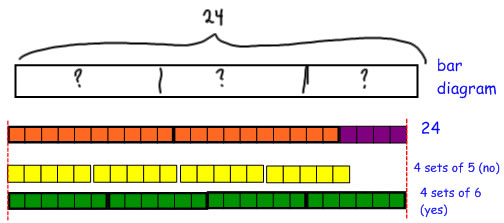
35 what is a bar diagram
Using Bar Models for Multiplication and Division in One-Step Multiplication Word Problems. Example (from Math in Focus workbook 3A): School A collects 76 bundles of newspaper for recycling. School B collects 5 times the number of bundles as School A. How many bundles of newspaper does School B collect? What is a bar chart? Looking for a bar chart definition? A lot can happen to a security in one day of trading, but thankfully the bar chart exists to help summarise all the important info. A bar chart or bar graph presents data with rectangular bars at heights or lengths proportional to the values they represent.
A bar chart is a common chart type for graphing categorical data or data sorted into groups. It consists of multiple rectangles aligned to a common baseline. The length of each is proportional to the value it represents—in other words, in a bar chart, the data is encoded by length. Our eyes are very good at comparing lengths when objects are ...

What is a bar diagram
What is the Bar Chart? A bar chart is a type of graph that is used to represent or summarize data using bars or rectangles of equal width but different heights or lengths. They can be either vertical or horizontal to graph data, more accurately measured data. These data are generally measures of frequency, number, or other means such as mean, median, mode, etc. The stacked bar graph is also called the composite bar chart, which divides the aggregate into different parts. In this type of bar graph, each part can be represented using different colours, which helps to easily identify the different categories. The stacked bar chart requires specific labelling to show the different parts of the bar. Nov 13, 2021 · Bar Diagrams. The Bar Diagram is the basic model of the Data Interpretation Problems. The bar diagram is a two dimensional graphic representation where the elementary graphic objects are a set of rectangles or bars drawn in parallel so that the extension of the same is proportional to the magnitude they intend to represent.
What is a bar diagram. A bar graph or a bar chart is used to represent data visually using bars of different heights or lengths. Data is graphed either horizontally or vertically, allowing viewers to compare different values and draw conclusions quickly and easily. A typical bar graph will have a label, axis, scales, and bars, which represent measurable values such as amounts or percentages. Bar Graph: A bar graph is a chart that plots data with rectangular bars representing the total amount of data for that category. A bar chart is a style of bar graph; it is often used to represent ... Construction of a Bar Graph. Draw two perpendicular lines intersecting each other at a point O. The vertical line is the y-axis and the horizontal is the x-axis. Choose a suitable scale to determine the height of each bar. On the horizontal line, draw the bars at equal distance with corresponding heights. The space between the bars should be equal. A histogram is a type of bar chart that displays the frequency distribution of continuous data. It is useful in representing statistical information, whereby the different heights of the bars depict observed frequencies. These adjacent bars are attached because the number of observations lies in-between the value range, known as bin or class.
Q #1) What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? Answer: A Bar Chart depicts the values of each data set or category across two axes. For example, in a class of 20 children with varying heights, if we were to draw a Bar Chart, one axis would represent the children and their corresponding height would be marked on the other axis ... A bar chart is used when you want to show a distribution of data points or perform a comparison of metric values across different subgroups of your data. From a bar chart, we can see which groups are highest or most common, and how other groups compare against the others. Since this is a fairly common task, bar charts are a fairly ubiquitous ... A bar graph is a chart that uses bars to show the differences and similarities between categories of data. Discover the definition, types, and examples of bar graphs, as well as how to create a ... Bar Graph. There are all kinds of charts and graphs, some are easy to understand while others can be pretty tricky. There are many different types because each one has a fairly specific use. Bar graphs can be used to show how something changes over time or to compare items. They have an x-axis (horizontal) and a y-axis (vertical).
How to create a bar graph. Enter the title, horizontal axis and vertical axis labels of the graph. Enter data label names or values or range. Set number of data series. For each data series, enter data values with space delimiter, label and color. Check horizontal bars or stacked bars if needed. Press the Draw button to generate the bar graph. Horizontal Bar Graph: It represents the grouped data horizontally. Stacked Bar Graph: Each bar in the graph is a whole, and segments or breaks in the bar are the different parts of that whole. Grouped Bar Graph: It allows to compare categories with the same level and use the same colors to compare the groups within them. A bar chart looks a little like a picture of a skyline, consisting of different heights of 'tower' lined up side-by-side. The heights of the towers represent the relative sizes of the categories they represent. Some graphs show the towers on their sides, but you can deal with those by tilting your head or turning […] A bar chart is a graphical representation of the categories as bars. Each bar's height is proportional to the quantity of the category that it represents. A bar chart can be plotted vertically or horizontally. Usually it is drawn vertically where x-axis represents the categories and y-axis represents the values for these categories.
