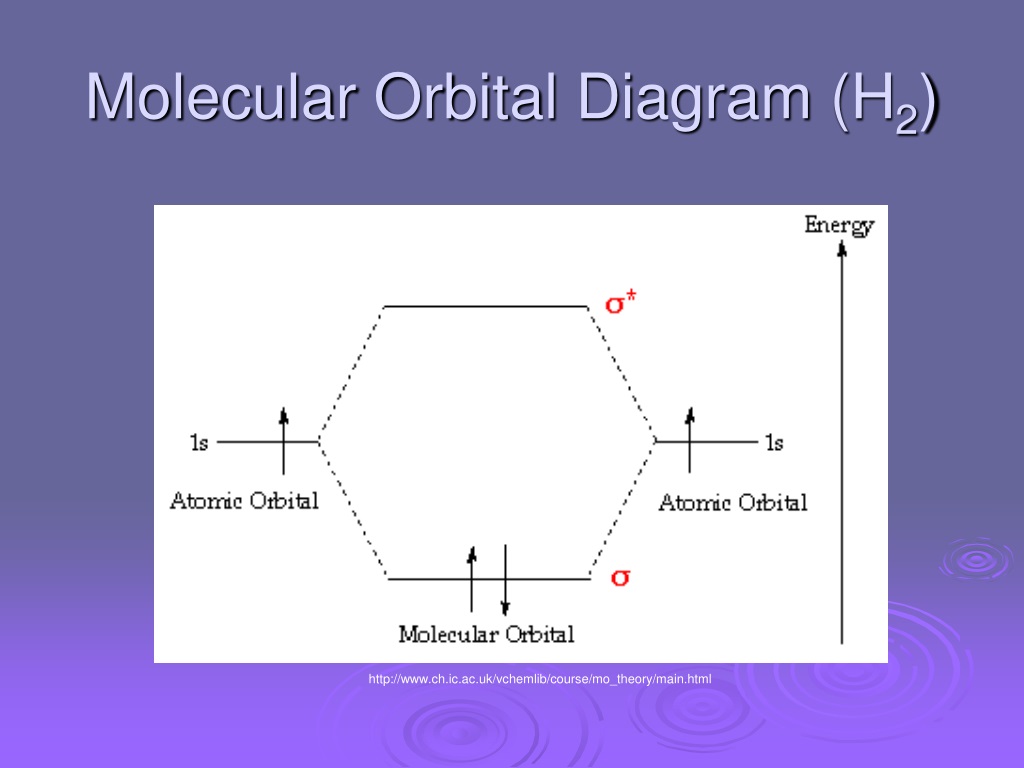
Chemistry questions and answers. The below Mo diagram is for H2. A hydrogen atom contains one valence electron, therefore the is atomic orbital contains a single electron. This is true for each hydrogen atom. The middle of the MO diagram shows the molecular orbitals that have been filled with the valence electrons from the original atoms.
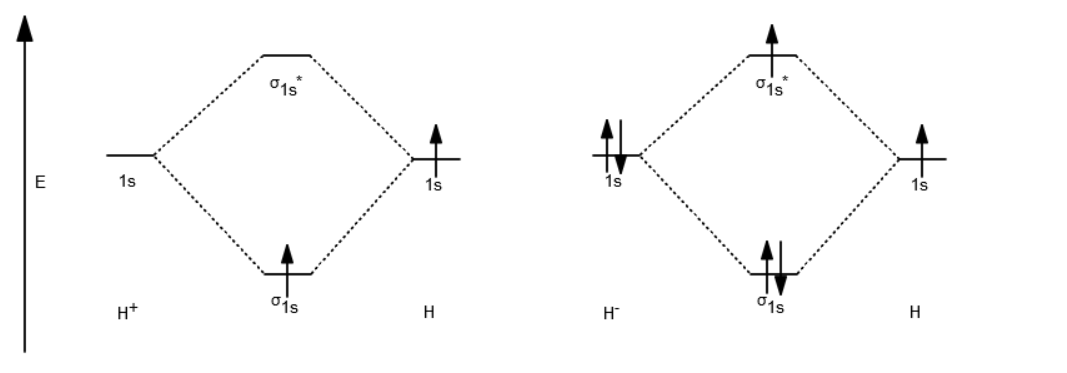
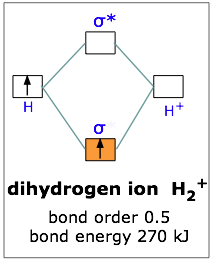
Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ...
molecular orbital theory build h2 for the ion h2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist. figshare. electron ejection from mo by he he and he 2 electron ejection from mo by he the slowest ions observed were found to eject 0 25 0 72 and 0 13 electron per ion for he he and he 2. wiki figure 10 MLCT.
A simple approach to molecular orbital (MO) theory for heterogeneous diatomic molecules is to show the energy level diagram. The MO energy levels can be worked out following these steps: Recall that the energy E n for the quantum number n is for an element with atomic Z is approximately. (1) E n = 13.6 Z E f f 2 n 2 e V.
In agreement with this description ... peaks for the 3a1 MO (14.7 eV), 1b2 MO (18.5 eV) and the 2a1 MO (32.2 eV). The 1b1 MO is a lone pair, while the 3a1, 1b2 and 2a1 MO's can be localized to give two O−H bonds and an in-plane lone pair. This MO treatment of water does not have two equivalent rabbit ear lone pairs. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) too has a ...
Chemical bonding molecular orbitals of h2 and he2. This problem has been solved. Description of the molecular orbitals of the h2 molecule with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for n2 and then identify the bond order. Draw the lewis structure of pf 3a how many share.
The lone pair is relatively high in energy, and is responsible for the well known Lewis base properties of ammonia. The next molecule in the series HF, H2O and H3N, is H4C (methane) - which was discussed earlier - and unlike the other three molecules has no non-bonding orbitals.

Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Molecule Molecular Orbital Theory Mermaid Angle Text Triangle Png Pngwing
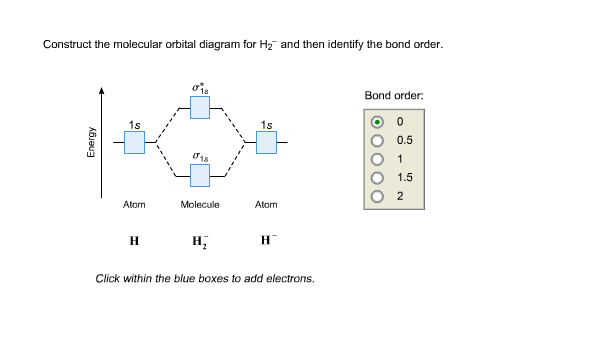
Question:Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click... ... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click...
When An Electron Of H2 Is Promoted To The Excited State Does The Molecule Continue To Exist Or Does Its Bond Break Quora
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals.
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Diatomic Species | MO theory | ChemogenesisChemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 ...
1)H2+. Molecular orbital energy level for H2+. The electronic configuration of H2+. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is .
This molecular orbital treatment can explain why H2 exists but He2 does not. Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene.© Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close windowProf Adam J Bridgeman | close window. Show transcribed image text Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2+ and then identify the bond order. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2+ and then identify the bond order.

Which Of The Following Statements About The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H 2 Is False A There Is A Non Zero Bond Order B There Is One Filled Bonding Orbital C Two Atomic
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
Answer: According to the molecular orbital theory, a molecular is viable of its bond order is more than or equal to one. The bond order is defined as number of bond between to two atoms of that molecule. It is calculated as the difference of electrons in bonding molecules and anti-bonding molecul...
site map
Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Number Molecule Atom Bond Order Multiple Bonds
March 2, 2021 - Note that there is a nodal plane in the anti-bonding MO. ... For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
August 15, 2020 - Check out our new LibreCommons search portal · Describe the hydrogen molecule in light of the following:
Explain about the molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule.
December 4, 2017 - Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
Use an mo diagram to find the bond order and predict whether h2 exists. H22 the mo scheme is σ σ with a bond order of 0 unbound. You may want to reference pages 371 382section. For the species n2 is diamagnetic because it has no unpaired electrons. The following is part of a molecular orbital energ.












0 Response to "36 mo diagram for h2"
Post a Comment