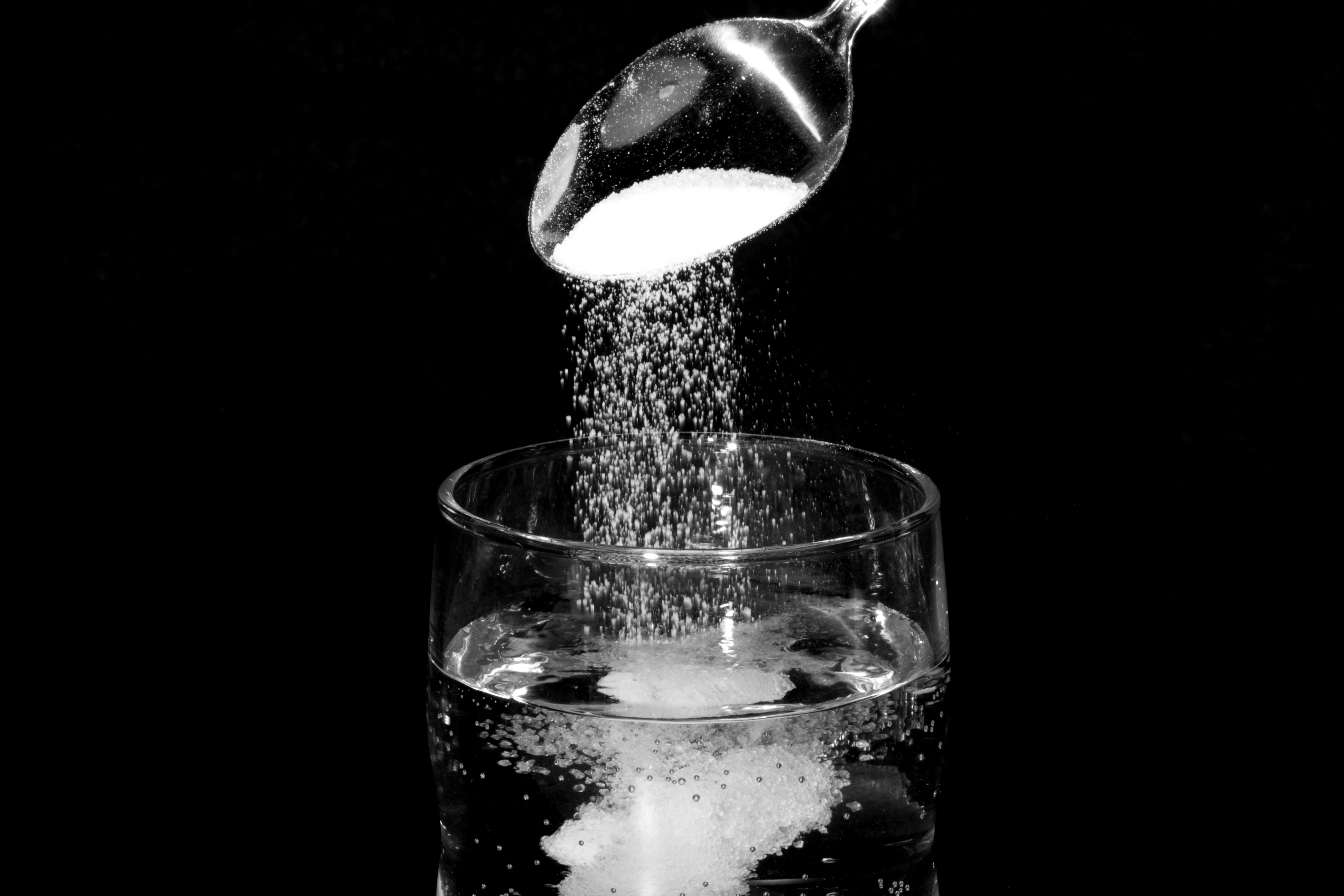
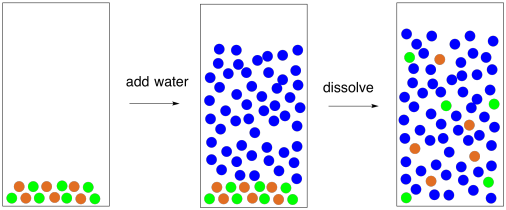
35 diagram of table salt dissolved in water
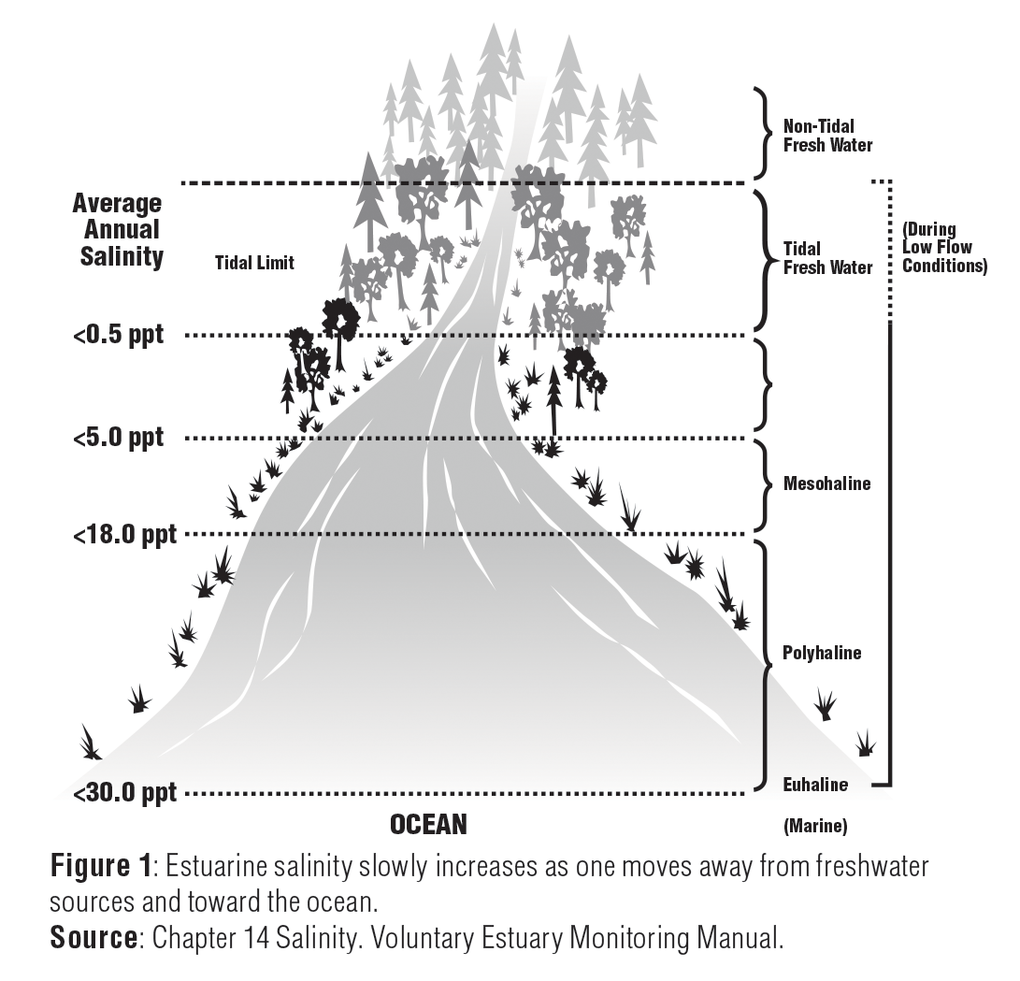
FIGURE: Piper diagram of water chemistry in bedrock wells in Ogden Valley, Weber County, Utah. The location of symbols in the triangles shows the relative proportion of cations and anions in samples, whereas the size of the symbols is proportional to the amount of total dissolved solids (TDS) in the samples. In a solution of table salt and water, the salt is the solute and the water is the solvent. In the cells of your body, substances such as calcium ions and sugar are solutes, and water is the solvent. Water is the most common and important solvent, but other substances can also be solvents. For example, if you have ever used an oil-based paint
1. Provide the formula for each ionic compound in the table. 2. Write the balanced reaction for the dissolution of each salt in water, including physical states. The convention is to leave water out of the equation, and simply write the reactant as the solid ionic compound and the product as ions in aqueous solution.

