35 converging lens ray diagram
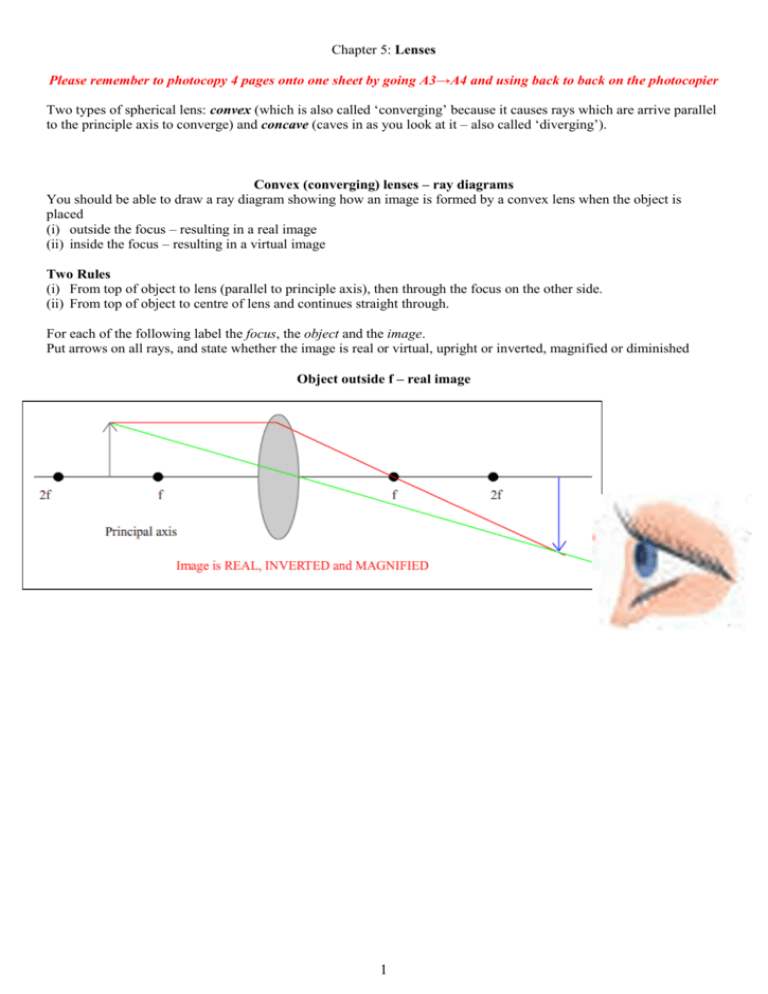
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for converging lenses for grade 10 science. (a) An object is placed 1 0 c m from a lens of focal length 5 c m.Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of image if the lens is (i) converging , and (ii) diverging. (b) State one practical use each of convex mirror , concave mirror , convex lens and concave lens.
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction.A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis.Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape.

