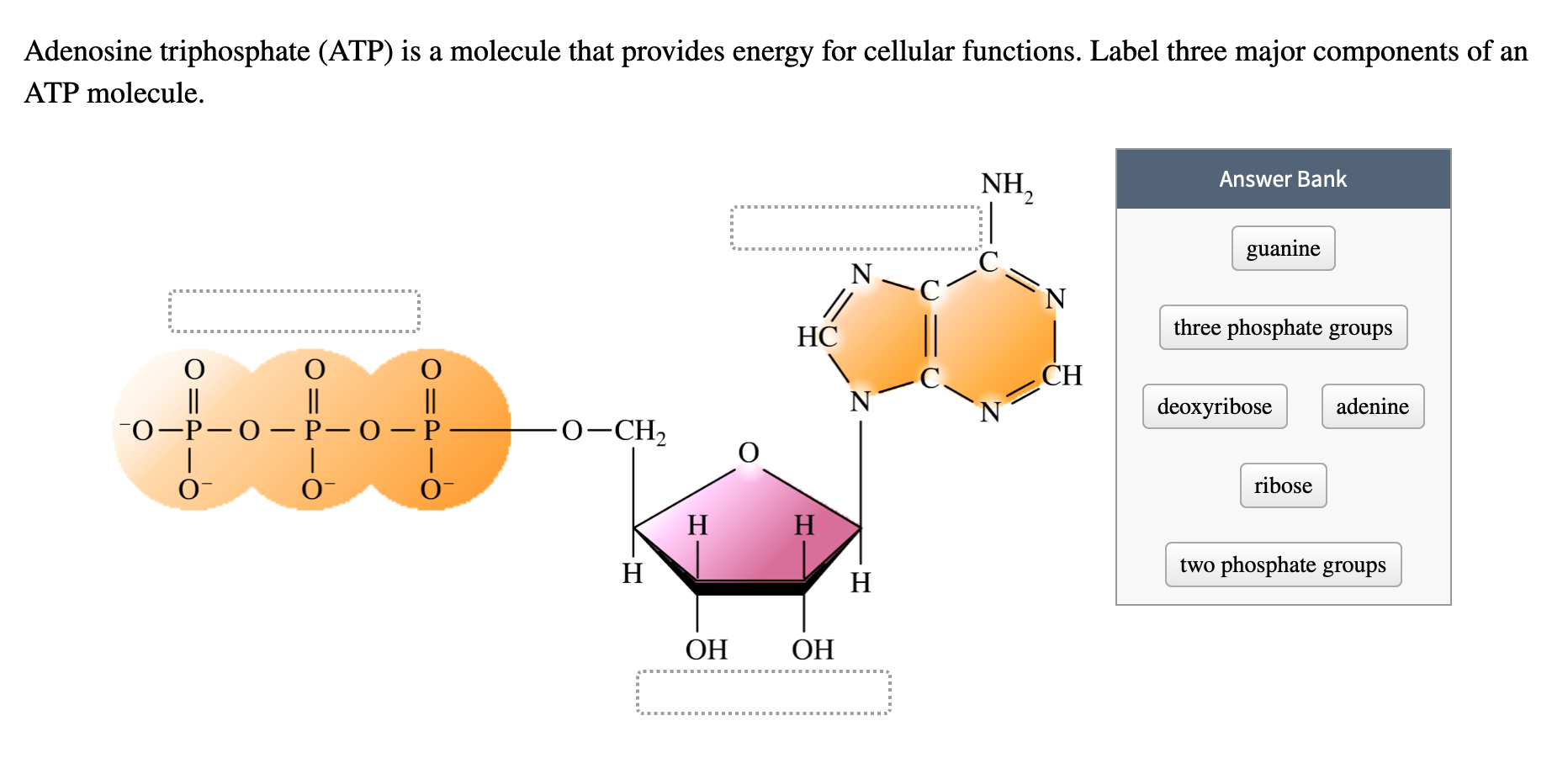
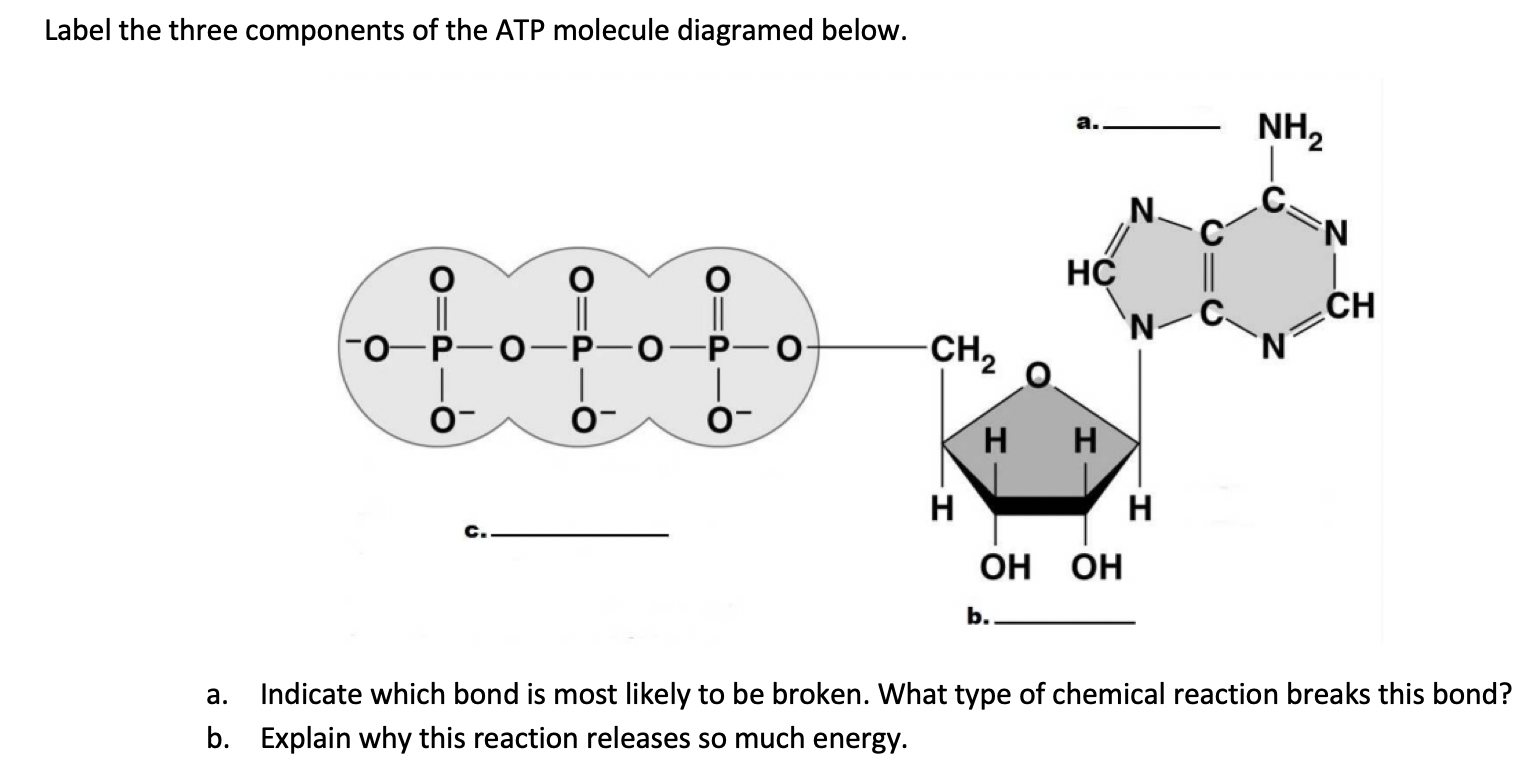
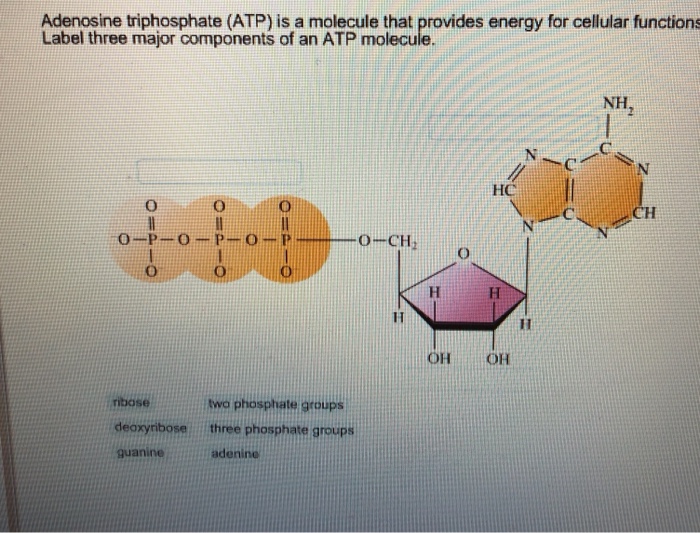
35 label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule
Cells release energy from ATP molecules by subtracting a phosphate group (breaking the bond ... Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below.3 pages The press release is of particular note. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1978 Press Release Peter D. Mitchell proposed a wild idea about how ATP was made...and he was subsequently validated by other researchers. Read the Nobel Foundation Press release announcing the prize. Small Molecules for Modern ...
Naina B. answered • 11/06/15 · Naina, a versatile tutor
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule
November 28, 2014 - Activity for students who are blind or visually impaired to create an ATP Molecule model. However, it is also necessary to ... with each phosphate, partially dissipating the proton gradient. After completing glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation, approximately 30–38 ATP molecules are produced per ... 