Diagram of table salt dissolved in water
4 A student investigated what happened when sodium thiosulphate dissolved in water. Experiment 1 By using a measuring cylinder, 20 cm 3 of distilled water was poured into a polystyrene cup. Use the thermometer diagram to record the temperature of the water in the table. 14. Salt A and salt B were each dissolved in separate beakers of water at 21°C. The temperature of the salt A solution decreased, and the temperature of the salt B solution increased. Based on these results, which conclusion is correct? 1) The water gained energy from both salt A and salt B. 2) The water lost energy to both salt A and salt B. Table salt is made of the ionic compound sodium chloride, which consists of the chemical elements sodium and chlorine.You probably learned from unintentional play at the kitchen table as a child that if you sprinkle salt into a glass of pure water, the salt disappears after a time; the more salt you add, the longer this takes, and it may require some shaking or stirring to bring about.
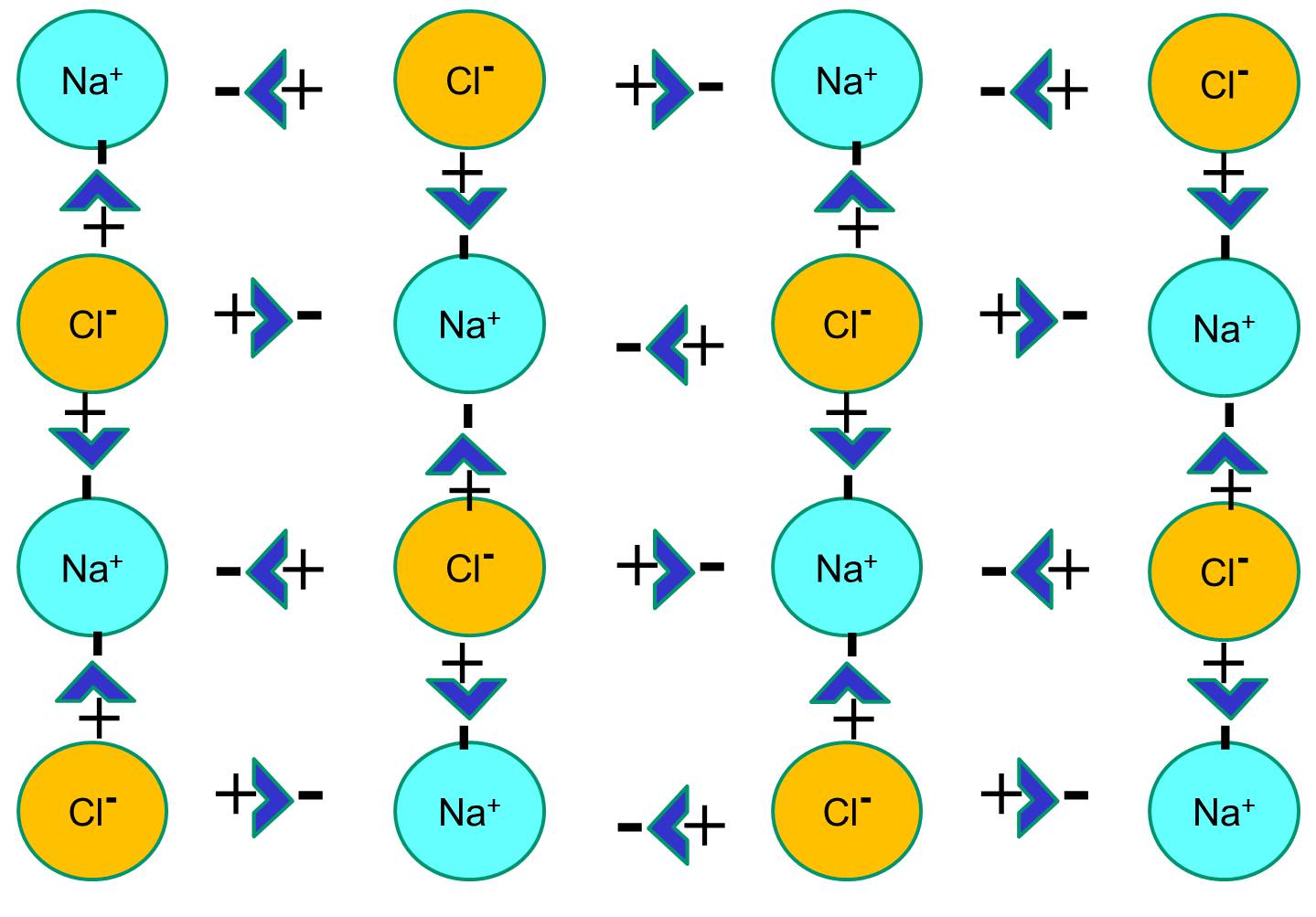
Diagram of table salt dissolved in water. 12.13 Calculate the density of FeO, given that it has the rock salt crystal structure. Solution We are asked to calculate the theoretical density of FeO. This density may be computed using Equation (12.1) as ! = n " (AFe+ AO) VCNA Since the crystal structure is rock salt, n' = 4 formula units per unit cell. Using the ionic radii for Fe2+ and O2-from Table 12.3, the unit cell volume is computed ... C reacting potassium with water D using petrol in a motor car engine 15 The diagrams show some pieces of laboratory equipment. 3 thermometer 60 30 45 15 2 stop-clock 1 balance Which equipment is needed to find out whether dissolving salt in water is an endothermic process? A 1 only B 1 and 3 C 2 and 3 D 3 only What happens when table salt dissolves in water? Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a ... Answer (1 of 6): The table salt quite quickly dissociated into ions, with Na+ as the cation and Cl- as the anion. Two oppositely charged ions of the same magnitude… a solvation shell forms around each ion, in which the Na+ cation will be surrounded by the water molecules with the negative dipole ...