Converging lens ray diagram
A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. The image can be magnified, diminished, or remain the same depending on the distance of the object from the lens. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of … Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
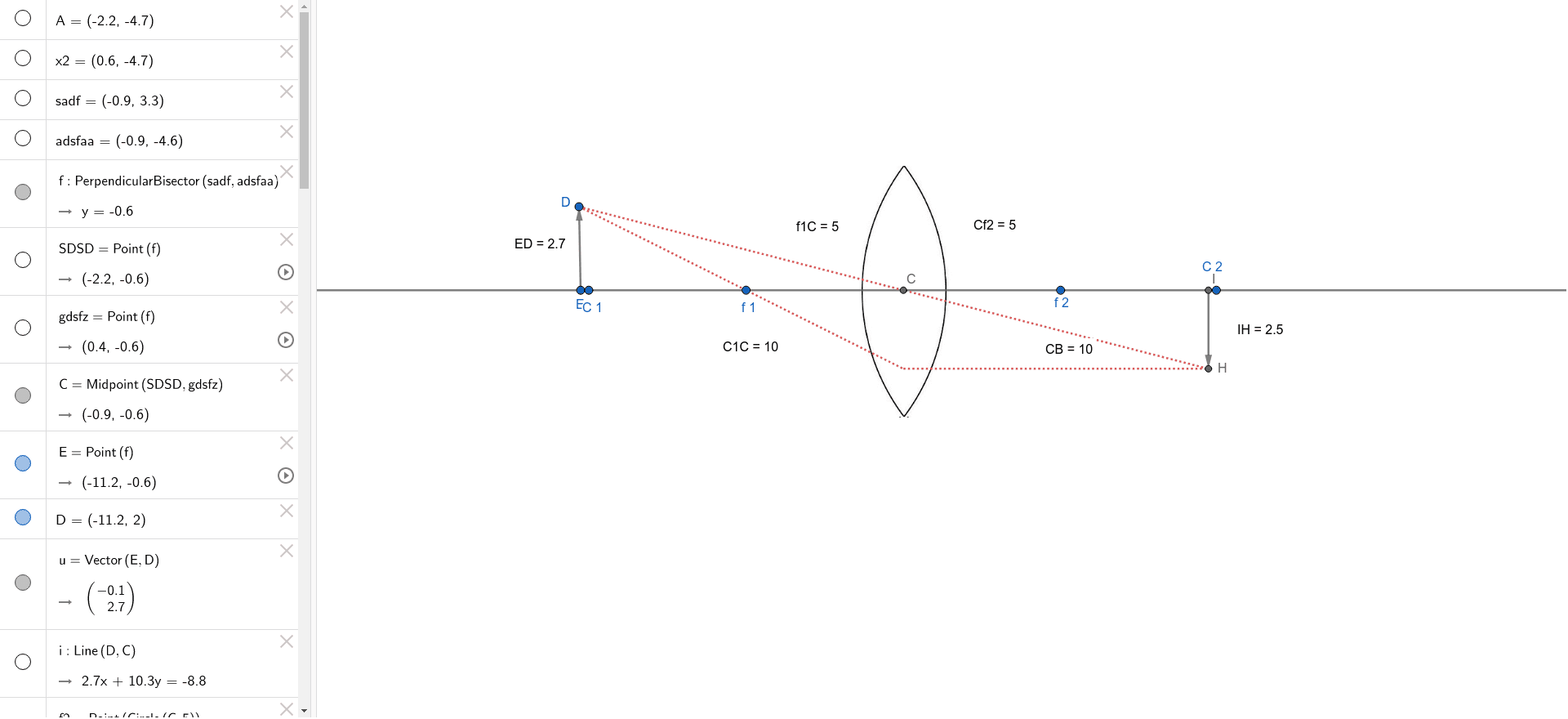
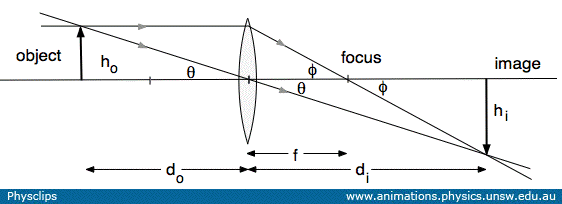
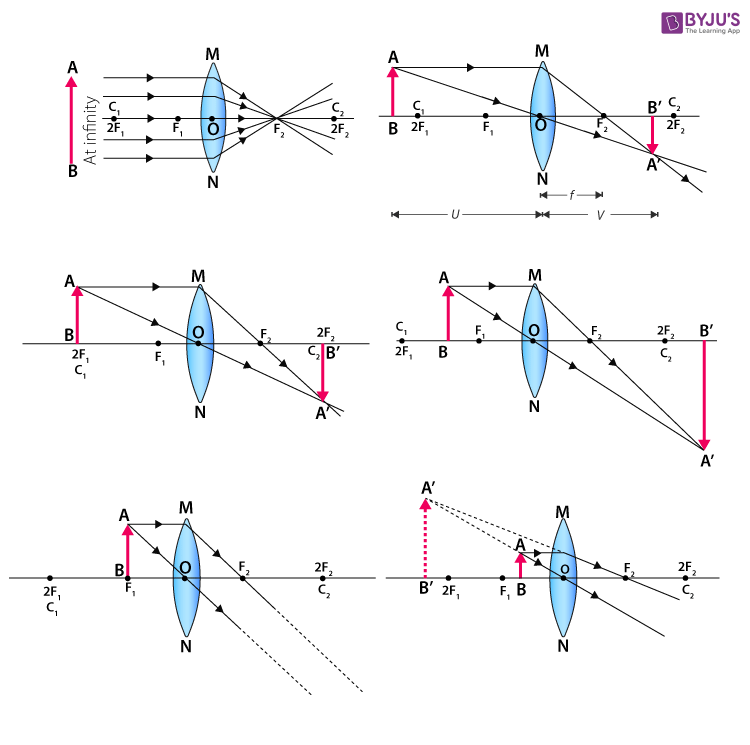
Converging lens ray diagram. Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the general location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double convex lenses.Perhaps you noticed that there is a definite