6. An ADP/ATP molecule consists of what three parts? Label these three parts in this diagram. NH, .CH OCH O H H H OH OH Is the molecule in this diagram ADP or ATP? How do you know? 7. What role does ADP/ATP play in living cells? 8. Explain how energy is stored and released by ADP and ATP. Question: 6. An ADP/ATP molecule consists of what three ...
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule. Start studying ATP. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. six atoms of carbon in each molecule. 3. How many carbon atoms are in ribose? Adenine Molecule Examine the sm.uctural formula of adenine. Materials tracing or typing paper light cardboard (optional) Procedure scissors paste (optional) Part A. The Chemical Structure of Adenosine Triphosphate ATP is made up of smaller molecules or Structure: ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions.( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group. 3 weeks ago - Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Learn more about the structure and function of ATP in this article.
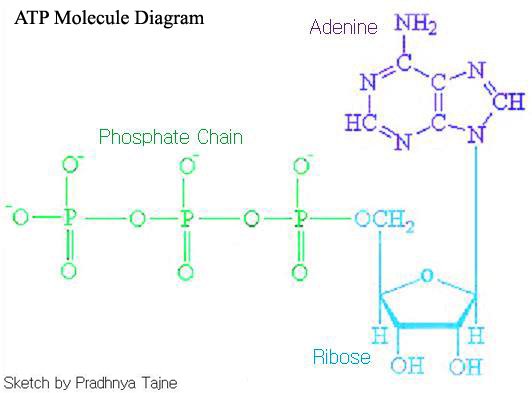
The left side of the diagram is adenine, the middle part is ribose which is a sugar. A sugar molecule is composed of 12 carbon, 22 hydrogen, and 11 oxygen atoms that is made the structure of the sugar.. In ATP molecules, energy is stored in the covalent bonds that is present between phosphates.The greatest amount of energy is present in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups. The Molecule of the Month home page, based at the School of Chemistry, University of Bristol Answer (1 of 2): There are four parts: a adenosine base and three phosphate groups in a chain. The molecule in itself does not perform any action, nor does any of the parts. But the ATP molecule, and especially the energetic bond between the first and second phosphate group, is used by many enzy... Use the following diagram to answer questions 7 to 15. 7. What are the reactants of Photosynthesis? a. b. c. 8. What are the ...4 pages
Website by SchoolMessenger Presence. © 2021 Intrado Corporation. All rights reserved 33 Draw And Label An Atp Molecule - Labels Information List. ATP molecule | Free SVG. Structure-of-ATP - PhD Muscle. Diagram,line,nucleotide - Atp Molecule Png Transparent ... Why is ATP an Important Molecule in Metabolism - Science ... Energy and Exercise - ScienceAid. Start studying Biology ATP. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and ...