A graph drawn using rectangular bars to show how large each value is. The bars can be horizontal or vertical. See: Histogram. Bar Graphs.
A divided bar graph is a rectangle divided into smaller rectangles along its length in proportion to the data. Segments in a divided bar represent a set of quantities according to the different proportion of the total amount. A divided bar diagram is created using rectangular bars to depict proportionally the size of each category.
Bar Diagrams. As the name suggests, when data is presented in form of bars or rectangles, it is termed to be a bar diagram.. Features of a Bar. The rectangular box in a bar diagram is known as a bar.
In statistics, a Q–Q (quantile-quantile) plot is a probability plot, which is a graphical method for comparing two probability distributions by plotting their quantiles against each other. First, the set of intervals for the quantiles is chosen. A point (x, y) on the plot corresponds to one of the quantiles of the second distribution (y-coordinate) plotted against the same quantile of the ...
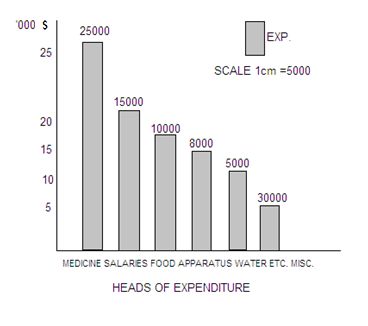
A bar chart or bar diagram is a chart that present qualitative (grouped) data with rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values that they represent. [N:B: In this type diagram, rectangular bars must be separated from each other by same distance. ] Page: 5. 6.
Q.1. Is the bar graph qualitative or quantitative? Ans: The bar graph is used for the qualitative data, whereas histogram, which is similar to bar graph is used for quantitative data. Q.2. What are the \(4\) types of the graph? Ans: There are different types of charts/graphs. The four most common diagrams used are: 1. Line graphs 2. Bar graphs 3.
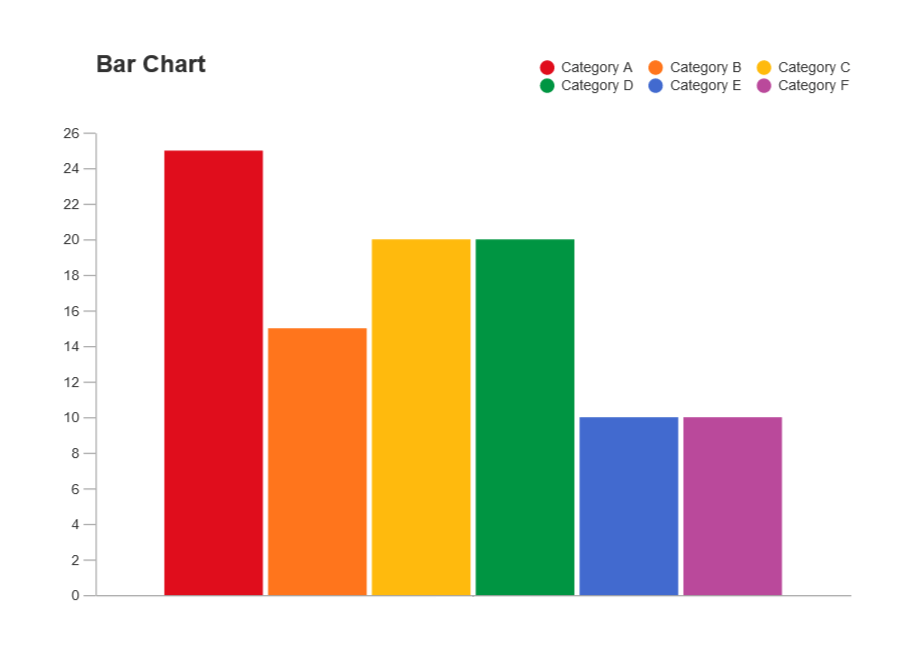
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart . A bar graph shows comparisons among discrete categories.
A bar chart or bar graph is a diagrammatic representation of data in quantities. It is a common statistical tool used for data categorization and it often highlights the differences in the numerical values of specific groups of data.

Use The Bar Diagram To Write An Equation Then Solve Drag Numbers To Complete The Equations Numbers Brainly Com
What is a bar graph? A bar graph can be defined as a chart or a graphical representation of data, quantities or numbers using bars or strips. Bar graphs are used to compare and contrast numbers, frequencies or other measures of distinct categories of data.
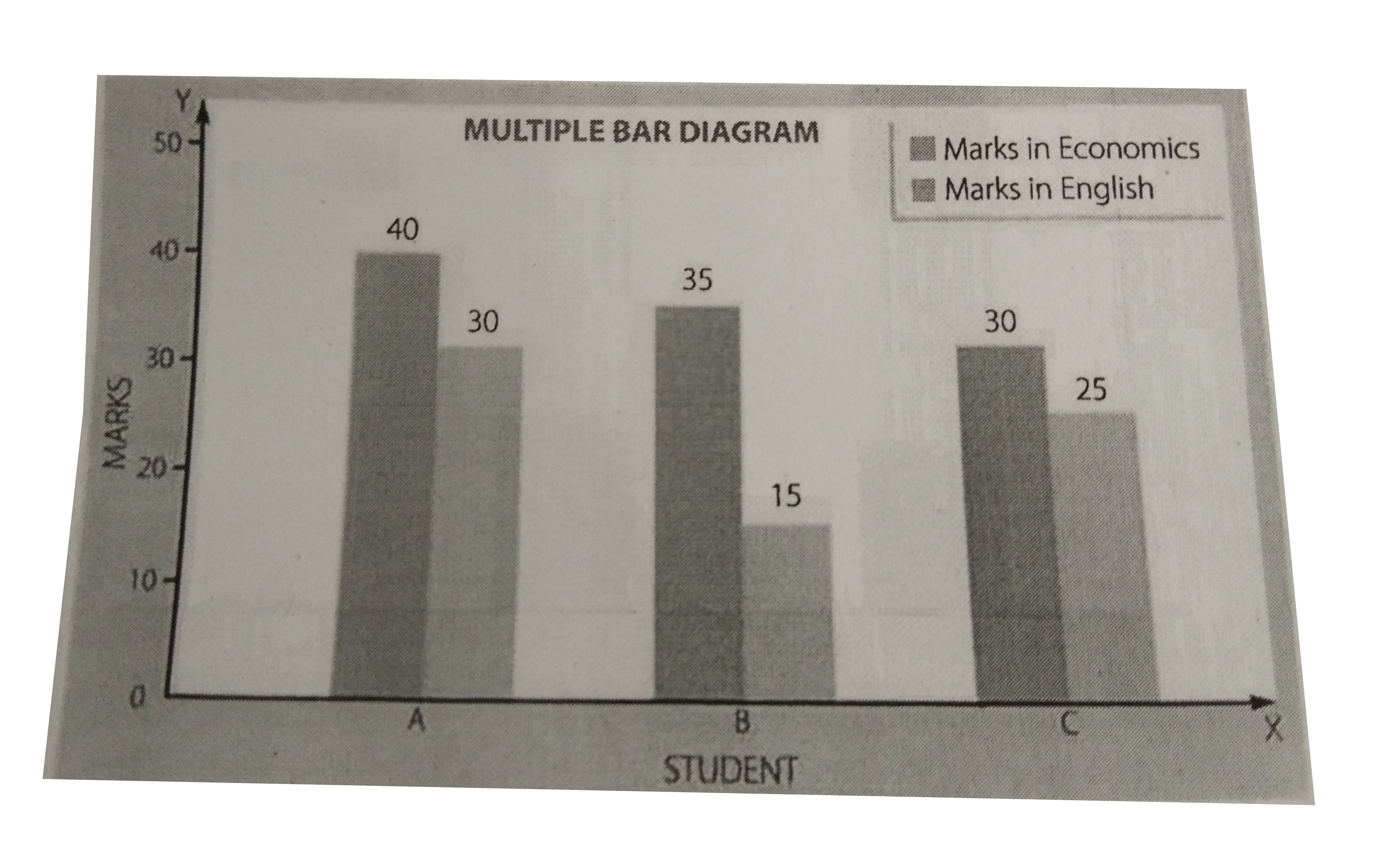
Draw A Multiple Bar Diagram To Show The Following Data Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Trj Eco Xi C06 S01 009 Q01 Png Width 80
What is a bar diagram? Types of bar diagram Pie or Circular diagrams Multiple bar diagram; T.R. Jain and V.K. Ohri Solutions for Class 11 Statistics for Economics Chapter 6 - Diagrammatic Presentation of Data- Bar Diagrams and Pies Diagrams. Question 1. Represent the following data by a percentage bar diagram.
Bar: A bar is a graphical representation of a stock's price movement that contains the open, high, low and closing prices for a set period of time or a specified set of data. For example, if a ...
Definition. A stacked bar graph (or stacked bar chart) is a chart that uses bars to show comparisons between categories of data, but with ability to break down and compare parts of a whole. Each bar in the chart represents a whole, and segments in the bar represent different parts or categories of that whole.
bar diagram: a method of presenting data in which frequencies are displayed along one axis and categories of the variable along the other, the frequencies being represented by the bar lengths.
A bar chart is a type of graph in which each column (plotted either vertically or horizontally) represents a categorical variable or a discrete ungrouped numeric variable. It is used to compare the frequency (count) for a category or characteristic with another category or characteristic.
Bar diagram definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Look it up now!
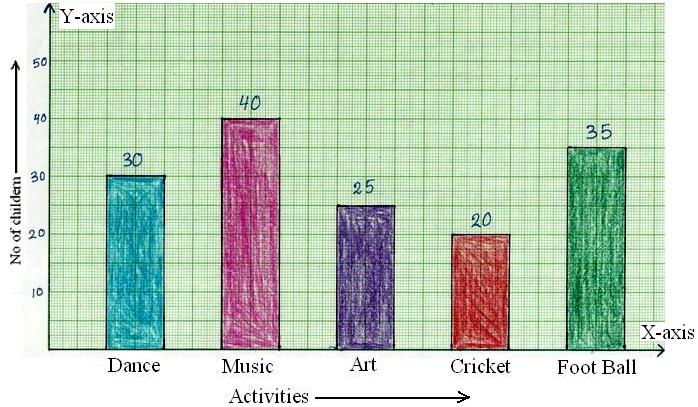
A bar graph is a diagram that compares different values, with longer bars representing bigger numbers. Bar graphs are also known as bar charts. You can make a horizontal bar graph or a vertical bar graph. Use a bar graph when you want to show how different things compare in terms of size or value.
A bar graph is a visual way to display and compare numerical data. The bars of a bar graph are drawn in relation to a horizontal axis and a vertical axis. A bar graph can have either vertical or horizontal bars. Example: Use the bar graph below to find the difference between the speed limit on a state highway and a suburban street? Show Video ...
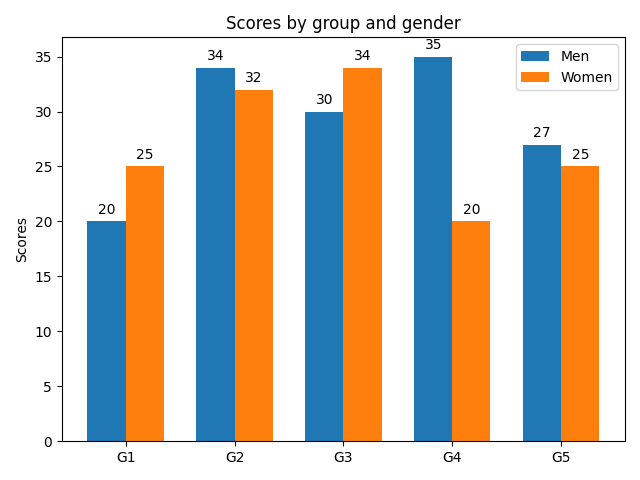
Hint: Simple bar diagram is the type of the chart which shows the values of the different categories of data as the rectangular bars with the different lengths whereas in the multiple bar diagrams the data sets are represented by drawing the bars side by side in a cluster.
A bar graph (also known as a bar chart or bar diagram) is a visual tool that uses bars to compare data among categories. A bar graph may run horizontally or vertically. The important thing to know is that the longer the bar, the greater its value. Bar graphs consist of two axes. On a vertical bar graph, as shown above, the horizontal axis (or x ...
Nov 13, 2021 · Bar Diagrams. The Bar Diagram is the basic model of the Data Interpretation Problems. The bar diagram is a two dimensional graphic representation where the elementary graphic objects are a set of rectangles or bars drawn in parallel so that the extension of the same is proportional to the magnitude they intend to represent.
The stacked bar graph is also called the composite bar chart, which divides the aggregate into different parts. In this type of bar graph, each part can be represented using different colours, which helps to easily identify the different categories. The stacked bar chart requires specific labelling to show the different parts of the bar.
What is the Bar Chart? A bar chart is a type of graph that is used to represent or summarize data using bars or rectangles of equal width but different heights or lengths. They can be either vertical or horizontal to graph data, more accurately measured data. These data are generally measures of frequency, number, or other means such as mean, median, mode, etc.

T R Jain And V K Ohri Solutions For Class 11 Statistics For Economics Chapter 6 Diagrammatic Presentation Of Data Bar Diagrams And Pies Diagrams

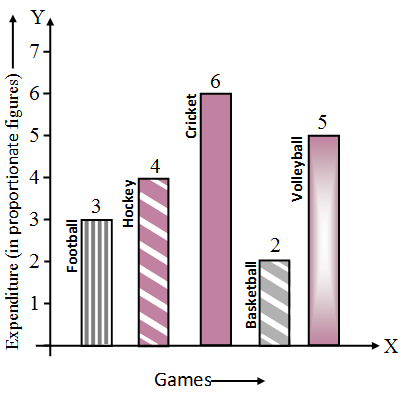

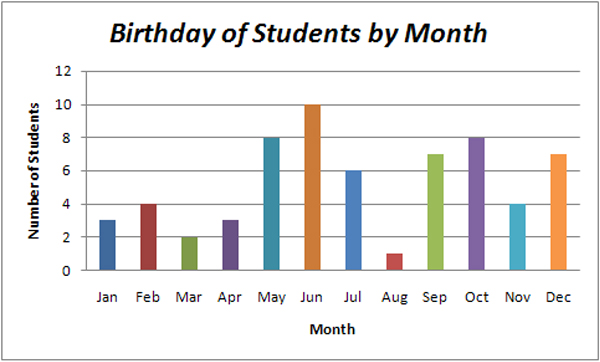
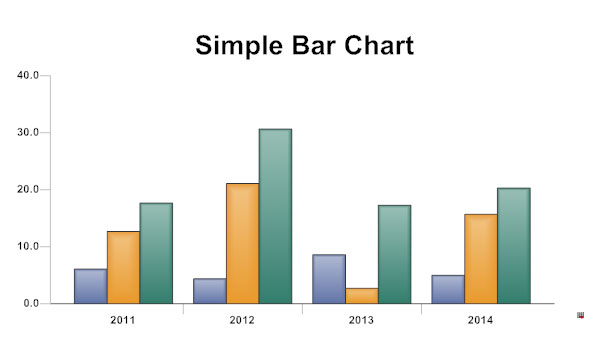






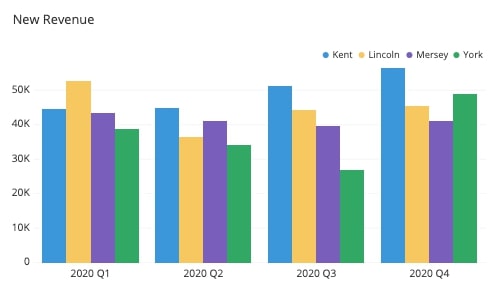
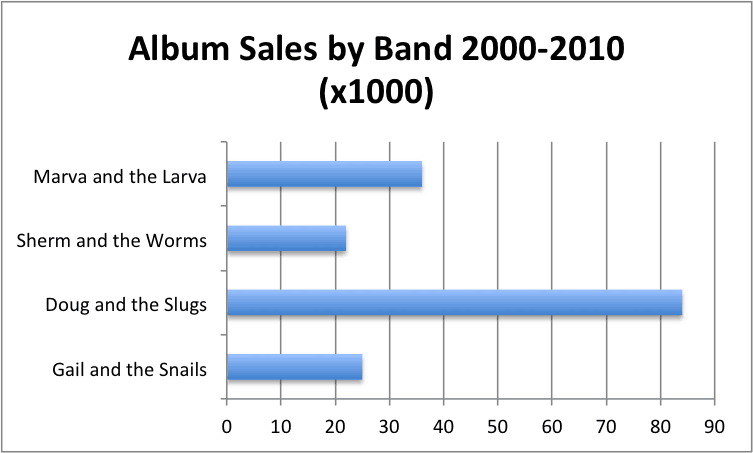
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Bar_Graph_Dec_2020-01-942b790538944ce597e92ba65caaabf8.jpg)






0 Response to "35 what is a bar diagram"
Post a Comment