relationship between the image characteristics and the location where an object placed in front of a double convex lens. Converging Lens. Diverging Lens. F. Ray 1. F Ray 1. Ray 2. Ray 2. Ray 3 Ray 3. Images’ ’ Tracing Points Draw an arrow to represent the location of an object, then draw any two of the rays from the tip of the arrow. The image is where lines cross. Draw an arrow to represent the location of an Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors
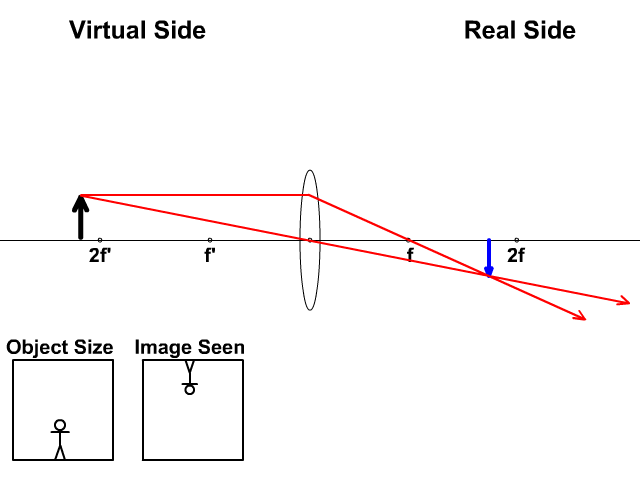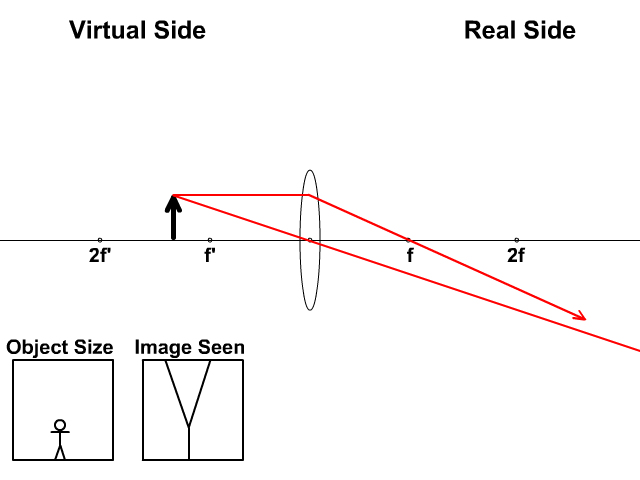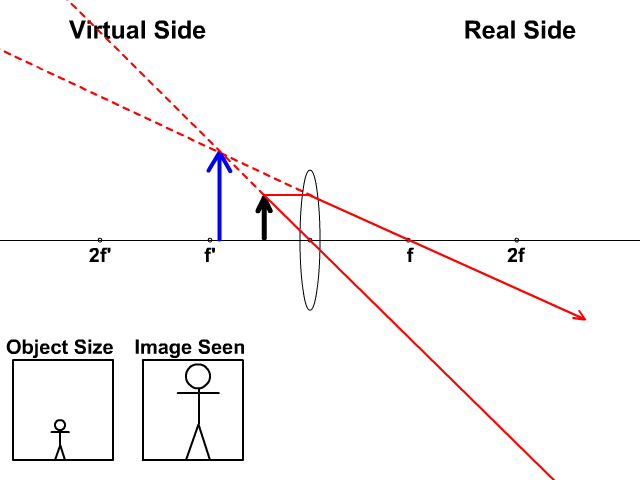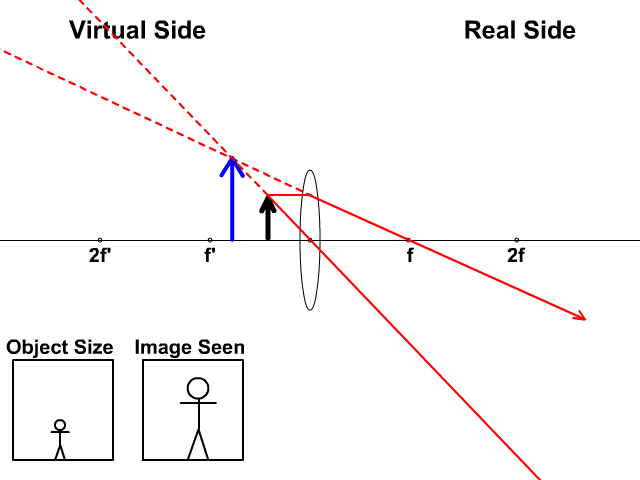