Mar 10, 2020 · Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. You could easily dissolve about 360 g of table salt in a liter of water, but the solubility of calcium carbonate is only about 0.01 grams per liter. That's partly due to the fact that the ions in sodium chloride, Na + and Cl-, have lower charges than the ions in calcium carbonate, Ca 2+ and CO 3 2- . Water dissolves salt by dissociating the ions in salt from each other. Because water is a polar molecule, each of its ends holds a slight positive or negative electrical charge. These ends attract the positive and negative ions in salt and pull them apart from each other. The polarity of water comes from the differences in electronegativity in ... 1. Use Microsoft Excel to construct a data table containing columns labeled with vial number, temperature (°C), mass of KNO 3, mass of water, and solubility (g salt /100 g solvent) for all six trials. Include a separate entry for the unknown solution's identification number, characteristic temperature, and concentration. 2.
When you dissolve table salt (sodium chloride, also known as NaCl) in water, are you producing a chemical change or a physical change? Well, a chemical change involves a chemical reaction, with new substances produced as a result of the change.A physical change, on the other hand, results in a change of the material's appearance, but no new chemical products result. Answer (1 of 2): If the salt,is really dissolved, it is a solution. Your teacher may want You to say that it is an aqueous solution of sodium chloride. You could also call it a homogeneous mixture. The salt is the solute and the water is the solvent. The chemical compound in table salt is sodium ... When a soluble ionic compound is placed in water, the solid is converted to the product of the dissolution reaction|the solid vanishes, converting to dissolved ions in solution. 3 Use the solubility rules to determine if the salt is soluble or insoluble, and enter that information in the table. Q. The diagram shows water molecules in an open beaker and water molecules that have evaporated into the air above the beaker. Which change in this system will increase the rate of evaporation? ... Salt is dissolved in water. ... 173 J of energy are absorbed by the metal. Determine the specific heat of this metal and use the table above to ...
Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal, pulling away the individual sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. To understand this process at the molecular level, we must apply the three steps we previously discussed.
Look at the pictures showing how water molecules dissolve salt. Then arrange the water molecules around the sodium and chloride ions in the correct orientation. The positive part of the water molecules should be near the negative chloride ion. The negative part of the water molecules should be near the positive sodium ion. Move the water molecules and sodium and chloride ions to model how water dissolves salt.
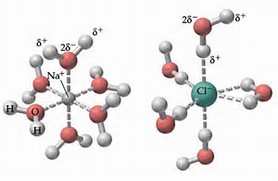
Detailed Description. This diagram shows the positive and negative parts of a water molecule. It also depicts how a charge, such as on an ion (Na or Cl, for example) can interact with a water molecule. At the molecular level, salt dissolves in water due to electrical charges and due to the fact that both water and salt compounds are polar, with positive and negative charges on opposite sides in the molecule.
Measure out a fixed amount of water (e.g., 1 liter). Add salt one gram at a time, stirring until it completely dissolves. Repeat until no more will dissolve. With table salt and pure water, you should get around 350-360 grams of salt per liter of water to dissolve. Thanks!
A mixture of crystals of salt and sugar is added to water and stirred until all solids have dissolved. Which statement best describes the resulting mixture? (1) The mixture is homogeneous and can be separated by filtration. (2) The mixture is homogeneous and cannot be separated by filtration.