ATP and energy release When energy is needed inside living cells, the enzyme ATPase hydrolyses the bond between the second and third phosphate group in ATP, removing the third group and leaving only...
ATP releases energy when it ______ bonds between its phosphate groups ... Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. ADENINE Rating: 4 · 1 review
label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below... what are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction? Carbon dioxide and water. what are the products of the light-dependent reactions? water and storage. ... label the internal parts of the chloroplast below....

Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Process Of Aerobic Respiration Include The Basic Equation For Cellular Respiration Study Com
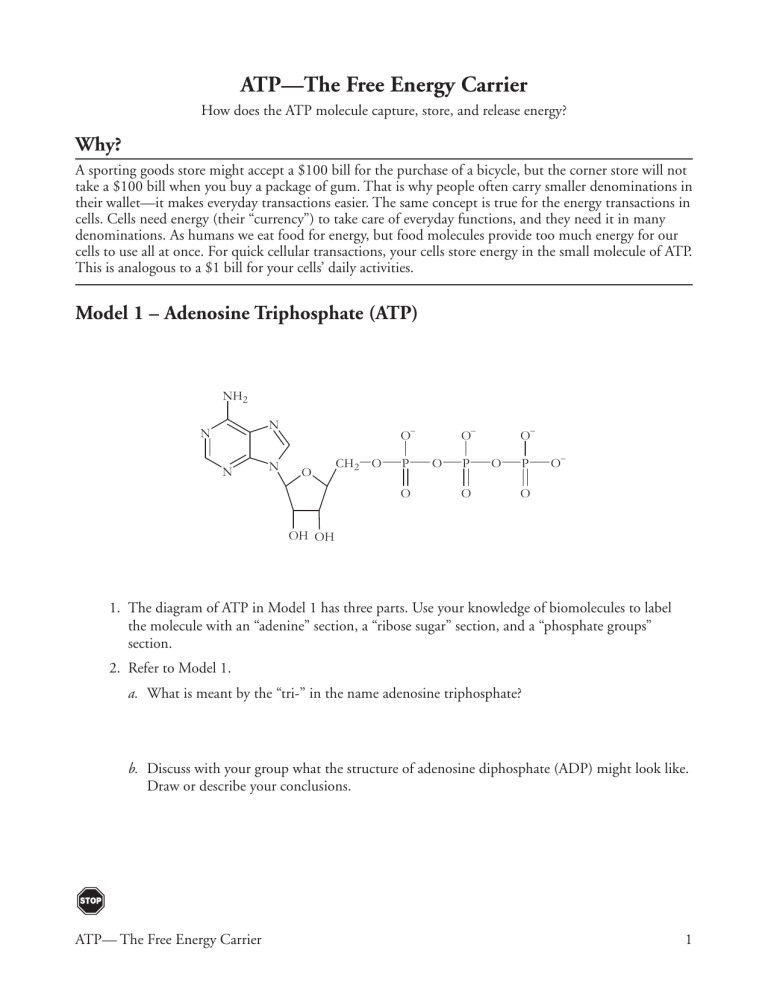
Part 1: The structure of ATP. ATP consists of 3 parts: 1 adenine molecule, 1 ribose sugar molecule, and 3 phosphate molecules. Energy is stored in the bond that is found between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. COLOR & LABEL the following in the ATP molecules below: adenine - red, ribose - orange, 3 phosphate groups - yellow. 3. 2. 1. 1 ...