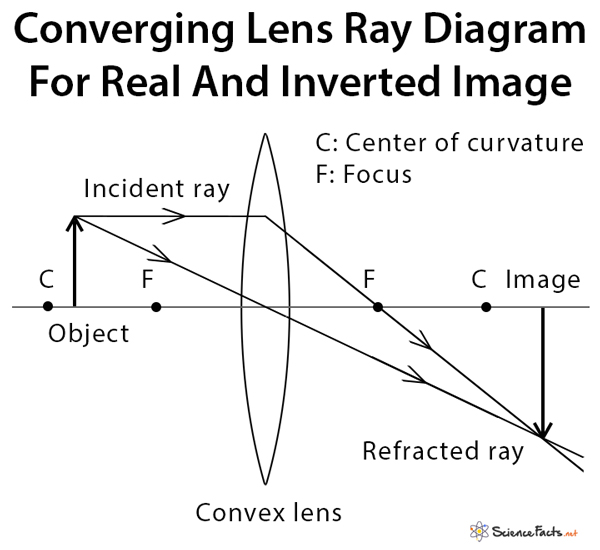
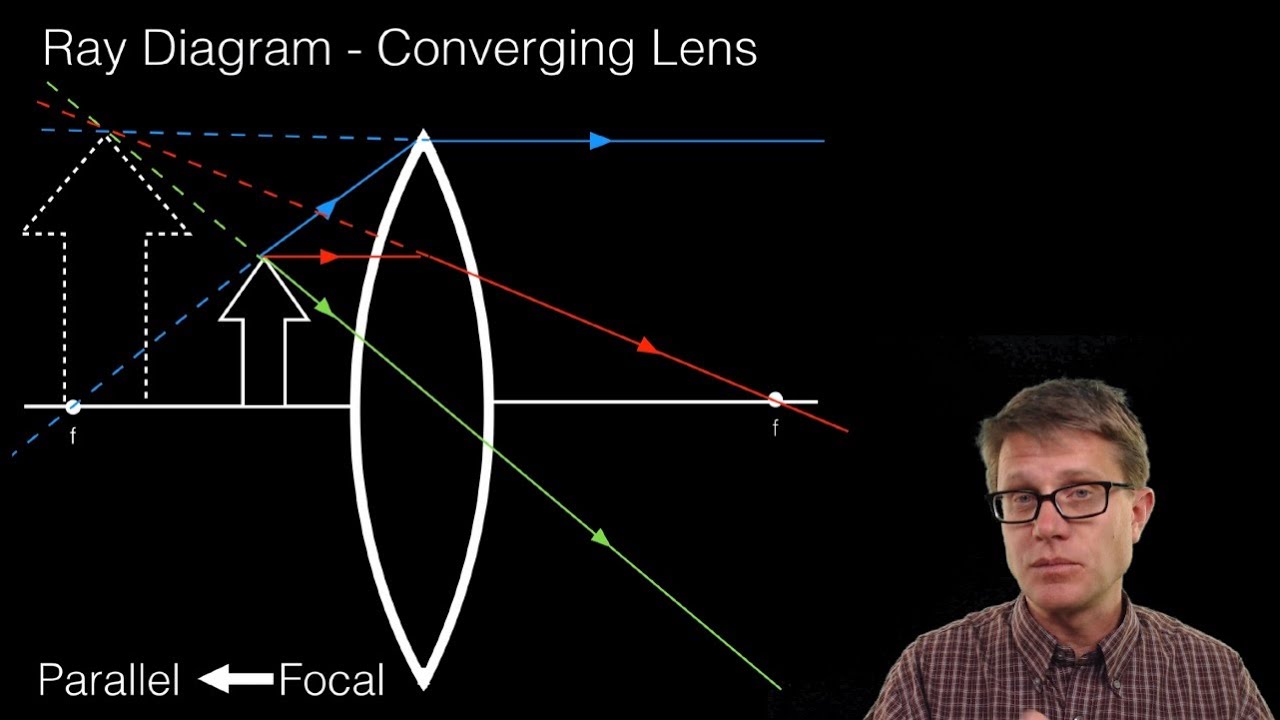
To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis are all refracted through the focal point. Application of converging lens. Trick to drawing ray diagrams for converging lens: There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. Always. 2 rays are enough to determine the position of image/object. The other ray of light ALWAYS passes through the focal point of the lens. Either the first focal point of the second focal point. Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed. Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules.