These free ions in a salt-water solution allow electricity to flow through water. Ionic compounds such as sodium chloride, that dissolve in water and dissociate to form ions, are called electrolytes. Please Watch animation 10.3 on ionic solutions.
Diagram shown represents rules obtained in a study of suspension containing both broken and whole cells. ... A mixture of sand and table salt can be separated by filtration because the substances in the mixture differ in ... Two grams of potassium chloride are completely dissolved in a sample of water in a beaker. This solution is classified as ...
Sodium chloride / ˌ s oʊ d i ə m ˈ k l ɔːr aɪ d /, commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 g Na and 60.66 g Cl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible ...
You know that the enthalpy of dissolution when 6.00⋅ 10−6 moles of sodium hydroxide are dissolved in water, so use this info to find the enthalpy of dissolution when 1 mole of the salt dissolves. 1mole NaOH ⋅ −63.22 J 6.00 ⋅ 10−6moles NaOH = −1.054 ⋅ 107 J. Finally, convert this to kilojoules. 1.054 ⋅ 107J ⋅ 1 kJ 103J = 1 ...
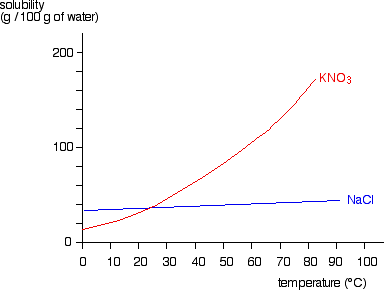
This page looks at the phase diagram for mixtures of salt and water - how the diagram is built up, and how to interpret it. It includes a brief discussion of solubility curves. Important: This page is only really designed to be an introduction to the topic suitable for courses for 16 -18 year olds, such as UK A level chemistry.
4 *P40134A0428* Answer ALL questions. 1 A student was asked to find the mass of salt dissolved in 100 cm3 of sea water. She was given the following instructions. Step A Weigh an empty evaporating basin Step B Transfer 50 cm3 of sea water into the basin Step C Heat the sea water in the basin until all the water has evaporated Step D Allow the basin and residue to cool
ELECTROLYSIS OF SALT WATER Unit: Salinity Patterns & the Water Cycle l Grade Level: High school l Time Required: Two 45 min. periods l Content Standard: NSES Physical Science, properties and changes of properties in matter; atoms have measurable properties such as electrical charge. l Ocean Literacy Principle 1e: Most of of Earth's water (97%) is in the ocean.
Solubility of a Salt In this experiment, you will study the effect of changing temperature on the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of water. Water solubility is an important physical property in chemistry, and is often expressed as the mass of solute that dissolves in 100 g of water at a certain temperature.
If you mix two substances and the result is a homogeneous mixture, you are dealing with a solution. In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Water is a solvent. The reasons are electrostatic in nature. The cohesion of atoms and molecules derive from electrostatic links between particles ...
Water consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen molecule connected by a covalent bond to form a charged H20 molecule. The biggest similarity between these two substances is that their molecules are charged, making them reactive. This is why salt dissolves in water.
we can easily draw a diagram of sodium chloride dissolved in water. Let's just do some quick review, though. Sodium chloride is in a C l. And remember, sodium has a positive charge because it has one extra proton in the nucleus than electrons in the outer cloud. And chloride has one extra electrons in the outer plowed compared to the neutrons, protons that are in the nucleus with you and sodium chloride that's held together with an ionic bond to a polar solvent such as water, which is held ...
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
Table salt is made of the ionic compound sodium chloride, which consists of the chemical elements sodium and chlorine.You probably learned from unintentional play at the kitchen table as a child that if you sprinkle salt into a glass of pure water, the salt disappears after a time; the more salt you add, the longer this takes, and it may require some shaking or stirring to bring about.
14. Salt A and salt B were each dissolved in separate beakers of water at 21°C. The temperature of the salt A solution decreased, and the temperature of the salt B solution increased. Based on these results, which conclusion is correct? 1) The water gained energy from both salt A and salt B. 2) The water lost energy to both salt A and salt B.
4 A student investigated what happened when sodium thiosulphate dissolved in water. Experiment 1 By using a measuring cylinder, 20 cm 3 of distilled water was poured into a polystyrene cup. Use the thermometer diagram to record the temperature of the water in the table.

/SaltingWater-58b5a52e3df78cdcd8853736.jpg)













0 Response to "35 diagram of table salt dissolved in water"
Post a Comment