1. The diagram of ATP in Model 1 has three parts. Use your knowledge of biomolecules to label the molecule with an “adenine” section, a “ribose sugar” section, and a “phosphate groups” section. 2. Refer to Model 1. a. What is meant by the “tri-” in the name adenosine triphosphate? b.

Atp And Adp Cycle Diagram To Label And Fill The Blanks Docx Name Taylor Merone Date 09 22 2020 Label The Diagrams Draw And Label Arrows To Show The Course Hero
Website by SchoolMessenger Presence. © 2021 Intrado Corporation. All rights reserved
On Diagram 4, label the following items. Multiple labels may apply to the same part of the diagram. x location of the light reactions x location of the Calvin cycle x thylakoid x stroma 2. On Diagram 5, fill in the labels with the following descriptions to show the connections between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Label the part of myosin structure ... Tail Actin binding sites ATP binding sites. Each myosin molecule has a head and a tail.Each myosin molecule is made of two subunits and each subunit has one ATP binding site and one actin binding site. Suggest corrections 0 Upvotes. Similar questions. Biology. Q3. Label the correct parts of the Myosin ...
Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp. Chemical bonds in phosphate groups what are the three parts of an atp molecule. n. Combined with microchannel flow cells and microfluidic control, allow individual fluorescently labeled protein and DNA ...
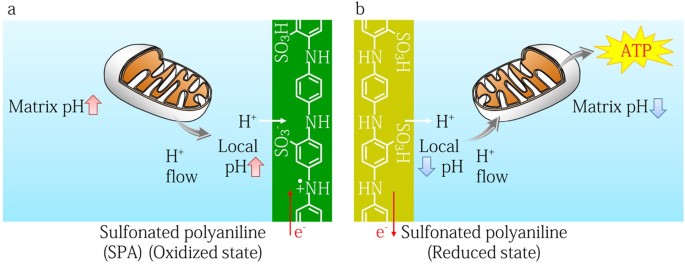
It takes the two, three carbon pyruvate molecules or the outcome of glycolysis and then recreates the pyruvate molecules into an additional amount of two ATP molecules per each glucose. The Krebs Cycle is an aerobic process. Meaning it requires oxygen to work. The Krebs Cycle occurs in the matrix part of the mitochondria.

1 Draw And Label The Parts Of An Atp And Adp Molecule 2 Explain In Diagrams How Energy Can Be Brainly Com
Use the following diagram to answer questions 5 to 13. 5. What are the reactants of Photosynthesis? a. b. c. 6.5 pages
The tertiary structure of all tRNAs is similar to that of tRNA Phe, at left, a canonical "L-shaped" molecule. As can be seen, the "cloverleaf" secondary structure shown in Figure 1 results in a complex three dimensional folding of the molecule.
The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Question: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions &-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? What arc two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? Describe the concepts shown in the diagram.
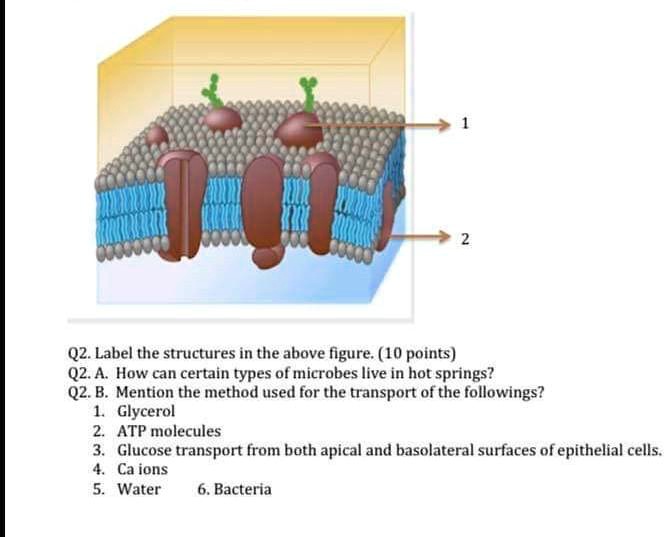
3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP. Identify these structures and the membrane phospholipids by color before continuing.
Label each of the parts of the ATP molecule and instruct students to do the same, using guided notes. Number each of the three major parts (sugar, adenosine and 3 phosphates) and point out each of the phosphate groups so that students gain an understanding of ATP's molecular structure.
5 (a) Fig. 5.1 is a diagram of an ATP molecule. Label Fig. 5.1 to show the structure of an ATP molecule. Fig. 5.1 [3] (b) Statements A, B, C and D are part of the sequence of events that occur during the loading of sucrose into a phloem sieve tube. A hydrogen ions bind to co-transporter protein B diffusion of sucrose via plasmodesmata
ATP is adenosine triphosphate, C10H16N5O13P3, a high energy complex providing the necessary power to push metabolistic reactions in the body. Its parts are an adenosine, a ribose sugar, and three ...
Glycolysis uses ATP to break a molecule of glucose in half, pro- ducing pyruvic acid. When oxygen is not present, glycolysis is followed by fermentation. Fermentation enables cells to produce energy in the absence of oxygen. Follow the prompts to identify important parts of glycolysis and fermentation. Color the carbon atoms blue.
Adenosine Triphosphate Definition. Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation.All living things use ATP.
Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions 8-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. 8. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low battery? 9. What are two ways in which the diagram shows an increase in energy? 10. Describe the concepts shown in the diagram. 11.
ATP releases energy when it breaks . bonds between its phosphate groups. Most cells only store enough ATP for a few seconds . of activity. Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. For Questions 8-10, refer to the Visual Analogy comparing ATP to a charged battery. In the visual analogy, what chemical is represented by the low ...
Label each part of the ATP molecule illustrated below. Type Description Examples Autotrophs Organisms that make their own food Plants Heterotrophs Organisms that obtain energy from Animals, mushrooms the food they eat Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups P P P 6.
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule below. Atp releases energy when it bonds between its phosphate groups. Atp is a 5 carbon sugar molecule that is part of an atp molecule. The of atp are the key to its ability to store and supply energy. A sugar ribose 3 phosphates the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds ...
Label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule below. In a process called cellular respiration chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use and stores it in molecules of atp. In the visual analogy what chemical is represented by the low battery. Unit 4 Photosynthesis Amp Respiration Unit 4 Essential Knowledge.

Which Label Identifies The Part Of The Atp Molecule That Changes When Energy Is Released In The Cells Brainly Com
November 22, 2016 - Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture:
Cells release energy from ATP molecules by subtracting a phosphate group. ... Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below. Adenine.6 pages
Write the number of ATP molecules produced by each process listed below. Then add up these numbers to get the total number of ATP molecules produced when one glucose molecule is broken down by cellular respiration. 4(2) ATP made in Glycolysis + 2. ATP made in Krebs cycle + 32 . ATP made in the Electron Transport Chain = 36. ATP total for the ...
6. An ADP/ATP molecule consists of what three parts? Label these three parts in this diagram. NH, .CH OCH O H H H OH OH Is the molecule in this diagram ADP or ATP? How do you know? 7. What role does ADP/ATP play in living cells? 8. Explain how energy is stored and released by ADP and ATP. Question: 6. An ADP/ATP molecule consists of what three ...
However, it is also necessary to ... with each phosphate, partially dissipating the proton gradient. After completing glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation, approximately 30–38 ATP molecules are produced per ...
November 28, 2014 - Activity for students who are blind or visually impaired to create an ATP Molecule model.
















0 Response to "35 label each part of the diagram of an atp molecule"
Post a Comment