This interactive tutorial utilizes ray traces to explore how images are formed by the three primary types of converging lenses, and the relationship between the object and the image formed by the lens as a function of distance between the object and the focal points. Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray. The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Refraction and Lenses » Ray Diagrams for Converging Lenses. The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum. Visit the Usage Policy page for additional information. The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. enter image. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such.Ray Diagrams for Lenses.
Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
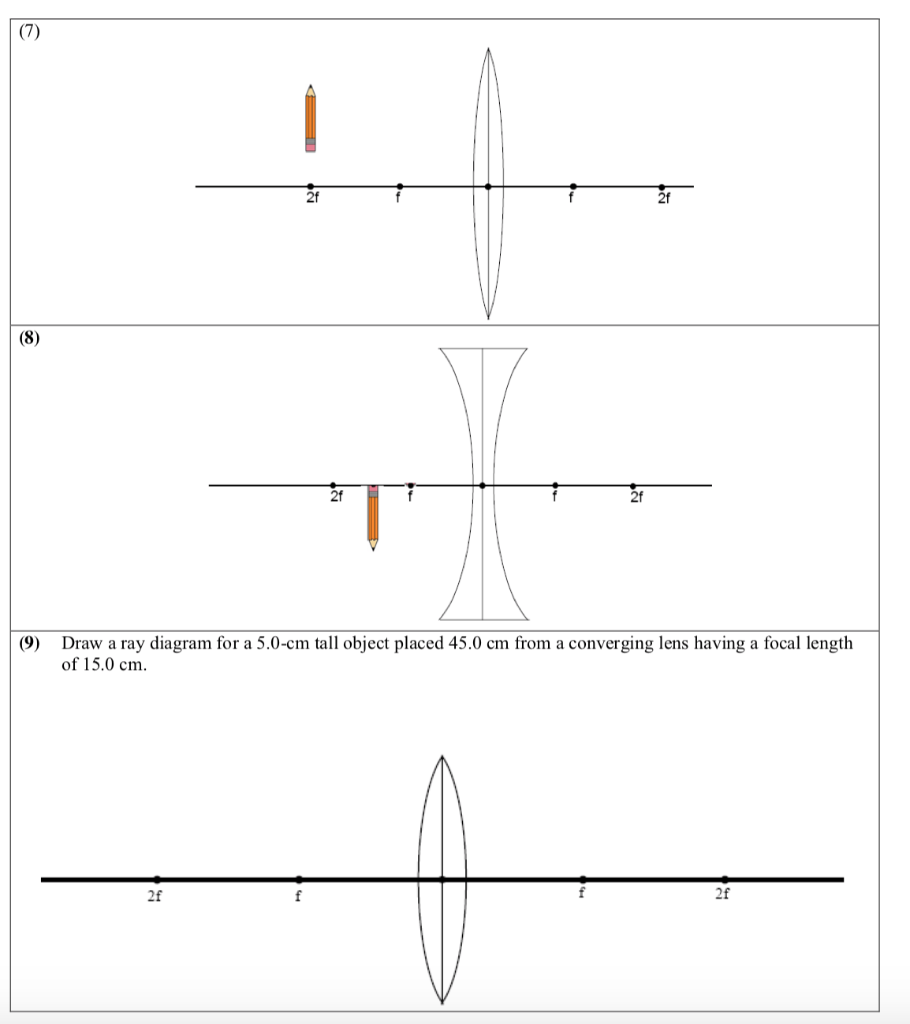
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of …
A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. The image can be magnified, diminished, or remain the same depending on the distance of the object from the lens.

Images Formed By Lenses Ray Diagrams For Lenses Ray Diagrams Can Be Used To Predict Characteristics Of Images Using 3 Rays Just Like For Concave Ppt Download

---teachoo.png)














0 Response to "35 converging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment